浏览器对象详解
一、参考资料
二、认识浏览器运行态下的 js
1.问:是否了解浏览器的执行态(分层设计)?
- ECMAScript - 基础逻辑、数据处理,js 语法块
- BOM - 浏览器本身的能力操作
- Browser Object Model(浏览器对象模型)
- 浏览器模型提供了独立于内容的、可以与浏览器窗口进行滑动的对象结构,就是浏览器提供的 API
- DOM - 浏览器文本的操作
2.BOM
1.location
提供当前窗口中的加载的文档有关的信息和一些导航功能。
既是 window 对象属性,也是 document 的对象属性
window.location === document.location; //true
// https://www.zhihu.com/search?type=content&q=123
location.href =
'https://www.zhihu.com/search?type=content&q=123'.origin = // 完整的url
'https://www.zhihu.com'.host = // 页面的标准域名
'www.zhihu.com'.hash = // 服务器名称+端口 例如:‘www.zhihu.com:8080’
'#hash'.pathname = // url中#号后面的哈希值
'/search'.search = // url中[/]后面内容
'?type=content&q=123'.protocol = // url中[?]后面内容
'https:'.port = // 协议[http:]
''; //端口号:[ 80 | 8080 | ... ]
方法:
- assign()
不会打开新窗口,把请求 url 中的资源,加载到当前窗口- 会给浏览器的
History中增加一条历史记录
- replace(url)
- 用 url 中的内容,替换掉当前的 location 资源
- 不会在浏览器的
History中增加记录,意味着用户不能使用回退按钮
- reload()
- 重新加载当前 url 的内容
- 当 reload(true)时,会
强制从服务器获取所有内容 - 若没有参数,重新加载时,
可能从浏览器缓存加载页面
拓展方向:
- location 本身 api 操作
- assign VS replace 的区别
- 解析 url 中的查询字符串,返回一个对象
- 思路:
- 可以通过
正则的方式获取,或者通过字符串分割的方式 - 通过
location.search获取查询字符串内容,如果有[?]就截取[?]后面的内容 - 然后通过
[&]进行分割成为['key=val1','key=val2']的形式 - 通过
[=]对数组进行分割,使用decodeURIComponent对 key 和 val 进行解码,存放到对象中
- 路由相关: 跳转、参数、操作
- 页面能否
返回(history) - 页面是否
刷新(hash) - reload、assign、replace 参数等
- 页面能否
- URI or URL 的区别?
- URI
Uniform Resource Identifier - 统一资源标识符 - URL
Uniform Resource Locator - 统一资源定位符
- URI
2.History
history.state.length; // 当前页面的状态 // 返回当前 `会话` 中的 history 个数
方法:
- pushState(state, title, url)
- 给当前的 history 中添加一个状态
- 浏览器地址会改变,但是不会加载页面,本质上页面还是停留在原来的页面
- replaceState()
- 与 pushState 方法类似,但是
不会添加一个新的 state 到 history 中,而是直接修改当前state
- 与 pushState 方法类似,但是
相关联的方法
- window.onpopstate()
- 每当处于激活状态的历史记录条目发生变化时,
popstate事件就会在对应 window 对象上触发 - 调用
history.pushState()或者history.replaceState()不会触发 popstate 事件。 - popstate 事件只会在
浏览器某些行为下触发 - 比如点击后退、前进按钮(或者在 JavaScript 中调用 history.back()、history.forward()、history.go()方法)
- 每当处于激活状态的历史记录条目发生变化时,
例子:
window.onpopstate = function (event) {
alert(
'location: ' +
document.location +
', state: ' +
JSON.stringify(event.state),
);
};
//绑定事件处理函数.
