在游戏中,空间哈希分区就是将空间划分成一个个网格之后,使用哈希表将每个空间小块中的物体存储起来,用空间的小块的位置为Key值,物体的集合为Value值,来加速查询物体的一种方法。
构建过程:
1.将地图分成小块。

2.遍历储存地图小格子上的物体(红色圆圈代表物体),将其按照计算存储到哈希表中。

3.查询某个点周围的物体时,只需要通过这个点计算出是属于在哪个格子中,就可以找到所在格子的所有物体,加快了查询的速度。

注:绿色格子代表某个点,黄色代表所在格子。
怎样计算所属格子?
以左上角为格子开始的位置,则绿色物体所属格子位置计算为
Mathf.Floor(绿色物体位置 / 格子间隔)* 格子间隔 + 格子间隔/2
代码实现:
空间哈希类:
public class SpatialHash
{
private Dictionary<Vector3, List<Transform>> spatialHash;
private int CELL_SIZE;
public SpatialHash(int CELL_SIZE)
{
spatialHash = new Dictionary<Vector3, List<Transform>>();
this.CELL_SIZE = CELL_SIZE;
}
public void AddGameObject(Vector3 grid,Transform obj)
{
if (!spatialHash.ContainsKey(grid))
{
var objs = new List<Transform>();
objs.Add(obj);
spatialHash[grid] = objs;
}
else
{
spatialHash[grid].Add(obj);
}
}
public void OnRemeveGameObject(Vector3 grid, Transform obj)
{
