一、定义
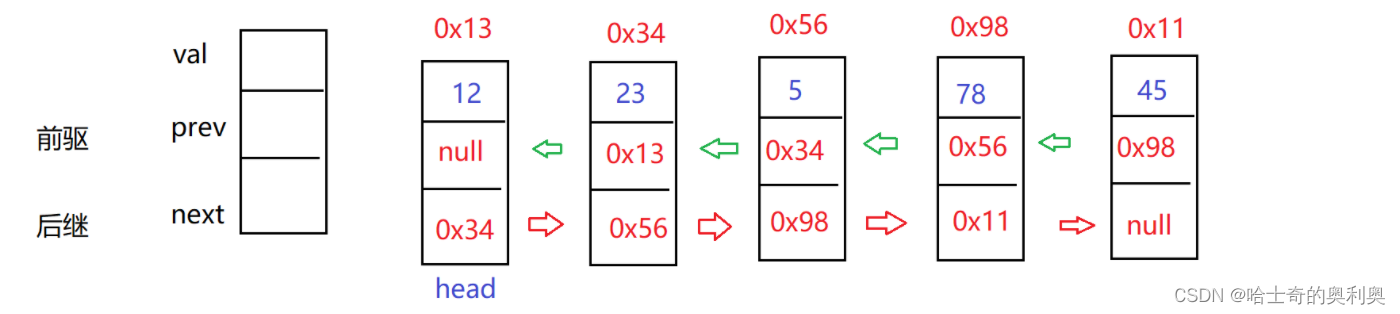
与单向无头非循环链表相比多了一个前驱
二、实现MyLinkedList
1.双向非循环链表的构建
public class MyLinkedList {
static class listNode{
public int val;
// 前驱
public listNode prev;
// 后继
public listNode next;
public listNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
// 头节点
public listNode head;
// 尾节点
public listNode last;
}2.头插法
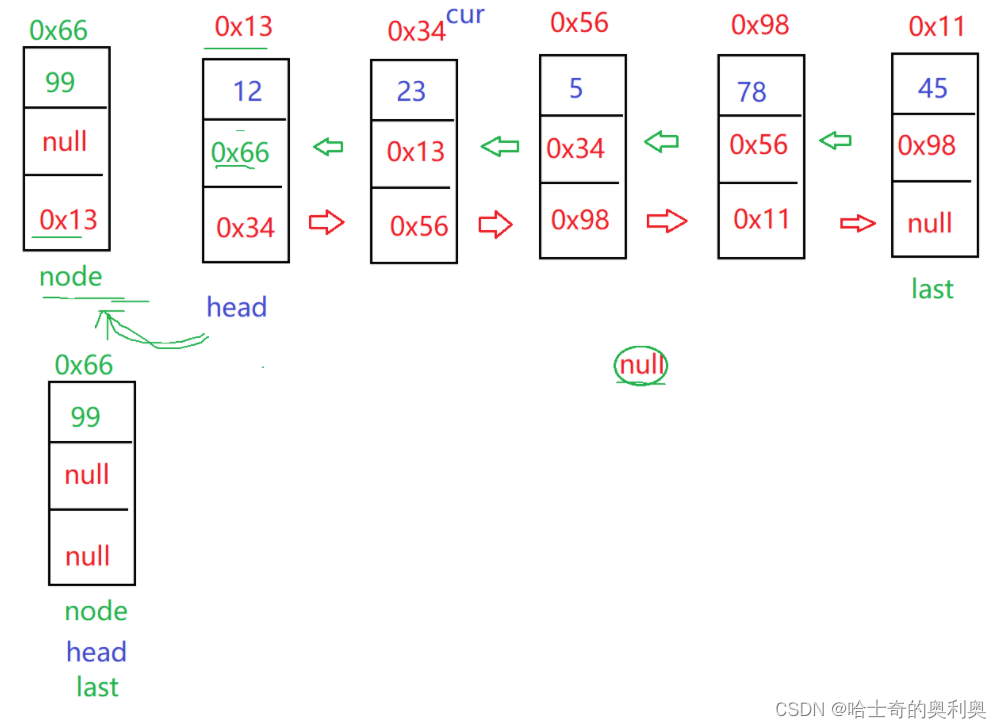
public void addFirst(int data){
listNode node = new listNode(data);
if(head == null){
head = node;
last = node;
}else{
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
} 
2.尾插法
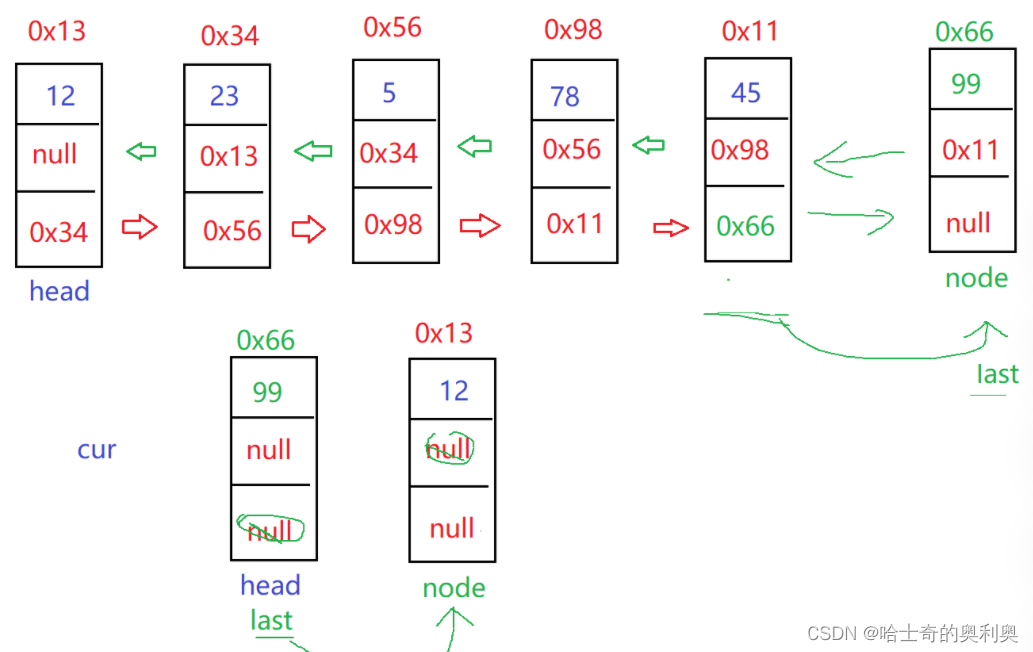
public void addLast(int data){
listNode node = new listNode(data);
if(head == null){
