目录
2.构造函数Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
3.赋值函数Date& operator=(const Date& d)
4.Date& Date::operator+=(int day)函数实现日期加天数的功能
运算符重载
Date operator=(const Date& d)注意:
- 不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
- 重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数
- 用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型+,不能改变其含义
- 作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为隐藏参数this
- .* :: sizeof ?: . 这五个运算符不能重载
日期类头文件time.h
time.h
日期类头文件包含头文件,类的定义,成员函数和成员变量的声明。代码如下:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day);//日期类构造函数
void Print(); //打印
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);//通过输入参数年和月,返回某年某月的天数
bool operator==(const Date& d); //对运算符“==”进行重载
bool operator!=(const Date& d);
bool operator<(const Date& d);
bool operator<=(const Date& d);
bool operator>(const Date& d);
bool operator>=(const Date& d);
Date& operator=(const Date& d);
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date operator+(int day);
Date& operator-=(int day);
//d1-100
Date operator-(int day); //日期减去天数
//d1-d2
int operator-(const Date& d); //日期减去日期,一般没有意义
//++d1
Date& operator++(); //前置++,返回的是++之后的值
//d1++
//int参数 仅仅是为了占位,跟前置重载区分
Date operator++(int); //后置++,先返回d1的值,再++
private:
int _year; //年
int _month; //月
int _day; //日
};以上代码中成员变量包含年月日,d1表示日期类实例,d2也是。
日期类成员函数文件time.cpp
成员函数包括日期类成员函数的定义:
#include"time.h"
int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int days[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
int day = days[month];
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
day += 1;
return day;
}
else
{
return day;
}
}
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
if (month > 0 && month < 13 && (day > 0 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month)))
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
}
void Date::Print()
{
cout << _year << "/" << _month << "/" << _day << endl;
}
//d1==d2
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
//d1<d2
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{
return _year < d._year
|| (_year == d._year && _month < d._month)
|| (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{
return *this < d || *this == d;
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this <= d);
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{
return !(*this < d);
}
//返回值为了支持连续赋值,保持运算符的特性
//d3=d2=d1;
//d1=d1
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{
if (this != &d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
return *this;
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month > 13)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
//Date Date::operator+(int day)
//{
// Date tmp(*this);
// tmp._day += day;
// while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month))
// {
// tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);
// ++tmp._month;
// if (tmp._month == 13)
// {
// ++tmp._year;
// tmp._month = 1;
// }
// }
// return tmp;
//}
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
tmp += day;
return tmp;
}
//++d1 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
//d1++ 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
--_year;
_month = 12;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += day;
return tmp;
}1.GetMonthDay函数
输入参数year和参数month,输出year和month对应的day。实现逻辑是先定义一个数组存放12个月每个月的天数,因为月份是从1月开始数的,而数组有days[0],所以给数组赋值时,days[0]=0;还有一个是闰年的计算,闰年的2月天数是28天,非闰年2月是29天。闰年2月天数的计算逻辑,如果月份是2月并且年份能整除4但是不能整除100或者年份能整除400
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
day += 1;
return day;
}
else
{
return day;
}2.构造函数Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
这里需要注意的是非法日期的检查,不可以输入一个不合理的日期,比如月份大于13或者月份小于0.月份和天数都要合理
if (month > 0 && month < 13 && (day > 0 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month)))3.赋值函数Date& operator=(const Date& d)
返回值为了支持连续赋值,保持运算符的特性,检查日期是否给自己赋值。

赋值运算符"=",是先将d3赋值给d2,再将d2赋值给d1,最后返回d1的值,从右往左赋值。
4.Date& Date::operator+=(int day)函数实现日期加天数的功能
实现逻辑是先加上天数,判断天数是否大于当月天数,如果大于则进入while循环,先减去当月天数,月份加1,返回*this.
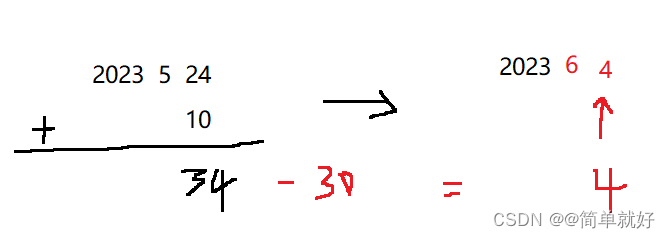
5.前置++和后置++
前置++是返回++之后的值,后置++先返回值,再++
++d1;//前置++
d1++;//后置++//++d1 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
//d1++ 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date tmp(*this);
*this += 1;
return tmp;
}tmp是*this的拷贝构造,因为后置++是先返回值才++,所以需要一个日期类的副本去保存它。
test.cpp
#include"time.h"
void TestDate1()
{
Date d1(2023, 2, 4);
Date d2(2023, 3, 4);
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
cout << d1.operator==(d2) << endl;
cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;//转换成去调用这个d1.operator==(d2);
cout << (d1 < d2) << endl;
}
void TestDate2()
{
Date d1(2023, 5, 6);
Date d2 = d1;
d2 += 1500;
d1.Print();
d2.Print();
Date d3 = d2 + 100;
d3.Print();
}
void TestDate3()
{
Date d1(2023, 5, 7);
d1.Print();
d1 -= 100;
d1.Print();
}
int main()
{
TestDate3();
return 0;
}






















 1294
1294

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










