医学术语是学习医学知识的基础和前提。公众号推出“医学双语术语”栏目,每一期采用英汉对照的模式,以双语的形式科普医学知识,同时也为医学英语与翻译专业人士提供学习素材。文中标有背景色的部分文字涉及通用学术英语和医学专门学术英语学习过程中常用的单词及短语表达等问题。
Key Facts 重要事实
--The global prevalence of diabetes among adults over 18 years of age has risen from 4.7% in 1980 to 8.5% in 2014.
全球18岁以上的成年人中糖尿病的患病率已经从1980年的4.7%增长到2014年的8.5%。
--In 2012, an estimated 1.5 million deaths were directly caused by diabetes.
2012年,估计糖尿病直接造成150万例死亡。
--WHO projects that diabetes will be the 7th leading cause of death in 2030 .
世卫组织预测,2030年糖尿病将成为第七大死因。
--Having healthy diet, keeping regular physical activity, maintaining a normal body weight and avoiding tobacco use are ways to prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
健康饮食、经常锻炼身体、保持正常体重和避免使用烟草,可预防Ⅱ型糖尿病或推迟其发病。
What is Diabetes? 什么是糖尿病?
Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs either when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar. Hyperglycaemia, or raised blood sugar, is a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes and over time leads to serious damage to many of the body's systems, especially the nerves and blood vessels.
糖尿病是一种慢性病,当胰腺产生不了足够的胰岛素或者人体无法有效地利用所产生的胰岛素时,就会出现糖尿病。胰岛素是一种调节血糖的激素。高血糖症或血糖升高,是糖尿病不加控制的一种通常结果,随着时间的推移会对人体的许多系统带来严重损害,特别是神经和血管。
Types and Symptoms 类型及症状
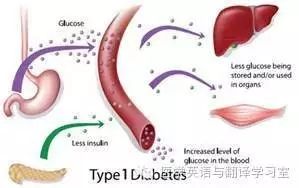
Type 1 DiabetesⅠ型糖尿病
Type 1 diabetes (previously known as insulin-dependent, juvenile or childhood-onset) is characterized by deficient insulin production and requires daily administration of insulin. The cause of type 1 diabetes is not known and it is not preventable with current knowledge.
Ⅰ型糖尿病(过去称为胰岛素依赖型,青少年或儿童期发病型糖尿病)的特征是缺乏胰岛素分泌能力,需要每天注射胰岛素。Ⅰ型糖尿病病因不详,利用现有的知识也无法预防。
Symptoms include excessive excretion of urine (polyuria), thirst (polydipsia), constant hunger, weight loss, vision changes and fatigue. These symptoms may occur suddenly.
症状包括尿液分泌过多(多尿)、口渴(多饮)、常有饥饿感、体重减轻、视力减退和疲乏。这些症状可突然出现。

Type 2 DiabetesⅡ型糖尿病
Type 2 diabetes (formerly called non-insulin-dependent or adult-onset) results from the body’s ineffective use of insulin. Type 2 diabetes comprises the majority of people with diabetes around the world , and is largely the result of excess body weight and physical inactivity.
Ⅱ型糖尿病(过去称为非胰岛素依赖或成人发病型糖尿病)由于人体无法有效利用胰岛素造成。世界各地的糖尿病患者多数人患有Ⅱ型糖尿病,主要是因体重过重和缺乏身体活动所致。
Symptoms may be similar to those of Type 1 diabetes, but are often less marked. As a result, the disease may be diagnosed several years after onset, once complications have already arisen.
症状可能与Ⅰ型糖尿病相似,但往往症状不明显。结果,可能在发病多年之后才诊断出患有糖尿病,此时则已出现并发症。
Until recently, this type of diabetes was seen only in adults but it is now also occurring increasingly frequently in children.
直到最近,这类糖尿病还只见于成人,但目前也有儿童发病情况。
Gestational Diabetes 妊娠期糖尿病
Gestational diabetes is hyperglycaemia with blood glucose values above normal but below those diagnostic of diabetes, occurring during pregnancy. Women with gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of complications during pregnancy and at delivery.They and their children are also at increased risk of type 2 diabetes in the future.
妊娠期糖尿病是高血糖症,血糖值高于正常水平但低于糖尿病的诊断值,发生在妊娠期间。患有妊娠期糖尿病的妇女在妊娠和分娩期间出现并发症的危险增大。她们及其子女日后患上Ⅱ型糖尿病的危险也增大。
Gestational diabetes is diagnosed through prenatal screening, rather than through reported symptoms.
妊娠期糖尿病通常可通过产前筛查而不是病例报告中的症状而得以诊断。
Impaired Glucose Tolerance and Impaired Fasting Glycaemia 糖耐量受损(IGT)和空腹血糖受损(IFG)
Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and impaired fasting glycaemia (IFG) are intermediate conditions in the transition between normality and diabetes. People with IGT or IFG are at high risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes, although this is not inevitable.
糖耐量受损(IGT)和空腹血糖受损(IFG)是指人体血糖值介于正常与糖尿病血糖值之间过渡阶段的一种中间状态。糖耐量受损患者或空腹血糖受损患者面临发展为Ⅱ型糖尿病的高度风险,虽然这并非不可避免。
Consequences 后果
--Over time, diabetes can damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
随着时间的推移,糖尿病可能损害心脏、血管、眼睛、肾脏和神经。
--Adults with diabetes have an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes.
