Java输入输出挂的妙处
众所周知,Java在I/O处理上效率不高,在内存耗时上与C/C++都有较大差距。(爆哭😭,没事,咱Java有挂🤣)
前言
以AtCoder Beginner Contest 164 C gacha (统计不同字串数量)为例(Java版)
题目
原文
You drew lottery N times. In the i-th draw, you got an item of the kind represented by a string Si.
How many kinds of items did you get?
Constraints
·1≤N≤2×105
·Si consists of lowercase English letters and has a length between 1 and 10 (inclusive).
输入
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
S1
:
SN
输出
Print the number of kinds of items you got.
输入数据
【样例1】
3
apple
orange
apple
【样例2】
5
grape
grape
grape
grape
grape
【样例3】
4
aaaa
a
aaa
aa
输出数据
【样例1】
2
【样例2】
1
【样例3】
4
一、三种方法对比
1.(错误典型)
用一个string字符串存入每个不同的字符串,同时用正则表达式查询是否已经存入,同时用count计数。但,,,爆内存。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
String z = scanner.nextLine();
String s = "#";
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
z = scanner.nextLine();
if (!s.matches("(.*)#" + z + "#(.*)")) {
s = s + z + "#";
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
 只怪我太天真 (
只怪我太天真 (心塞塞 )
😕哼,不怕咱有其他方法。
(用链表会超时)
2.排序
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
String z = scanner.nextLine();
String[] a = new String[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
a[i] = scanner.nextLine();
}
Arrays.sort(a);
int count = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++) {
if (!a[i].equals(a[i - 1])) {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println(count);
}
}
结果超时,,,(Java用Scanner处理大量的输入,耗时较多)

3.用HashSet
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
String z = scanner.nextLine();
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
z = scanner.nextLine();
hashSet.add(z);
}
System.out.println(hashSet.size());
}
}
结果依旧超时!!!不应该啊,,,

用挂
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader in =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(System.out);
int n = in.nextInt();
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
hashSet.add(in.next());
}
out.print(hashSet.size());
out.close();
}
}

