1. 反转链表
给你单链表的头节点head,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。

//方法一:迭代
//将当前节点的next 指针改为指向前一个节点
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
//方法二:递归
public ListNode reverseList1(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode newHead = reverseList1(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}2. 合并两个升序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
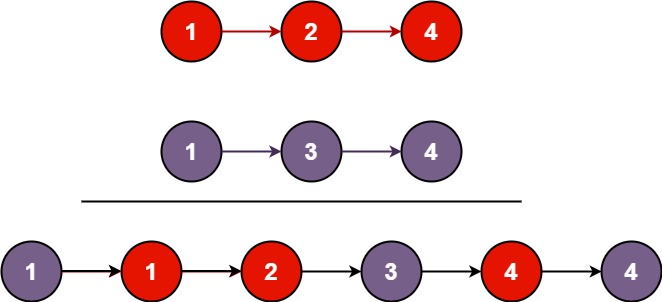
//方法一-迭代
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode list = new ListNode();
ListNode p = list;
while(list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if(list1.val <= list2.val) { //list1小,list1合并、后移
p.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
else { //list2小,list2合并、后移
p.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
p = p.next; //合并list指针后移
}
//将剩余部分合并
p.next = (list1 == null ? list2 : list1);
return list;
}
//方法二-递归
public ListNode mergeTwoLists1(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null)
return list2;
else if(list2 == null)
return list1;
else if(list1.val < list2.val) {
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
}else {
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}
}3. 判断是否环形链表
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。

//方法一:哈希表
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
Set<ListNode> seen = new HashSet<ListNode>();
while(head != null) {
if(!seen.add(head))
return true;
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
//方法二:快慢指针
//如果在移动的过程中,快指针反过来追上慢指针,就说明该链表为环形链表
public boolean hasCycle1(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null) return false;
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while(slow != fast) {
if(fast == null || fast.next == null)
return false;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return true;
}4. 回文链表
给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。
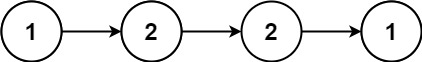
//方法一:将链表复制到数组中后使用双指针法
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> vals = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//将链表的值复制到数组中
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
vals.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.next;
}
//使用双指针判断是否回文
int front = 0, back = vals.size() - 1;
while(front < back) {
if(!vals.get(front).equals(vals.get(back)))
return false;
front++;
back--;
}
return true;
}
//方法二:递归
private ListNode frontPointer; //递归函数外的指针
public boolean isPalindrome1(ListNode head) {
frontPointer = head;
return recursivelyCheck(head);
}
private boolean recursivelyCheck(ListNode currentNode) {
if(currentNode != null) {
if(!recursivelyCheck(currentNode.next))
return false;
if(currentNode.val != frontPointer.val)
return false;
frontPointer = frontPointer.next;
}
return true;
}
//方法三:快慢指针
/*
* 1. 找到前半部分链表的尾节点。
* 2. 反转后半部分链表。
* 3. 判断是否回文。
* 4. 恢复链表。
* 5. 返回结果。
*/
public boolean isPalindrome2(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return true;
//找到前半部分链表的尾结点并翻转后半部分链表
ListNode firstHalfEnd = endOfFirstHalf(head);
ListNode secondHalfStart = reverseList(firstHalfEnd.next);
//判断是否回文
ListNode p1 = head;
ListNode p2 = secondHalfStart;
boolean result = true;
while(result && p2 != null) {
if(p1.val != p2.val)
return false;
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
}
//还原链表并返回结果
firstHalfEnd.next = reverseList(secondHalfStart);
return result;
}
private ListNode endOfFirstHalf(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr != null) {
ListNode temp = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = temp;
}
return prev;
}5. 回文数
给你一个整数x,如果 x 是一个回文整数,返回 tru ;否则,返回 false 。
回文数是指正序(从左向右)和倒序(从右向左)读都是一样的整数。
-
例如,
121是回文,而123不是。
public static boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
if(x<0)
return false;
int rem,y=0;
int quo=x;
while(quo!=0){
rem=quo%10;
y=y*10+rem;
quo=quo/10;
}
return y==x;
}6. 合并二叉树
给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 ,返回合并后的二叉树。