history.pushState({ page: 1 }, 'title 1', '?page=1'); //添加并激活一个历史记录条目 http://example.com/example.html?page=1,条目索引为1
history.pushState({ page: 2 }, 'title 2', '?page=2'); //添加并激活一个历史记录条目 http://example.com/example.html?page=2,条目索引为2
history.replaceState({ page: 3 }, 'title 3', '?page=3'); //修改当前激活的历史记录条目 http://ex..?page=2 变为 http://ex..?page=3,条目索引为3
history.back(); // 弹出 "location: http://example.com/example.html?page=1, state: {"page":1}"
history.back(); // 弹出 "location: http://example.com/example.html, state: null
history.go(2); // 弹出 "location: http://example.com/example.html?page=3, state: {"page":3}
3.navigator
浏览器系统信息大集合
- clipboard
- 系统剪切板相关信息
- userAgent
- 当前用户的设备信息
- onLine
- 返回浏览器的在线状态
- serial
- 返回串口对象,Web Serial API 的入口点
- bluetooth
- 系统蓝牙相关
…
- 系统蓝牙相关
4.screen
用来表示浏览器窗口外部的显示器的信息等
window.screen.deviceXDPI/deviceYDPI 屏幕实际的水平 DPI、垂直 DPI
三、浏览器事件
浏览器事件模型主要分为三个阶段:
- 捕获阶段(IE)
- 事件由最外层元素(window),层层向内传递,直到最具体的元素
- 目标阶段
- 冒泡阶段(网景)
- 事件由最具体的元素(事件的触发者),层层向外传递(传递给父节点),直到 window 对象停止
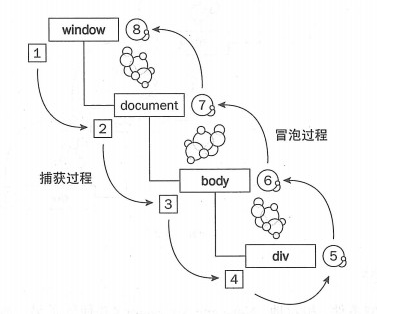
1.addEventListener 第三个参数
el.addEventListener(event, function, useCapture)
// useCapture默认值false,也就是默认冒泡
// true为捕获阶段
2.阻断事件传播
- event.stopPropagation()
阻断事件的传播- 但是无法阻止默认事件
- event.stopImmediatePropagation()
- 如果有多个
相同类型的事件监听函数绑定到同一个元素 - 当该类型的事件触发时,它们会按照被
添加的顺序执行 - 如果其中某个监听函数执行了此方法,则当前元素
剩下的监听函数将不会被执行
- 如果有多个
3.阻止默认行为
- e.preventDefault()
- e.preventDefault()可以阻止事件的默认行为发生
- 默认行为是指:点击 a 标签就转跳到其他页面、拖拽一个图片到浏览器会自动打开、点击表单的提交按钮会提交表单等等,因为有的时候我们并不希望发生这些事情,所以需要阻止默认行为
拓展方向
性能方向
- 如:事件委托的运用,一个 ul 和多个 li,点击 li 时,改变背景颜色
{
/*
<ul class="list">
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
*/
}
var list = document.querySelector('list');
function onClick(e) {
var e = e || window.event;
if (e.target.tagName.toLowerCase() === 'li') {
// 业务逻辑...
e.target.style.backgroundColor = 'pink';
}
}
list.addEventListener('click', onClick, false);
兼容性方向
- 如:写一个兼容 IE 的事件绑定
先区别 IE 的不同之处
- 绑定事件的函数和传参不同: 使用
attachEvent绑定,事件名要加on - 解绑时使用的函数和参数不同: 使用
detachEvent解绑 - 阻断时的不同:
event.cancelBubble = true - 阻止默认行为的不同:
event.returnValue = false
class BindEvent {
constructor(el) {
this.el = el;
}
addEventListener(type, handler) {
if (this.el.addEventListener) {
this.el.addEventListener(type, handler, false);