if (spatialHash.ContainsKey(grid) && spatialHash[grid].Contains(obj))
{
spatialHash[grid].Remove(obj);
if (spatialHash[grid].Count <= 0)
{
spatialHash.Remove(grid);
}
}
}
public List<Transform> GetGameObject(Vector3 grid)
{
if (spatialHash.ContainsKey(grid))
{
return spatialHash[grid];
}
return null;
}
}格子控制类:
public class GridControl : MonoBehaviour
{
public int gridNum;
public int gridInterval;
public Transform objRoot;
public Material red;
public Material green;
private float width;
private float height;
private SpatialHash spatialHash;
private int layerAsLayerMask;
private List<Transform> selectObjs = null;
public void Start()
{
//移除层
layerAsLayerMask |= ~(1 << LayerMask.NameToLayer("hashObj"));
Vector3 size = this.GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh.bounds.size;
this.width = size.x * this.transform.localScale.x;
this.height = size.z * this.transform.localScale.z;
spatialHash = new SpatialHash(gridInterval);
this.SpawnObj();
}
public Vector3 CalcGrid(Vector3 pos)
{
int X = Mathf.FloorToInt(pos.x / gridInterval)* gridInterval + gridInterval/2;
int Z = Mathf.FloorToInt(pos.z / gridInterval)* gridInterval + gridInterval/2;
return new Vector3(X,0,Z);
}
public void SpawnObj()
{
for(int i = 0; i< 100; i++)
{
var obj = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
obj.transform.position = this.transform.position + new Vector3(Random.Range(-width/2,width/2),0,Random.Range(-height/2,height/2));
obj.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().sharedMaterial = green;
obj.transform.localScale *= 3;
int LayerIgnoreRaycast = LayerMask.NameToLayer("hashObj");
obj.layer = LayerIgnoreRaycast;
obj.transform.SetParent(objRoot);
