一、前置知识
官方解读
在使用v-for进行列表渲染时,我们通常会给元素或者组件绑定一个key属性。那么这个key属性有什么作用呢?我们先来看一下官方的解释:
- key 这个特殊的 attribute 主要作为 Vue 的虚拟 DOM 算法提示,在比较新旧节点列表时用于识别 vnode。
- 在没有 key 的情况下,Vue 将使用一种最小化元素移动的算法,并尽可能地就地更新/复用相同类型的元素。
- 如果传了 key,则将根据 key 的变化顺序来重新排列元素,并且将始终移除/销毁 key 已经不存在的元素。
- 同一个父元素下的子元素必须具有唯一的 key。重复的 key 将会导致渲染异常。
VNode
VNode的全称是Virtual Node,也就是虚拟节点;事实上,无论是组件还是元素,它们最终在Vue中表示出来的都是一个个VNode。VNode的本质是一个JavaScript对象。大概是这个样子。
<div class="title" style="color: red;">Vue</div>
const vnode = {
type: "div",
props: {
class: "title",
style: {
color: "red",
},
},
children: "Vue"
}
二、一个小例子
想象这样一个例子,v-for渲染一个包含[ ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’ ]的数组,然后定义一个方法,可以往’b’后插入’d’。
我们可以先想一下要进行上面的操作的话,可以有几种实现方式。
全部干掉——完全不推荐
即将原先的内容全部删除,然后再重新生成一个新数组再进行渲染。
修改部分——也不推荐
这个算法其实是vue中对没key时的一个处理,所以这里我就不再赘述,下面会有演示。
了解了上面那些东西之后,你就可以相对比较轻松地学习接下来的内容了。
三、diff算法
新旧vnode对比以达到尽可能地复用地这个算法就叫做diff。
而Vue对有key和没key会调用两种不同的方法;有key,那么就使用patchKeyedChildren方法;没key,就使用patchUnkeyedChildren方法。
如果你有下载vue3源码的话,可以在下载后的代码的‘packages\runtime-core\src\renderer.ts’中找到对应的代码,不过没有下载也不影响你接下来的阅读。
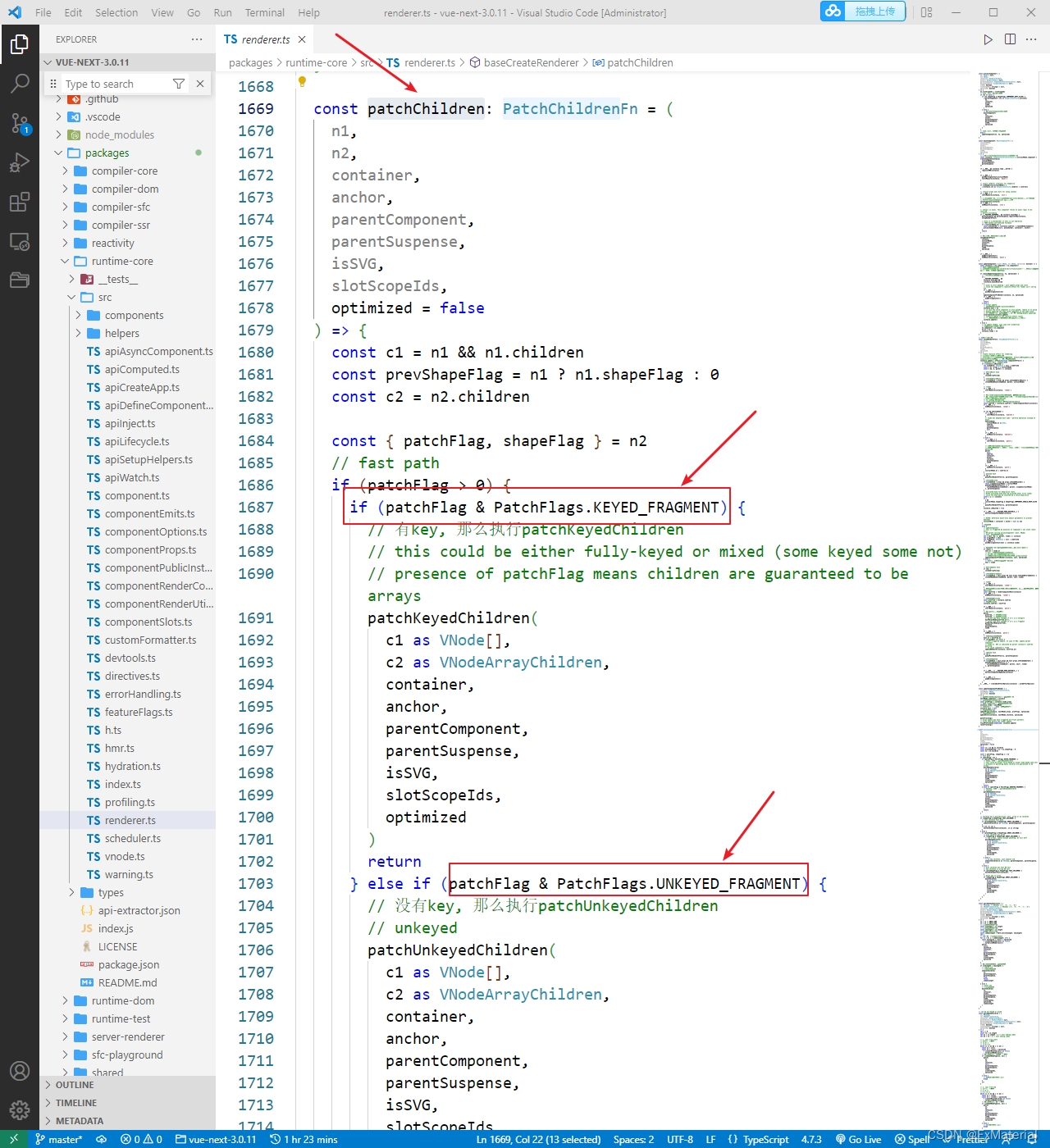
此时vue内部会对是否有key进行判断,上图中已经给出判断的具体位置。
无key
因为vue3是用typescript写的,所以可能有些代码你看不懂,但是逻辑上还是挺容易理解的,应该不影响你继续阅读。
如果你懒得看源码的话,我可以大致说一下做了什么事情:
- 首先对新旧节点的长度进行比较,然后获取最小的那个长度
- 从0位置开始进行patch比较,直到最小长度的节点遍历完成
- 如果旧的节点比新的长,则直接把多余的节点删除
- 如果旧的节点比新的短,则把新节点添加进来,即创建新的节点
const patchUnkeyedChildren = (
c1: VNode[], // 旧nodes ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
c2: VNodeArrayChildren, // 旧nodes ['a', 'b', 'f', 'c', 'd']
container: RendererElement,
anchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
c1 = c1 || EMPTY_ARR
c2 = c2 || EMPTY_ARR
// 1.获取旧节点的长度
const oldLength = c1.length
// 2.获取新节点的长度
const newLength = c2.length
// 获取最小的那个长度
const commonLength = Math.min(oldLength, newLength)
let i
// 从0位置开始依次patch比较
for (i = 0; i < commonLength; i++) {
const nextChild = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
patch(
c1[i],
nextChild,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
}
// 如果旧的节点数大于新的节点数
if (oldLength > newLength) {
// remove old
// 移除剩余的节点
unmountChildren(
c1,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
true,
false,
commonLength
)
} else {
// mount new
// 创建新的节点
mountChildren(
c2,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized,
commonLength
)
}
}
有key
有key的diff算法比没key的要复杂一点,为了避免你看源码时一头雾水,我先讲一下大概的实现思路:
- 首先计算出新旧节点的长度,然后从头部开始遍历,如果节点相同,那么就继续遍历。如果不同就直接跳出循环
- 根据前面计算出来的长度,从尾部开始遍历,如果节点相同,那么就继续遍历,不同就直接跳出循环
- 如果旧节点遍历完了,依然有新的节点,那么新的节点就是添加
- 第四步是如果新的节点遍历完毕,但是依然有旧的节点,那么就移除旧节点
- 第五步是最特色的情况,中间还有很多未知的或者乱序的节点:
const patchKeyedChildren = (
c1: VNode[],
