 图的表示
图的表示
图的遍历
深度优先:连通性路径,二分图的检测,环的检测,fllodfill
广度优先:无权图的最短路径
使用图论对问题建模
欧拉路径
哈密尔顿路径 状态压缩
桥
割点
有向图算法: DAG 环检测 拓扑排序 强连通分量
最小生成树: Kruskal Prim
最短路径: Dijkstra Floyed Bellman-Ford
网络流: 最大流-最小割 Ford-Fulkerson
图的表示
图的分类
无向图 Undirected Graph

有向图 Directed Graph

无权图
有权图

总的来说分四类

图的基本概念
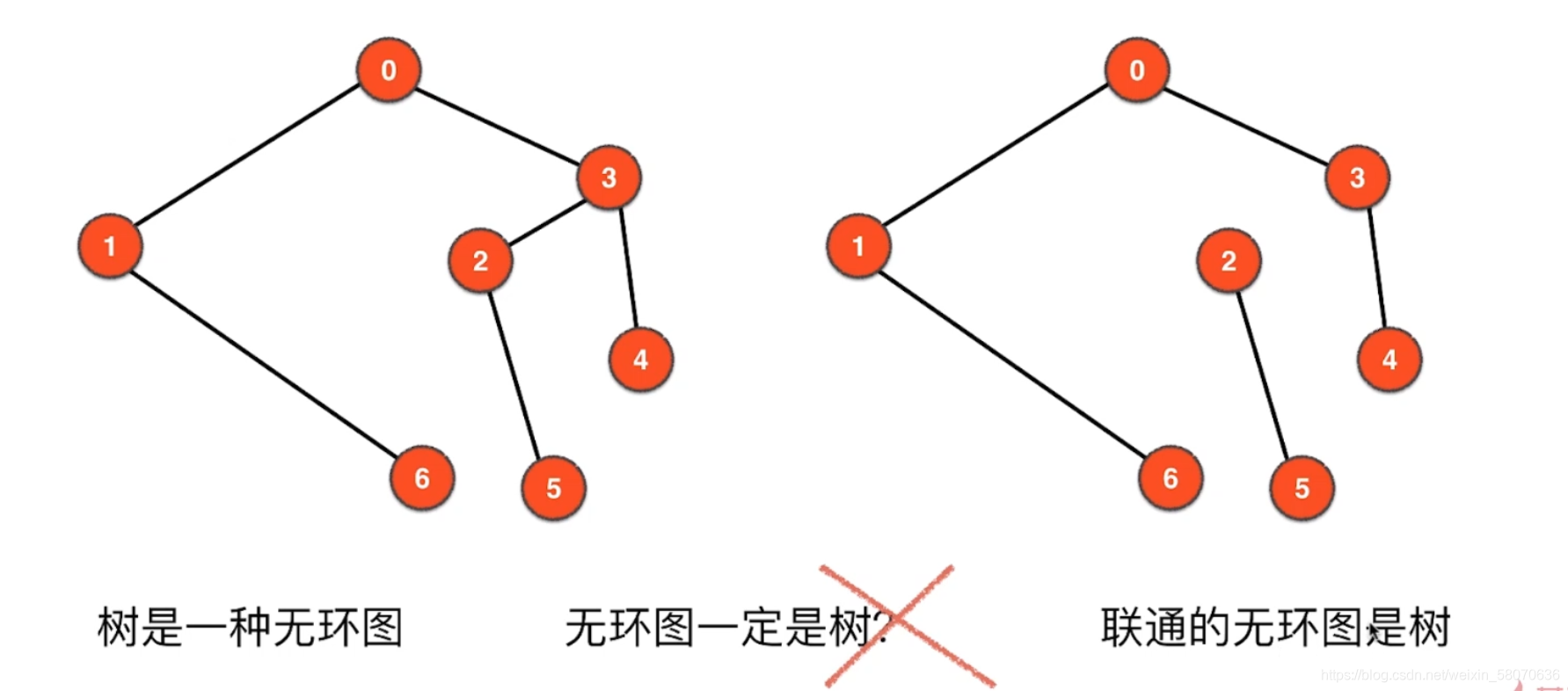
无向无权图






邻接矩阵
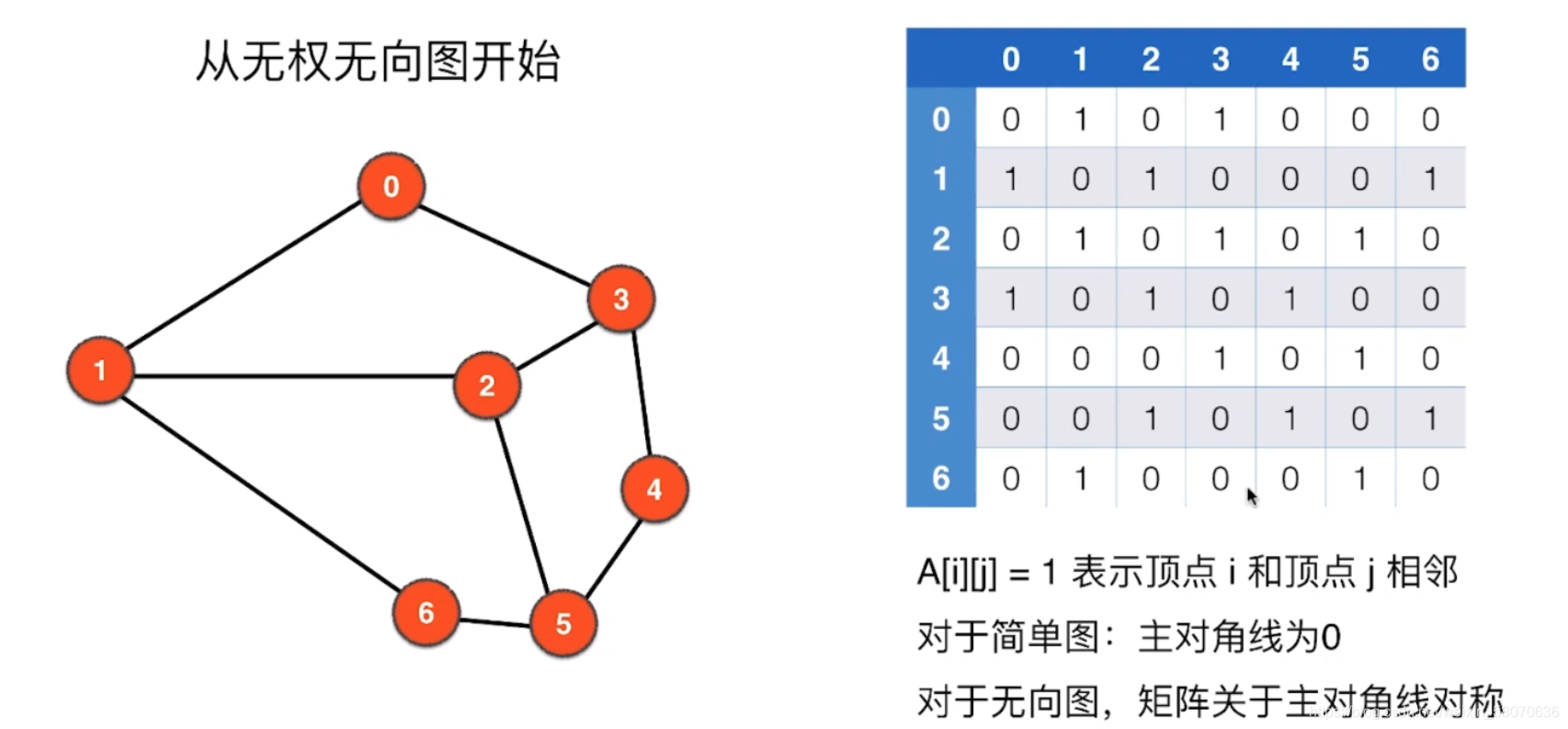

01表示在0-1之间存在一条边,以此类推
package com.graph.adjacencyMatrix;
import java.io.*;//为了使用File类和异常抛出
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;//为了读取File里面的内容
public class AdjMatrix {
private int V;//顶点
private int E;//边
private int[][] adj;//邻接矩阵
public AdjMatrix(String filename){
//用绝对路径可以避免一些相对路径时的bug,这里他说的把“。。。”这里替换成filename就是相对路径但是会报错
File file = new File("C:/Users/81909/Desktop/JavaSE/基础语法/g.txt");
//捕获一个异常
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){//scanner存了file里面的内容
V = scanner.nextInt();//根据Scanner声明时括号里的内容来决定从哪里读取一个整型数字,先读V
