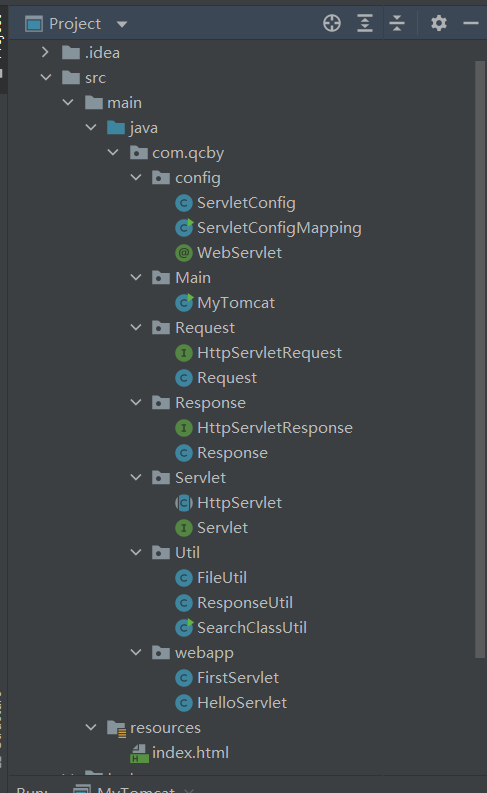
1. 文件夹分布
2. 静态资源的访问
2.1 先写MyTomcat
package com.Main;
import com.Request.Request;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class MyTomcat {
private static final Request request = new Request();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 先打开端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(4090);
System.out.println("我已经开始运行了。。。");
// 接受请求数据
while(true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("有客户访问我了!!!");
// 开启线程进行处理数据
new Thread(()->{
try {
hander(socket);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
// 线程里面处理数据的
public static void hander(Socket socket) throws IOException {
// 读取数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); // 打开输入流对象,读取socket对象当中的数据
requestContext(inputStream);
}
public static void requestContext(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
// 将bit流转为文字信息
int count = 0;
while (count == 0) {
count = inputStream.available();
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[count];
inputStream.read(bytes);
String Context = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(Context);
// 解析数据
if (Context.equals("")) {
System.out.println("你输入了一个空请求");
} else {
String firstLine = Context.split("\\n")[0];
request.setUrl(firstLine.split("\\s")[1]);
request.setMethod(firstLine.split("\\s")[0]);
System.out.println(firstLine.split("\\s")[1]);
System.out.println(firstLine.split("\\s")[0]);
}
}
}
2.2 将Request导入
package com.Request;
public class Request implements HttpServletRequest{
private String url;// 地址
private String method;// 请求方法
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
}
2.3 接口HttpServletRequest(其实啥也没有)
package com.Request;
public interface HttpServletRequest {
}
2.4 启动MyTomcat,可以访问到4090端口
结果
我已经开始运行了。。。
有客户访问我了!!!
有客户访问我了!!!