} else if (this.el.attachEvent) {
this.el.attachEvent('on' + type, handler);
} else {
this.el['on' + type] = handler;
}
}
removeEventListener(type, handler) {
if (this.el.removeEventListener) {
this.el.removeEventListener(type, handler, false);
} else if (this.el.detachEvent) {
this.el.detachEvent('on' + type, handler);
} else {
this.el['on' + type] = null;
}
}
static stopPropagation() {
if (e.stopPropagation) {
e.stopPropagation();
} else {
e.cancelBubble = true;
}
}
static preventDefault() {
if (e.preventDefault) {
e.preventDefault();
} else {
e.returnValue = false;
}
}
}
四、网络请求
1.XMLHttpRequest
- 属性
- responseText(服务端响应的文本数据)
- responseXML(服务点响应的 xml 或者 html 类型数据)
- status(响应 HTTP 状态)
- statusText(响应 HTTP 状态描述)
- readyState(发出请求的状态码)对应
onreadystatechange事件- 0:创建成功,但是没有调用 open 方法
- 1:open 方法被调用
- 2:send 方法被调用
- 3:loading,下载中
- 4:下载操作完成
- timeout(超时时间,对应超时事件
ontimeout,ontimeout 事件被弃用) - upload(上传进度)
- 方法
- open() 初始化请求(method, url, async),async 表示是否异步操作,默认 true
- send() 发送请求数据,get 请求时,send 可以不传或者 null
- abort() 中止已经发出的请求
- setRequestHeader() 设置请求头信息
- getRequestHeader() 获取指定响应头信息
- getAllResponseHeaders() 获取所有响应头信息
封装 XMLHttpRequest 请求
function ajax({ method = 'get', url = '', params = undefined }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
if (method.toLowerCase() === 'get' && params !== undefined) {
url = url + '?' + params;
}
xhr.open(method, url, true);
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
if (xhr.status === 200) {
resolve(xhr.responseText);
} else {
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
};
if (method.toLocaleLowerCase() === 'get') {
xhr.send();
} else {
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
xhr.send(params);
}
xhr.onerror = (err) => reject(err);
xhr.timeout = () => reject('timeout');
// progress事件可以报告长时间运行的文件上传
xhr.upload.onprogress = (p) => {
console.log(Math.round((p.loaded / p.total) * 100) + '%');
};
});
}
2.fetch
- 方法:fetch(url,{}| init 对象 ),返回 Promise 对象,只支持异步
- 响应通过 response 对象获取:
fetch().then((response)=>{}).catch(()=>{})- response 对象混入了 body,提供了 5 个方法,将 ReadableStream 转存到缓冲区的内存里,将缓冲区转换为 js 对象,通过 Promise 返回
- response.text() //转为 text
- response.json() //转为 json
- response.formData()
- response.arrayBuffer()
- response.blob()