if(V<0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V需要是正数");
adj = new int[V][V];//创建一个V*V的二维数组
E = scanner.nextInt();//第二个读的是E
if(E<0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E需要是正数");
for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){//往矩阵里填1
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);//判断顶点合法性
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
if(a==b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("self loop is detected");//判断是否自环边
if(adj[a][b]==1) throw new IllegalArgumentException("paralle edges are detected");//判断是否平行边
adj[a][b] = 1;
adj[b][a] = 1;
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();//栈中信息打印一下
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v){
if(v<0||v>=V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex"+v+"is invalid");
}
public int V(){return V;};//之所以不直接把它俩定义为public,是为了不让用户修改变量
public int E(){return E;};
//判断两点直接是否有边
public boolean hasEdge(int v,int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v][w]==1;
}
//返回和顶点v相邻的边
public ArrayList<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
ArrayList<Integer>res=new ArrayList<>();//将和v相邻的所有顶点存到res里然后反悔哦
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if(adj[v][i]==1)
res.add(i);
}
return res;
}
//返回顶点相对的度
public int degree(int v){
return adj(v).size();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));//先说有多少顶点,有多少边
for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++){
for(int j = 0; j < V; j ++)
sb.append(String.format("%d ", adj[i][j]));//把行列式给填充进去
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AdjMatrix adjMatrix = new AdjMatrix("g.txt");
System.out.print(adjMatrix);
}
}
结果
V = 7, E = 9
0 1 0 1 0 0 0
1 0 1 0 0 0 1
0 1 0 1 0 1 0
1 0 1 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 1 0 1
0 1 0 0 0 1 0
Process finished with exit code 0
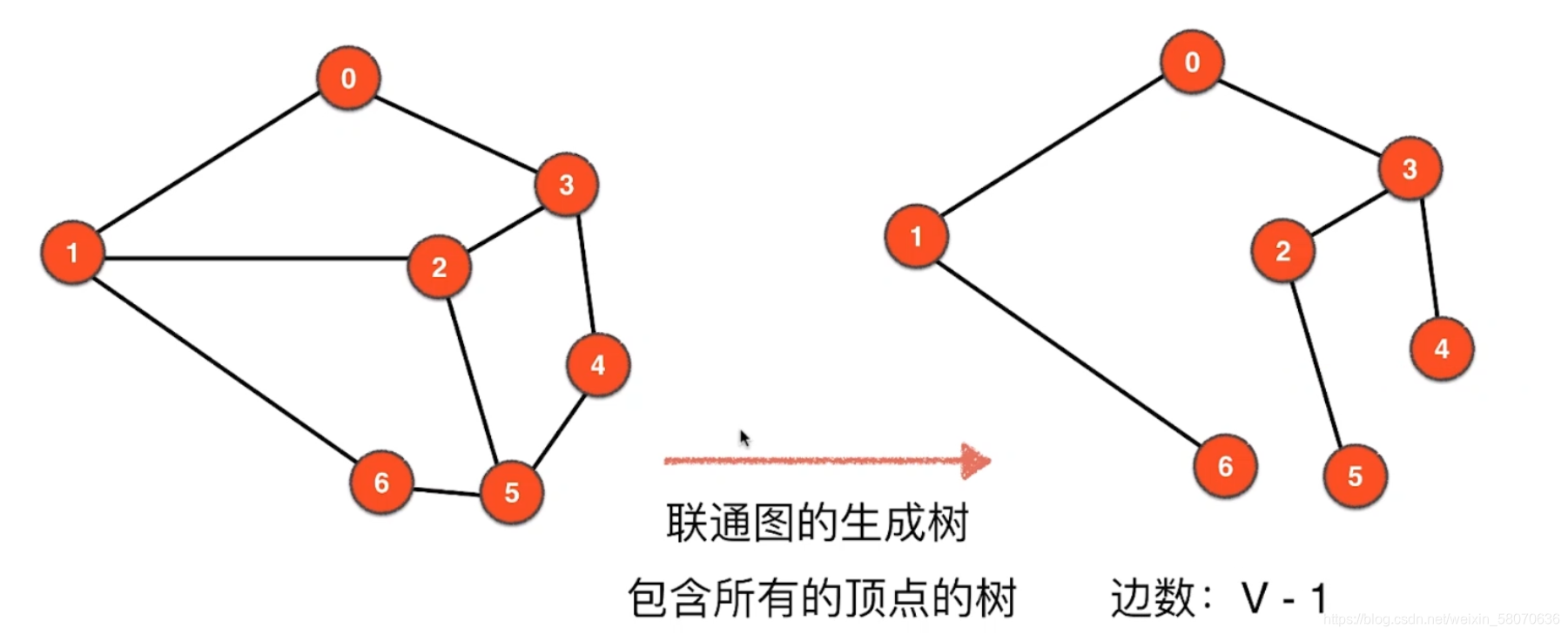
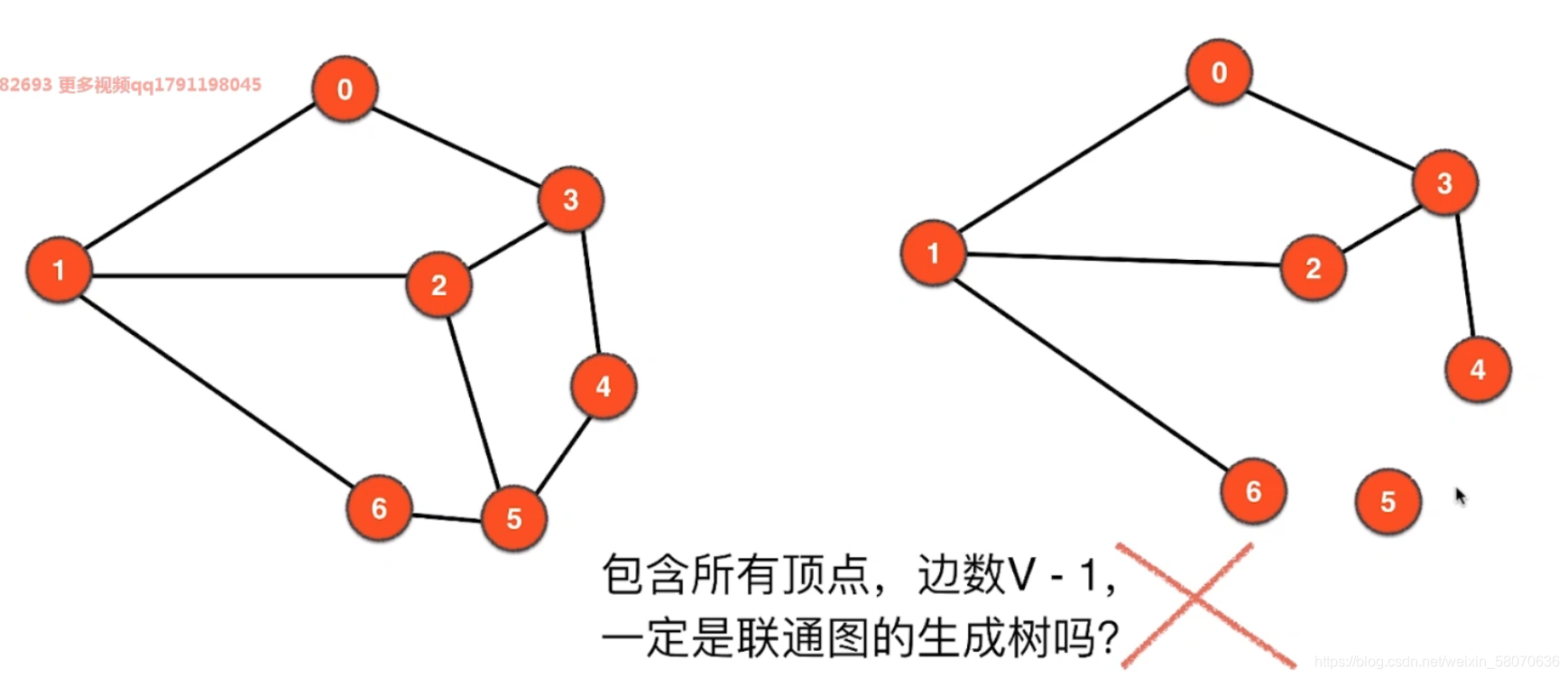
图的基本表示:邻接矩阵