GET /hello HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:4090
Connection: keep-alive
sec-ch-ua: "Chromium";v="9", "Not?A_Brand";v="8"
sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0
sec-ch-ua-platform: "Windows"
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/109.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 SLBrowser/9.0.3.1311 SLBChan/10
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9
Sec-Fetch-Site: none
Sec-Fetch-Mode: navigate
Sec-Fetch-User: ?1
Sec-Fetch-Dest: document
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
/hello
GET
2.5 接下来根据访问地址返回静态资源
2.5.1 MyTomcat进行修改
package com.Main;
import com.Request.Request;
import com.Response.Response;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class MyTomcat {
private static final Request request = new Request();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 先打开端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(4090);
System.out.println("我已经开始运行了。。。");
// 接受请求数据
while(true){
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("有客户访问我了!!!");
// 开启线程进行处理数据
new Thread(()->{
try {
hander(socket);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
// 线程里面处理数据的
public static void hander(Socket socket) throws Exception {
// 读取数据
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); // 打开输入流对象,读取socket对象当中的数据
requestContext(inputStream);
// 数据的输出
Response response = new Response(socket.getOutputStream());
response.writeHtml(request.getUrl());
}
public static void requestContext(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
// 将bit流转为文字信息
int count = 0;
while (count == 0) {
count = inputStream.available();
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[count];
inputStream.read(bytes);
String Context = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(Context);
// 解析数据
if (Context.equals("")) {
System.out.println("你输入了一个空请求");
} else {
String firstLine = Context.split("\\n")[0];
request.setUrl(firstLine.split("\\s")[1]);
request.setMethod(firstLine.split("\\s")[0]);
System.out.println(firstLine.split("\\s")[1]);
System.out.println(firstLine.split("\\s")[0]);
}
}
}
2.5.2 返回数据
Response
package com.Response;
import com.Util.FileUtil;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
public class Response implements HttpServletResponse{
// 获得输入流
private OutputStream outputStream;
public Response(OutputStream outputStream){
this.outputStream = outputStream;
}
// 读取静态资源
public void writeHtml(String path) throws Exception{
String resourcesPath = FileUtil.getResoucePath(path);
File file = new File(resourcesPath);
if(file.exists()){ // 静态资源存在
System.out.println("静态资源存在");
FileUtil.writeFile(file,outputStream);
}else{
System.out.println("静态资源不存在");
}
}
// 数据写回的方法
public void write(String context) throws IOException {
outputStream.write(context.getBytes());
}
}
HttpServletResponse
package com.Response;
public interface HttpServletResponse {
}
2.5.3 读取文件
FileUtil
package com.Util;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 该类的主要作用是进行读取文件
*/
public class FileUtil {
public static boolean writeFile(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream){
boolean success = false ;
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream ;
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream;
try {
bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(outputStream);
bufferedOutputStream.write(ResponseUtil.responseHeader200.getBytes());
int count = 0;
while (count == 0){
count = inputStream.available();
}
int fileSize = inputStream.available();
long written = 0;
int beteSize = 1024;
byte[] bytes = new byte[beteSize];
while (written < fileSize){
if(written + beteSize > fileSize){
beteSize = (int)(fileSize - written);
bytes = new byte[beteSize];
}
bufferedInputStream.read(bytes);
bufferedOutputStream.write(bytes);
bufferedOutputStream.flush();
written += beteSize;
}
success = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return success;
}
public static boolean writeFile(File file,OutputStream outputStream) throws Exception{
return writeFile(new FileInputStream(file),outputStream);
}
/**
* 获取资源地址
* @param path
* @return
*/
public static String getResoucePath(String path){
String resource = FileUtil.class.getResource("/").getPath();
return resource + "\\" + path;
}
}
2.5.4 响应头
ResponseUtil
package com.Util;
public class ResponseUtil {
public static final String responseHeader200 = "HTTP/1.1 200 \r\n" +
"Content-Type:text/html \r\n" + "\r\n";
public static String getResponseHeader200(String context){
return "HTTP/1.1 200 \r\n" + "Content-Type:text/html \r\n" + "\r\n" + context;
}
}
2.5.5 添加静态文件在resources中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
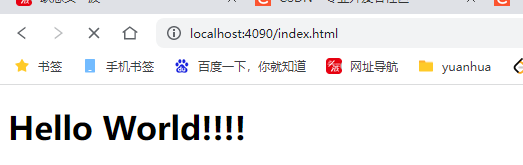
<h1>Hello World!!!!</h1>
</body>
</html>
2.6 进行访问
地址:
http://localhost:4090/index.html
3. 动态资源的访问
