6.3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fact(int val)
{
int ret = 1;
while (val > 1)
ret *= val--;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int j = fact(5);
cout << "5! is " << j << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.4
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fact(int val)
{
int ret = 1;
while (val > 1)
ret *= val--;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int num;
cout << "请输入数字:" << endl;
cin >> num;
int j = fact(num);
cout << num << "! is " << j << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.5
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int abs(int val)
{
int ret = 1;
if (val >= 0)
ret = val;
else
ret = -val;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int num;
cout << "请输入数字:" << endl;
cin >> num;
int j = abs(num);
cout << num << "的绝对值为:" << j << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.6
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int count_calls()
{
static int ctr = 0;//局部静态变量
int a = 2;//局部变量
ctr += a;
return ctr;
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
cout << count_calls() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.7
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int count_calls()
{
static int ctr = 0;//局部静态变量
return ctr++;
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
cout << count_calls() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.8
6.9
6.10
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void exchange(int *p, int *q)
{
int c;
c = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = c;
}
int main()
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
exchange(&a, &b);
cout << a << " " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.11
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void reset(int &p)
{
p = 0;
}
int main()
{
int a = 1;
reset(a);
cout << a << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.12
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void exchange(int &p, int &q)
{
int c;
c = p;
p = q;
q = c;
}
int main()
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
exchange(a, b);
cout << a << " " << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.16
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string::size_type find_uchar(const string &s)
{
auto ret = s.size();
int flag = 0;
for (decltype(ret) i = 0; i != s.size(); ++i)
if (isupper(s[i]))
++flag;
return flag;
}
int main()
{
string s;
int num=0;
cout << "请输入字符串:" << endl;
getline(cin, s);
num=find_uchar(s);
cout << "大写字母的个数为:" << num << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.17
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string upper_to_lower (string &s)
{
auto ret = s.size();
for (decltype(ret) i = 0; i != s.size(); ++i)
s[i]=tolower(s[i]);
return s;
}
int main()
{
string s;
cout << "请输入字符串:" << endl;
getline(cin, s);
cout << "修改之后的字符串:" << upper_to_lower(s) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.18
bool compare(matrix &a, matrix &b){ /.../ }
vector<int>::iterator change_val(int, vector<int>::iterator) { /.../ }6.21
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int compare(int num1, int *num2)
{
if (num1 > *num2)
return num1;
else
return *num2;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
int *c=&b;
cout << "请输入两个数字:" << endl;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << "两者中较大的数字为:" << compare(a,c) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.22
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int* &num1, int *&num2)//该参数是一个引用(由右向左读),引用对象是int指针。这样会交换指针本身的值,即地址
{
int *temp;
temp = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = temp;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
int *a1 = &a, *b1 = &b;
cout << "请输入两个数字:" << endl;
cin >> a >> b;
cout << "交换之前:" << *a1<<" "<<*b1 << endl;
swap(a1, b1);
cout << "交换之后:" << *a1 << " " << *b1 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.23
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void print(const int *beg, const int *end)//该参数是一个引用(由右向左读),引用对象是int指针。这样会交换指针本身的值,即地址
{
while (beg != end)