这里树形状的空间为点的个数加边的个数就足够存下所有信息了,degree(v)也可以小于O(v)
稀疏图与稠密图



图的基本表示:邻接表

package com.graph.adjacencyMatrix;
import java.util.LinkedList;//邻接表是链表
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjList {
private int V;
private int E;
private LinkedList<Integer>[] adj;
public AdjList(String filename){
File file = new File("C:/Users/81909/Desktop/JavaSE/基础语法/g.txt");
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
if(V<0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V需要是正数");
adj = new LinkedList[V];//创建一个空间为V的链表
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i]=new LinkedList<Integer>();//为每一个元素申请空间,不写Integer这个泛型也可以
}
E = scanner.nextInt();
if(E<0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E需要是正数");
for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
if(a==b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("self loop is detected");
if(adj[a].contains(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("paralle edges are detected");
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v){
if(v<0||v>=V) throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex"+v+"is invalid");
}
public int V(){return V;};
public int E(){return E;};
//判断两点直接是否有边
public boolean hasEdge(int v,int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
//返回和顶点v相邻的边
public LinkedList<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
//返回顶点相对的度
public int degree(int v){
return adj(v).size();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));//先说有多少顶点,有多少边
for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){
sb.append(String.format("%d:",v));//每一轮v相邻的顶点都有谁
for(int w:adj[v])
sb.append(String.format("%d ", w));//把行列式给填充进去
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AdjList adjList = new AdjList("g.txt");
System.out.print(adjList);
}
}
结果
V = 7, E = 9
0:1 3
1:0 2 6
2:1 3 5
3:0 2 4
4:3 5
5:2 4 6
6:1 5
Process finished with exit code 0
邻接表的问题和改进

有的只有顶点没有边,用O(E)代替不可取



package com.graph.adjacencyMatrix;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjSet {
private int V;
private int E;
private TreeSet<Integer>[] adj;
public AdjSet(String pathStr){
File file = new File(pathStr);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
adj = new TreeSet[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++)
adj[i] = new TreeSet<Integer>();
E = scanner.nextInt();
if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");
if(adj[a].contains(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v){
if(v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + "is invalid");
}
public int V(){
return V;
}
public int E(){
return E;
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){
// public TreeSet<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
public int degree(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){
sb.append(String.format("%d : ", v));
for(int w : adj[v])
sb.append(String.format("%d ", w));
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AdjSet adjSet = new AdjSet("g.txt");
System.out.print(adjSet);
}
}
图的基本表示比较

遍历的意义

 很多算法的本质都是遍历,对图论问题来说,绝大部分问题都依托于遍历
很多算法的本质都是遍历,对图论问题来说,绝大部分问题都依托于遍历

图的深度优先遍历
树与图的优先遍历比较



实现图的深度优先遍历
package com.graph.GraphDFS;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GraphDFS {
private Graph G;
private boolean[] visited;
private ArrayList<Integer> order = new ArrayList<>();
public GraphDFS(Graph G){//构造函数
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];//图中每一个顶点对应一个visited记录值
dfs(0);
}
//递归遍历
private void dfs(int v){
visited[v] = true;
order.add(v);
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
dfs(w);
}
public Iterable<Integer> order(){
return order;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("C:/Users/81909/Desktop/JavaSE/基础语法/g.txt");
GraphDFS graphDFS = new GraphDFS(g);
System.out.println(graphDFS.order());
}
}
结果
[0, 1, 3, 2, 6, 5, 4]
package com.graph.GraphDFS;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GraphDFS {
private Graph G;
private boolean[] visited;
private ArrayList<Integer> order = new ArrayList<>();
public GraphDFS(Graph G){//构造函数
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];//图中每一个顶点对应一个visited记录值
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if(!visited[v])
dfs(v);
}
}
//递归遍历
private void dfs(int v){
visited[v] = true;
order.add(v);
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
dfs(w);
}
public Iterable<Integer> order(){
return order;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("C:/Users/81909/Desktop/JavaSE/基础语法/g.txt");
GraphDFS graphDFS = new GraphDFS(g);
System.out.println(graphDFS.order());
}
}
对象与结果
7 6
0 1
0 2
1 3
1 4
2 3
2 6
[0, 1, 3, 2, 6, 4, 5]二叉树的遍历

图的遍历

package com.graph.GraphDFS;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class GraphDFS {
private Graph G;
private boolean[] visited;
private ArrayList<Integer> pre = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<Integer> post = new ArrayList<>();
public GraphDFS(Graph G){//构造函数
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];//图中每一个顶点对应一个visited记录值
for (int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
if(!visited[v])
dfs(v);
}
}
//递归遍历
private void dfs(int v){
visited[v] = true;
pre.add(v);
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
dfs(w);
post.add(v);
}
public Iterable<Integer> pre(){
return pre;
}
public Iterable<Integer> post(){
return post;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("C:/Users/81909/Desktop/JavaSE/基础语法/g.txt");
GraphDFS graphDFS = new GraphDFS(g);
System.out.println(graphDFS.pre());
System.out.println(graphDFS.post());
}
}
结果
[0, 1, 3, 2, 6, 4, 5]
[6, 2, 3, 4, 1, 0, 5]深度优先遍历复杂度:O(V+E)
深度优先遍历的应用


