1、LRU Cache 淘汰规则
Least Recently Used,将最近最少使用的 key 从缓存中淘汰掉。以链表法为例,最近访问的 key 移动到链表头,不常访问的自然靠近链表尾,如果超过容量、个数限制,移除尾部的
-
例如有原始数据如下,容量规定为 3

- 时间上,新的留下,老的淘汰,比如 put d,那么最老的 a 被淘汰

- 如果访问了某个 key,则它就变成最新的,例如 get b,则 b 被移动到链表头

2、LRU Cache 链表实现
-
如何断开节点链接
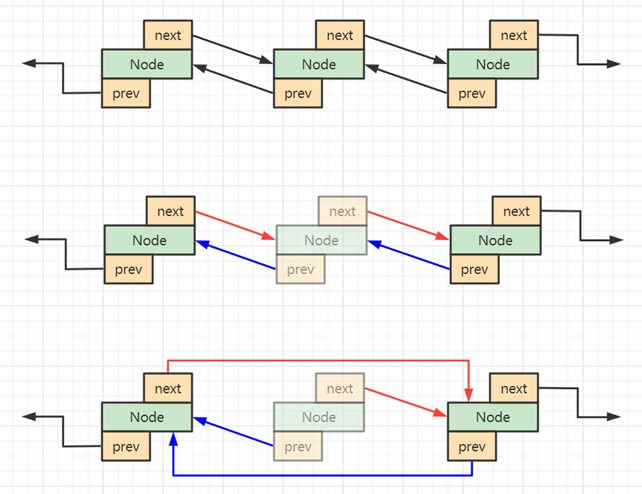
-
如何链入头节点
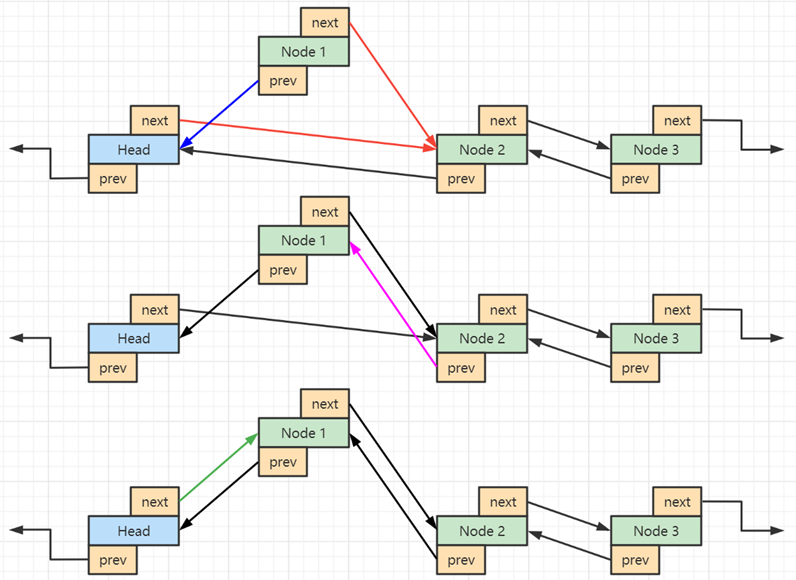
参考代码一(纯手写实现)
package day06;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class LruCache1 {
static class Node {
Node prev;
Node next;
String key;
Object value;
public Node(String key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
// (prev <- node -> next)
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(128);
sb.append("(");
sb.append(this.prev == null ? null : this.prev.key);
sb.append("<-");
sb.append(this.key);
sb.append("->");
sb.append(this.next == null ? null : this.next.key);
sb.append(")");
return sb.toString();
}
}
public void unlink(Node node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
public void toHead(Node node) {
node.prev = this.head;
node.next = this.head.next;
this.head.next.prev = node;
