@[TOC](目录)
# 前言:
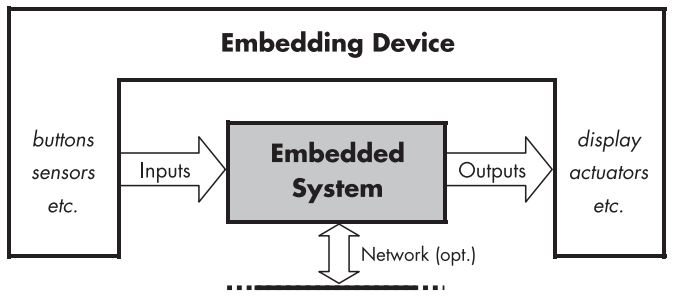
embedded linux开发有个好处就是开源的,总的来说涉及五个部分:
1、工具链Toolchain:为目标设备创建代码需要的编译器和其他工具。其他一切都取决于工具链。
2、引导程序Bootloader:它初始化板并加载Linux kernal。
3、内核kernal:这是系统的core核心,管理系统资源和各种硬件接口。
4、根文件系统root filesystem:包含一次性运行的初始化的lib库和program程序。
5、应用embedded application。
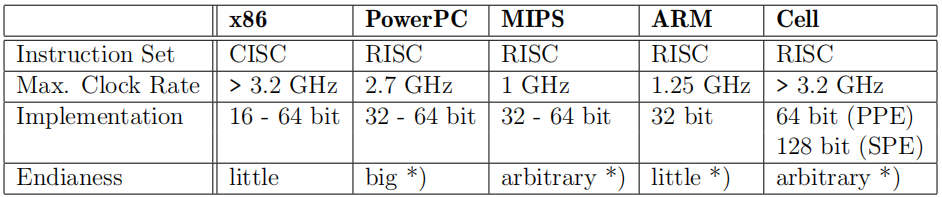
其实很多嵌入式系统不带linux的,直接就是单片机或者MCU微控制器,带一个HAL底层抽象库,一个函数直接就可以访问硬件,这样的系统简洁,比如在车用芯片领域,在域控等都是主流,不需要带额外系统,实时响应速度相对还慢。但带os的,也是有要求的,比如CPU架构行不行,当然linux4.9版本已经支持了31个架构architechure,32位和64位都有,ARM, MIPS, x86_64等等,









 订阅专栏 解锁全文
订阅专栏 解锁全文















 477
477











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