无向图的联通分量Connected Component

无向图的联通分量个数
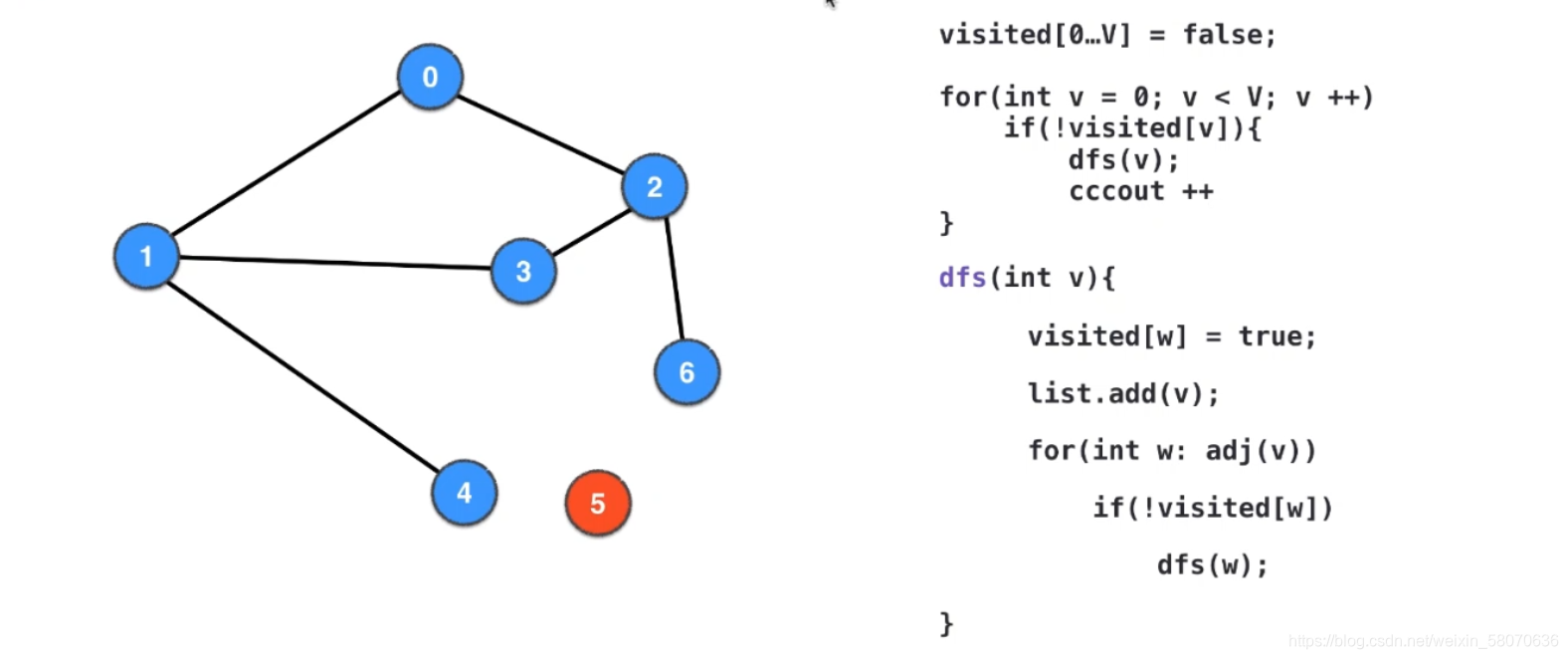
具体求解无向图的联通分量

更进一步

import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CC {
private Graph G;
private int[] visited;
private int cccount = 0;
public CC(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new int[G.V()];
for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i ++)
visited[i] = -1;
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(visited[v] == -1){
dfs(v, cccount);
cccount ++;
}
}
private void dfs(int v, int ccid){
visited[v] = ccid;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(visited[w] == -1)
dfs(w, ccid);
}
public int count(){
// for(int e: visited)
// System.out.print(e + " ");
// System.out.println();
return cccount;
}
//判断俩顶点是否在一个联通分量里面
public boolean isConnected(int v, int w){
G.validateVertex(v);
G.validateVertex(w);
return visited[v] == visited[w];
}
//返回每张图有多少联通分量,每个联通分量对应的顶点分别是谁
public ArrayList<Integer>[] components(){
ArrayList<Integer>[] res = new ArrayList[cccount];
for(int i = 0; i < cccount; i ++)
res[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
res[visited[v]].add(v);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
CC cc = new CC(g);
System.out.println(cc.count());
System.out.println(cc.isConnected(0, 6));
System.out.println(cc.isConnected(5, 6));
ArrayList<Integer>[] comp = cc.components();
for(int ccid = 0; ccid < comp.length; ccid ++){
System.out.print(ccid + " : ");
for(int w: comp[ccid])
System.out.print(w + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
路径问题

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class SingleSourcePath {
private Graph G;
private int s;
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] pre;
public SingleSourcePath(Graph G, int s){
G.validateVertex(s);
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
pre = new int[G.V()];
dfs(s, s);
}
private void dfs(int v, int parent){
visited[v] = true;
pre[v] = parent;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
dfs(w, v);
}
//判断是不是和源在一起
public boolean isConnectedTo(int t){
G.validateVertex(t);
return visited[t];
}
//输出路径
public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(!isConnectedTo(t)) return res;//不能到达路径就返回空路径
int cur = t;
while(cur != s){
res.add(cur);
cur = pre[cur];
}
res.add(s);
Collections.reverse(res);//颠倒过来,返回正序
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
SingleSourcePath sspath = new SingleSourcePath(g, 0);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + sspath.path(6));
System.out.println("0 -> 5 : " + sspath.path(5));
}
}
点对点路径问题

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Path {
private Graph G;
private int s, t;
private int[] pre;
private boolean[] visited;
public Path(Graph G, int s, int t){//源点与终止点
G.validateVertex(s);
G.validateVertex(t);
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
this.t = t;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
pre = new int[G.V()];
for(int i = 0; i < pre.length; i ++)
pre[i] = -1;
dfs(s, s);
for(boolean e: visited)
System.out.print(e + " ");
System.out.println();
}
private boolean dfs(int v, int parent){
visited[v] = true;
pre[v] = parent;
if(v == t) return true;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w])
if(dfs(w, v))
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean isConnected(){
return visited[t];
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(){
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(!isConnected()) return res;
int cur = t;
while(cur != s){
res.add(cur);
cur = pre[cur];
}
res.add(s);
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
Path path = new Path(g, 0, 6);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + path.path());
Path path2 = new Path(g, 0, 5);
System.out.println("0 -> 5 : " + path2.path());
Path path3 = new Path(g, 0, 1);
System.out.println("0 -> 1 : " + path3.path());
}
}
无向图中的环检测问题

public class CycleDetection {
private Graph G;
private boolean[] visited;
private boolean hasCycle = false;
public CycleDetection(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(!visited[v])
if(dfs(v, v)){
hasCycle = true;
break;
}
}
// 从顶点 v 开始,判断图中是否有环
private boolean dfs(int v, int parent){
visited[v] = true;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
if(dfs(w, v)) return true;
}
else if(w != parent)
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean hasCycle(){
return hasCycle;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
CycleDetection cycleDetection = new CycleDetection(g);
System.out.println(cycleDetection.hasCycle());
Graph g2 = new Graph("g2.txt");
CycleDetection cycleDetection2 = new CycleDetection(g2);
System.out.println(cycleDetection2.hasCycle());
}
}二分图检测