/*
* 两个二叉树的对应节点可能存在以下三种情况,对于每种情况使用不同的合并方式。
* 1. 如果两个二叉树的对应节点都为空,则合并后的二叉树的对应节点也为空;
* 2.如果两个二叉树的对应节点只有一个为空,则合并后的二叉树的对应节点为其中的非空节点;
* 3.如果两个二叉树的对应节点都不为空,则合并后的二叉树的对应节点的值为两个二叉树的对应节点的值之和,此时需要显性合并两个节点。
*/
//方法一:深度优先搜索
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null) return root2;
if(root2 == null) return root1;
TreeNode merged = new TreeNode(root1.val + root2.val);
merged.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left);
merged.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right);
return merged;
}7. 返回二叉树最大
深给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
//方法一:深度优先遍历
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
else {
int left = maxDepth(root.left);
int right = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
}
//方法二:广度优先遍历
public int maxDepth1(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q.offer(root);
int ans = 0;
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int size = q.size();
while(size > 0) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if(node.left != null)
q.offer(node.left);
if(node.right != null)
q.offer(node.right);
size--;
}
ans++;
}
return ans;
}8. 翻转二叉树
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
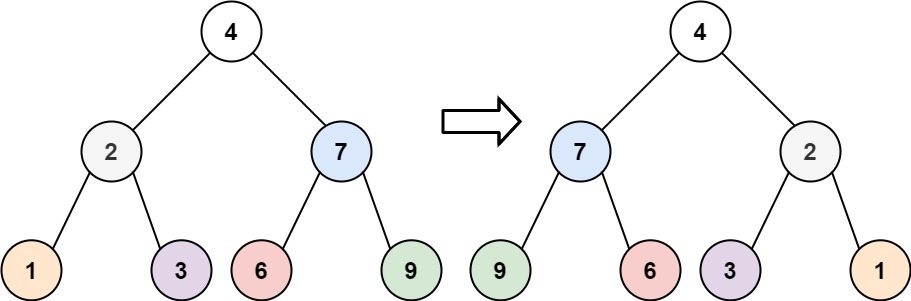
//递归
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return null;
TreeNode left = invertTree(root.left);
TreeNode right = invertTree(root.right);
root.left = right;
root.right = left;
return root;
}9. 二叉树中序遍历
//二叉树的中序遍历
public class InorderTraversal {
//方法一:递归
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if(root == null) return;
inorder(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, res);
}
//方法二:迭代
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal1(TreeNode root){
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
while(root != null || !stk.isEmpty()) {
while(root != null) {
stk.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stk.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
return res;
}
//方法三:Morris遍历算法
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal2(TreeNode root){
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
TreeNode predecessor = null;
while(root != null) {
//predecessor 节点就是当前 root 节点向左走一步,然后一直向右走至无法走为止
if(root.left != null) {
predecessor = root.left;
while(predecessor.right != null && predecessor.right != root)
predecessor = predecessor.right;
// 让 predecessor 的右指针指向 root,继续遍历左子树
if(predecessor.right == null) {
predecessor.right = root;
root = root.left;
// 说明左子树已经访问完了,我们需要断开链接
}else {
res.add(root.val);
predecessor.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
}else { // 如果没有左孩子,则直接访问右孩子
res.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}10. 爬楼梯
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
//动态规划-f(x)=f(x−1)+f(x−2)
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int p = 0, q = 0, r = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p = q;
q = r;
r = p + q;
}
return r;
}11. 有效括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
//方法一
public boolean isValid(String s) {
int n = s.length();
if(n % 2 == 1) return false; //如果字符长度为奇数,则无法匹配
Map<Character,Character> map = new HashMap<Character,Character>(){{
put(')', '(');
put(']', '[');
put('}', '{');
}};
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i); //依次取字符串中的括号
if(map.containsKey(ch)) { //是否为右括号
if(stack.isEmpty() || stack.peek() != map.get(ch)) //如果栈为空,或者栈中剩余的括号不匹配,则返回false
return false;
stack.pop(); //匹配完成,则弹出
}else {
stack.push(ch); //将左括号入栈
}
}
return stack.isEmpty(); //判断栈中的括号是否匹配完毕
}
//方法二
public boolean isValid1(String s) {
Stack<Character>stack = new Stack<Character>();
for(char c: s.toCharArray()){
if(c=='(')
stack.push(')');
else if(c=='[')
stack.push(']');
else if(c=='{')
stack.push('}');
else if(stack.isEmpty() || c != stack.pop())
return false;
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}12. 比特位计数
给你一个整数 n ,对于 0 <= i <= n 中的每个 i ,计算其二进制表示中 1 的个数 ,返回一个长度为 n + 1 的数组 ans 作为答案。
//方法一:使用内置函数Integer.bitCount()
public static int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] ans = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
int count = Integer.bitCount(i);
ans[i] = count;
}
return ans;
}
//方法二:Brian Kernighan算法
//对于任意整数 x,令 x=x & (x−1),该运算将 x 的二进制表示的最后一个 1 变成 0。
//因此,对 x 重复该操作,直到 x 变成 0,则操作次数即为 x 的「一比特数」。
public int[] countBits1(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) {
bits[i] = countOnes(i);
}
return bits;
}
private int countOnes(int x) {
int ones = 0;
while(x > 0) {
x &= (x - 1);
ones++;
}
return ones;
}
//方法三:动态规划-最高有效位
public int[] countBits2(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
int highBit = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if((i & (i - 1)) == 0)
highBit = i;
bits[i] = bits[i - highBit] + 1;
}
return bits;
}
//方法四:动态规划-最低有效位
public int[] countBits3(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
bits[i] = bits[i >> 1] + (i & 1);
return bits;
}
//方法五:动态规划-最低设置位
public int[] countBits4(int n) {
int[] bits = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
bits[i] = bits[i & (i - 1)] + 1;
return bits;
}来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:题库 - 力扣 (LeetCode) 全球极客挚爱的技术成长平台























 1470
1470











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










