文章目录
为什么需要树
- 数组存储方式分析:
优点:通过下标方式访问元素,速度快。对于有序数组还可以使用二分查找提高检索速度。
缺点:如果要检索具体某个值,或者插入值(按一定顺序)会整体移动,效率较低。

- 链式存储方式分析:
优点:在一定程度上对数组存储方式有优化(比如:插入一个数值节点,只需要将插入节点,链接到链表中即可,删除效率也很好)。
缺点:在进行检索时,效率仍然较低,比如(检索某个值,需要从头节点开始遍历)。

- 树存储方式分析:
能提高数据存储、读取的效率,比如利用二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),既可以保证数据的检索速度,同时也可以保证数据的插入、删除、修改的速度。

树示意图及常用术语

二叉树
二叉树概念
- 树有很多种,每个节点最多只能有两个子节点的一种形式称为二叉树。
- 二叉树的子节点分为左节点和右节点。

- 如果二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层,并且结点总数=2^n-1,n为层数,则称为满二叉树。
- 如果二叉树的所有叶子节点都在最后一层或者倒数第二层,而且最后一层的叶子节点在左边连续,倒数第二层的叶子节点在右边连续,称为完全二叉树。

前序中序后序遍历二叉树
前序遍历:先输出父节点,再遍历左子树和右子树
中序遍历:先遍历左子树,再输出父节点,再遍历右子树
后序遍历:先遍历左子树,再遍历右子树,最后输出父节点
小结:看输出父节点的顺序,就确定是前序、中序还是后序

代码实现前序中序后序遍历二叉树
package com.datastructures.tree;
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先需要创建一颗二叉树
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
//创建需要的结点
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "宋江");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "吴用");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "卢俊义");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5, "关胜");
//说明:二叉树应该递归创建。这里为了测试,先手动创建。后续会使用递归
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setRight(node4);
node3.setLeft(node5);
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
//测试
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTree.preOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("后序遍历");
binaryTree.postOrder();
}
}
//定义一个BinaryTree 二叉树
class BinaryTree {
private HeroNode root; //根结点
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
}
//先创建HeroNode结点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); //先输出父结点
//递归向左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
//递归向右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
//递归向左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
//输出当前结点,即父结点
System.out.println(this);
//递归向右子树中序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
//递归向左子树后序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
//递归向右子树后序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
//输出当前结点
System.out.println(this);
}
}
二叉树查找指定结点

代码实现二叉树查找指定结点
package com.datastructures.tree;
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先需要创建一颗二叉树
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
//创建需要的结点
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "宋江");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "吴用");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "卢俊义");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5, "关胜");
//说明:二叉树应该递归创建。这里为了测试,先手动创建。后续会使用递归
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setRight(node4);
node3.setLeft(node5);
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
//测试
// System.out.println("前序遍历");
// binaryTree.preOrder();
// System.out.println("中序遍历");
// binaryTree.infixOrder();
// System.out.println("后序遍历");
// binaryTree.postOrder();
int no = 5;
System.out.println("前序遍历查找");
HeroNode resNode = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(no);
if (resNode != null) {
System.out.printf("找到:no = %d, name = %s", resNode.getNo(), resNode.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到no = %d 的英雄", no);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("中序遍历查找");
resNode = null;
resNode = binaryTree.infixOrderSearch(no);
if (resNode != null) {
System.out.printf("找到:no = %d, name = %s", resNode.getNo(), resNode.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到no = %d 的英雄", no);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("后序遍历查找");
resNode = null;
resNode = binaryTree.postOrderSearch(no);
if (resNode != null) {
System.out.printf("找到:no = %d, name = %s", resNode.getNo(), resNode.getName());
} else {
System.out.printf("没有找到no = %d 的英雄", no);
}
}
}
//定义一个BinaryTree 二叉树
class BinaryTree {
private HeroNode root; //根结点
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//前序遍历查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
//中序遍历
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
//后序遍历
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
//先创建HeroNode结点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); //先输出父结点
//递归向左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
//递归向右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
//递归向左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
//输出当前结点,即父结点
System.out.println(this);
//递归向右子树中序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
//递归向左子树后序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
//递归向右子树后序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
//输出当前结点
System.out.println(this);
}
//前序遍历查找
/**
* @param no 要查找的no
* @return 如果找到就返回该Node,没有就返回null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("进入前序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//左子树递归
HeroNode resNode = null; //结果结点,判断是否找到
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { //说明在左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode; //找没找到都返回
}
//中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
//左子树递归
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入中序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
//后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
HeroNode resNode = null;
//左子树递归
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { //说明左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入后序遍历查找");
//与当前结点比较
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
}
二叉树删除结点
要求:
- 如果删除的结点是叶子结点,则删除该结点
- 如果删除的结点是非叶子结点,则删除该子树