染色处理

import java.util.ArrayList;
public class BipartitionDetection {
private Graph G;
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] colors;
private boolean isBipartite = true;
public BipartitionDetection(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
colors = new int[G.V()];
for(int i = 0; i < G.V(); i ++)
colors[i] = -1;
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(!visited[v])
if(!dfs(v, 0)){
isBipartite = false;
break;
}
}
private boolean dfs(int v, int color){
visited[v] = true;
colors[v] = color;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
if(!dfs(w, 1 - color)) return false;
}
else if(colors[w] == colors[v])
return false;
return true;
}
public boolean isBipartite(){
return isBipartite;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
BipartitionDetection bipartitionDetection = new BipartitionDetection(g);
System.out.println(bipartitionDetection.isBipartite);
// true
Graph g2 = new Graph("g2.txt");
BipartitionDetection bipartitionDetection2 = new BipartitionDetection(g2);
System.out.println(bipartitionDetection2.isBipartite);
// false
Graph g3 = new Graph("g3.txt");
BipartitionDetection bipartitionDetection3 = new BipartitionDetection(g3);
System.out.println(bipartitionDetection3.isBipartite);
// true
}
}
小节


图的广度优先遍历
从树的广度优先遍历到图的广度优先遍历




广度优先:对一个节点,先把所有子节点都遍历了再操作

从边遍历,只能遍历同一联通分量
需要一层外循环调用各个联通分量
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class GraphBFS {
private Graph G;
private boolean[] visited;
private ArrayList<Integer> order = new ArrayList<>();//广度优先没有前序后序,这里order代表遍历顺序
public GraphBFS(Graph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];//为visited开空间,有多少顶点就开多少个
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)//如果从0遍历就只能遍历0所在联通分量,所以需要从所有节点开始
if(!visited[v])
bfs(v);
}
private void bfs(int s){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();//Queue是一个接口,所以要具体一个实践的类,这里用链表类
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;//入队了就visited=true
while(!queue.isEmpty()){//链表队列不为空时
int v = queue.remove();//队首取出元素v
order.add(v);//添加到order这个队列中
for(int w: G.adj(v))//查看v顶点所有相邻顶点w
if(!visited[w]){
queue.add(w);//如果w没被遍历过,入队
visited[w] = true;//设为已访问
}
}
}
public Iterable<Integer> order(){
return order;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
GraphBFS graphBFS = new GraphBFS(g);
System.out.println("BFS Order : " + graphBFS.order());
}
}
复杂度:O(V+E)
使用BFS求解单源路径问题


import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class SingleSourcePath {
private Graph G;
private int s;
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] pre;
//没有顺序问题,所以去除了BFS中的ArrayList<>order
public SingleSourcePath(Graph G, int s){//创建对象时考虑源是谁
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
pre = new int[G.V()];//路径问题,记录pre这个信息,给pre开空间
for(int i = 0; i < pre.length; i ++)//再赋初值
pre[i] = -1;
bfs(s);//单源问题,只需要从s出发就行
}
private void bfs(int s){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
pre[s] = s;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int v = queue.remove();
for(int w: G.adj(v))//求v的相邻节点w
if(!visited[w]){
queue.add(w);
visited[w] = true;
pre[w] = v;//w上一个节点是v
}
}
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int t){//判断是不是连接到了t节点
G.validateVertex(t);
return visited[t];
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){//求解路径
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();//定义res用来之后存路径
if(!isConnectedTo(t)) return res;//到达不了t就返回空
int cur = t;//从终值t出发,记为cur
while(cur != s){//只要还没回到起点s
res.add(cur);//往存路径的res里add一个cur
cur = pre[cur];//往前面一个点跑
}
res.add(s);//最后添加源点s
Collections.reverse(res);//反转一下
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
SingleSourcePath sspath = new SingleSourcePath(g, 0);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + sspath.path(6));
}
}

其他BFS应用

BFS的重要性

树的广度优先遍历(层序遍历

图

import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
// Unweighted Single Source Shortest Path
public class USSSPath {
private Graph G;
private int s;
private boolean[] visited;
private int[] pre;
private int[] dis;
public USSSPath(Graph G, int s){
this.G = G;
this.s = s;
visited = new boolean[G.V()];
pre = new int[G.V()];
dis = new int[G.V()];//给dis看空间
for(int i = 0; i < G.V(); i ++) {//给他俩所有值初始化
pre[i] = -1;
dis[i] = -1;
}
bfs(s);
for(int i = 0; i < G.V(); i ++)//遍历所有点,打印所有点的dis值,不联通时值为-1
System.out.print(dis[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
private void bfs(int s){
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(s);
visited[s] = true;
pre[s] = s;
dis[s] = 0;//源点s到s的距离初始化为0
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int v = queue.remove();
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w]){
queue.add(w);
visited[w] = true;
pre[w] = v;
dis[w] = dis[v] + 1;//距离为源点到v的距离+1
}
}
}
public boolean isConnectedTo(int t){
G.validateVertex(t);
return visited[t];
}
public int dis(int t){//源点到目标t的最短路径长度
G.validateVertex(t);
return dis[t];
}
public Iterable<Integer> path(int t){//源点到目标t的最短路径
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(!isConnectedTo(t)) return res;
int cur = t;
while(cur != s){
res.add(cur);
cur = pre[cur];
}
res.add(s);
Collections.reverse(res);
return res;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Graph g = new Graph("g.txt");
USSSPath ussspath = new USSSPath(g, 0);
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + ussspath.path(6));
System.out.println("0 -> 6 : " + ussspath.dis(6));
}
}

