共享模型之不可变
从一个日期转换的问题开始
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test1")
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("{}", sdf.parse("1951-04-21"));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("{}", e);
}
}).start();
}
}
}这里出现了异常
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "4E14"
at java.base/java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65)
at java.base/java.lang.Long.parseLong(Long.java:692)
at java.base/java.lang.Long.parseLong(Long.java:817)
at java.base/java.text.DigitList.getLong(DigitList.java:195)
at java.base/java.text.DecimalFormat.parse(DecimalFormat.java:2121)
at java.base/java.text.SimpleDateFormat.subParse(SimpleDateFormat.java:1933)
at java.base/java.text.SimpleDateFormat.parse(SimpleDateFormat.java:1541)
at java.base/java.text.DateFormat.parse(DateFormat.java:393)
at n7.Test1.lambda$main$0(Test1.java:14)
at java.base/java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:829)加锁当然能解决这个问题
synchronized (sdf){
try {
log.debug("{}", sdf.parse("1951-04-21"));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("{}", e);
}
}换一个不可变类
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test1")
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DateTimeFormatter stf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
TemporalAccessor parse = stf.parse("1951-04-21");
log.debug("{}",parse);
}).start();
}
}
}不可变类的设计
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
/** The value is used for character storage. */
private final char value[];
/** Cache the hash code for the string */
private int hash; // Default to 0
// ...
}
北比如String这个类,他的两个成员变量,一个value[]使用final修饰,一个hash是私有的并且没有get方法,类也加上了fianl修饰,防止子类对其有影响,属性用 final 修饰保证了该属性是只读的,不能修改,类用 final 修饰保证了该类中的方法不能被覆盖,防止子类无意间破坏不可变性
保护性拷贝
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;
if (subLen < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
}发现其内部是调用 String 的构造方法创建了一个新字符串,再进入这个构造看看,是否对 final char[] value 做出了修改:
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= value.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}享元模式
定义 英文名称:Flyweight pattern. 当需要重用数量有限的同一类对象时
在JDK中 Boolean,Byte,Short,Integer,Long,Character 等包装类提供了 valueOf 方法,例如 Long 的valueOf 会缓存 -128~127 之间的 Long 对象,在这个范围之间会重用对象,大于这个范围,才会新建 Long 对象:
public static Long valueOf(long l) {
final int offset = 128;
if (l >= -128 && l <= 127) { // will cache
return LongCache.cache[(int)l + offset];
}
return new Long(l);
}Byte, Short, Long 缓存的范围都是 -128~127
Character 缓存的范围是 0~127
Integer的默认范围是 -128~127
最小值不能变
但最大值可以通过调整虚拟机参数 `
-Djava.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high` 来改变
Boolean 缓存了 TRUE 和 FALSE
例如:一个线上商城应用,QPS 达到数千,如果每次都重新创建和关闭数据库连接,性能会受到极大影响。 这时预先创建好一批连接,放入连接池。一次请求到达后,从连接池获取连接,使用完毕后再还回连接池,这样既节约了连接的创建和关闭时间,也实现了连接的重用,不至于让庞大的连接数压垮数据库。
一个小的连接池例子:
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pool pool=new Pool(2);
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
new Thread(()->{
Connection conn=pool.borrow();
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
pool.free(conn);
}).start();
}
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Pool")
class Pool{
//1.连接池大小
private final int poolSize;
//2.连接对象数组
private Connection[] connections;
//3.连接状态数组,0表示空闲,1表示繁忙
private AtomicIntegerArray states;
//4.构造方法
public Pool(int poolSize){
this.poolSize=poolSize;
this.connections=new Connection[poolSize];
this.states=new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[poolSize]);