c2: VNodeArrayChildren,
container: RendererElement,
parentAnchor: RendererNode | null,
parentComponent: ComponentInternalInstance | null,
parentSuspense: SuspenseBoundary | null,
isSVG: boolean,
slotScopeIds: string[] | null,
optimized: boolean
) => {
let i = 0
const l2 = c2.length
let e1 = c1.length - 1 // prev ending index
let e2 = l2 - 1 // next ending index
// 1. sync from start
// 从头部开始遍历
// (a b) c
// (a b) d e
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[i]
const n2 = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
// 如果节点相同, 那么就继续遍历
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) { // 这里isSameVNodeType这个函数所做的操作是比较n1和n2的type和key是否相同
patch(
n1,
n2,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
// 节点不同就直接跳出循环
break
}
i++
}
// 2. sync from end
// 从尾部开始遍历
// a (b c)
// d e (b c)
while (i <= e1 && i <= e2) {
const n1 = c1[e1]
const n2 = (c2[e2] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[e2] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[e2]))
// 如果节点相同, 就继续遍历
if (isSameVNodeType(n1, n2)) {
patch(
n1,
n2,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else {
// 不同就直接跳出循环
break
}
e1--
e2--
}
// 3. common sequence + mount
// 如果旧节点遍历完了, 依然有新的节点, 那么新的节点就是添加(mount)
// (a b)
// (a b) c
// i = 2, e1 = 1, e2 = 2
// (a b)
// c (a b)
// i = 0, e1 = -1, e2 = 0
if (i > e1) {
if (i <= e2) {
const nextPos = e2 + 1
const anchor = nextPos < l2 ? (c2[nextPos] as VNode).el : parentAnchor
while (i <= e2) {
patch(
null,
(c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i])),
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
i++
}
}
}
// 4. common sequence + unmount
// 如果新的节点遍历完了, 还有旧的节点, 那么旧的节点就是移除的
// (a b) c
// (a b)
// i = 2, e1 = 2, e2 = 1
// a (b c)
// (b c)
// i = 0, e1 = 0, e2 = -1
else if (i > e2) {
while (i <= e1) {
unmount(c1[i], parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
i++
}
}
// 5. unknown sequence
// 如果是位置的节点序列,
// 如果有多余的节点, 那么就移除节点
// 之后是移动节点和挂载新节点
// [i ... e1 + 1]: a b [c d e] f g
// [i ... e2 + 1]: a b [e d c h] f g
// i = 2, e1 = 4, e2 = 5
else {
const s1 = i // prev starting index
const s2 = i // next starting index
// 5.1 build key:index map for newChildren
// 根据key建立map索引图
const keyToNewIndexMap: Map<string | number, number> = new Map()
for (i = s2; i <= e2; i++) {
const nextChild = (c2[i] = optimized
? cloneIfMounted(c2[i] as VNode)
: normalizeVNode(c2[i]))
if (nextChild.key != null) {
if (__DEV__ && keyToNewIndexMap.has(nextChild.key)) {
warn(
`Duplicate keys found during update:`,
JSON.stringify(nextChild.key),
`Make sure keys are unique.`
)
}
keyToNewIndexMap.set(nextChild.key, i)
}
}