呼,终于A了,用挂后内存与运行时间都有了一个质的飞跃。
二、Atcoder 中数据对比
1.用Scanner
 图1 用上述方法(2)排序 图1 用上述方法(2)排序
|
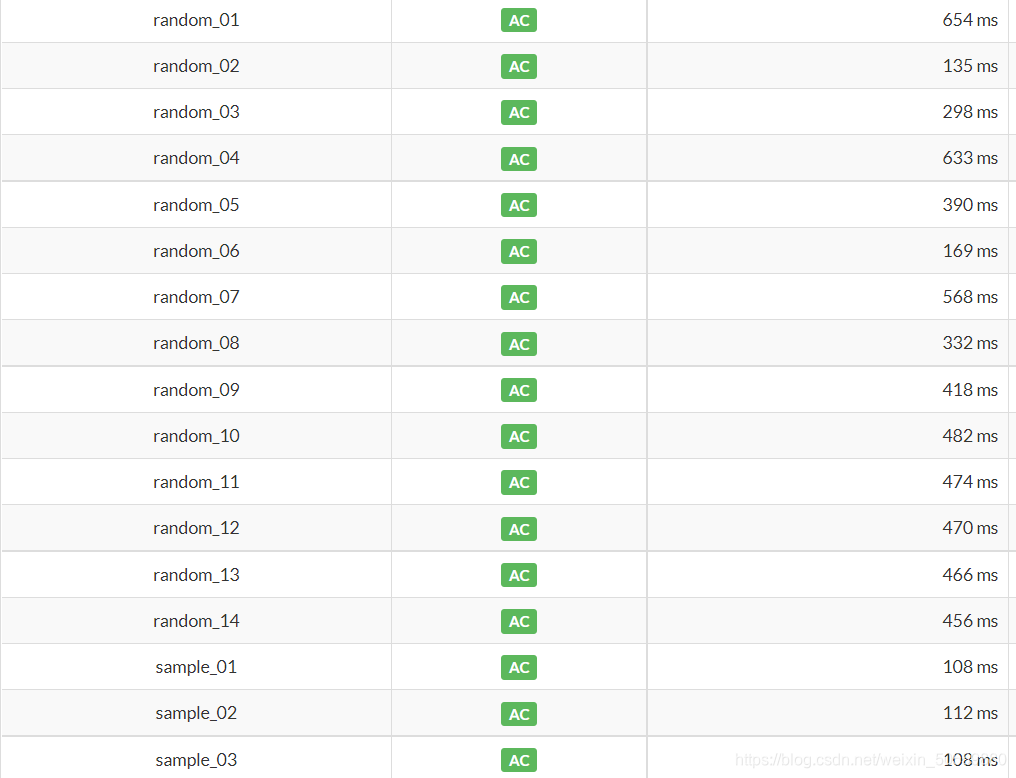 图2用HashSet 图2用HashSet
|
2.用挂
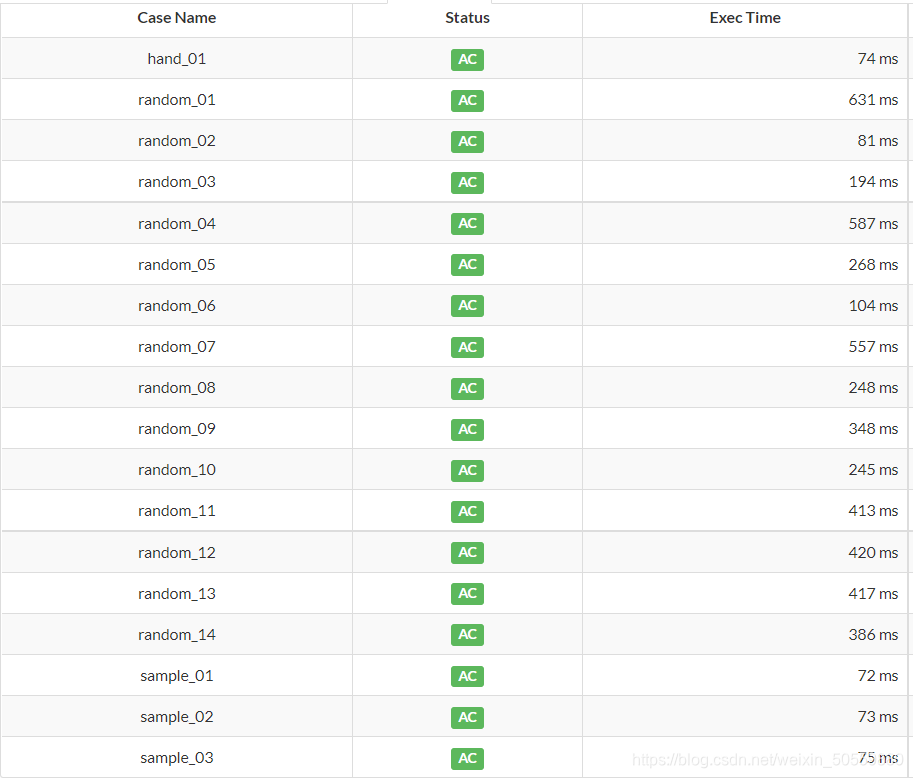 图1 用上述方法(2)排序 图1 用上述方法(2)排序
|
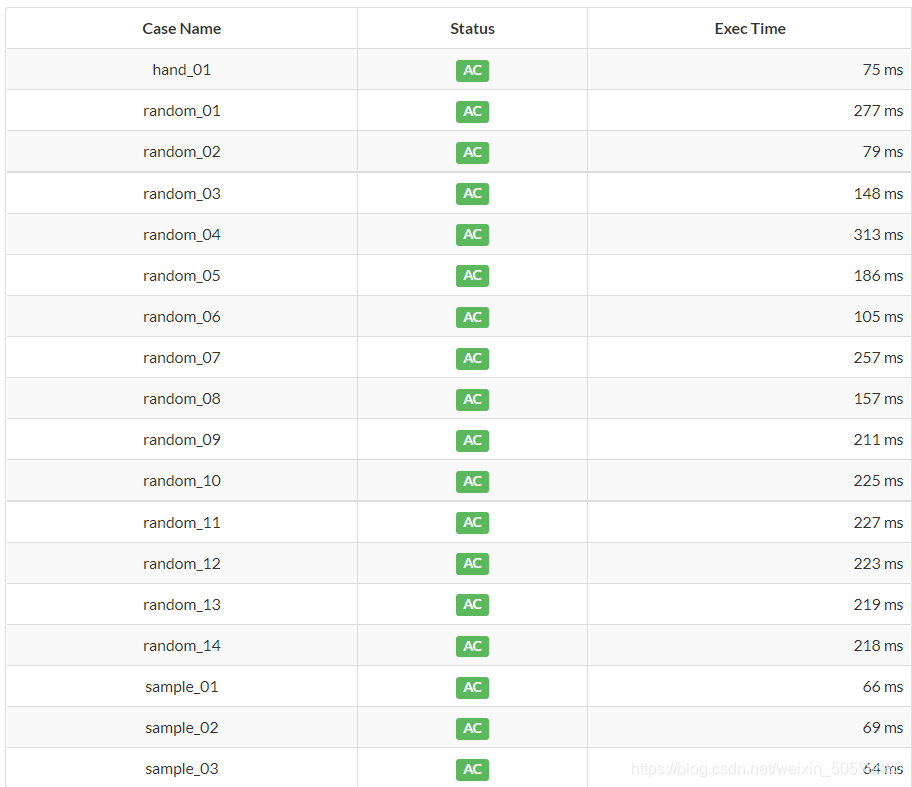 图2用HashSet 图2用HashSet
|
三、Java输入输出挂模板
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputReader in = new InputReader();
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(System.out);
...
...
out.close();
}
}
class InputReader {
BufferedReader buf;
StringTokenizer tok;
InputReader() {
buf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
boolean hasNext() {
while (tok == null || !tok.hasMoreElements()) {
try {
tok = new StringTokenizer(buf.readLine());
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
String next() {
if (hasNext())
return tok.nextToken();
return null;
}
int nextInt() {
return Integer.parseInt(next());
}
long nextLong() {
return Long.parseLong(next());
}
double nextDouble() {
return Double.parseDouble(next());
}
BigInteger nextBigInteger() {
return new BigInteger(next());
}
BigDecimal nextBigDecimal() {
return new BigDecimal(next());
}
}
总结
1.对于注重时间复杂度,算法的题目用Scanner与system.out尚可。但一旦碰到大量的输入输出建议用Bufferedreader与PrintWriter(挂)(system.out也很慢)
2.bufferedreader类这个虽然用着不方便,但是可以提升输入速度,输入缺点就是只能按行读取数据,必要时需要字符串分割,转成其他数据类型还需要转换,所有用一个类提前封装好各类方法极为重要,相当于重建了一个输入类。
功夫不负有心人,终于AC了,好耶。
路漫漫其修远兮,吾将上下而求索


























 2268
2268

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