不支持超时设置- 但是可以使用
promise+setTimeout进行控制
- 但是可以使用
- 默认
不携带cookies,但是可以设置fetch(url, {credentials: 'include'});- omit 不发送 cookie
- same-origin 同源发送 cookie(默认)
- include 都发送 cookie
- resolve 若发生在网络通信正常(404,500)也是 resolve
- .catch()也不会被执行。
- reject 只发生在网络通信异常
- 想要精确的判断 fetch 是否成功
- 需要包含 promise resolved 的情况,此时再判断 response.ok 是不是为 true
- 需要借用 AbortController 中止 fetch
// resolve若发生在网络通信正常(404,500)也是resolve
fetch('http://domain/service', {
method: 'GET',
})
.then((response) => {
// 想要精确的判断 fetch是否成功
// 需要包含 promise resolved 的情况,此时再判断 response.ok是不是为 true
if (response.ok) {
return response.json();
}
throw new Error('Network response was not ok.');
})
.then((json) => console.log(json))
// .catch()也不会被执行
.catch((error) => console.error('error:', error));
// ************************************
// 不支持直接设置超时, 可以用promise
function fetchTimeout(url, init, timeout = 3000) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fetch(url, init).then(resolve).catch(reject);
setTimeout(reject, timeout);
});
}
// ************************************
// 中止fetch
// signal用于支持AbortController中断请求
const controller = new AbortController();
// AbortController接口表示一个控制器对象
// 允许你根据需要中止一个或多个 Web请求
fetch('http://domain/service', {
method: 'GET',
signal: controller.signal,
})
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((json) => console.log(json))
.catch((error) => console.error('Error:', error));
controller.abort();
3.Http 状态码和 Header
1.状态码
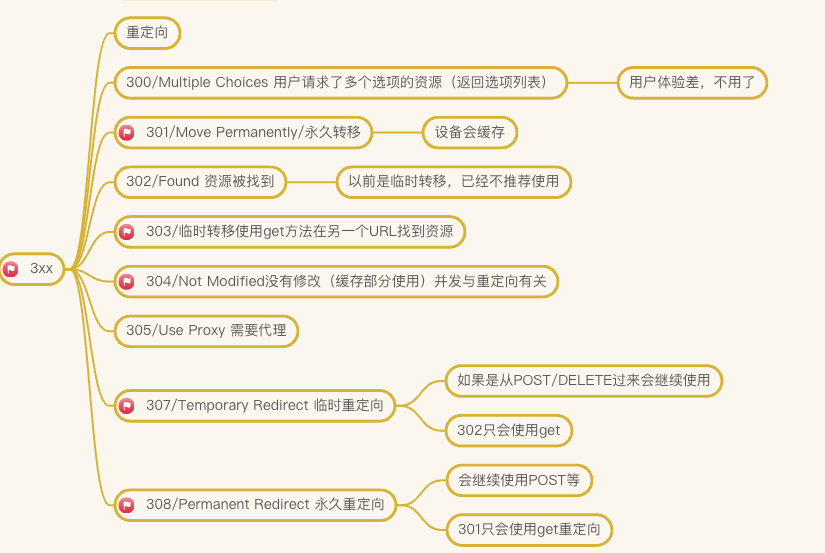
100 信息性|200 成功|300 重定向|400 客户端错误|500 服务器错误
[1|2|3]xx
- 101 切换协议
- 200 Ok
- 301 永久重定向(设备会缓存)
- 302 临时重定向(以前是临时转移,已经不推荐使用了,建议使用 307)
- 307 临时重定向
- 如果是 POST/DELETE 过来的会继续使用
- 302 只会使用 get
- 304 (Not Modified)服务器文件未修改,协商缓存
- 308 永久重定向
4xx
- 400 客户端请求有语法错误,不能被服务器识别
- 403 服务器受到请求,但是拒绝提供服务,可能是跨域也可是权限不够
- 404 请求的资源不存在
- 405 请求的 method 不允许

5xx
- 500 服务器发生不可预期的错误

2.字段
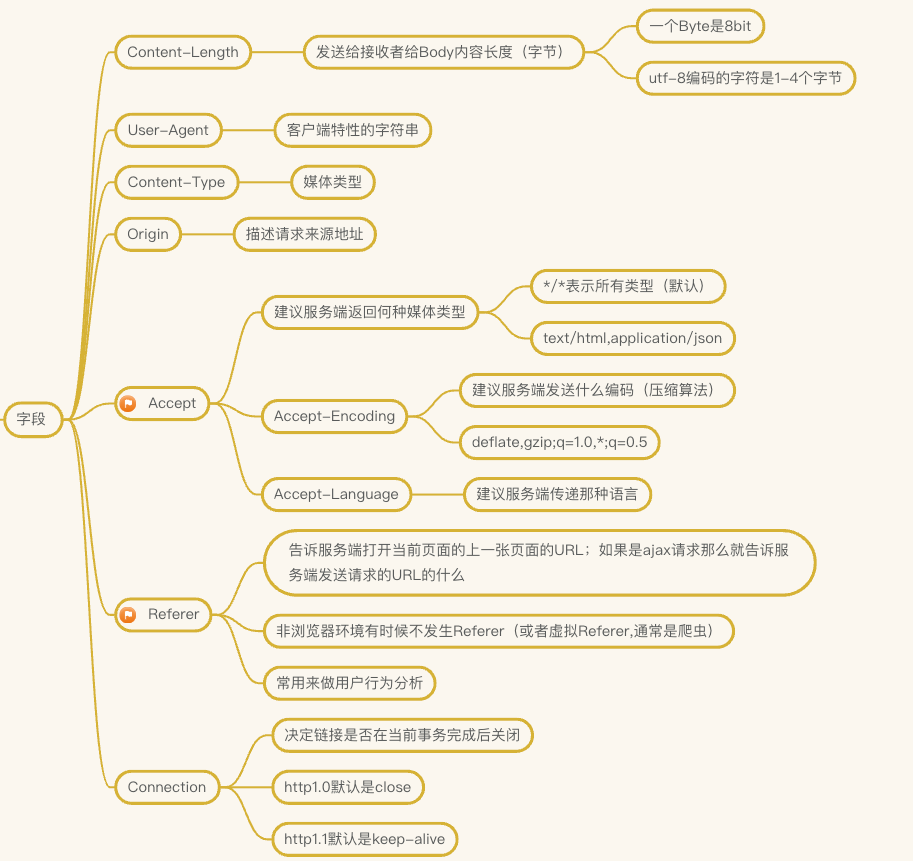
- Content-Length: 发送给接收者给 Body 内容长度(字节)
- 一个 Byte 是 8bit
- utf-8 编码的字符是 1-4 个字节
- User-Agent:客户端特性的字符串
- Content-Type: 媒体类型
- Origin:描述请求来源地址
- Accept
- 建议服务端返回何种媒体类型
- */*表示所有类型(默认)
- text/html,application/json
- 建议服务端返回何种媒体类型
- Accept-Encoding
- 建议服务端发送什么编码(压缩算法)
- deflate,gzip;q=1.0,*;q=0.5
- Accept-Language: 建议服务端传递那种语言
- Referer
- 告诉服务端打开当前页面的上一张页面的 URL;