this.head.next = node;
}
int limit;
Node head;
Node tail;
Map<String, Node> map;
public LruCache1(int limit) {
this.limit = Math.max(limit, 2);
this.head = new Node("Head", null);
this.tail = new Node("Tail", null);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
this.map = new HashMap<>();
}
public void remove(String key) {
Node old = this.map.remove(key);
unlink(old);
}
public Object get(String key) {
Node node = this.map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
unlink(node);
toHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(String key, Object value) {
Node node = this.map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
node = new Node(key, value);
this.map.put(key, node);
} else {
node.value = value;
unlink(node);
}
toHead(node);
if(map.size() > limit) {
Node last = this.tail.prev;
this.map.remove(last.key);
unlink(last);
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(this.head);
Node node = this.head;
while ((node = node.next) != null) {
sb.append(node);
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LruCache1 cache = new LruCache1(5);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("1", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("2", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("3", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("4", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("5", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("6", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.get("2");
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("7", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
}
}参考代码二(借助LinkedHashMap实现)
package day06;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LruCache2 extends LinkedHashMap<String, Object> {
private int limit;
public LruCache2(int limit) {
// 1 2 3 4 false
// 1 3 4 2 true
super(limit * 4 /3, 0.75f, true); // 参数一:列表容量; 参数二:扩容因子; 参数三:true代表开启淘汰元素规则,当容量满后开启淘汰队尾的元素,但是当我们访问队尾的元素后,这个元素会被放到队首,从而不会被淘汰
this.limit = limit;
}
// 淘汰执行方法
@Override
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<String, Object> eldest) {