带权图和最小生成树
带权图

输入
7 12
0 1 2
0 3 7
0 5 2
1 2 1
1 3 4
1 4 3
1 5 5
2 4 4
2 5 4
3 4 1
3 6 5
4 6 7代码
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
/// 暂时只支持无向带权图
public class WeightedGraph implements Cloneable{
private int V;
private int E;
private TreeMap<Integer, Integer>[] adj;//TreeMap比TreeSet多存一个值,可以当权,<顶点,权值类型>
public WeightedGraph(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();//读取顶点数
if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
adj = new TreeMap[V];//定义一个数组
for(int i = 0; i < V; i ++)//为每个TreeMap开空间
adj[i] = new TreeMap<Integer, Integer>();
E = scanner.nextInt();
if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
for(int i = 0; i < E; i ++){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt();
validateVertex(b);
int weight = scanner.nextInt();//读取权值
if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected!");
if(adj[a].containsKey(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected!");
//adj的TreeMap里不包含以b元素为键的数据对,带权图处理平行边挺常见的,如果两个点直接有多条边,保留最短边
adj[a].put(b, weight);//从a-b之间有一条边,权值为weight
adj[b].put(a, weight);
}
}
catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void validateVertex(int v){
if(v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex " + v + "is invalid");
}
public int V(){
return V;
}
public int E(){
return E;
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].containsKey(w);
}
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
//不能直接返回TreeMap类的adj[v],TreeMap中封装了一个keySet方法,可以返回所有的键对应的集合
return adj[v].keySet();
}
public int getWeight(int v, int w){//获得v-w边所对应的权值
if(hasEdge(v, w)) return adj[v].get(w);//有边抛权,无边抛异常
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("No edge %d-%d", v, w));
}
public int degree(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size();//返回v所对顶点对应的度
}
//带权图基本不会有删边操作,把这个和clone移除基本不会影响
public void removeEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
if(adj[v].containsKey(w)) E --;
adj[v].remove(w);
adj[w].remove(v);
}
@Override
public Object clone(){
try{
WeightedGraph cloned = (WeightedGraph) super.clone();
cloned.adj = new TreeMap[V];
for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){
cloned.adj[v] = new TreeMap<Integer, Integer>();//对每一个adj[v]开空间
//遍历TreeMap,遍历它所有的键;Map接口下封装的Entry类,从adj[v]这个TreeMap中,
// entrySet里面存的就是一个个键值数据对,把键和对应值放入entry中
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry: adj[v].entrySet())
//adj[v]中put(键,值)
cloned.adj[v].put(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
return cloned;
}
catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for(int v = 0; v < V; v ++){
sb.append(String.format("%d : ", v));
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry: adj[v].entrySet())//从adj[v].entrySet()中取出键值数据对
sb.append(String.format("(%d: %d) ", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
System.out.print(g);
}
}运行结果

