目录
15 查找算法
15.1 顺序查找原理及实战
15.2 折半查找原理及实战
15.3 二叉排序树原理及建树实战
15.4 二叉排序树删除实战
15.5 真题实战(2011.42)
OJ作业
15 查找算法
15.1 顺序查找原理及实战
定义(顺序查找)
顺序查找(线性查找),适用于顺序表和链表。对于顺序表,通过数组下标递增扫描每个元素;对于链表,通过指针next依次扫描每个元素。
代码描述(动态分配的数组实现)
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct {
ElemType *elem; //整形指针,申请的堆空间的起始地址存入elem
int TableLen; //存储动态数组中元素个数
} SSTable;
//这里选择存哨兵,所以需要多申请一个位置
void InitST(SSTable &ST, int len) {
ST.elem = (ElemType *) malloc(sizeof(ElemType) * len);
ST.TableLen = len + 1;
//存取0-99随机数在链表中
int i;
srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 1; i < ST.TableLen; i++) {
ST.elem[i] = rand() % 100;
}
}
int PrintST(SSTable ST) {
for (int i = 1; i < ST.TableLen; i++) {
printf("%3d",ST.elem[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int SearchSeq(SSTable ST, ElemType key) {
ST.elem[0] = key; //下标0的位置存哨兵
int i;
for (i = ST.TableLen - 1; ST.elem[i] != key; --i);
return i;
}
int main() {
SSTable ST;
InitST(ST, 10);
PrintST(ST);
ElemType key;
scanf("%d", &key);
int pos;
pos =SearchSeq(ST, key);
if(pos){
printf("success find! pos = %d\n",pos);
} else{
printf("not find!\n");
}
return 0;
} |
15.2 折半查找原理及实战
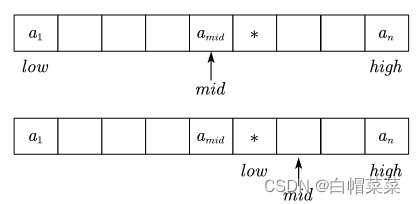
定义(折半查找)
折半查找(二分查找)。仅支持有序的顺序表,链表不支持二分查找。
代码
| #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct SSTable {
ElemType *elem;
int TableLen;
} SSTable;
void InitST(SSTable &ST, int len) {
ST.elem = (ElemType *) malloc(sizeof(ElemType) * len);
ST.TableLen = len;
srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < ST.TableLen; i++) {
ST.elem[i] = rand() % 100;
}
}
void PrintST(SSTable ST) {
for (int i = 0; i < ST.TableLen; i++) {
printf("%3d", ST.elem[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//二分查找
int BinarySearch(SSTable L, ElemType key) {
int low = 0;
int high = L.TableLen - 1;
int mid;
while (low <= high) {
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (key > L.elem[mid]) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (key < L.elem[mid]) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
//函数名compare存储的是函数的入口地址,也是一个指针,是函数指针类型
//left指针、right指针是指向数组中的任意两个元素
int compare(const void *left, const void *right) {
return *(ElemType *) left - *(ElemType *) right; //强制类型转换,从小到大
}
int main() {
SSTable ST;
InitST(ST, 10);
qsort(ST.elem, ST.TableLen, sizeof(ElemType), compare);
PrintST(ST);
ElemType key;
scanf("%d", &key);
int pos;
pos = BinarySearch(ST, key);
if (pos >= 0) {
printf("Success find the local:%d\n", pos + 1);
} else {
printf("not find!\n");
}
return 0;
} |
【注意】:
(1)low和high一定是mid的前面一个或者后面一个,不能等于mid。如果这样循环条件就一定要取等。
(2)qsort规定:如果left指针指向的值大于right指针指向的值,返回正值;小于返回负值;相等返回0。
动画链接:“https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/Search.html”。
15.3 二叉排序树原理及建树实战
二叉排序树(二叉查找树)。或者是空树,或者是二叉树。
二叉树特性:
1)若左子树非空,左子树上的所有结点均小于根节点的值。
2)若右子树非空,右子树上的所有结点均大于根节点的值。
3)左右子树也分别是一颗二叉排序树。
代码(递归、非递归、中序遍历、查找)
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int BiElemType;
typedef struct BiTNode {
BiElemType key;
struct BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;
} BiTree;
//二叉排序树算法(递归)
int BST_Insert1(BiTree *&T, BiElemType key) {
if (NULL == T) {
T = (BiTree *) calloc(1, sizeof(BiTree));