代码实现二叉树删除结点
package com.datastructures.tree;
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先需要创建一颗二叉树
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
//创建需要的结点
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "宋江");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "吴用");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "卢俊义");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5, "关胜");
//说明:二叉树应该递归创建。这里为了测试,先手动创建。后续会使用递归
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setRight(node4);
node3.setLeft(node5);
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
//测试删除
System.out.println("删除前,前序遍历");
binaryTree.preOrder();
// binaryTree.delNode(5);
binaryTree.delNode(3);
System.out.println("删除后,前序遍历");
binaryTree.preOrder();
//测试
// System.out.println("前序遍历");
// binaryTree.preOrder();
// System.out.println("中序遍历");
// binaryTree.infixOrder();
// System.out.println("后序遍历");
// binaryTree.postOrder();
// int no = 5;
// System.out.println("前序遍历查找");
// HeroNode resNode = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(no);
// if (resNode != null) {
// System.out.printf("找到:no = %d, name = %s", resNode.getNo(), resNode.getName());
// } else {
// System.out.printf("没有找到no = %d 的英雄", no);
// }
//
// System.out.println();
// System.out.println("中序遍历查找");
// resNode = null;
// resNode = binaryTree.infixOrderSearch(no);
// if (resNode != null) {
// System.out.printf("找到:no = %d, name = %s", resNode.getNo(), resNode.getName());
// } else {
// System.out.printf("没有找到no = %d 的英雄", no);
// }
//
// System.out.println();
// System.out.println("后序遍历查找");
// resNode = null;
// resNode = binaryTree.postOrderSearch(no);
// if (resNode != null) {
// System.out.printf("找到:no = %d, name = %s", resNode.getNo(), resNode.getName());
// } else {
// System.out.printf("没有找到no = %d 的英雄", no);
// }
}
}
//定义一个BinaryTree 二叉树
class BinaryTree {
private HeroNode root; //根结点
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//前序遍历查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
//中序遍历
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
//后序遍历
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
//删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
//判断root是否为空 root是否为要被删除的结点
if (root != null) {
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
} else {
System.out.println("空树,不能删除");
}
}
}
//先创建HeroNode结点
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); //先输出父结点
//递归向左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
//递归向右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
//递归向左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
//输出当前结点,即父结点
System.out.println(this);
//递归向右子树中序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
//递归向左子树后序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
//递归向右子树后序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
//输出当前结点
System.out.println(this);
}
//前序遍历查找
/**
* @param no 要查找的no
* @return 如果找到就返回该Node,没有就返回null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("进入前序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//左子树递归
HeroNode resNode = null; //结果结点,判断是否找到
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { //说明在左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode; //找没找到都返回
}
//中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
//左子树递归
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入中序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
//后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
HeroNode resNode = null;
//左子树递归
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { //说明左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入后序遍历查找");
//与当前结点比较
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
//递归删除结点
//如果删除的结点是叶子结点,则删除该结点
//如果删除的结点是非叶子结点,则删除该子树
public void delNode(int no) {
//判断左子结点是否是要被删除的结点
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
//判断右子结点是否是要被删除的结点
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
//左子树递归删除
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
//右子树递归删除
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
}
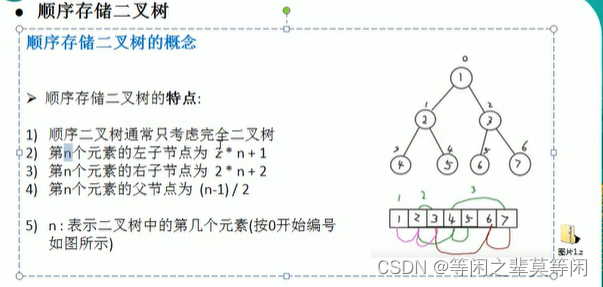
顺序存储二叉树
概念
从数据存储来看,数组存储方式和树的存储方式可以互相转换,即数组可以转换成树,树也可以转换成数组。在堆排序中会使用到顺序存储二叉树。