cout << *beg++ << endl;
}
int main()
{
int i[] = { 0 }, j[2] = { 0,1 };
print(begin(i), end(i));
print(begin(j), end(j));
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.25
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
string str;
for (int i = 1; i != argc; ++i) {
str += argv[i];
str += " ";
}
cout << str << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
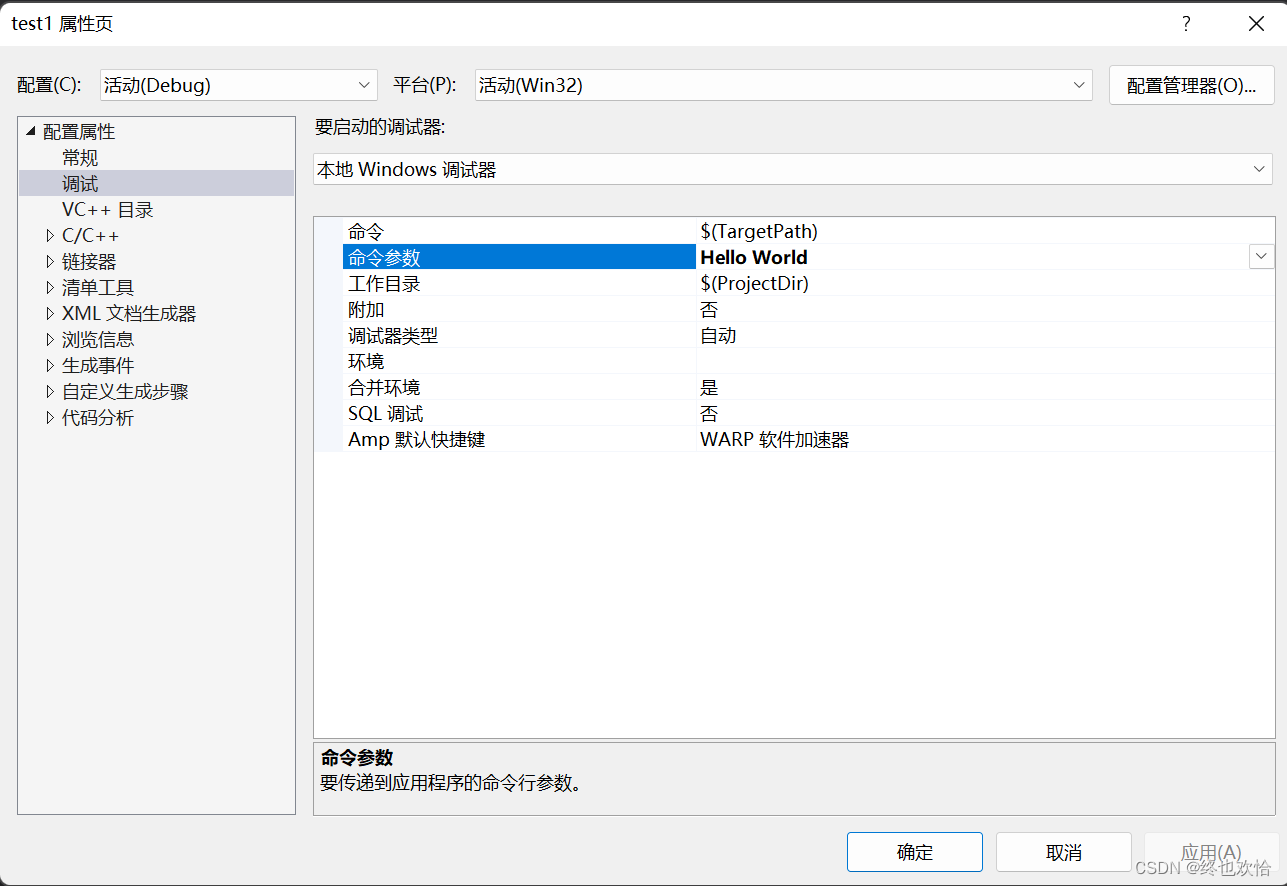
}通过操作系统命令行获取参数:在VS中设置时右键项目->属性->调试->命令参数,在命令参数中添加所需参数,字符串之间用空格分开即可。
6.26
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
for (int i = 1; i != argc; ++i)
cout << argv[i] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.27
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int sum(initializer_list<int> i)
{
int sum = 0;
for (auto beg = i.begin(); beg != i.end(); ++beg)
sum += *beg;
/*也可以使用for循环
for (auto &c : i)
sum += c;*/
return sum;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
//cout << sum({ 1, 2, 3, 4 }) << endl;
initializer_list<int> ia = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
cout << sum(ia) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.30
6.33
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int print(vector<int> v,int num1,const int num2)
{
if (num1 != num2)//num1为当前打印的元素,num2为总元素数量
{
cout << v[num1] << endl;
return print(v, ++num1, num2);
}
else
return 0;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
vector<int> ia(10, -1);//创建vector容器
print(ia, 0, 10);
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.37
//直接声明一个返回数组引用的函数
string(&func())[10];
//使用类型别名
typedef string arrT1[10];//using arrT1 = string[10];
arrT1& func( );
//使用尾置返回类型
auto func( )->int(&)[10];
//使用decltype关键字
int arrT2[10];
decltype(arrT2) &func();6.38
int odd[] = { 1,3,5,7,9 };
int even[] = { 0,2,4,6,8 };
decltype(odd) &arrPtr(int i)
{
return(i % 2) ? odd : even;//返回数组的引用
}6.42
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string make_plural(size_t ctr, const string &word, const string &ending="s")
{
return (ctr > 1) ? word + ending : word;
}
int main()
{
cout << make_plural(2, "success", "es") << endl;
cout << make_plural(2, "failure") << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.44 在函数返回类型前面加上关键字inline
inline bool isShorter(const string &s1, const string &s2)
{
return s1.size < s2.size();
}6.48
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
while(cin>>s && s!="sought"){}//空函数体,循环读入,遇到结束符或者sought结束循环
assert(cin);//assert为预处理宏,首先对cin求值判断真假,cin为结束符则为假,assert输出提示信息并终止程序执行,为真则什么也不做
/*
int a;
cin >> a;
assert(a >= 10);//若a<10则条件为假,assert输出提示信息并终止程序执行,为真则什么也不做
cout << "a=" << a;*/
system("pause");
}6.51
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void f() { puts("void f()"); }//1
void f(int) { puts("void f(int)"); }//2
void f(int, int) { puts("void f(int, int)"); }//3
void f(double, double = 3.14) { puts("void f(double, double = 3.14)"); }//4
int main()
{
f();//调用1
f(true);//调用2
f(1, 'a');//调用3
f(3.34);//调用4
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.52
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void manip(int, int);
double dobj;
int main()
{
manip('a', 'z');//类型提升,char到int
manip(55.4, dobj);//类型转换,double转换成int
}6.53
(a)
int calc(int&, int&);
int calc(const int&, const int&);//当传入形参为const int型时调用
(b)
int calc(char*, char*);
int calc(const char*, const char*);//当传入形参为const char*型时(指向常量的指针)调用
(c)
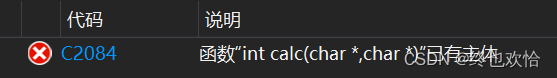
int calc(char*, char*);
int calc(char* const, char* const);//不合法,顶层const被忽略,实际上并未形成函数重载
6.54~6.56
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int func1(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int func2(int a, int b)
{
return a - b;
}
int func3(int a, int b)
{
return a*b;
}
int func4(int a, int b)
{
return a/b;
}
int main()
{
int (*p)(int a, int b);//指针p指向函数,该函数的形参为两个int,返回类型为int
vector<decltype(p)> v;
v.push_back(func1);
v.push_back(func2);
v.push_back(func3);
v.push_back(func4);
//测试
int a = 3;
int b = 1;
for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it)(a, b) << endl;
}
system("pause");
}



















 32万+
32万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