head = node;
last = node;
}else{
last.next = node;
node.prev = last;
last = node;
}
}
3.打印链表
public void display(){
listNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}与单向无头非循环链表一样
4.链表长度
public int size(){
listNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}与单向无头非循环链表一样
5.判断是否包含关键字key在双向链表中
public boolean contains(int key){
listNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
与单向无头非循环链表一样
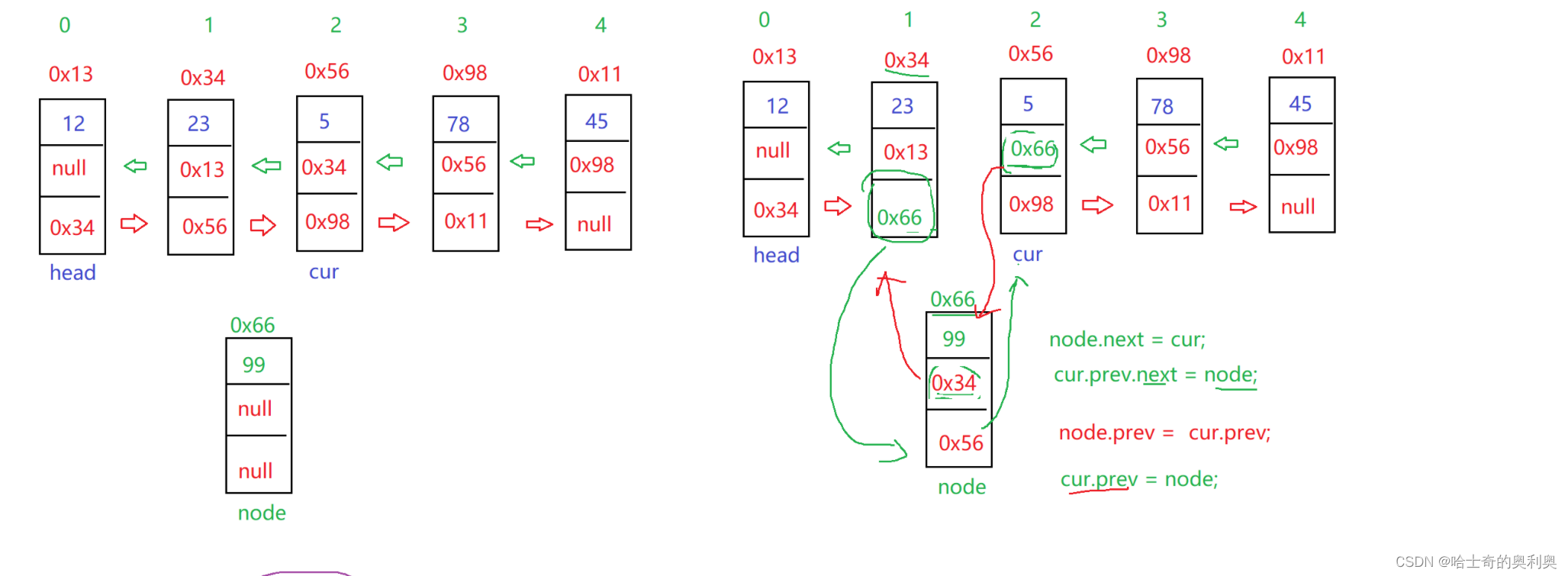
6.任意位置插入一个数据节点
思路:1.检查index是否越界
2.检查index==0 >> 头插法
3.检查index==size() >> 尾插法
4.正常插入
public void addIndex(int index,int data) throws ListIndexOutOfException{
if(index<0 || index > size()){
throw new ListIndexOutOfException("越界");
}