特点
- 顺序二叉树通常只考虑完全二叉树
- 第n个元素的左子节点为 2 * n + 1
- 第n个元素的右子结点为 2 * n + 2
- 第n个元素的父节点为 (n - 1) / 2
- n:表示二叉树中的第几个元素(从0开始编号—跟数组保持一致)
代码实现
package com.datastructures.tree;
public class ArrBinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};
//创建一个ArrBinaryTree
ArrBinaryTree arrBinaryTree = new ArrBinaryTree(arr);
System.out.println("前序遍历:");
arrBinaryTree.preOrder(); // 1 2 4 5 3 6 7
System.out.println("中序遍历:");
arrBinaryTree.infixOrder(0); // 4 2 5 1 6 3 7
System.out.println("后序遍历:");
arrBinaryTree.postOrder(0); // 4 5 2 6 7 3 1
}
}
//编写一个ArrBinaryTree,实现顺序存储二叉树遍历
class ArrBinaryTree {
private int[] arr; //存储数据结点的数组
public ArrBinaryTree(int[] arr) {
this.arr = arr;
}
//重载preOrder
public void preOrder() {
this.preOrder(0);
}
//编写一个方法,完成顺序存储二叉树的前序遍历
//index表示数组的下标,即n
public void preOrder(int index) {
//如果数组为空,或者 arr.length = 0
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
}
//输出当前元素
System.out.println(arr[index]);
//向左递归遍历
if ((index * 2 + 1) < arr.length) {
preOrder(index * 2 + 1);
}
//向右递归遍历
if ((index * 2 + 2) < arr.length) {
preOrder(index * 2 + 2);
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder(int index) {
//如果数组为空,或者 arr.length = 0
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
}
//向左递归遍历
if ((index * 2 + 1) < arr.length) {
infixOrder(index * 2 + 1);
}
//输出当前元素
System.out.println(arr[index]);
//向右递归遍历
if ((index * 2 + 2) < arr.length) {
infixOrder(index * 2 + 2);
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder(int index) {
//如果数组为空,或者 arr.length = 0
if (arr == null || arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("数组为空,不能按照二叉树的前序遍历");
}
//向左递归遍历
if ((index * 2 + 1) < arr.length) {
postOrder(index * 2 + 1);
}
//向右递归遍历
if ((index * 2 + 2) < arr.length) {
postOrder(index * 2 + 2);
}
//输出当前元素
System.out.println(arr[index]);
}
}
线索化二叉树
基本介绍
- n个结点的二叉链表中含有n+1(公式2n-(n-1)=n+1)个空指针域。利用二叉链表中的空指针域,存放指向该结点在某种遍历次序下的前驱和后继结点的指针(这种附加的指针称为“线索”)
- 这种加上了线索的二叉链表称为线索链表,相应的二叉树称为线索二叉树(Threaded BinaryTree)。根据线索性质的不同,线索二叉树可分为前序线索二叉树、中序线索二叉树和后序线索二叉树三种
- 一个结点的前一个结点,称为前驱结点
- 一个结点的后一个结点,称为后继节点
思路图解