for(int i=0;i<poolSize;i++){
connections[i]=new MockConnection("连接"+i);
}
}
//借连接
public Connection borrow() {
while (true){
for (int i=0;i<poolSize;i++){
if(states.get(i)==0){
log.debug("成功进入");
if(states.compareAndSet(i,0,1)){
log.debug("borrow{}",connections[i]);
return connections[i];
}
}
}
//没有空闲连接进入等待
synchronized (this){
try {
log.debug("wait...");
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
//归还连接
public void free(Connection conn){
for (int i=0;i<poolSize;i++){
if(connections[i]==conn){
states.set(i,0);
log.debug("free{}",conn);
synchronized (this){
this.notifyAll();
}
break;
}
}
}
}final原理
设置 final 变量的原理
public class TestFinal {
final int a = 20;
}字节码
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: aload_0
5: bipush 20
7: putfield #2 // Field a:I
<-- 写屏障
10: return获取final变量的原理
1. 编译时的行为
-
编译期常量:如果一个
final变量在声明时就被显式初始化(例如,基本类型或字符串字面量),并且它是静态的(static),那么它会被视为编译期常量。Java编译器会将这些常量的值嵌入到任何使用它们的代码中。这意味着,如果这些final常量的值在编译时是已知的,则它们的使用可以在编译时被直接替换为实际的值。 -
非编译期常量:对于非静态的
final变量,或者其值在运行时才能确定的final变量(例如,通过方法计算得到的值),则它们不是编译期常量。这些变量的值存储在类的实例中(非静态)或类本身(静态但非常量)。
2. 运行时的行为
-
内存模型和可见性:
final字段的最大特点之一在于它们对内存模型的影响。在Java内存模型中,正确构造的对象(在对象的构造函数完成后,final字段的值就不再改变)中的final字段,可以保证被不同线程安全地读取,无需额外的同步措施。这种行为是通过在构造器结束时对final字段的写入,以及每次读取final字段时都建立的“初始化安全性”保证来实现的。 -
构造器内的赋值:Java允许在构造器内部对
final变量进行赋值。一旦构造器完成,final变量的值就固定下来,任何尝试修改final变量的操作都将导致编译错误。
共享模型之工具
线程池
自定义线程池
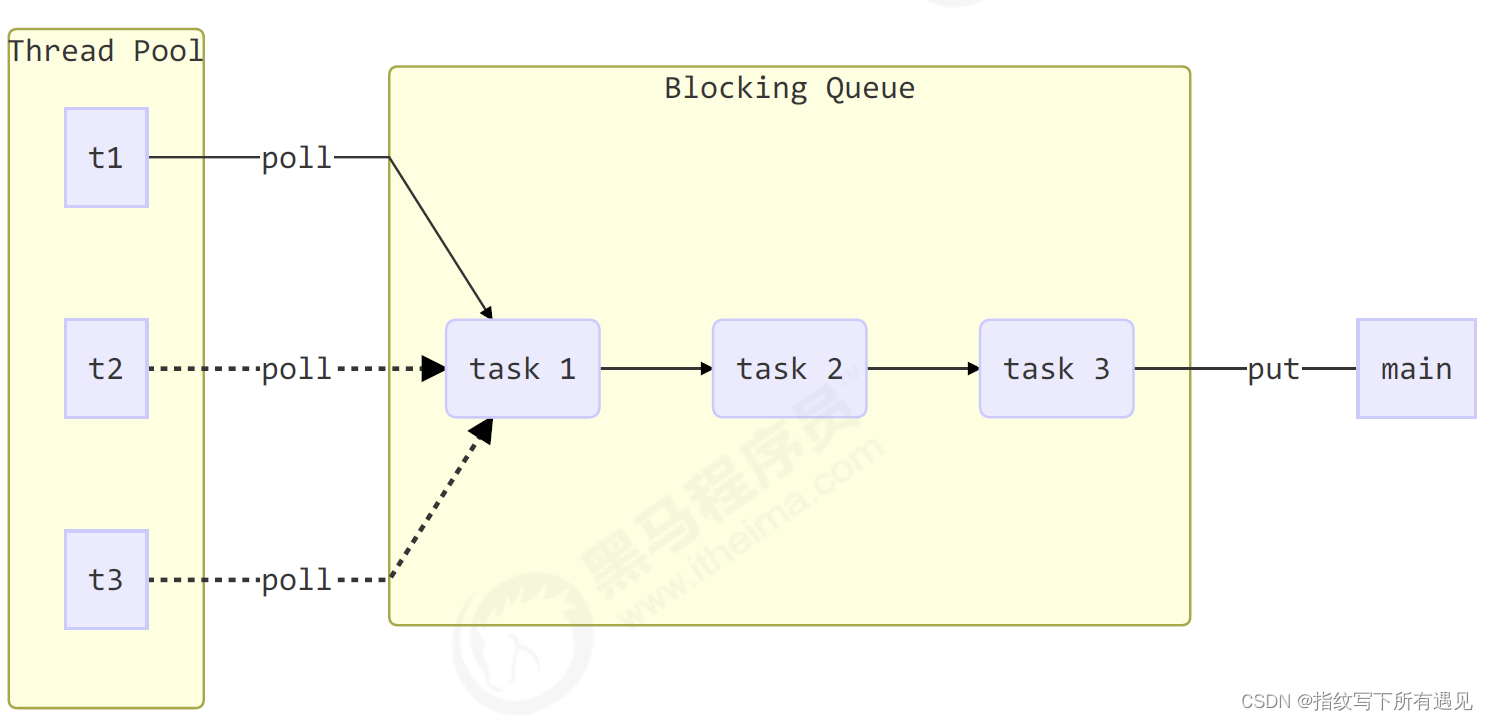
终于成功了
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test1")
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool= new ThreadPool(2,1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,10);
for (int i=0;i<5;i++){
int j=i;
threadPool.excute(()->{
log.debug("{}",j);
});
}
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool{
//任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
//线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers=new HashSet();
//核心线程数
private int coreSize;
//获取任务的超时时间
private long timeout;
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
//执行任务
public void excute(Runnable task){
//当任务数没有超过coreSize时,交给worker对象执行,如果超过了,加入任务队列暂存
synchronized (workers){
if(workers.size()<coreSize){
Worker worker=new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增worker {},{}",worker,task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
}else {
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}",task);
taskQueue.put(task);
}
}
}
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit,int queueCapCIty) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue=new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapCIty);
}
class Worker extends Thread{
private Runnable task;
public Worker( Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run(){
//执行任务1.当task不为空,直接执行任务2.当task执行完毕,接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
while (task!=null||(task=taskQueue.take())!=null){
try {
log.debug("正在执行...{}",task);
task.run();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
task=null;
}
}
synchronized (workers){
log.debug("worker被移除{}",this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}
}
class BlockingQueue<T>{
//1.任务队列
private Deque<T> queue=new ArrayDeque<>();
//2.锁
private ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock();
//3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet=lock.newCondition();
//4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet=lock.newCondition();
//5.容量
