实验7 输入输出流I/O
实验要求:
(1)掌握File类;
(2)掌握常用字节流类;
(3)掌握常用的字符流及缓冲流的使用。
实验内容:
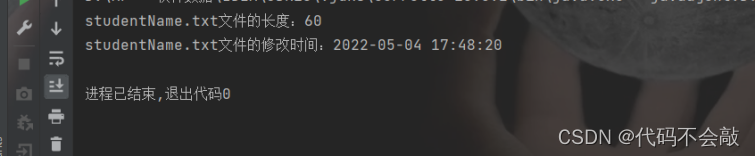
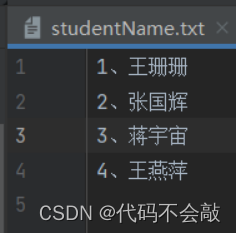
(1)按行读取文件studentInfo.txt的内容,获取学生姓名并写入到studentName.txt文件中,且给每一行按序加上行号;获取studentName.txt文件的长度及修改时间。
studentInfo.txt文件内容格式如下:
王珊珊,王珊珊,20132213806,2015-10-10 14:30:56
张国辉,张国辉,20132213944,2015-10-10 14:31:05
蒋宇宙,蒋宇宙,20132213906,2015-10-10 14:31:24
王燕萍,王燕萍,20132213847,2015-10-10 14:31:16
import java.io.*;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class StudentIO1 {
private static final String fr ="test7/src/studentInfo.txt";
private static final String fw ="test7/src/studentName.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fr));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(fw));
){
String line;
Integer cnt = 1;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
String[] arr = line.split(","); //根据逗号分割
bw.write( cnt.toString()+"、"+arr[0]);
bw.newLine();
cnt++;
// System.out.println(line);
}
File f = new File(fw);
System.out.println("studentName.txt文件的长度:"+f.length());
SimpleDateFormat time = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("studentName.txt文件的修改时间:"+time.format(f.lastModified()));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
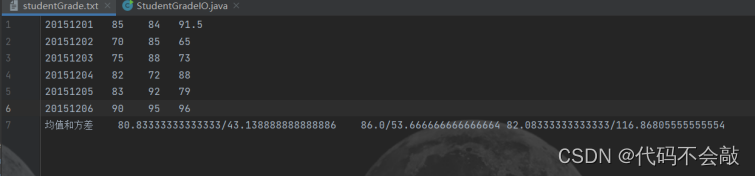
(2)学生成绩存储在文件中,每行一个学生成绩,形如:
20151201 85 84 91.5
20151202 70 85 65
…
请编程读入学生成绩,并计算各门课程的均值和方差,写入文件的最后一行,如:
均值和方差 71/10 81.2/11.3 76/15.3
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class StudentGradeIO {
private static final String f ="test7/src/studentGrade.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(BufferedReader br1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
BufferedReader br2 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(f, true))
) {
String line;
int n = 0; //总人数
String[] arr = null;
ArrayList<Double> sc = new ArrayList<>(100); //存放每一科成绩的平均分
ArrayList<Double> var = new ArrayList<>(100); //存放每一科成绩的方差
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++){ //初始化
sc.add(0.0);
var.add(0.0);
}
while ((line = br1.readLine()) != null)
{
arr = line.replaceAll(" +", " ").split(" "); //根据空格分割
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
sc.set(i, sc.get(i) + Double.parseDouble(arr[i]));
// System.out.print(sc.get(i)); System.out.print(" ");
}
n++;
}
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) //求每科的平均分
sc.set(i, sc.get(i) / n);
//求方差
while ((line = br2.readLine()) != null)
{
arr = line.replaceAll(" +", " ").split(" "); //根据空格分割
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
var.set(i, var.get(i) + (Double.parseDouble(arr[i]) - sc.get(i)) * (Double.parseDouble(arr[i]) - sc.get(i)));
}
}
bw.newLine();
bw.write("均值和方差");
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) //求每科的方差---并写入文件
{
var.set(i, var.get(i) / n);
bw.write("\t"+String.valueOf(sc.get(i))+"/"+String.valueOf(var.get(i)));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
























 379
379











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