通过注解和反射获取路径,根据路径和访问方式对相关的资源进行操作
3.1 注解
package com.config;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface WebServlet {
String url() default "";
String name() default "";
}
3.2 ServletConfig
记录url和路径
package com.config;
public class ServletConfig {
private String url;
private String classPath;
public ServletConfig(String url, String path) {
this.url = url;
this.classPath = path;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getClassPath() {
return classPath;
}
public void setClassPath(String classPath) {
this.classPath = classPath;
}
}
3.3 利用反射配置ServletConfig
ServletConfigMapping
package com.config;
import com.Servlet.HttpServlet;
import com.Util.ServletClassUtil;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class ServletConfigMapping {
// 定义容器
public static Map<String, Class<HttpServlet>> classMap = new HashMap<>();
public static List<ServletConfig> configs = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取注解信息--->1.利用反射获取每一个类的注解信息
static {
List<String> classPaths = ServletClassUtil.searchClass();
for(String path : classPaths){
try {
getMessage(path);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 利用反射获取注解信息
public static void getMessage(String path) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class clazz = Class.forName(path);
WebServlet webServlet = (WebServlet)clazz.getDeclaredAnnotation(WebServlet.class);
System.out.println(webServlet.url());
configs.add(new ServletConfig(webServlet.url(),path));
}
public static void init() throws ClassNotFoundException {
for(ServletConfig s:configs){
String url = s.getUrl();
String path = s.getClassPath();
System.out.println("名称:"+url + ", 路径" + path);
classMap.put(url, (Class< HttpServlet>) Class.forName(path));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
init();
}
}
3.4 扫描指定包,获取该包下所有的类的全路径信息
ServletClassUtil
package com.Util;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 扫描指定包,获取该包下所有的类的全路径信息
*/
public class ServletClassUtil {
public static List<String> classPaths = new ArrayList<String>();
public static List<String> searchClass(){
//需要扫描的包名
String basePack = "com.webapp";
//将获取到的包名转换为路径
String classPath = ServletClassUtil.class.getResource("/").getPath();
basePack = basePack.replace(".", File.separator);
String searchPath = classPath + basePack;
doPath(new File(searchPath),classPath);
//这个时候我们已经得到了指定包下所有的类的绝对路径了。我们现在利用这些绝对路径和java的反射机制得到他们的类对象
return classPaths;
}
/**
* 该方法会得到所有的类,将类的绝对路径写入到classPaths中
* @param file
*/
private static void doPath(File file,String classpath) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {//文件夹
//文件夹我们就递归
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f1 : files) {
doPath(f1,classpath);
}
} else {//标准文件
//标准文件我们就判断是否是class文件
if (file.getName().endsWith(".class")) {
String path = file.getPath().replace(classpath.replace("/","\\").
replaceFirst("\\\\",""),"").replace("\\",".").
replace(".class","");
//如果是class文件我们就放入我们的集合中。
classPaths.add(path);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> classes = ServletClassUtil.searchClass();
for (String s: classes
) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
3.5 写Servlet
接口Servlet
package com.Servlet;
import com.Request.Request;
import com.Response.Response;
import java.io.IOException;
public interface Servlet {
public void service(Request request, Response response) throws IOException;
}
HttpServlet
package com.Servlet;
import com.Request.HttpServletRequest;
import com.Request.Request;
import com.Response.HttpServletResponse;
import com.Response.Response;
import java.io.IOException;
public abstract class HttpServlet implements Servlet{
// 进行定义
public abstract void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException;
public abstract void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException;
@Override
public void service(Request request, Response response) throws IOException {
if("GET".equals(request.getMethod())){
doGet(request, response);
}else{
doPost(request, response);
}
}
}
3.6 写个HelloServlet
HelloServlet
package com.webapp;
import com.Request.HttpServletRequest;
import com.Response.HttpServletResponse;
import com.Servlet.HttpServlet;
import com.Util.ResponseUtil;
import com.config.WebServlet;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet(url = "/hello")
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
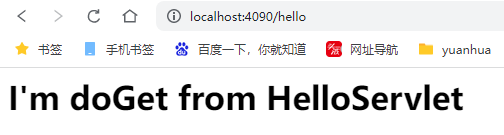
String context = "<h1>I'm doGet from HelloServlet</h1>";
response.write(ResponseUtil.getResponseHeader200(context));
}
@Override
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String context = "<h1>I'm doPost from HelloServlet</h1>";
response.write(ResponseUtil.getResponseHeader200(context));
}
}
3.7 进行访问
地址:
http://localhost:4090/hello
思考:如何访问静态图片资源
目前还没有解决,正在思考中。。。
























 530
530

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