// 5.2 loop through old children left to be patched and try to patch
// matching nodes & remove nodes that are no longer present
// 遍历剩下的旧节点, 新旧对比, 移除不使用的旧节点
let j
let patched = 0
const toBePatched = e2 - s2 + 1
let moved = false
// used to track whether any node has moved
let maxNewIndexSoFar = 0
// works as Map<newIndex, oldIndex>
// Note that oldIndex is offset by +1
// and oldIndex = 0 is a special value indicating the new node has
// no corresponding old node.
// used for determining longest stable subsequence
const newIndexToOldIndexMap = new Array(toBePatched)
for (i = 0; i < toBePatched; i++) newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] = 0
for (i = s1; i <= e1; i++) {
const prevChild = c1[i]
if (patched >= toBePatched) {
// all new children have been patched so this can only be a removal
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
continue
}
let newIndex
if (prevChild.key != null) {
newIndex = keyToNewIndexMap.get(prevChild.key)
} else {
// key-less node, try to locate a key-less node of the same type
for (j = s2; j <= e2; j++) {
if (
newIndexToOldIndexMap[j - s2] === 0 &&
isSameVNodeType(prevChild, c2[j] as VNode)
) {
newIndex = j
break
}
}
}
if (newIndex === undefined) {
unmount(prevChild, parentComponent, parentSuspense, true)
} else {
newIndexToOldIndexMap[newIndex - s2] = i + 1
if (newIndex >= maxNewIndexSoFar) {
maxNewIndexSoFar = newIndex
} else {
moved = true
}
patch(
prevChild,
c2[newIndex] as VNode,
container,
null,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
patched++
}
}
// 5.3 move and mount
// generate longest stable subsequence only when nodes have moved
// 拿到最长递增子序列进行move 和 mount
const increasingNewIndexSequence = moved
? getSequence(newIndexToOldIndexMap)
: EMPTY_ARR
j = increasingNewIndexSequence.length - 1
// looping backwards so that we can use last patched node as anchor
for (i = toBePatched - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const nextIndex = s2 + i
const nextChild = c2[nextIndex] as VNode
const anchor =
nextIndex + 1 < l2 ? (c2[nextIndex + 1] as VNode).el : parentAnchor
if (newIndexToOldIndexMap[i] === 0) {
// mount new
patch(
null,
nextChild,
container,
anchor,
parentComponent,
parentSuspense,
isSVG,
slotScopeIds,
optimized
)
} else if (moved) {
// move if:
// There is no stable subsequence (e.g. a reverse)
// OR current node is not among the stable sequence
if (j < 0 || i !== increasingNewIndexSequence[j]) {
move(nextChild, container, anchor, MoveType.REORDER)
} else {
j--
}
}
}
}
}
理解了上面的内容之后,你也就明白了为什么使用v-for遍历时要添加key作为标识,而且不推荐使用index作为key。





















 1525
1525