private int capcity;
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capcity=capacity;
}
//带超时的阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit){
lock.lock();
try {
//将超时时间转化为纳秒
long nanos=unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()){
try {
//返回的是剩余时间
if(nanos<=0){
return null;
}
nanos= emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
T t=queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞获取
public T take(){
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()){
try {
emptyWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
T t=queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞添加
public void put(T element){
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size()==capcity){
try {
fullWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
queue.addLast(element);
//放完了之后唤醒一下等着队列元素的线程
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//获取大小
public int size(){
lock.lock();
try {
return capcity;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}17:16:48 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增worker Thread[Thread-0,5,main],n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@77167fb7
17:16:48 [main] c.ThreadPool - 新增worker Thread[Thread-1,5,main],n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@3c9d0b9d
17:16:48 [main] c.ThreadPool - 加入任务队列 n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@2f112965
17:16:48 [Thread-0] c.ThreadPool - 正在执行...n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@77167fb7
17:16:48 [main] c.ThreadPool - 加入任务队列 n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@1a04f701
17:16:48 [main] c.ThreadPool - 加入任务队列 n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@4e91d63f
17:16:48 [Thread-1] c.ThreadPool - 正在执行...n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@3c9d0b9d
17:16:48 [Thread-0] c.Test1 - 0
17:16:48 [Thread-1] c.Test1 - 1
17:16:48 [Thread-1] c.ThreadPool - 正在执行...n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@1a04f701
17:16:48 [Thread-0] c.ThreadPool - 正在执行...n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@2f112965
17:16:48 [Thread-1] c.Test1 - 3
17:16:48 [Thread-0] c.Test1 - 2
17:16:48 [Thread-1] c.ThreadPool - 正在执行...n8.Test1$$Lambda$30/0x00000008000d5440@4e91d63f
17:16:48 [Thread-1] c.Test1 - 4
下面这个加了拒绝策略
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test1")
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool= new ThreadPool(1,1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,1,(queue,task)->{
//1.死等
//queue.put(task);
//2.带超时等待
//queue.offer(task,500,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//3.让调用者放弃执行
//log.debug("放弃",task);
//4.抛出异常
//throw new RuntimeException("任务执行失败"+task);
//5.让调用者自己执行任务
task.run();
});
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
int j=i;
threadPool.excute(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
log.debug("{}",j);
});
}
}
}
@FunctionalInterface//拒绝策略
interface RejectPolicy<T>{
void reject(BlockingQueue queue,T task);
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ThreadPool")
class ThreadPool{
//任务队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
//线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers=new HashSet();
//核心线程数
private int coreSize;
//获取任务的超时时间
private long timeout;
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
private RejectPolicy<Runnable>rejectPolicy;
//执行任务
public void excute(Runnable task){