遍历线索化二叉树思路
**说明:**对进行中序线索化的二叉树,进行遍历
分析:因为线索化后,各个结点指向有所变化,因此原来的遍历方式不能使用,否则会死递归,这时需要使用新的方式遍历线索化二叉树,各个结点可以通过线性方式遍历,无需使用递归方式,可以提高效率。遍历后的顺序应当和使用线索化的方式的遍历(前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历)保持一致。
代码实现
package com.datastructures.tree.threadedbinarytree;
public class ThreadedBinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试中序线索二叉树的功能
// HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "tom");
// HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(3, "jack");
// HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(6, "smith");
// HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(8, "mary");
// HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(10, "king");
// HeroNode node6 = new HeroNode(14, "dim");
// //二叉树后面会递归创建
// root.setLeft(node2);
// root.setRight(node3);
// node2.setLeft(node4);
// node2.setRight(node5);
// node3.setLeft(node6);
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "宋江");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "吴用");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "卢俊义");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲");
HeroNode node5 = new HeroNode(5, "关胜");
HeroNode node6 = new HeroNode(6, "秦明");
HeroNode node7 = new HeroNode(7, "花荣");
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node2.setLeft(node4);
node2.setRight(node5);
node3.setLeft(node6);
node3.setRight(node7);
//测试线索化
ThreadedBinaryTree threadedBinaryTree = new ThreadedBinaryTree();
threadedBinaryTree.setRoot(root);
//中序线索化
// threadedBinaryTree.threadedNodes();
//前序线索化
// threadedBinaryTree.threadedPreNodes(root);
//后序线索化
threadedBinaryTree.threadedPostNodes(root);
//测试node5结点
HeroNode leftNode = node5.getLeft();
System.out.println("node5的前驱结点=" + leftNode);
System.out.println("node5的后继结点=" + node5.getRight());
//线索化遍历
//中序线索化遍历
// System.out.println("使用中序线索化遍历的方式遍历中序线索化二叉树");
// threadedBinaryTree.threadedList();
//前序线索化遍历
// System.out.println("使用前序线索化遍历的方式遍历前序线索化二叉树");
// threadedBinaryTree.threadedPreList();
//后序线索化遍历
System.out.println("使用后序线索化遍历的方式遍历后序线索化二叉树");
threadedBinaryTree.threadedPostList();
}
}
//定义一个ThreadedBinaryTree 实现了线索化功能的二叉树
class ThreadedBinaryTree {
private HeroNode root; //根结点
//为了实现线索化,需要创建一个指向当前结点的前驱结点的指针
//在递归进行线索化时,pre总是保留前一个结点
private HeroNode pre = null;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//重载threadedNodes方法
public void threadedNodes() {
this.threadedNodes(root);
}
//遍历中序线索化的方法
public void threadedList() {
//定义一个变量,存储当前遍历的结点,从root开始
HeroNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
//循环的找到leftType == 1的结点
//随着遍历而变化,因为当leftType == 1时,说明该结点是按照线索化处理后的有效结点
while (node.getLeftType() == 0) {
node = node.getLeft();
}
//打印当前这个结点
System.out.println(node);
//如果当前结点的右指针指向的是后继结点,就一直输出
while (node.getRightType() == 1) {
node = node.getRight();
System.out.println(node);
}
//说明找到了一个node.getRightType() != 1的结点
//替换遍历的结点
node = node.getRight();
}
}
//编写对二叉树进行中序线索化的方法
/**
* @param node 就是当前需要线索化的结点
*/
public void threadedNodes(HeroNode node) {
//如果node == null,不能线索化
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//中序线索化
//1.线索化左子树
threadedNodes(node.getLeft());
//2.线索化当前结点
//处理当前结点的前驱结点
if (node.getLeft() == null) {
//让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.setLeft(pre);
//修改当前结点的左指针类型,指向前驱结点
node.setLeftType(1);
}
//处理后继结点
if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) {
//让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.setRight(node);
//修改前驱结点的右指针类型
pre.setRightType(1);
}
//每处理一个结点后,让当前结点是下一个结点的前驱结点
pre = node;
//3.线索化右子树
threadedNodes(node.getRight());
}
//遍历前序线索化的方法
public void threadedPreList() {
//定义一个变量,存储当前遍历的结点,从root开始
HeroNode node = root;
while (node != null) {
System.out.println(node);
//循环的找到leftType == 1的结点
//随着遍历而变化,因为当leftType == 1时,说明该结点是按照线索化处理后的有效结点
while (node.getLeftType() == 0) {
node = node.getLeft();
System.out.println(node);
}
if (node.getRightType() == 1) {
node = node.getRight();
} else if (node.getRight() == null) {
break;
}
}
}
//编写对二叉树进行前序线索化的方法
/**
* @param node 就是当前需要线索化的结点
*/
public void threadedPreNodes(HeroNode node) {
//如果node == null,不能线索化
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//前序线索化
//1.线索化当前结点
//处理当前结点的前驱结点
if (node.getLeft() == null) {
//让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.setLeft(pre);
//修改当前结点的左指针类型,指向前驱结点
node.setLeftType(1);
}
//处理后继结点
/**
* 如果前一处理节点pre的left结点为当前节点node,则不能把pre的right结点设为node
* 否则preThreadedNodes(node.getLeft())会出现死循环
*/
if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null && pre.getLeft() != node) {
//让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.setRight(node);
//修改前驱结点的右指针类型
pre.setRightType(1);
}
//每处理一个结点后,让当前结点是下一个结点的前驱结点
pre = node;
//2.线索化左子树 因为已经对node.getLeft进行了处理,所以要判断,不然会死循环
if (node.getLeftType() == 0) {
threadedPreNodes(node.getLeft());
}
//3.线索化右子树
/**
* 此处判断右子节点是否为后继节点,故不会陷入死循环
* 所以可不加条件pre.getLeft() != node(加上最好)
*/
if (node.getRightType() == 0) {
threadedPreNodes(node.getRight());
}
