类锁
如果有n个加锁的静态方法,在多线程情况下,其中一个线程访问了这个类的某个静态方法,则这个类其他加锁的静态方法不能被访问,要等被访问的那个方法彻底执行完,其他方法才可被调用,不加锁的方法不参与
public class Person {
public static synchronized void m1(String a) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(a+"开始m1");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(a+"结束m1");
}
public static synchronized void m2(String a) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(a+"开始m2");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(a+"结束m2");
}
}public class personTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
@SneakyThrows
public void run(){
Person.m1("线程1");
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread(){
@SneakyThrows
public void run(){
Person.m2("线程2");
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
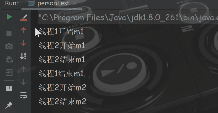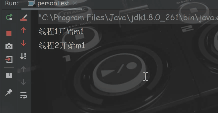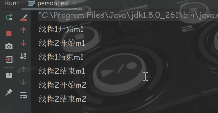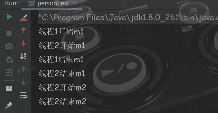
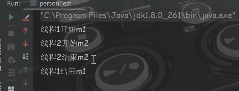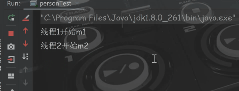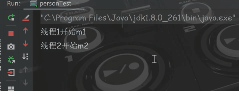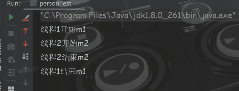
从运行结果可以看出 ,第二个线程要等一个线程将静态方法执行完,第二个线程调用的静态方法才开始执行
对象锁
一个对象有n个加锁的方法,在多线程情况下,其中一个线程访问了这个对象的某个加锁的非静态方法,这个对象的加锁的其他非静态方法不能被访问,要等访问的那个方法彻底执行完,其他方法才可执行调用,不加锁的不参与(不同对象无法互相影响)
public class Person {
public synchronized void m1(String a) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(a+"开始m1");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(a+"结束m1");
}
public synchronized void m2(String a) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(a+"开始m2");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(a+"结束m2");
}
}public class personTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
@SneakyThrows
public void run(){
p1.m1("线程1");
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread(){
@SneakyThrows
public void run(){
p2.m1("线程2");
p1.m2("线程2");
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
对象锁和类锁互不干扰
public class Person {
public synchronized void m1(String a) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(a+"开始m1");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(a+"结束m1");
}
public static synchronized void m2(String a) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(a+"开始m2");
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(a+"结束m2");
}
}public class personTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
Thread t1 = new Thread(){
@SneakyThrows
public void run(){
p1.m1("线程1");
}
};
Thread t2 = new Thread(){
@SneakyThrows
public void run(){
p1.m2("线程2");
}
};
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}






















 3826
3826











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