//当任务数没有超过coreSize时,交给worker对象执行,如果超过了,加入任务队列暂存
synchronized (workers){
if(workers.size()<coreSize){
Worker worker=new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增worker {},{}",worker,task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
}else {
log.debug("加入任务队列 {}",task);
taskQueue.put(task);
/*
* 1.死等
* 2..带超时等待
* 3.放弃执行
* 4.抛出异常
* */
taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPolicy,task);
}
}
}
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeout, TimeUnit timeUnit,int queueCapCIty,RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPolicy) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeout = timeout;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue=new BlockingQueue<>(queueCapCIty);
this.rejectPolicy=rejectPolicy;
}
class Worker extends Thread{
private Runnable task;
public Worker( Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run(){
//执行任务1.当task不为空,直接执行任务2.当task执行完毕,接着从任务队列获取任务并执行
while (task!=null||(task=taskQueue.poll(timeout,timeUnit))!=null){
try {
log.debug("正在执行...{}",task);
task.run();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
task=null;
}
}
synchronized (workers){
log.debug("worker被移除{}",this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.BlockingQueue")
class BlockingQueue<T>{
//1.任务队列
private Deque<T> queue=new ArrayDeque<>();
//2.锁
private ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock();
//3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet=lock.newCondition();
//4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet=lock.newCondition();
//5.容量
private int capcity;
public BlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.capcity=capacity;
}
//带超时的阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit){
lock.lock();
try {
//将超时时间转化为纳秒
long nanos=unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()){
try {
//返回的是剩余时间
if(nanos<=0){
return null;
}
nanos= emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
T t=queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞获取
public T take(){
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()){
try {
emptyWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
T t=queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞添加
public void put(T element){
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size()==capcity){
try {
log.debug("等待加入任务队列{}...",element);
fullWaitSet.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列{}",element);
queue.addLast(element);
//放完了之后唤醒一下等着队列元素的线程
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//带超时时间的阻塞添加
public boolean offer(T task,long timeout,TimeUnit timeUnit){
lock.lock();
try {
long nanos=timeUnit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.size()==capcity){
try {
log.debug("等待加入任务队列{}...",task);
if(nanos<=0){
return false;
}
nanos= fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列{}",task);
queue.addLast(task);
//放完了之后唤醒一下等着队列元素的线程
emptyWaitSet.signal();
return true;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//获取大小
public int size(){
lock.lock();
try {
return capcity;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void tryPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPolicy,T task){
lock.lock();
try {
if(queue.size()==capcity){
rejectPolicy.reject(this,task);
}else {
log.debug("加入任务队列{}",task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}




















 131
131

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