spatialHash.AddGameObject(CalcGrid(obj.transform.position),obj.transform);
}
}
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0))
{
Ray r = Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition);
RaycastHit hit;
if (Physics.Raycast(r, out hit, 1000, layerAsLayerMask , QueryTriggerInteraction.Collide))
{
this.UpdateObjsDisplay(green);
selectObjs = spatialHash.GetGameObject(this.CalcGrid(hit.point));
this.UpdateObjsDisplay(red);
}
}
}
private void UpdateObjsDisplay(Material mat)
{
if(selectObjs != null && selectObjs.Count > 0)
{
for(int i = 0; i < selectObjs.Count; i++)
{
selectObjs[i].GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().sharedMaterial = mat;
}
}
}
#if UNITY_EDITOR
private void DrawGrid()
{
Vector3 startPos = this.transform.position + new Vector3(-width/2,0,height/2);
for(int i = 0; i<= gridNum; i++)
{
Gizmos.DrawLine(startPos + new Vector3(i*gridInterval,0,0), startPos + new Vector3(i * gridInterval,0,-width));
}
for (int i = 0; i <= gridNum; i++)
{
Gizmos.DrawLine(startPos - new Vector3(0, 0, i * gridInterval), startPos - new Vector3(-height, 0, i * gridInterval));
}
}
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Gizmos.color = Color.green;
DrawGrid();
}
#endif
}演示:
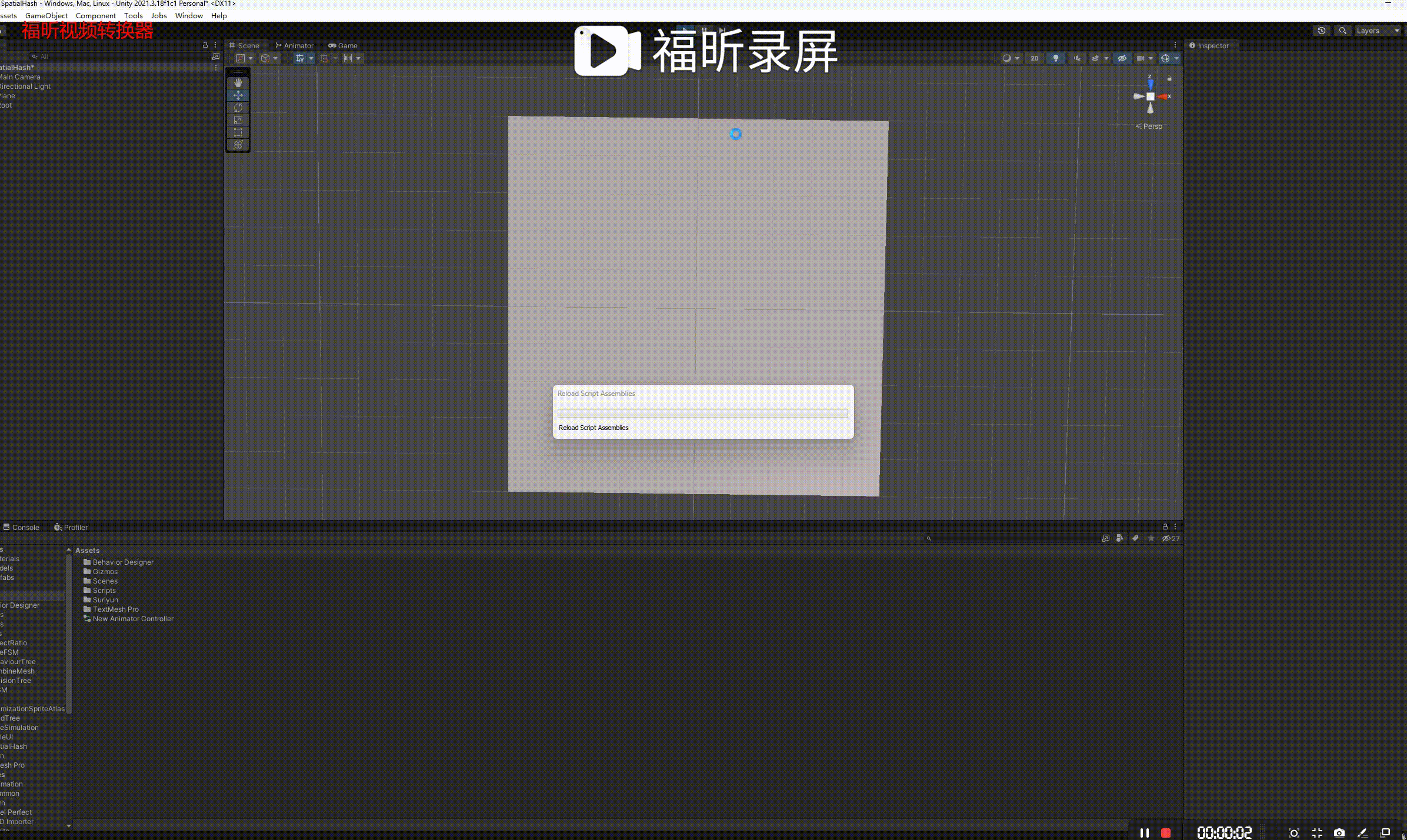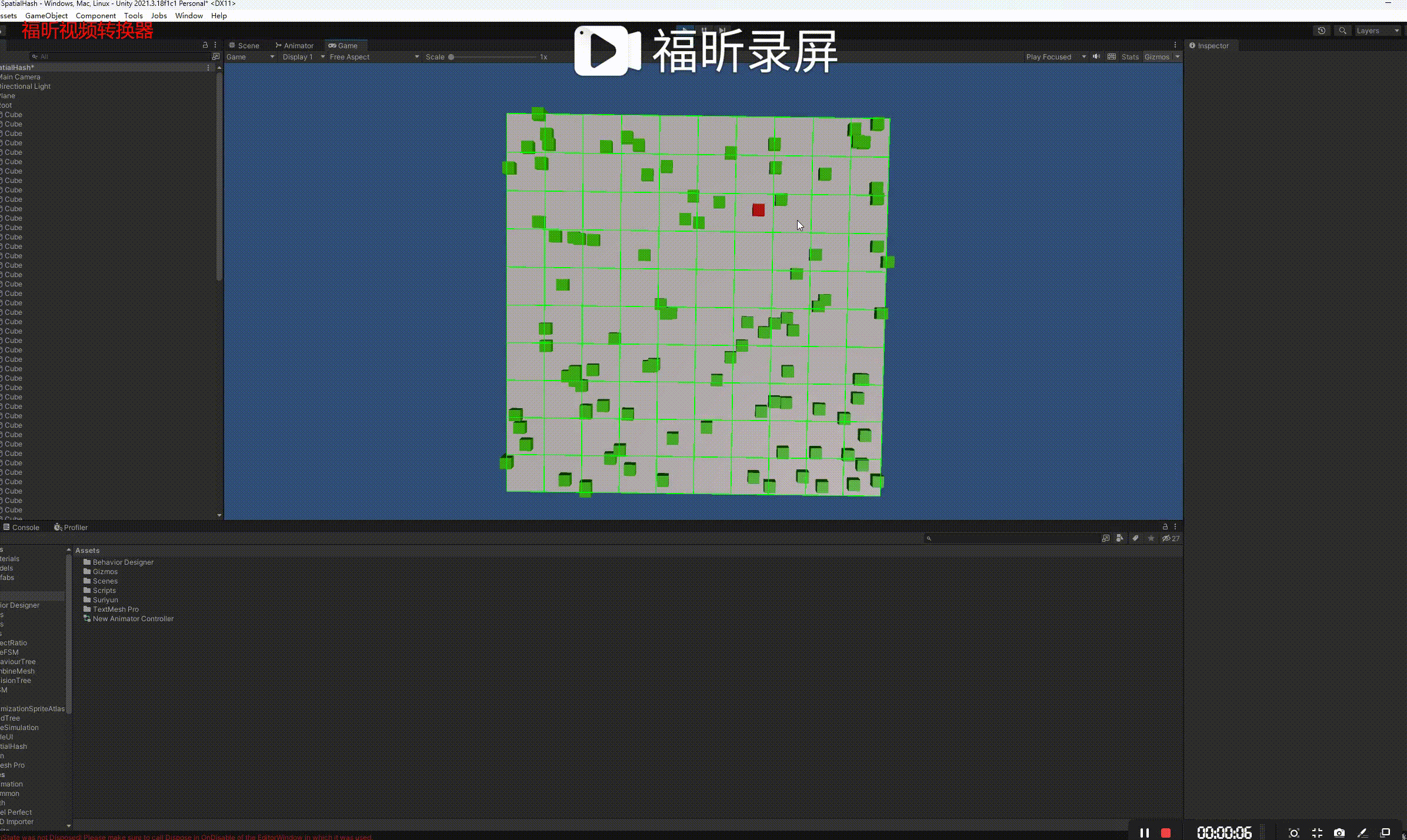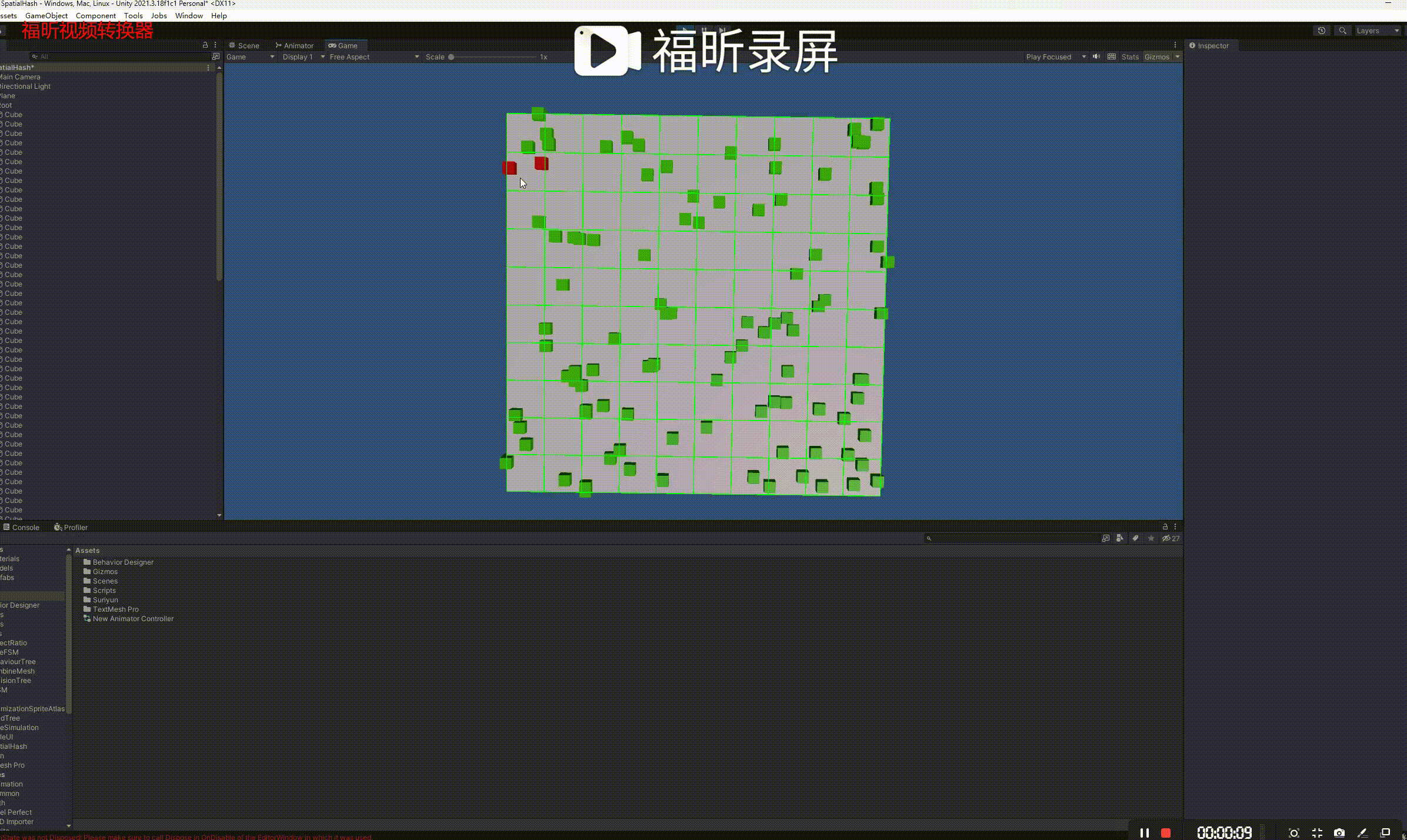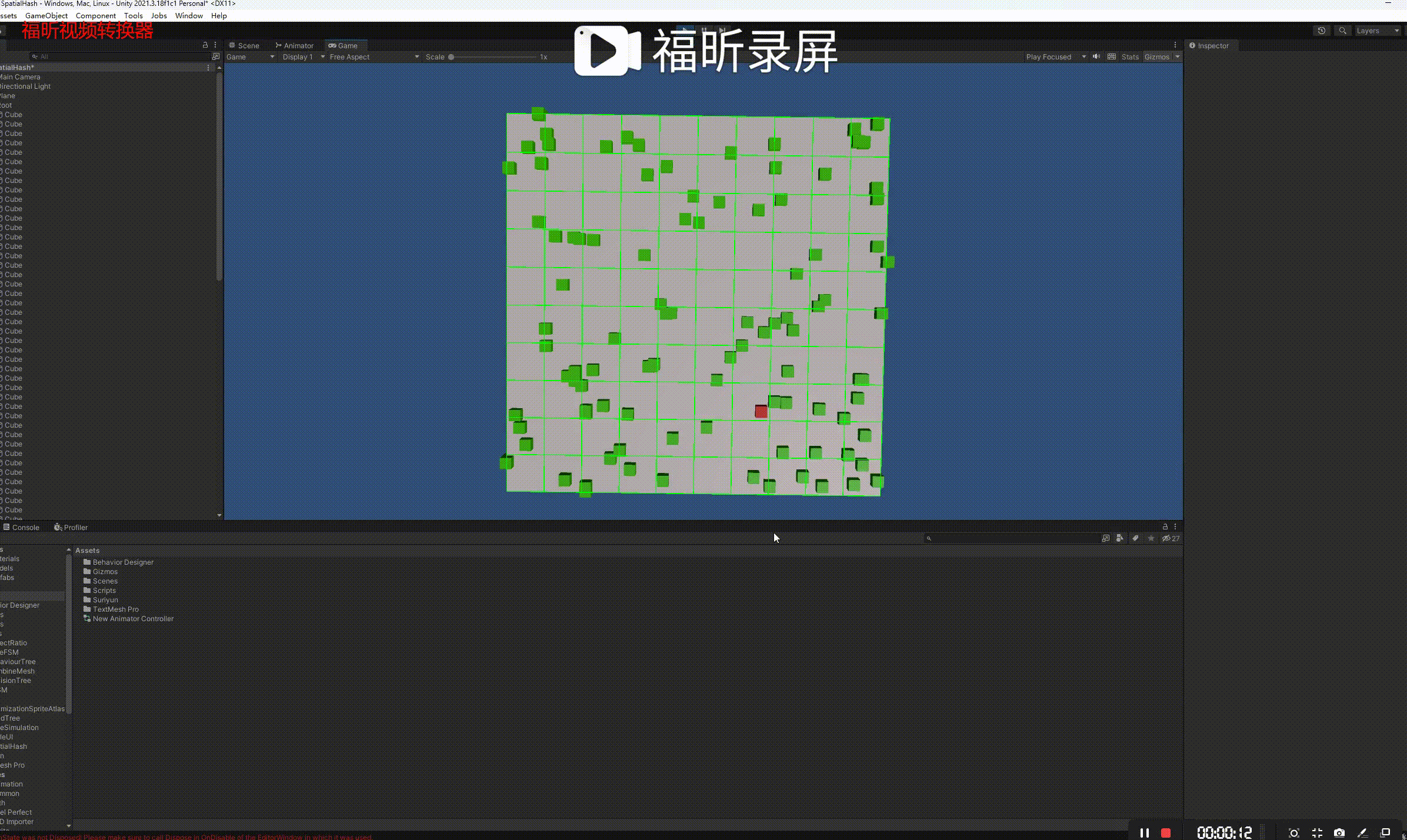
参考链接:
使用空间哈希重新设计显示列表 |Envato Tuts+ (tutsplus.com)
Spatial Hash Grids & Tales from Game Development (youtube.com)
Envato. Everything you need, all in one place. (youtube.com)

























 1397
1397

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








