1 线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,
常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储。
2 顺序表
2.1 概念与结构
顺序表是用一段
物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
- 静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储。
- 动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。
静态顺序表数组长度是固定的,只适合我们知道容量的情况,一般情况下我们会采用动态顺序表,这样更加灵活。下面我们来实现一个动态的顺序表。
代码实现:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: admin
* Date: 2021-12-11
* Time: 15:19
*/
public class MyArrayList {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;//有效的数据个数
public MyArrayList() {
this.elem = new int[10];
}
// 打印顺序表
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// 获取顺序表的有效数据长度
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data) {
if (pos < 0 || pos > usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法!");
return;
}
if (isFull()) {
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, 2 * this.elem.length);
}
//3、
for (int i = this.usedSize - 1; i >= pos; i--) {
this.elem[i + 1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if (this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
// 查找某个元素对应的位置,找不到返回-1
public int search(int toFind) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if (this.elem[i] == toFind) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int getPos(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法");
return -1;//所以 这里说明一下,业务上的处理,这里不考虑 后期可以抛异常
}
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为/更新 value
public void setPos(int pos, int value) {
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize) {
System.out.println("pos位置不合法");
return;
}
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("顺序表为空!");
return;
}
int index = search(toRemove);
if (index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有你要删除的数字!");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < this.usedSize - 1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i + 1];
}
this.usedSize--;
//this.elem[usedSize] = null; 如果数组当中是引用数据类型。
}
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
/*for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
this.elem[i] = null;
}
this.usedSize = 0;
*/
}
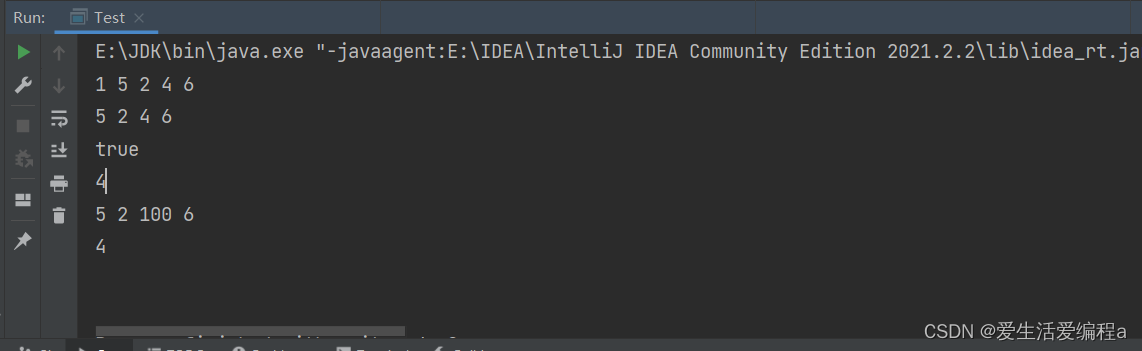
主函数测试代码:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(0,1);
myArrayList.add(1,5);
myArrayList.add(2,2);
myArrayList.add(3,4);
myArrayList.add(4,6);
myArrayList.display();
myArrayList.remove(1);
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println(myArrayList.contains(6));
System.out.println(myArrayList.getPos(2));
myArrayList.setPos(2,100);
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println(myArrayList.size());
myArrayList.clear();
myArrayList.display();
}
}
2.2 顺序表相关问题
- 顺序表
中间/头部的插入删除,时间复杂度为O(N)- 增容需要申请新空间,拷贝数据,释放旧空间。会有不小的消耗。
增容一般是呈2倍的增长,势必会有一定的空间浪费。例如当前容量为100,满了以后增容到200,我们再继续插入了5个数据,后面没有数据插入了,那么就浪费了95个数据空间。
3 链表
3.1 初识链表
链表的出现刚好就可以解决上面顺序表的一些问题,链表是一种
物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
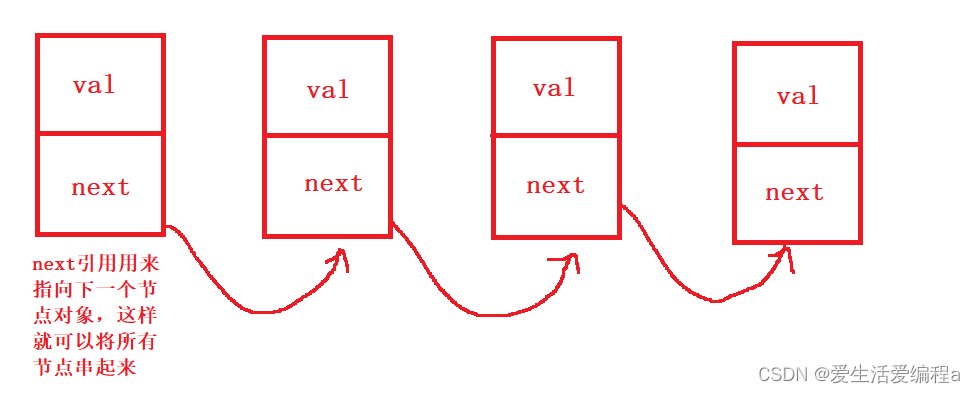
链表结构中我们重点掌握两种:
1.无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希表、图的邻接表等等。另外这种结构在笔试面试中出现很多。
2.无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
3.2 单向链表实现
无头单向非循环链表代码实现:
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: admin
* Date: 2021-11-02
* Time: 20:04
*/
//ListNode代表一个节点
class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;//null
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public class MyLinkedList {
public ListNode head;//链表的头引用
public void createList() {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(56);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
listNode5.next = null;
this.head = listNode1;
}
public void display() {
//this.head.next != null
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public void display2(ListNode newHead) {
ListNode cur = newHead;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
/*if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
}else {
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}*/
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
/* ListNode node = new ListNode(1);
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur != null){
cur.next = node;
}else {
return;
}*/
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public boolean addIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index > 0 && index < size() - 1) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (index != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
return true;
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return true;
}
if (index == size() - 1) {
addLast(data);
return true;
}
System.out.println("位置不合法!");
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
if (this.head == null) {
System.out.println("单链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == key) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(this.head.val == key){
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
System.out.println("链表中没有该关键字");
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
if (this.head == null) {
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
ListNode prev = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
prev.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if (this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
}
//清空链表
public void clear() {
while (this.head != null) {
ListNode curNext = this.head.next;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = curNext;
}
}
//反转链表
public ListNode reverseList() {
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
ListNode pre = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
return pre;
}
//找中间节点(若为偶数返回第二个),只遍历一遍
public ListNode findMid2() {
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = this.head;
ListNode slow = this.head;
//这里优先判断fast,保证fast.next有意义!!