T->key = key;
return 1;
} else if (key < T->key) {
return BST_Insert1(T->lchild, key);
} else if (key > T->key) {
return BST_Insert1(T->rchild, key);
} else {
return 0;
}
}
//二叉排序树算法(非递归)
int BST_Insert(BiTree *&T, BiElemType key) {
BiTree *Tnew = (BiTree *) calloc(1, sizeof(BiTree));
Tnew->key = key;//为数据申请空间
if (NULL == T) {//此值作为根结点
T = Tnew;
return 0;
}
BiTree *p = T;//用来查找树
BiTree *parent;
while (p) {
parent = p;
if (key < p->key) {
p = p->lchild;
} else if (key > p->key) {
p = p->rchild;
} else {
return -1; //值相等就不插入
}
}
if (key < parent->key) {
parent->lchild = Tnew;
} else if (key > parent->key) {
parent->rchild = Tnew;
}
return 1;
}
//构建二叉排序树
void Creat_BST(BiTree *&T, BiElemType *str, int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
BST_Insert1(T, str[i]);
}
}
//中序遍历
void InOrder(BiTree *T) {
if (T != NULL) {
InOrder(T->lchild);
printf("%3d", T->key);
InOrder(T->rchild);
}
}
BiTree *BST_Search(BiTree *T, BiElemType searchnum, BiTree *&parent) {
parent = NULL;
while (T && searchnum != T->key) {
parent = T;
if (searchnum > T->key) {
T = T->rchild;
} else {
T = T->lchild;
}
}
return T;
}
int main() {
BiTree *tree = NULL;
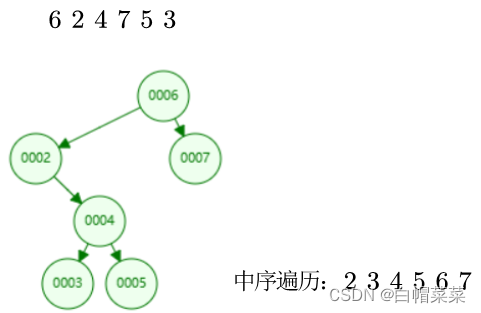
BiElemType str[6] = {6, 2, 4, 7, 5, 3};
Creat_BST(tree, str, 6); //二叉排序树
InOrder(tree); //中序遍历
BiTree *parent, *search;
search = BST_Search(tree, 2, parent); //查找元素和该值的父结点
if (search) {
printf("\n parent:%d", search->key);
} else {
printf("\n not find!");
}
return 0;
} |
【注意】:
1)查找的次数就是树的高度。
2)插入树的根节点是在循环的前面就判断树空。
3)数据插入返回的是:二叉树,而不是其他节点。
动画链接:“https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BST.html”。
15.4 二叉排序树删除实战
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int BiElemType;
typedef struct BiTNode {
BiElemType key;
struct BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;
} BiTNode;
int Insert_BST(BiTNode *&T, BiElemType str) {
if (T == NULL) {
T = (BiTNode *) calloc(1, sizeof(BiTNode));
T->key = str;
return 1;
}
if (str < T->key) {
return Insert_BST(T->lchild, str);
} else if (str > T->key) {
return Insert_BST(T->rchild, str);
}
}
void Create_BST(BiTNode *&T, BiElemType *str, int len) {
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Insert_BST(T, str[i]);
}
}
void Inorder(BiTNode *T) {
if (T) {
Inorder(T->lchild);
printf("%3d", T->key);
Inorder(T->rchild);
}
}
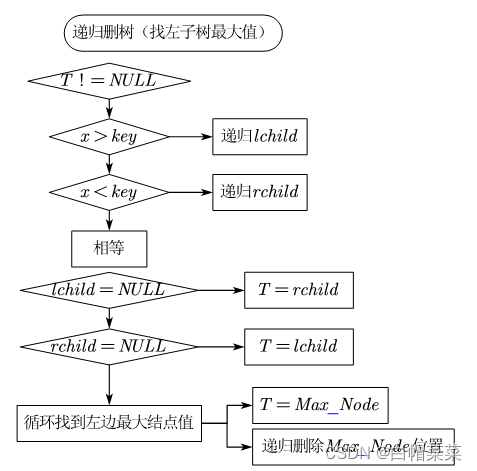
void Delect_T(BiTNode *&T, BiElemType elem) {//找左子树最大的结点
if (T == NULL) {
return;
}
if (elem < T->key) {//值小,递归找左子树
Delect_T(T->lchild, elem);
} else if (elem > T->key) {//值大,递归找右子树
Delect_T(T->rchild, elem);
} else {//相等,即找到删除的结点
if (T->lchild == NULL) {//删除结点左子树为空
BiTNode *tempnode = T;
T = T->rchild;
free(tempnode);
} else if (T->rchild == NULL) {//删除结点右子树为空
BiTNode *tempnode = T;
T = T->lchild;
free(tempnode);
} else {//删除结点左右子树都不为空
BiTNode *tempnode = T->lchild;
while (tempnode->rchild) {//找到删除结点左子树最大值
tempnode = tempnode->rchild;
}
T->key = tempnode->key;
Delect_T(T->lchild, tempnode->key);
}
}
}
int main() {
BiTNode *tree = NULL;
BiElemType str[6] = {6, 2, 4, 7, 5, 3};
Create_BST(tree, str, 6);
Inorder(tree);
printf("\n");