if (this.size() > this.limit) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LruCache2 cache = new LruCache2(5);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("1", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("2", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("3", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("4", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("5", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("6", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
cache.get("2");
System.out.println(cache);
cache.put("7", 1);
System.out.println(cache);
}
}3、Redis LRU Cache 实现
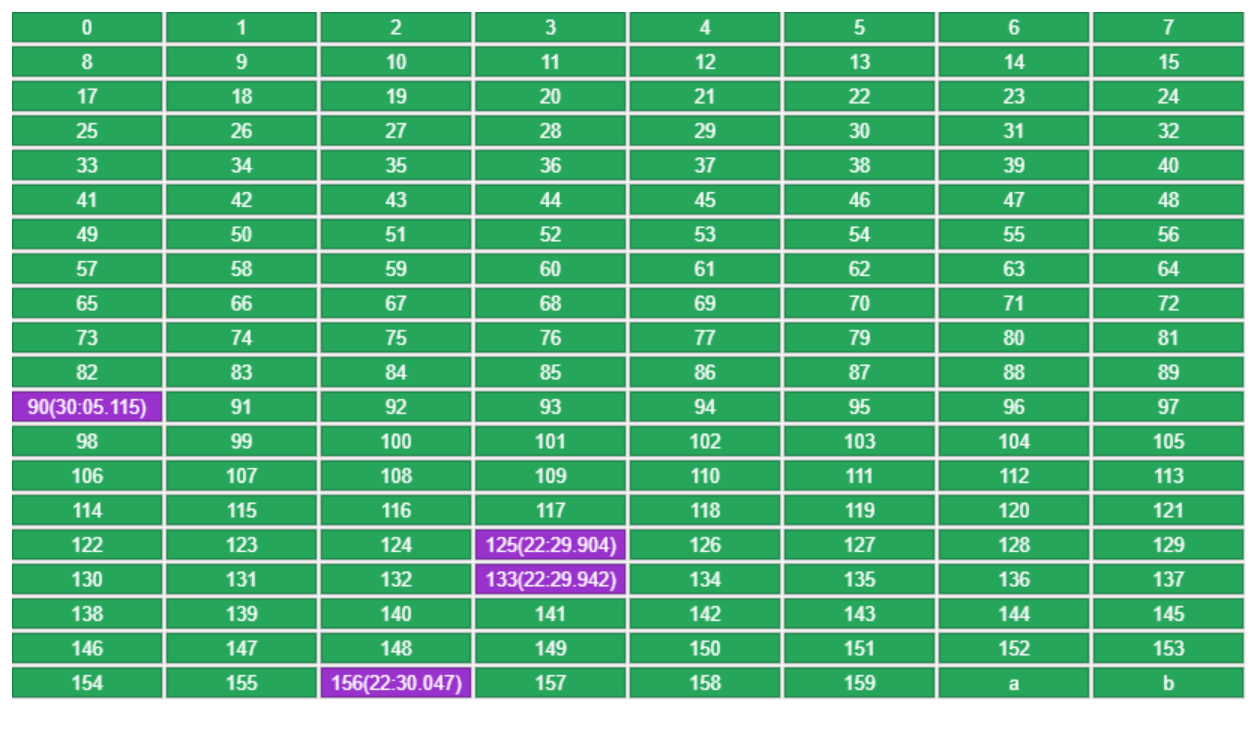
Redis 采用了随机取样法,较之链表法占用内存更少,每次只抽 5 个 key,每个 key 记录了它们的最近访问时间,在这 5 个里挑出最老的移除
-
例如有原始数据如下,容量规定为 160,put 新 key a
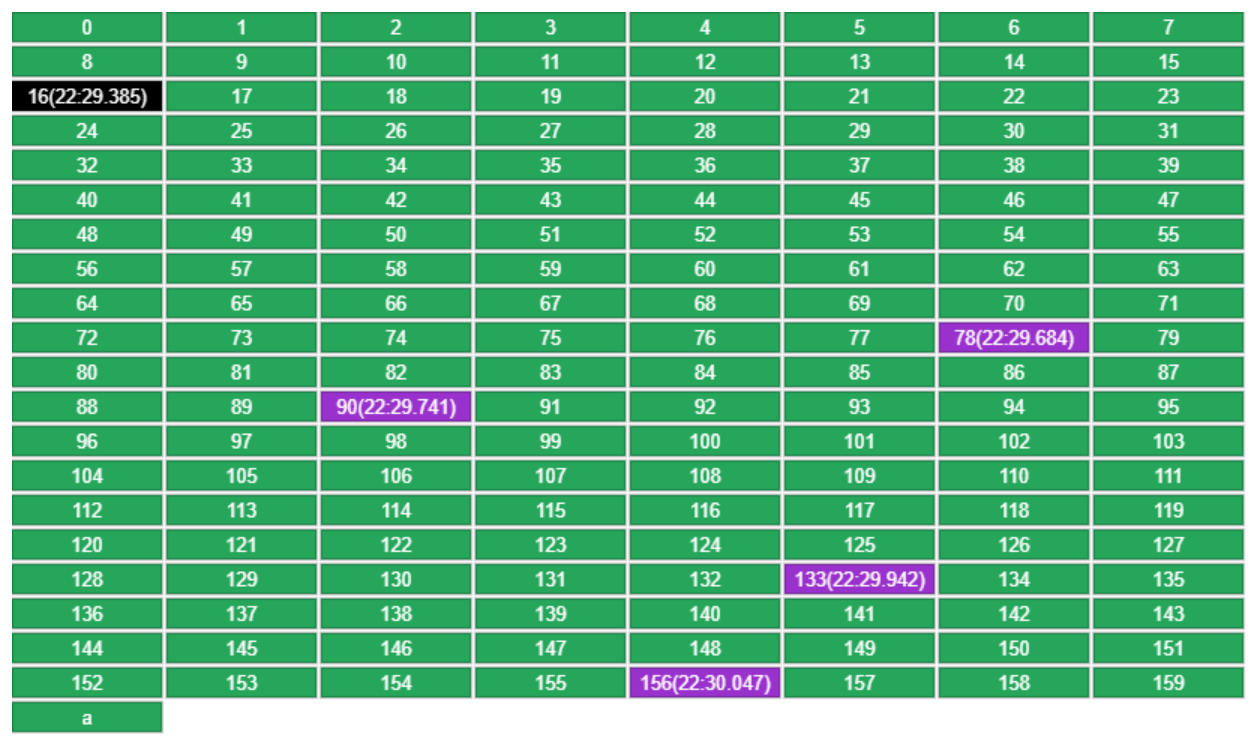
-
每个 key 记录了放入 LRU 时的时间,随机挑到的 5 个 key(16,78,90,133,156),会挑时间最老的移除(16)
-
再 put b 时,会使用上轮剩下的 4 个(78,90,133,156),外加一个随机的 key(125),这里面挑最老的(78)
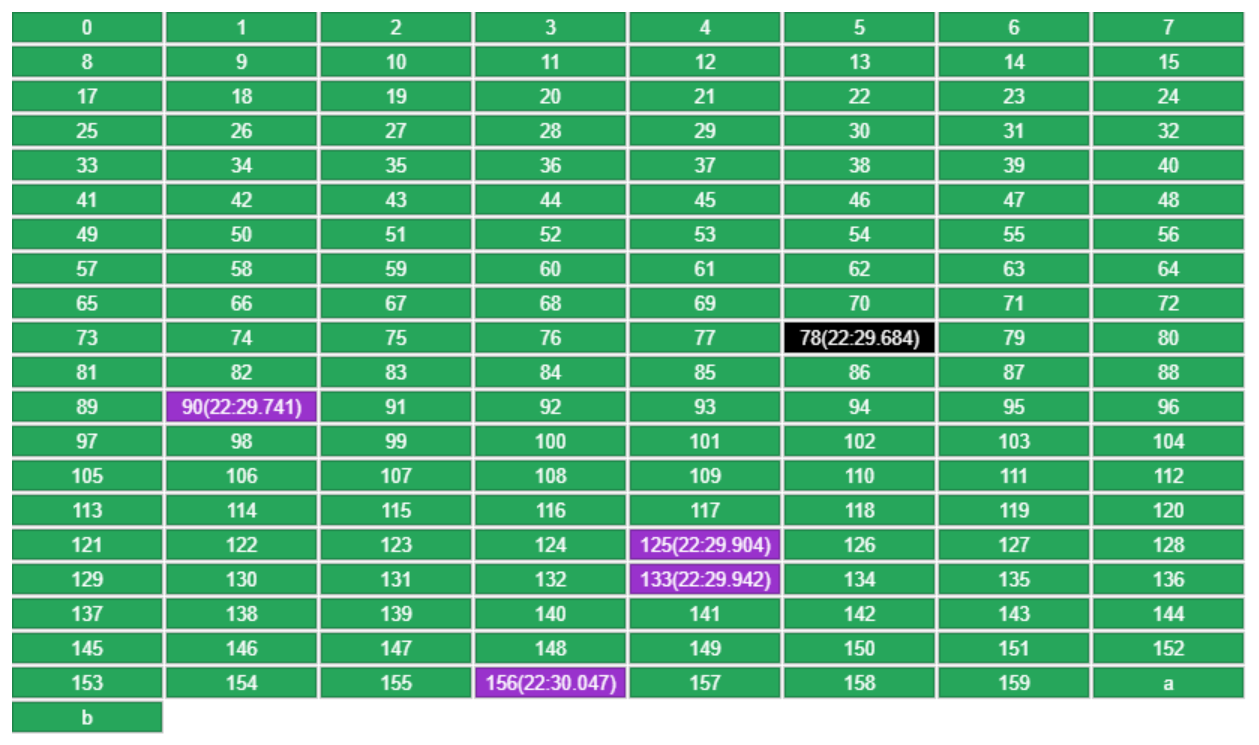
- 如果 get 了某个 key,它的访问时间会被更新(下图中 90)这样就避免了它下一轮被移除

























 358
358











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