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
public ListNode findMid1() {
if (this.head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = this.head;
ListNode slow = this.head;
//这里正常应该优先判断fast,保证fast.next有意义,但是在该while循环里若fast = null就直接返回了,不会进入到while条件判断里面,所以可以不用判断fast是否为空
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
if (fast == null) {
return slow;
}
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
public ListNode findLastK(int k) {
if (this.head == null || k <= 0) {
return null;
}
ListNode fast = this.head;
ListNode slow = this.head;
while (k - 1 != 0) {
fast = fast.next;
if (fast == null) {
return null;
}
k--;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
//分割链表
public ListNode cutList(int num) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
ListNode dm = null;
ListNode dx = null;
ListNode hm = null;
ListNode hx = null;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val < num) {
if (dm == null) {
dm = cur;
dx = cur;
} else {
dx.next = cur;
dx = dx.next;
}
} else {
if (hm == null) {
hm = cur;
hx = cur;
} else {
hx.next = cur;
hx = hx.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if (dx == null) {
return hm;
}
if (hm == null) {
dx.next = null;
return dm;
}
dx.next = hm;
hx.next = null;
return dm;
}
//删除重复节点
public ListNode deleteOverList(){
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while (cur != null) {
if(cur.next != null && cur.val == cur.next.val) {
while (cur.next != null && cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur = cur.next;
}
//多走一步
cur = cur.next;
}else {
tmp.next = cur;
tmp = tmp.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//防止最后一个节点的值也是重复的
tmp.next = null;
return newHead.next;
}
//判断是否为回文链表
public boolean cllBackList() {
ListNode slow = this.head;
ListNode fast = this.head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
while (head != slow) {
if (head.val != slow.val) {
return false;
} else {
if (head.next == slow) {
return true;
}
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
}
return true;
}
//判断链表是否有环,有则找出入口点
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
ListNode ptr = head;
while (ptr!=slow){
ptr = ptr.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return ptr;
}
}
return null;
}
}
测试代码(包含两个链表合并和判断是否相交代码):
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: admin
* Date: 2021-11-02
* Time: 20:28
*/
public class TestDemo {
//合并两个链表
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode headA,ListNode headB){
if(headA==null || headB==null){
return null;
}
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(1);
ListNode tep = newHead;
while (headA != null && headB != null){
if (headA.val < headB.val) {
tep.next = headA;
headA = headA.next;
tep = tep.next;
} else {
tep.next = headB;
headB = headB.next;
tep = tep.next;
}
}
if (headA != null){
tep.next = headA;
}
if (headB != null){
tep.next = headB;
}
return newHead.next;
}
/*public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tmp = newHead;
while (headA != null && headB != null) {
if(headA.val < headB.val) {
tmp.next = headA;
headA = headA.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}else {
tmp.next = headB;
headB = headB.next;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
if(headA != null) {
tmp.next = headA;
}
if(headB != null) {
tmp.next = headB;
}
return newHead.next;
}*/
//判断链表是否相交
public static ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode A,ListNode B){
ListNode pl = A;
ListNode ps = B;
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
while(pl != null){
lenA++;
pl = pl.next;
}
pl = A;
while(ps != null){
lenB++;
ps = ps.next;
}
ps = B;
int len = lenA-lenB;
if(len < 0) {
pl = B;
ps = A;
len = lenB-lenA;
}
//1、pl永远指向了最长的链表 ps 永远指向了最短的链表 2、求到了差值len步
//走差值len步
while(len!=0){
pl = pl.next;
len--;
}
//同时走 直到相遇
while(pl != ps){
pl = pl.next;
ps = ps.next;
}
return pl;
}
public static void creatCut(ListNode A,ListNode B){
A.next.next = B.next.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(12);
myLinkedList.addLast(13);
myLinkedList.addLast(14);
myLinkedList.addLast(14);
/*ListNode ret = myLinkedList.findMid1();
System.out.println(ret.val);*/
/*ListNode ret = myLinkedList.cutList(43);
myLinkedList.display2(ret);*/
myLinkedList.deleteOverList();
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.display2(myLinkedList.deleteOverList());
}
}
4 顺序表和链表区别
💡顺序表:
优点:
空间连续,支持随机访问。
缺点:
1.中间或前面部分的插入删除时间复杂度O(N)
2.增容的代价比较大
💡链表:
缺点:
以节点为单位存储,不支持随机访问
优点:
1.任意位置插入删除时间复杂度为O(1)
2.没有增容问题,插入一个开辟一个空间
在平时写代码过程中
注意选择合适的数据结构来,否则会得不偿失。
作者水平有限,若文章有任何问题欢迎私聊或留言,希望和大家一起学习进步!!!
创作不易,再次希望大家👍支持下,谢谢大家🙏






















 203
203











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