}
//遍历后序线索化的方法
public void threadedPostList() {
//存储当前遍历的结点,从 root 开始
HeroNode node = root;
// 先从左子树开始,找到第一个开始遍历的线索化左子节点
while (node != null && node.getLeftType() == 0) {
node = node.getLeft();
}
HeroNode pre = null;
while (node != null) {
if (node.getRightType() == 1) {
System.out.println(node);
pre = node;
node = node.getRight();
} else {
// 判断当前节点的右子节点是否与前一个处理的节点为同一节点
if (node.getRight() == pre) {
System.out.println(node);
if (node == root) {
break;
}
pre = node;
node = root;
} else {
node = node.getRight();
// 从根节点的右子树,开始寻找第一个开始遍历的左子节点
while (node != null && node.getLeftType() == 0) {
node = node.getLeft();
}
}
}
}
}
//编写对二叉树进行后序线索化的方法
/**
* @param node 就是当前需要线索化的结点
*/
public void threadedPostNodes(HeroNode node) {
//如果node == null,不能线索化
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//后序线索化
//1.线索化左子树
threadedPostNodes(node.getLeft());
//2.线索化右子树
threadedPostNodes(node.getRight());
//3.线索化当前结点
//处理当前结点的前驱结点
if (node.getLeft() == null) {
//让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.setLeft(pre);
//修改当前结点的左指针类型,指向前驱结点
node.setLeftType(1);
}
//处理后继结点
if (pre != null && pre.getRight() == null) {
//让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.setRight(node);
//修改前驱结点的右指针类型
pre.setRightType(1);
}
//每处理一个结点后,让当前结点是下一个结点的前驱结点
pre = node;
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.postOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//前序遍历查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.preOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
//中序遍历
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
//后序遍历
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
if (root != null) {
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
} else {
return null;
}
}
//删除结点
public void delNode(int no) {
//判断root是否为空 root是否为要被删除的结点
if (root != null) {
if (root.getNo() == no) {
root = null;
} else {
root.delNode(no);
}
} else {
System.out.println("空树,不能删除");
}
}
}
//创建HeroNode
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;
private HeroNode right;
//1.如果leftType == 0,表示指向左子树,如果 1 表示指向前驱结点
//2.rightType == 0,表示指向右子树,如果 1 表示指向后继结点
private int leftType;
private int rightType;
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public int getLeftType() {
return leftType;
}
public void setLeftType(int leftType) {
this.leftType = leftType;
}
public int getRightType() {
return rightType;
}
public void setRightType(int rightType) {
this.rightType = rightType;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this); //先输出父结点
//递归向左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
//递归向右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder() {
//递归向左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.infixOrder();
}
//输出当前结点,即父结点
System.out.println(this);
//递归向右子树中序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder() {
//递归向左子树后序遍历
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.postOrder();
}
//递归向右子树后序遍历
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.postOrder();
}
//输出当前结点
System.out.println(this);
}
//前序遍历查找
/**
* @param no 要查找的no
* @return 如果找到就返回该Node,没有就返回null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) {
System.out.println("进入前序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//左子树递归
HeroNode resNode = null; //结果结点,判断是否找到
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { //说明在左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode; //找没找到都返回
}
//中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) {
//左子树递归
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入中序遍历查找");
//比较当前结点
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
//后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no) {
HeroNode resNode = null;
//左子树递归
if (this.left != null) {
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) { //说明左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//右子树递归
if (this.right != null) {
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null) {
return resNode;
}
System.out.println("进入后序遍历查找");
//与当前结点比较
if (this.no == no) {
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
//递归删除结点
//如果删除的结点是叶子结点,则删除该结点
//如果删除的结点是非叶子结点,则删除该子树
public void delNode(int no) {
//判断左子结点是否是要被删除的结点
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no) {
this.left = null;
return;
}
//判断右子结点是否是要被删除的结点
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no) {
this.right = null;
return;
}
//左子树递归删除
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.delNode(no);
}
//右子树递归删除
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
}
树实际应用
堆排序
堆排序和其他排序整合在单独文档中:
算法-排序算法(冒泡、快排、直接插入、希尔、简单选择、堆排序、归并、基数)
赫夫曼树(霍夫曼树)
基本介绍
- 给定N个权值作为N个叶子结点,构造一颗二叉树,若该树的带权路径长度(wpl)达到最小,称这样的二叉树为最优二叉树,也称为哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree),还有的书翻译为霍夫曼树。
- 赫夫曼树是带权路径长度最短的树,权值较大的结点离根较近。
概念及举例
- 路径和路径长度:在一棵树中,从一个结点往下可以达到的孩子或孙子结点之间的通路,称为路径。通路中分支的数目称为路径长度。若规定根结点的层数为1,则从根结点到第L层结点的路径长度为L-1
- 结点的权及带权路径长度:若将树中结点赋给一个有着某种含义的数值,则这个数值称为该结点的权。结点的带权路径长度为:从根结点到该结点之间的路径长度与该结点的权的乘积