- 如果是 ajax 请求那么就告诉服务端发送请求的 URL 的什么
- 非浏览器环境有时候不发生 Referer(或者虚拟 Referer,通常是爬虫)
- 常用来做用户行为分析
- Connection
- 决定链接是否在当前事务完成后关闭
- http1.0 默认是 close
- http1.1 默认是 keep-alive
4.拓展方向
如何应对网络不稳定(波动)的情况?
- 失败了重发,指数补偿
const request = (url) => {
let resolved = false;
let t = 1;
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// Promise.race([
// fetch(url),
// wait(100, () => fetch(url)),
// wait(200, () => fetch(url)),
// wait(400, () => fetch(url)),
// wait(800, () => fetch(url)),
// wait(1600, () => fetch(url)),
// ])
function doFetch() {
if (resolved || t > 16) return;
fetch(url)
.then((resp) => resp.text())
.then((data) => {
if (!resolved) {
resolved = true;
resolve(data);
}
});
setTimeout(() => {
doFetch();
t *= 2;
}, t * 100);
}
doFetch();
});
};
如何处理并发请求?
- 若
相同的请求,多次发送,会照成带宽的浪费 - 处理思路:做
缓存 - 因为请求具有
时效性,所以不能做永久缓存 - 相同的请求在
一定的时间内只发生一次- 使用
w保存请求信息,若同一时间发送多次相同对请求 - 使用
w[hash].resolves保存 resolve 函数- 当请求函数
w[hash].func发送成功,执行 resolves 中的函数,保证每次请求都有响应信息
- 当请求函数
- 使用
import fetch from 'node-fetch';
function hash(...args) {
return args.join(',');
}
function window_it(fn, time = 50) {
let w = {}; // 时间窗口
let flag = false;
return (...args) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (!w[hash(args)]) {
w[hash(args)] = {
resolves: [],
func: fn,
args,
};
}
if (!flag) {
flag = true;
setTimeout(() => {
Object.keys(w).forEach((key) => {
console.log(`run ${key}`);
const { func, args, resolves } = w[key];
func(...args)
.then((res) => res.text())
.then((data) => {
resolves.forEach((r) => {
console.log(`resolve ${key}`);
r(data);
});
flag = false;
delete w[key];
});
});
}, time);
}
w[hash(args)].resolves.push(resolve);
});
};
}
const request = window_it(fetch, 20);
request('http://www.baidu.com').then((txt) => console.log(txt.length));
request('http://www.baidu.com').then((txt) => console.log(txt.length));
request('http://www.baidu.com').then((txt) => console.log(txt.length));
request('http://www.zhihu.com').then((txt) => console.log(txt.length));
request('http://www.zhihu.com').then((txt) => console.log(txt.length));
request('http://www.zhihu.com').then((txt) => console.log(txt.length));























 5295
5295











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