Delect_T(tree, 1);
Inorder(tree);
return 0;
} |
15.5 真题实战(2011.42)

| (1) 算法基本思想 比较两个数组元素的中位数a、b, 如果a=b,则中位数是a / b; 如果a>b,删除比a大的元素值,删除比b小的元素值,两个数组删除的元素个数要相等。 如果a<b,删除比a小的元素值,删除比b大的元素值,两个数组删除的元素个数要相等。 循环遍历上述步骤直到删到最后数组元素个数是偶数个,将删除小的自身,删除比b大的元素值。最终两个数组都只剩一个元素时,较小的元素就是中位数。 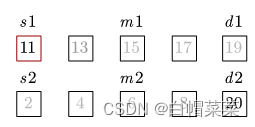
|
| (2) 算法描述 #include <stdio.h>
#define MaxSize 50
int MidSearch(int *A, int *B, int len) {
int s1 = 0, s2 = 0, d1 = len - 1, d2 = len - 1, mid1, mid2;
//直到数组中都只剩一个元素结束循环
while (s1 != d1 || s2 != d2) {
mid1 = (d1 + s1) / 2;
mid2 = (d2 + s2) / 2;
if (A[mid1] == B[mid2]) {
return A[mid1];
} else if (A[mid1] > B[mid2]) {//a > b
if ((d1 + s1) % 2 == 0) {//元素为奇数个
d1 = mid1;
s2 = mid2;
} else {//元素为偶数个
d1 = mid1;
s2 = mid2 + 1;//小的元素舍弃本身
}
} else {//a < b
if ((d1 + s1) % 2 == 0) {//元素为奇数个
s1 = mid1;
d2 = mid2;
} else {
s1 = mid1 + 1;//小的元素舍弃本身
d2 = mid2;
}
}
}
return A[s1] < B[s2] ? A[s1] : B[s2];
}
int main() {
int A[MaxSize] = {11, 13, 15, 17, 19};
int B[MaxSize] = {2, 4, 6, 8, 20};
int mid = MidSearch(A, B, 5);
printf("%d", mid);
return 0;
} |
| (3) 时间复杂度和空间复杂度 算法的时间复杂度为O(log2 n),空间复杂度为O(1)。因为我们没有使用额外的跟n相关的空间,因为不断的二分,次数是log2 n,所以时间复杂度是O(log2 n)。 |
OJ作业
Description
读取10个元素87 7 60 80 59 34 86 99 21 3,然后建立二叉查找树,中序遍历输出3 7 21 34 59 60 80 86 87 99,针对有序后的元素,存入一个长度为10的数组中,通过折半查找找到21的下标(下标为2),然后输出2
Input
标准输入读取10个元素 87 7 60 80 59 34 86 99 21 3
Output
中序遍历输出有序,每个元素占3个字母位置3 7 21 34 59 60 80 86 87 99
接着输出2即可(就是元素21的下标),注意2直接在行首输出即可。
Sample Input 1
87 7 60 80 59 34 86 99 21 3
Sample Output 1
3 7 21 34 59 60 80 86 87 99
2
| #include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int BiElemType;
typedef struct BiTNode {
BiElemType data;
struct BiTNode *lchild, *rchild;
} BiTNode;
int Insert_BST(BiTNode *&T, BiElemType x) {
if (T == NULL) {
T = (BiTNode *) calloc(1, sizeof(BiTNode));
T->data = x;
return 1;
} else if (x < T->data) {
return Insert_BST(T->lchild, x);
} else if (x > T->data) {
return Insert_BST(T->rchild, x);
} else {
return 0;
}
}
//中序遍历
int num = 0;
void InOrder(BiTNode *T, int *str) {
if (T) {
InOrder(T->lchild, str);
printf("%3d", T->data);
str[num++] = T->data;
InOrder(T->rchild, str);
}
}
int MidSearch(int *str, int key) {
int low = 0, high = 9;
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
while (low <= high) {
if (key < str[mid]) {
high = mid - 1;
mid = (low + high) / 2;
} else if (key > str[mid]) {
low = mid + 1;
mid = (low + high) / 2;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
}
int main() {
int x;
int str[10] = {0};
BiTNode *tree = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
scanf("%d", &x);//87 7 60 80 59 34 86 99 21 3
Insert_BST(tree, x);
}
InOrder(tree, str);
int mid = MidSearch(str, 21);
printf("\n%d", mid);
return 0;
} |












 本文介绍了几种常见的查找算法,包括顺序查找、折半查找以及二叉排序树的相关操作。顺序查找适用于顺序表和链表,而折半查找仅适用于有序的顺序表。二叉排序树是一种高效的查找数据结构,具有特定的性质保证查找效率。文章提供了相关算法的C语言实现,并包含实际操作示例和相关动画链接,帮助读者理解和掌握这些概念。
本文介绍了几种常见的查找算法,包括顺序查找、折半查找以及二叉排序树的相关操作。顺序查找适用于顺序表和链表,而折半查找仅适用于有序的顺序表。二叉排序树是一种高效的查找数据结构,具有特定的性质保证查找效率。文章提供了相关算法的C语言实现,并包含实际操作示例和相关动画链接,帮助读者理解和掌握这些概念。

















 96
96

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