糖尿病成人患者罹患心脏病和中风的风险增加。
--Combined with reduced blood flow, neuropathy (nerve damage) in the feet increases the chance of foot ulcers, infection and eventual need for limb amputation.
足部神经病变(神经受损),血流量减少,可增加足部溃疡、感染以及最终需要截肢的可能。
--Diabetic retinopathy is an important cause of blindness, and occurs as a result of long-term accumulated damage to the small blood vessels in the retina. 2.6% of global blindness can be attributed to diabetes.
糖尿病视网膜病变是失明的一主要病因,它是视网膜小血管长期累积受损的结果。全球2.6%的盲症可归咎于糖尿病。
--Diabetes is among the leading causes of kidney failure .
糖尿病位居肾衰竭主要病因之列。
Prevention 预防
Simple lifestyle measures have been shown to be effective in preventing or delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes. To help prevent type 2 diabetes and its complications, people should:
事实表明,改变一下生活方式,对预防Ⅱ型糖尿病或推迟发病是有效的。为有助于预防Ⅱ型糖尿病及其并发症,人们应当:
--achieve and maintain healthy body weight;
达到和保持健康的体重;
--be physically active – at least 30 minutes of regular, moderate-intensity activity on most days. More activity is required for weight control;
积极进行体力活动——经常定期进行至少30分钟强度适中的活动。需要增加活动来控制体重;
--eat a healthy diet, avoiding sugar and saturated fats intake;
保证健康饮食,并减少糖和饱和脂肪的摄入量;
--avoid tobacco use – smoking increases the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
避免使用烟草——吸烟增加患糖尿病和心血管病的危险。
Diagnosis and treatment 诊断和治疗
Early diagnosis can be accomplished through relatively inexpensive testing of blood sugar.
可以通过相对价廉的验血进行早期诊断。
Treatment of diabetes involves diet and physical activity along with lowering blood glucose and the levels of other known risk factors that damage blood vessels. Tobacco use cessation is also important to avoid complications.
糖尿病的治疗包括饮食疗法、运动疗法、降低血糖和其他损害血管的已知危险因素水平。戒烟对避免并发症也具有重要意义。
Interventions that are both cost-saving and feasible in developing countries include :
对发展中国家来说即节省费用又具可行性的干预措施包括:
--blood glucose control, particularly in type 1 diabetes. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin, people with type 2 diabetes can be treated with oral medication, but may also require insulin;
适当控制血糖,尤其是Ⅰ型糖尿病患者。Ⅰ型糖尿病患者需要注射胰岛素;Ⅱ型糖尿病患者可采用口服药物治疗,但也可能需要胰岛素治疗;
--blood pressure control;
血压控制;
--foot care.
足部护理。
Other cost saving interventions include:
其他可节省成本的干预措施包括:
--screening and treatment for retinopathy (which causes blindness);
视网膜病(造成失明)筛查和治疗;
--blood lipid control (to regulate cholesterol levels);
血脂控制(调节胆固醇水平);
--screening for early signs of diabetes-related kidney disease and treatment.
筛查与糖尿病有关的肾脏疾病的早期征兆和治疗方案。
![]()
重点医学单词及词汇汇总:
1.prevalence ['prevələns] 患病率
2.diabetes [.daɪə'bitiz] 糖尿病
3.chronic ['krɒnɪk] 慢性的
4.pancreas ['pæŋkriəs] 胰腺
5.insulin ['ɪnsəlɪn] 胰岛素
6.hormone [ 'hɔr.moʊn] 激素
7.hyperglycaemia [.haɪpərɡlaɪ'simiə] 高血糖
8.blood vessel [blʌd 'ves(ə)l] 血管
9.excessive excretion of urine [ɪk'sesɪv ɪk'skriʃ(ə)n əv 'jʊrɪn] 尿液分泌过多
10.polyuria ['pɒlɪ'jərɪə] 多尿症
11.polydipsia [ˌpɒlɪ'dɪpsɪə] 多饮;烦渴
12.complication [.kɑmplɪ'keɪʃ(ə)n] 并发症
13.gestational diabetes [dʒe'steɪʃənəl .daɪə'bitiz] 妊娠期糖尿病
14.blood glucose value [blʌd 'ɡlu.koʊz 'vælju] 血糖值
15.prenatal screening [.pri'neɪt(ə)l 'skrinɪŋ] 产前筛查
16.impaired glucose tolerance [ɪm'perd 'ɡlu.koʊz 'tɑlərəns] 糖耐量受损
17.impaired fasting glycaemia [ɪm'perd 'fɑːstɪŋ ɡlai'si:miə] 空腹血糖受损
18.stroke [stroʊk] 中风
19.neuropathy [nʊ'rɒpəθɪ] 神经病,神经病变
20.ulcer ['ʌlsər] 溃疡
21.limb amputation [lɪmˌæmpjʊ'teɪʃ(ə)n] 截肢
22.diabetic retinopathy [.daɪə'betɪk retɪ'nɒpəθɪ] 糖尿病性视网膜病
23.retina ['retɪnə] 视网膜
24.saturated fat ['sætʃə.reɪtɪd fæt] 饱和脂肪
25.cardiovascular disease [.kɑrdioʊ'væskjələr dɪ'ziz] 心血管疾病
26.glucose ['ɡlu.koʊz] 葡萄糖
27.blood lipid control [blʌd 'lɪpɪd kən'troʊl] 血脂控制
注:英汉文字材料整理自WHO官网。致敬 英语翻译学习者



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