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if(index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
listNode cur = head;
while (index != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
listNode node = new listNode(data);
node.next = cur;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
}
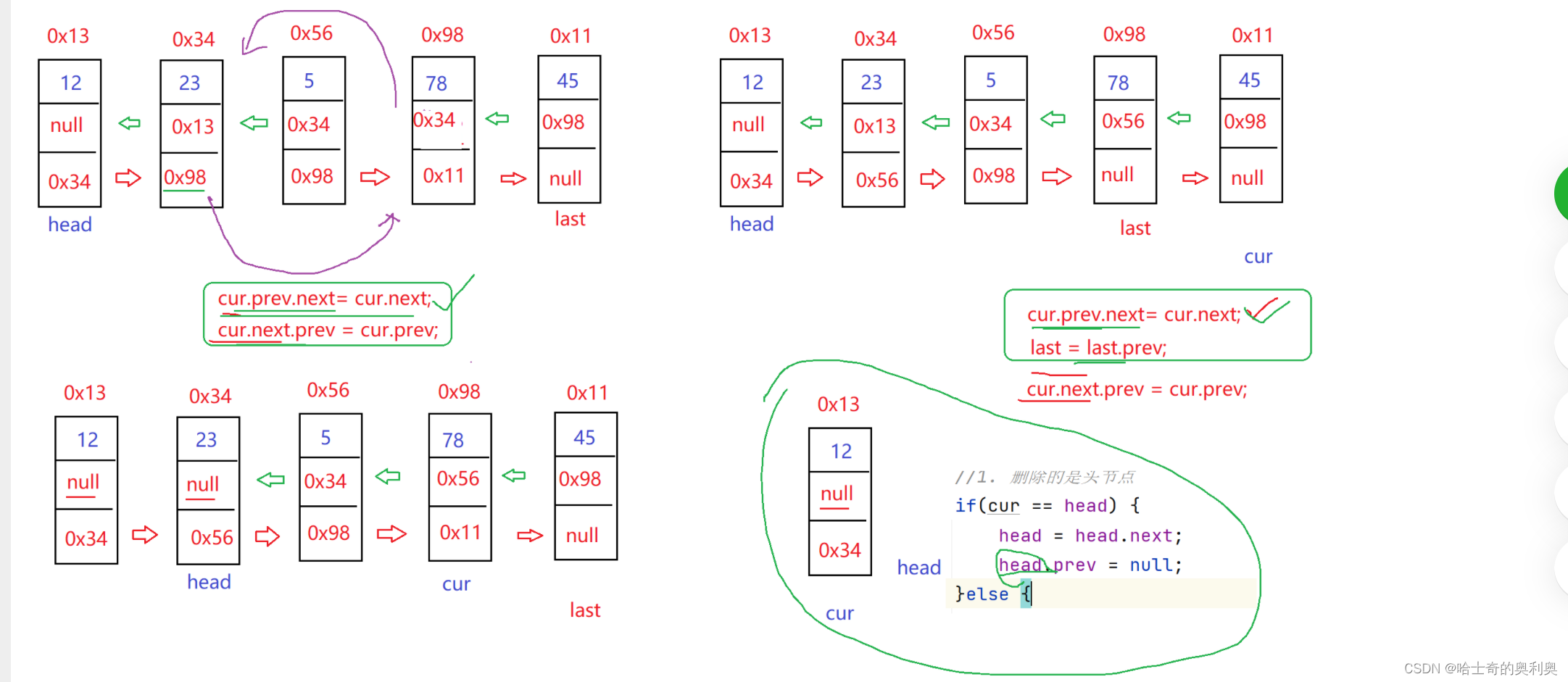
7.删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
思路:分删除头节点,中间节点,尾节点
删除头结点,考虑链表只有头结点,要是有大于两个以上的节点,需要将head = head.next 然后head.prev = null;
删除中间节点 cur.prev.next = cur.next cur.next.prev = cur.prev
删除尾节点 cur.prev.next = cur.next 此时cur.next == null,需要将last = last.prev;
public void remove(int key){
listNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