- 树的带权路径长度:树的带权路径长度规定为所有叶子结点的带权路径长度之和,记为WPL(weighted path length),权值越大的结点离根结点越近的二叉树才是最优二叉树
- WPL最小的就是赫夫曼树

创建思路图解







代码实现
package com.datastructures.huffmantree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class HuffmanTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {13, 7, 8, 3, 29, 6, 1};
Node root = createHuffmanTree(arr);
//测试
preOrder(root);
}
//编写一个前序遍历的方法
public static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("空树,不能遍历");
}
}
//创建赫夫曼树的方法
/**
* @param arr 需要创建成赫夫曼树的数组
* @return 创建好的赫夫曼树的root结点
*/
public static Node createHuffmanTree(int[] arr) {
//第一步 为了操作方便
//1.遍历arr数组
//2.将arr的每个元素构建成一个Node
//3.将Node放入到ArrayList中
List<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<Node>();
for (int value : arr) {
nodes.add(new Node(value));
}
//我们处理的过程是循环的过程
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
//排序 从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出根结点权值最小的两颗二叉树
//1.取出权值最小的结点(二叉树)---一个结点就是一个最简单的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//2.再取出第二小的结点
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//3.构建一颗新的二叉树
Node parent = new Node(leftNode.value + rightNode.value);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//4.从ArrayList中删除处理过的二叉树
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//5.将parent加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//返回赫夫曼树的头结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建结点类
//为了让Node对象支持排序Collections集合排序
//让Node实现Comparable接口
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int value; //结点的权值
Node left; //指向左子结点
Node right; //指向右子结点
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"value=" + value +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
//表示从小到大排序
return this.value - o.value;
}
}
赫夫曼编码
基本介绍
- 赫夫曼编码也翻译为哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding),又称霍夫曼编码,是一种编码方式,属于一种程序算法
- 赫夫曼编码是赫夫曼树在电讯通信中的经典应用之一
- 赫夫曼编码广泛的用于数据文件压缩。其压缩率通常在20%~90%之间
- 赫夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。Huffman于1952年提出的一种编码方法,称之为最佳编码
原理剖析






注意:赫夫曼树根据排序方法不同,也可能不太一样,这样对应的赫夫曼编码也不完全一样,但是WPL是一样的,都是最小的。

实际案例-数据压缩及解压

压缩思路分析


解压思路分析
- 将huffmanCodeBytes[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28]先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制字符串
- 将赫夫曼编码对应的二进制字符串,对应赫夫曼编码,转成原来的字符串
文件压缩分析
注意事项:
- 如果文件本身就是经过压缩处理的,那么使用赫夫曼编码再压缩效率不会有明显提升,比如:视频、PPT等文件
- 赫夫曼编码是按字节来处理的,因此可以处理所有的文件(二进制文件、文本文件)
- 如果一个文件中重复数据不多,压缩效果也不会很明显