最小生成树

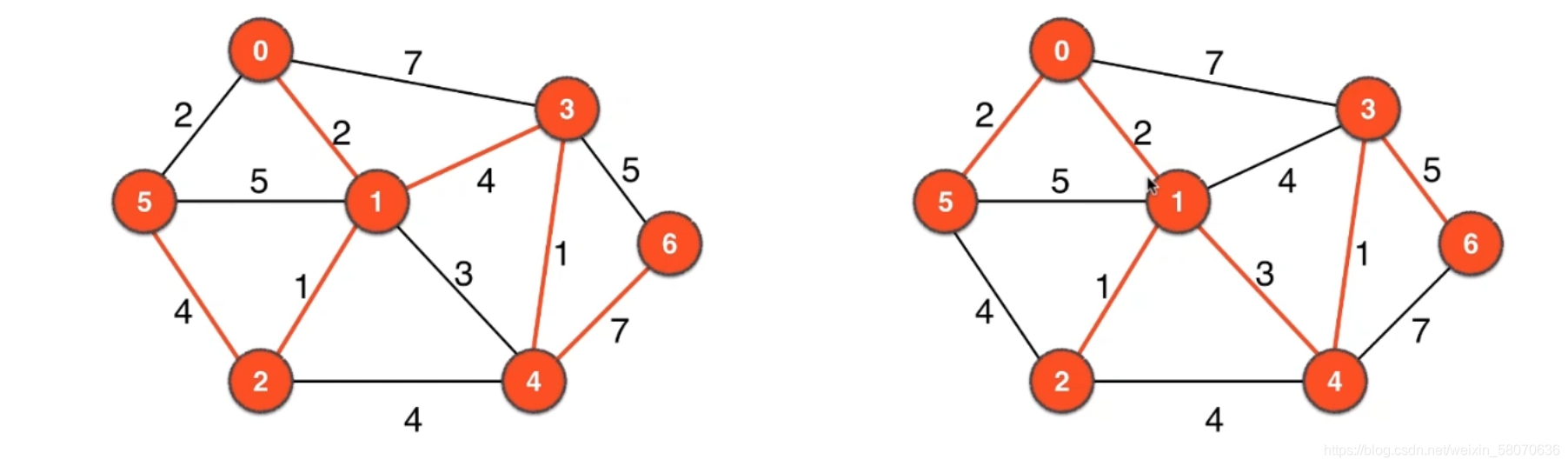

应用


从最小权值开始选边
用了4的这条边,就导致和其他小边构成了一个环

贪心算法难点在于,它为什么是对的
切分定理



横切边中的最短边,属于最小生成树

可以用用数学归纳法证明
Kruskal算法实现
public class WeightedEdge implements Comparable<WeightedEdge>{
private int v, w, weight;
public WeightedEdge(int v, int w, int weight){
this.v = v;
this.w = w;
this.weight = weight;
}
public int getV(){return v;}
public int getW(){return w;}
public int getWeight(){return weight;}
@Override
public int compareTo(WeightedEdge another){
return weight - another.weight;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return String.format("(%d-%d: %d)", v, w, weight);
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CC {//求带权图的联通分量个数
private WeightedGraph G;
private int[] visited;
private int cccount = 0;
public CC(WeightedGraph G){
this.G = G;
visited = new int[G.V()];
for(int i = 0; i < visited.length; i ++)
visited[i] = -1;
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
if(visited[v] == -1){
dfs(v, cccount);
cccount ++;
}
}
private void dfs(int v, int ccid){
visited[v] = ccid;
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(visited[w] == -1)
dfs(w, ccid);
}
public int count(){
return cccount;
}
public boolean isConnected(int v, int w){
G.validateVertex(v);
G.validateVertex(w);
return visited[v] == visited[w];
}
public ArrayList<Integer>[] components(){
ArrayList<Integer>[] res = new ArrayList[cccount];
for(int i = 0; i < cccount; i ++)
res[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)
res[visited[v]].add(v);
return res;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Kruskal {
private WeightedGraph G;
private ArrayList<WeightedEdge> mst;//最小生成树返回的是用ArrayList存储的一个个边
public Kruskal(WeightedGraph G){//用户传来一个带权图G
this.G = G;
mst = new ArrayList<>();//开空间
CC cc = new CC(G);//带权图中联通分量个数
if(cc.count() > 1) return;//有断开区域,最小生成树是null
//Kruskal
ArrayList<WeightedEdge> edges = new ArrayList<>();//存储所有的边
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)//把所有边放入edges中
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(v < w)//防止类似0-2,2-0重复遍历的问题
edges.add(new WeightedEdge(v, w, G.getWeight(v, w)));
Collections.sort(edges);//把边传进去排序,记得设定WeightedEdge为可比较的类
//判断是否行成环
UF uf = new UF(G.V());//有几个顶点UF中就有多少元素
for(WeightedEdge edge: edges){
int v = edge.getV();
int w = edge.getW();
if(!uf.isConnected(v, w)){//v和w不在一个集合时才连成边
mst.add(edge);
uf.unionElements(v, w);
}
}
}
public ArrayList<WeightedEdge> result(){
return mst;
}//返回最小生成树
public static void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
Kruskal kruskal = new Kruskal(g);
System.out.println(kruskal.result());
}
}
其中,Kruskal算法中快速判断是否生成环

public class UF{
private int[] parent;
public UF(int n){
parent = new int[n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
parent[i] = i;
}
public int find(int p){
if( p != parent[p] )
parent[p] = find( parent[p] );
return parent[p];
}
public boolean isConnected(int p , int q){
return find(p) == find(q);
}
public void unionElements(int p, int q){
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if( pRoot == qRoot )
return;
parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
}
}时间复杂度:O(ElogE)
Prim算法







import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Prim {
private WeightedGraph G;
private ArrayList<WeightedEdge> mst;
public Prim(WeightedGraph G){
this.G = G;
mst = new ArrayList<>();
CC cc = new CC(G);
if(cc.count() > 1) return;//判断联通图
//Prim
boolean[] visited = new boolean[G.V()];//切分在初始时,只有一个点切了
visited[0] = true;
for(int i = 1; i < G.V(); i ++){//共切V-1次
WeightedEdge minEdge = new WeightedEdge(-1, -1, Integer.MAX_VALUE);//声明一个最大权值,用来用后面的小权值覆盖它
for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v ++)//每次切的时候扫描所有的边
if(visited[v])//当一个边访问过了,再访问它所有的邻边
for(int w: G.adj(v))
if(!visited[w] && G.getWeight(v, w) < minEdge.getWeight())//如果没访问过,且权值小于minEdge
minEdge = new WeightedEdge(v, w, G.getWeight(v, w));//更新一下minEdge这条边
mst.add(minEdge);
visited[minEdge.getV()] = true;
visited[minEdge.getW()] = true;
}
}
public ArrayList<WeightedEdge> result(){
return mst;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
Prim prim = new Prim(g);
System.out.println(prim.result());
}
}
输入
7 12
0 1 2
0 3 7
0 5 2
1 2 1
1 3 4
1 4 3
1 5 5
2 4 4
2 5 4
3 4 1
3 6 5
4 6 7输出
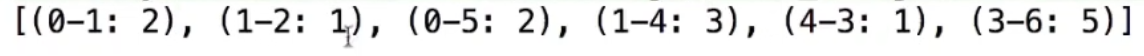
时间复杂度:O((V-1)*(V+E))=O(VE)

优先队列中所有的横切边不一定合法

这里的1-5,2-5,使用时先判断,非法的话直接扔掉就行
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class Prim {
private WeightedGraph G;
private ArrayList<WeightedEdge> mst;
public Prim(WeightedGraph G){
this.G = G;
mst = new ArrayList<>();
CC cc = new CC(G);
if(cc.count() > 1) return;//判断联通图
//Prim
boolean visited[] = new boolean[G.V()];//切分在初始时,只有一个点切了
visited[0] = true;
Queue pq = new PriorityQueue<WeightedEdge>();//声明优先队列,里面存储带权边
for(int w: G.adj(0))//添加初始状态下的横切边,即所有和0相邻的边
pq.add(new WeightedEdge(0, w, G.getWeight(0, w)));
while(!pq.isEmpty()){//如果用V-1个循环来弄的话还要判断是否合法
WeightedEdge minEdge = (WeightedEdge) pq.remove();//这个minEdge有可能是最短横切边
if(visited[minEdge.getV()] && visited[minEdge.getW()])//如果minEdge两个端点都访问过,则非法,跳过它
continue;
mst.add(minEdge);//合法边加入mst最小生成树中
//拓展切分,有可能产生新的最小横切边
int newv = visited[minEdge.getV()] ? minEdge.getW() : minEdge.getV();//判断哪个点没有被访问
visited[newv] = true;//没有访问的那个点设为已访问
for(int w: G.adj(newv))//取出newv的所有邻边
if(!visited[w])
//把有可能的最小横切边加入优先队列,在下一次的循环中从优先队列中取出最小的那个边
pq.add(new WeightedEdge(newv, w, G.getWeight(newv, w)));
}
}
public ArrayList<WeightedEdge> result(){
return mst;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
WeightedGraph g = new WeightedGraph("g.txt");
Prim prim = new Prim(g);
System.out.println(prim.result());
}
}
时间复杂度:O(Elog E)首选(因为其他语言几乎没有并查集





















 215
215











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