if(head == cur){
//只有一个head节点
head = head.next;
if(head != null){
head.prev =null;
}
}else{
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if(cur.next != null){
cur.next.pev = cur.prev;
}else{
last = last.prev;
}
}
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
8.删除所有key值节点
public void remove(int key){
listNode cur = head;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
if(cur == head){
head = head.next;
if(head != null){
head.prev = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if(cur.next!=null){
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
last = last.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}去掉return继续进行查找进行删除。
清空MyLnkedList
public void clear(){
listNode cur = head;
// 遍历链表,将节点的前驱和后继进行置为null
while (cur != null){
listNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.prev = null;
cur.next =null;
cur = curNext;
}
// 将头结点和last节点引用进行置为null
head = null;
last = null;
}三、什么是LinkedLIst
LinkedList的底层是双向链表结构(链表后面介绍),由于链表没有将元素存储在连续的空间中,元素存储在单独的节
点中,然后通过引用将节点连接起来了,因此在在任意位置插入或者删除元素时,不需要搬移元素,效率比较高
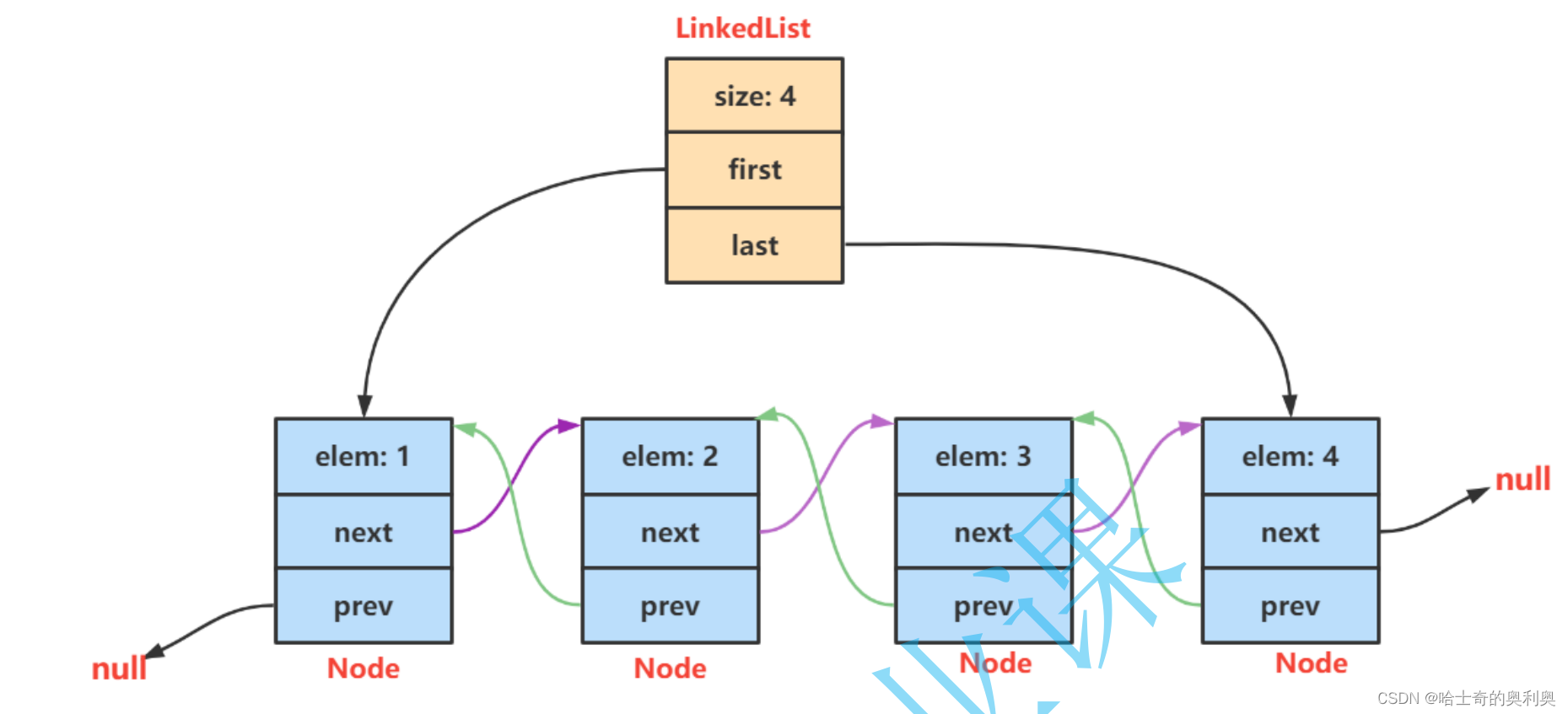
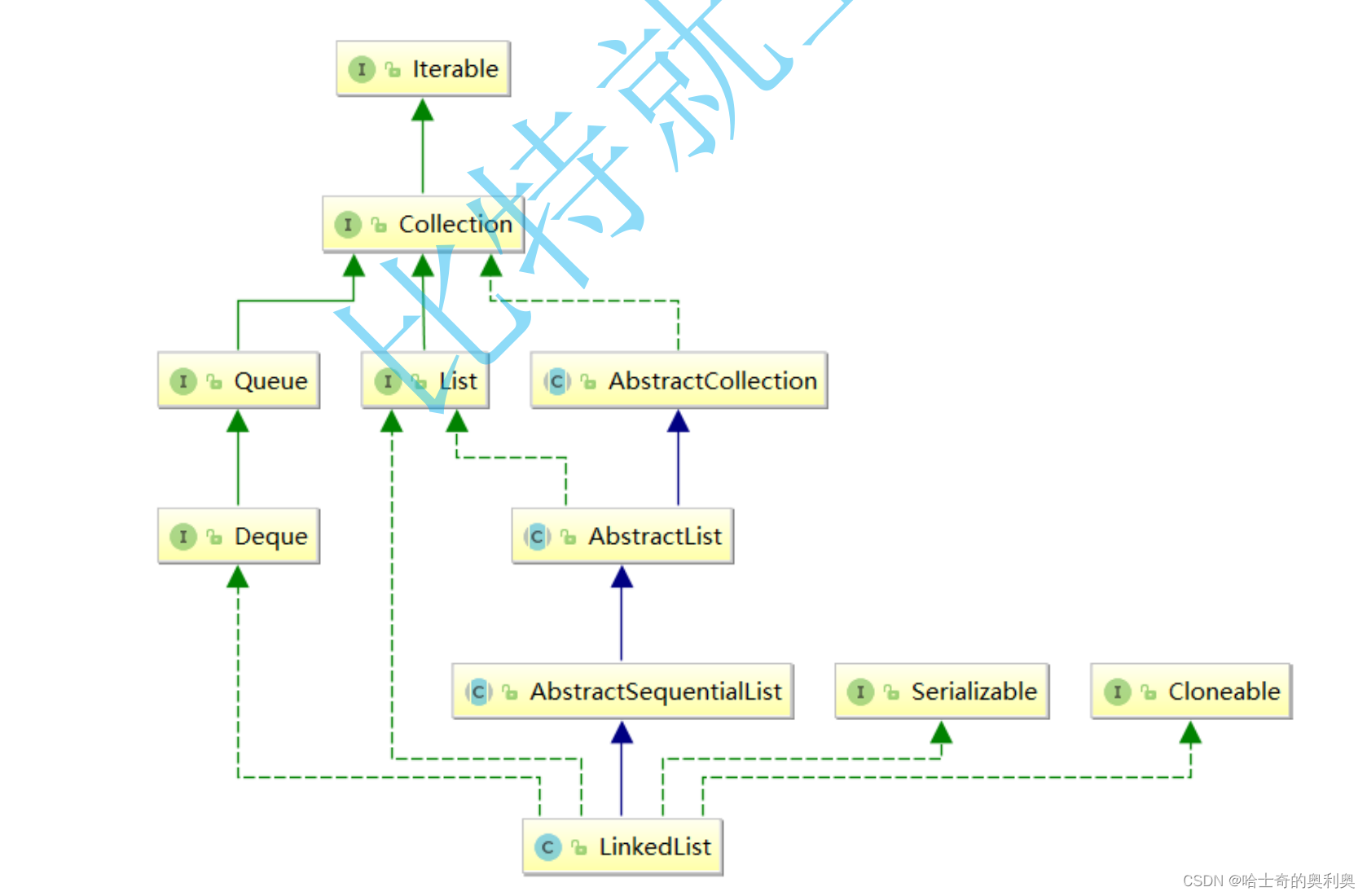
1. LinkedList实现了List接口
2. LinkedList的底层使用了双向链表
3. LinkedList没有实现RandomAccess接口,因此LinkedList不支持随机访问
4. LinkedList的任意位置插入和删除元素时效率比较高,时间复杂度为O(1)
5. LinkedList比较适合任意位置插入的场景
四、LinkedList的使用
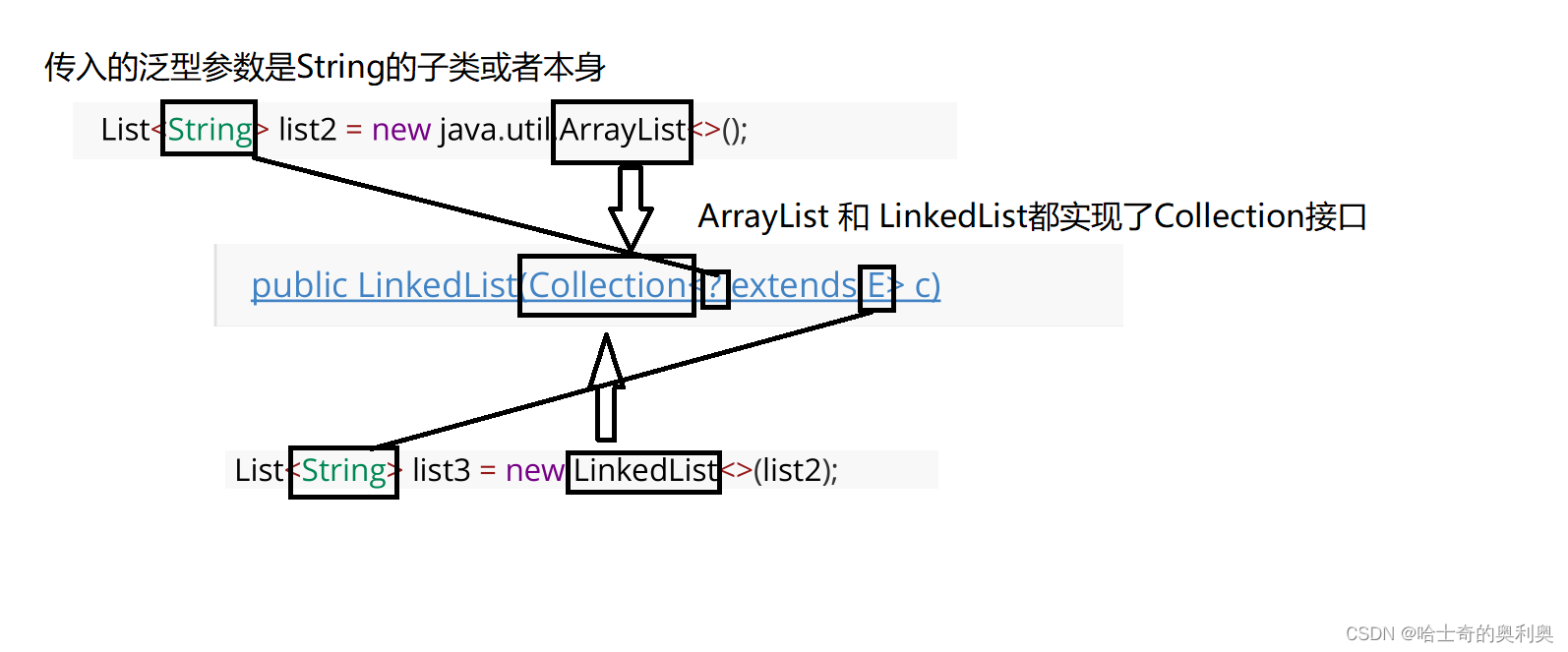
1. LinkedList的构造方法
方法 | 解释 |
LinkedList() | 无参构造 |