文件解压分析

代码实现
package com.datastructures.huffmancode;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试压缩文件
// String srcFile = "d://src.bmp";
// String dstFile = "d://dst.zip";
// zipFile(srcFile, dstFile);
// System.out.println("压缩文件成功");
//测试解压文件
String zipFile = "d://dst.zip";
String dstFile = "d://src2.bmp";
unZipFile(zipFile, dstFile);
System.out.println("解压成功");
/*
String content = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
System.out.println(contentBytes.length); //40
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = huffmanZip(contentBytes);
System.out.println("压缩后的结果是:" + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodeBytes));
System.out.println("压缩后的结果长度是:" + huffmanCodeBytes.length);
//测试解压
byte[] sourceBytes = decode(huffmanCodes, huffmanCodeBytes);
System.out.println("原来的字符串=" + new String(sourceBytes));
*/
/*分步过程
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(contentBytes);
System.out.println("nodes=" + nodes);
//测试创建的二叉树
System.out.println("赫夫曼树");
Node huffmanTreeRoot = createHuffmanTree(nodes);
System.out.println("前序遍历");
huffmanTreeRoot.preOrder();
//测试赫夫曼编码
// getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot, "", stringBuilder);
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot);
System.out.println("生成的赫夫曼编码表" + huffmanCodes); //17
//测试压缩后
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = zip(contentBytes, huffmanCodes);
System.out.println("huffmanCodeBytes=" + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodeBytes));
*/
}
//编写一个方法,完成对压缩文件的解压
/**
* @param zipFile 准备解压的文件
* @param dstFile 将文件解压到哪个位置
*/
public static void unZipFile(String zipFile, String dstFile) {
//定义文件的输入流
InputStream is = null;
//定义一个对象输入流
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
//定义文件的输出流
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//创建文件输入流
is = new FileInputStream(zipFile);
//创建一个和is关联的对象输入流
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
//读取byte数组
byte[] huffmanBytes = (byte[]) ois.readObject();
//读取赫夫曼编码表
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = (Map<Byte, String>) ois.readObject();
//解码
byte[] bytes = decode(huffmanCodes, huffmanBytes);
//将bytes写入到目标文件
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
//写数据到文件中
os.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
os.close();
ois.close();
is.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.println(e2.getMessage());
}
}
}
//编写方法 将文件进行压缩
/**
* @param srcFile 原文件的完整路径
* @param dstFile 压缩后文件的存放路径
*/
public static void zipFile(String srcFile, String dstFile) {
//创建输出流
OutputStream os = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
//创建一个文件的输入流 准备读取文件
FileInputStream is = null;
try {
//创建一个文件的输入流 准备读取文件
is = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
//创建一个和原文件大小一样的byte[]
byte[] b = new byte[is.available()];
//读取文件
is.read(b);
//使用赫夫曼编码进行编码
//获取文件对应的赫夫曼编码表,直接对原文件进行压缩
byte[] huffmanBytes = huffmanZip(b);
//创建文件的输出流,准备存放压缩文件
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
//创建一个和文件输出流关联的ObjectOutputStream
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
//把 赫夫曼编码后的字节数组写入压缩文件
oos.writeObject(huffmanBytes);
//这里以对象流的方式写入赫夫曼编码,是为了以后恢复原文件时使用
//一定要把赫夫曼编码写入到压缩文件,不然以后恢复不了
oos.writeObject(huffmanCodes);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
is.close();
oos.close();
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
//完成数据的解压
//解压
//1.将huffmanCodeBytes[-88, -65, -56, -65, -56, -65, -55, 77, -57, 6, -24, -14, -117, -4, -60, -90, 28]
//先转成赫夫曼编码对应的二进制字符串
//2.将赫夫曼编码对应的二进制字符串,对应赫夫曼编码,转成原来的字符串
//编写一个方法,完成对压缩数据的解码
/**
* @param huffmanCodes 赫夫曼编码表map
* @param huffmanBytes 赫夫曼编码处理后得到的字节数组
* @return 返回原来字符串对应的数组
*/
private static byte[] decode(Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes, byte[] huffmanBytes) {
//1.先得到huffmanBytes对应的二进制的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//2.将byte数组转成二进制的字符串
for (int i = 0; i < huffmanBytes.length; i++) {
byte b = huffmanBytes[i];
//判断是不是最后一个字节
boolean flag = (i == huffmanBytes.length - 1);
stringBuilder.append(byteToBitString(!flag, b));
}
//把字符串按照指定的赫夫曼编码进行解码
//把赫夫曼编码表进行调换,因为要反向查询a->100 100->a
Map<String, Byte> map = new HashMap<String, Byte>();
for (Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry : huffmanCodes.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
//创建集合,存放byte
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>();
//i可以理解成一个索引,扫描stringBuilder
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); ) {
int count = 1; //小的计数器
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
while (flag) {
//1010100010111...
//每次递增的取出一个'1'或者'0'
//i不动,让count移动,直到匹配到一个字符
String key = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + count);
b = map.get(key);
if (b == null) { //说明没有匹配到
count++;
} else { //匹配到
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
//i直接增加count移动
i += count;
}
//当for循环结束后 list中就存放了所有的字符 "i like like like java do you like a java"
//把list中的数据放入到byte[]数组并返回
byte[] b = new byte[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = list.get(i);
}
return b;
}
/**
* 将一个byte转成一个二进制的字符串(补码)
*
* @param flag 标识是否需要补高位(是否满足8位,最后一个数不一定是8位,无需补高位),如果是true表示需要补高位,如果是false表示不需要
* @param b 传入的byte
* @return 是该b对应的二进制的字符串(是按照补码返回的)
*/
private static String byteToBitString(boolean flag, byte b) {
//使用变量保存 b
int temp = b; //将b转成int
//如果是正数 需要补高位