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) | 使用其他集合容器中元素构造List |
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造一个空的LinkedList
List<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add("JavaSE");
list2.add("JavaWeb");
list2.add("JavaEE");
// 使用ArrayList构造LinkedList
List<String> list3 = new LinkedList<>(list2);
}含参的构方法
2.LinkedList其他方法
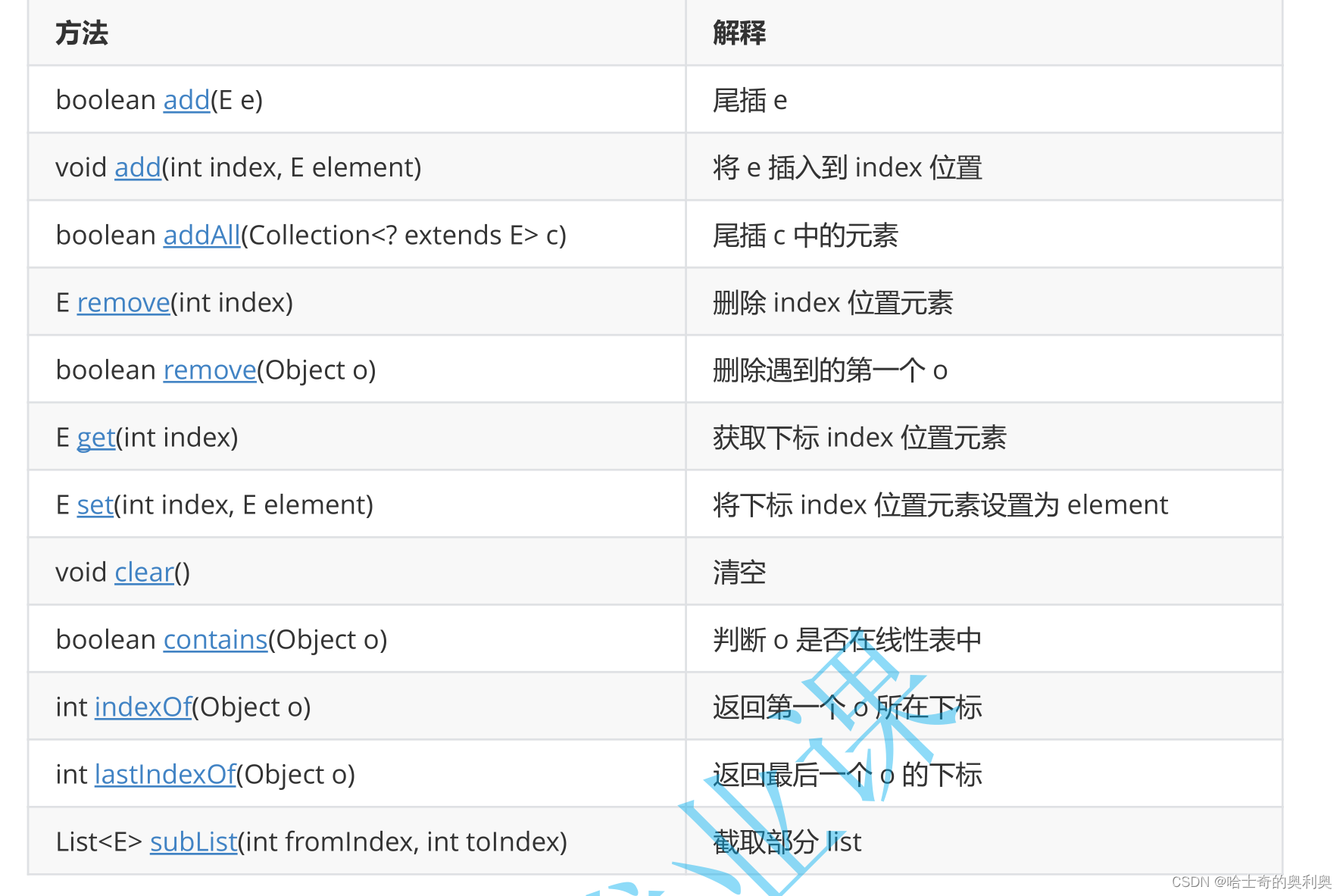
1.尾插法
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list);
}2.在指定位置插入
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 在起始位置插入0
list.add(1, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
}3.删除元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
System.out.println(list);
// contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
if(!list.contains(1)){
list.add(0, 1);
}
}4.是否包含元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
// contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
boolean ret = list.contains(1);
}5.查找元素以及设置指定位置的元素
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(list.indexOf(1)); // indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第一个elem的位置
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1)); // lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第一个1的位置
int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
System.out.println(list);
}6.copyLinkedLIst(指定范围)——subList(from,to) [from,to)
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(copy);
}3. LinkedList的遍历
for循环
for-each进行遍历
迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
// 1.for循环
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
// 2.for each
for (Integer x :list) {
System.out.print(x+" ");
}
System.out.println();
// 3.迭代器
ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+" ");
}
// 4.迭代器反向迭代 传入迭代链表的长度,使用Previous
ListIterator<Integer> it2 = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (it2.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(it2.previous()+" ");
}
}五、ArrayList和LinkedList的区别
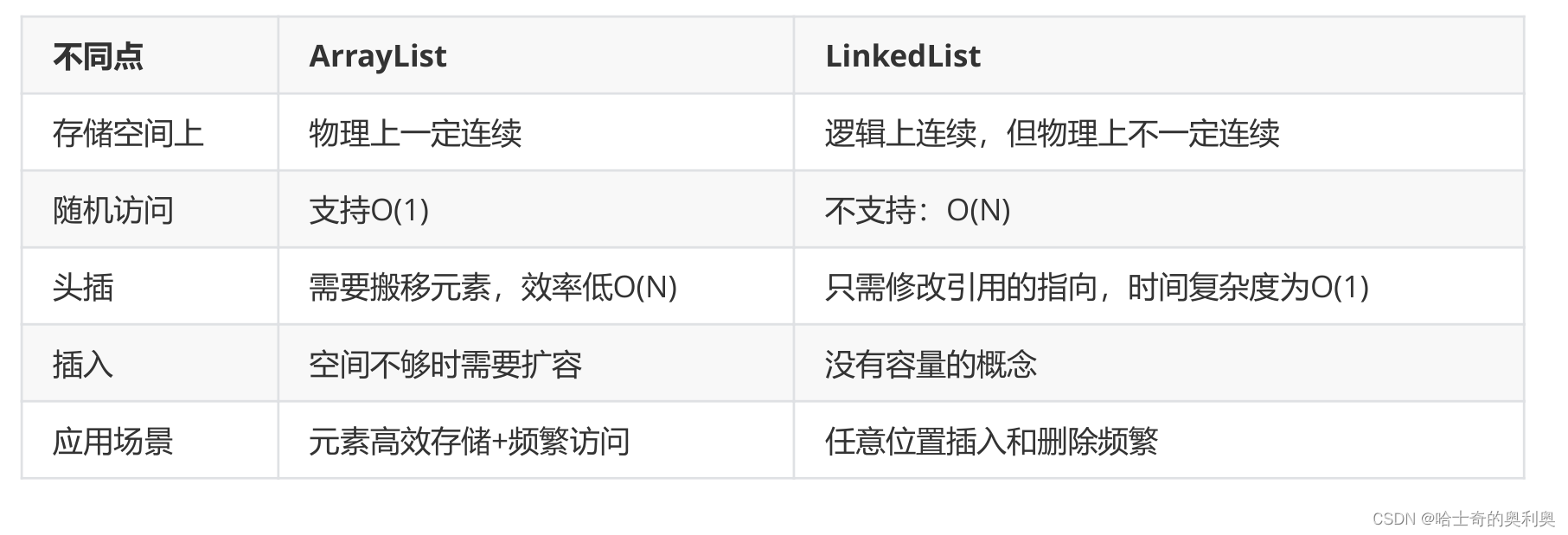























 218
218

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