if (flag) {
temp |= 256; //按位与256
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); //返回的是temp对应的二进制的补码
if (flag) {
return str.substring(str.length() - 8);
} else {
return str;
}
}
//使用一个方法,将前面的方法封装起来,便于我们的调用
/**
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 返回的是经过赫夫曼编码处理后的字节数组(压缩后的数组)
*/
private static byte[] huffmanZip(byte[] bytes) {
//byte数据创建为结点
List<Node> nodes = getNodes(bytes);
//根据nodes创建赫夫曼树
Node huffmanTreeRoot = createHuffmanTree(nodes);
//生成对应的赫夫曼编码(根据赫夫曼树来创建对应的赫夫曼编码)
Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = getCodes(huffmanTreeRoot);
//根据生成的赫夫曼编码,压缩得到压缩后的赫夫曼编码字节数组
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = zip(bytes, huffmanCodes);
return huffmanCodeBytes;
}
//编写一个方法,将一个字符串对应的byte数组,通过生成的赫夫曼编码表,返回赫夫曼编码压缩过的byte数组
/**
* @param bytes 原始的字符串对应的byte[]
* @param huffmanCodes 生成的赫夫曼编码map
* @return 返回赫夫曼编码处理后的byte[]
* String content = "i like like like java do you like a java"; => byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
* 返回的是二进制字符串对应的byte[] huffmanCodeBytes,即8位对应一个byte
* 补码->反码->原码
*/
private static byte[] zip(byte[] bytes, Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes) {
//1.先利用赫夫曼编码表将传进来的byte[]转成赫夫曼编码后的字符串
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//遍历bytes数组
for (byte b : bytes) {
stringBuilder.append(huffmanCodes.get(b));
}
// System.out.println("测试stringBuilder=" + stringBuilder.toString());
//将赫夫曼编码后的字符串转成byte[]
//统计返回的huffmanCodeBytes长度
//一句话 int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8
int len;
if (stringBuilder.length() % 8 == 0) {
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8;
} else {
len = stringBuilder.length() / 8 + 1;
}
//创建存储压缩后的byte数组
byte[] huffmanCodeBytes = new byte[len];
int index = 0; //记录是第几个byte
//每8位对应一个byte 所以步长应该是8
for (int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); i += 8) {
String strByte;
if (i + 8 > stringBuilder.length()) { //不够8位
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i);
} else {
strByte = stringBuilder.substring(i, i + 8);
}
//将strByte转成一个byte,放入到huffmanCodeBytes
huffmanCodeBytes[index] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(strByte, 2);
index++;
}
return huffmanCodeBytes;
}
//生成赫夫曼树对应的赫夫曼编码
//思路:
//1.将赫夫曼编码表存放在Map<Byte,String>形式
// {32=01, 97=100, 100=11000, 117=11001, 101=1110, 118=11011, 105=101, 121=11010, 106=0010, 107=1111, 108=000, 111=0011}
static Map<Byte, String> huffmanCodes = new HashMap<Byte, String>();
//2.在生成赫夫曼编码表时,需要拼接路径,定义一个StringBuilder存储某个叶子结点的路径
static StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//为了调用方便,重载getCodes
private static Map<Byte, String> getCodes(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
//处理root的左子树
getCodes(root.left, "0", stringBuilder);
//处理root的右子树
getCodes(root.right, "1", stringBuilder);
return huffmanCodes;
}
/**
* 功能:将传入的node结点的所有叶子结点的赫夫曼编码得到,并放入到huffmanCodes集合
*
* @param node 传入的结点
* @param code 路径:左子结点是0,右子结点是1
* @param stringBuilder 用于拼接路径
*/
private static void getCodes(Node node, String code, StringBuilder stringBuilder) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder2 = new StringBuilder(stringBuilder);
//将code加入到stringBuilder2
stringBuilder2.append(code);
if (node != null) { //如果node==null 不处理
//判断当前node 是叶子结点还是非叶子节点
if (node.data == null) { //非叶子节点
//递归处理
//向左递归
getCodes(node.left, "0", stringBuilder2);
//向右递归
getCodes(node.right, "1", stringBuilder2);
} else { //说明是叶子结点
//表示找到了某个叶子结点的最后
huffmanCodes.put(node.data, stringBuilder2.toString());
}
}
}
//前序遍历
private static void preOrder(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
root.preOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("赫夫曼树为空");
}
}
/**
* @param bytes 接收一个字节数组
* @return 返回的就是List 形式 [Node[data=97,weight=5],Node[data=32,weight=9]......]
*/
private static List<Node> getNodes(byte[] bytes) {
//1.创建一个ArrayList
ArrayList<Node> nodes = new ArrayList<>();
//2.遍历bytes,统计每个byte出现的次数->map
HashMap<Byte, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
for (byte b : bytes) {
Integer count = counts.get(b);
if (count == null) { //Map还没有这个字符数据,第一次存放
counts.put(b, 1);
} else {
counts.put(b, count + 1);
}
}
//把每个键值对转成一个Node对象,并加入nodes集合
//遍历map
for (Map.Entry<Byte, Integer> entry : counts.entrySet()) {
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
//通过List,创建赫夫曼树
private static Node createHuffmanTree(List<Node> nodes) {
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
//排序,从小到大
Collections.sort(nodes);
//取出第一颗最小的二叉树
Node leftNode = nodes.get(0);
//取出第二棵最小的二叉树
Node rightNode = nodes.get(1);
//创建一颗新的二叉树,它的根结点没有data,只有权值
Node parent = new Node(null, leftNode.weight + rightNode.weight);
parent.left = leftNode;
parent.right = rightNode;
//将已经处理过的二叉树从nodes删除
nodes.remove(leftNode);
nodes.remove(rightNode);
//将新的二叉树加入到nodes
nodes.add(parent);
}
//nodes中最后的结点就是哈夫曼树的根结点
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
//创建Node,带数据和权值
class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
Byte data; //存放数据(字符你)本身,比如'a' => 97
int weight; //权值,表示字符出现的次数
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
//从小到大排序
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"data=" + data +
", weight=" + weight +
'}';
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
}





















 2565
2565











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








