目录
6.给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
自己实现一个链表(无头单向不循环链表)
项目架构
测试类,方法类,抛出异常

测试类:
package dataStructLinkedList;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createLink();
myLinkedList.display();
System.out.println(myLinkedList.contains(100));
System.out.println(myLinkedList.size());
System.out.println("====测试 头插法 尾插法");
myLinkedList.addFirst(10);
myLinkedList.addLast(20);
myLinkedList.addLast(30);
myLinkedList.display();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("====== 测试任意位置插入");
myLinkedList.addIndex(2,88);
myLinkedList.display();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("====== 测试 remove");
myLinkedList.remove(88);
myLinkedList.display();
System.out.println("====== 测试 removeAllKey");
myLinkedList.addIndex(3,88);
myLinkedList.addIndex(2,88);
myLinkedList.display();
System.out.println();
myLinkedList.removeAllKey(88);
myLinkedList.display();
}
}
方法类:
重点理解 删除链表中第一个key(倒数第三个方法) 和 删除链表中所有的key(倒数第二个方法)
package dataStructLinkedList;
public class MyLinkedList {
class Node {
public int val; // 存储的数据
public Node next; // 存储下一个节点的地址
public Node(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public Node head; // 当前链表的头结点
public void createLink(){
Node node1 = new Node(12);
Node node2 = new Node(45);
Node node3 = new Node(23);
Node node4 = new Node(90);
node1.next = node2;
node2.next = node3;
node3.next = node4;
head = node1;
}
// 遍历链表
public void display() {
Node tmp = head;
while (tmp != null){
System.out.print(tmp.val+" ");
tmp = tmp.next;
}
}
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
Node tmp = head;
while (tmp != null){
if(tmp.val == key){
return true;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return false;
}
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
int count = 0;
Node tmp = head;
while (tmp != null){
count++;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return count;
}
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
Node node0 = new Node(data);
node0.next = head;
head = node0;
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
Node nodeLast = new Node(data);
if(head == null){
head = nodeLast;
return;
}
Node tmp = head;
while (tmp.next != null){
tmp = tmp.next;
}
tmp.next = nodeLast;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data) throws ListIndexOutOfException{
// 也可能下标不合法,比如负数
checkIndex(index);
Node addIndex = new Node(data);
// 如果插入的下标为0 ,相当于头插法
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
// 如果插入的下标为最后 ,相当于尾插法
if(index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
// 下标在范围内的情况
Node tmp = findIndexDelOne(index);
addIndex.next = tmp.next;
tmp.next = addIndex;
}
// 找到index-1 位置的节点的地址
private Node findIndexDelOne(int index){
Node tmp = head;
int count = 0;
while (count != index-1){
count++;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return tmp;
}
// 判断index位置是否合法,超出范围就抛出异常
private void checkIndex(int index) throws ListIndexOutOfException{
if(index < 0 || index > size()){
throw new RuntimeException("index位置不合法");
}
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
// 如果key在头结点head
if(head.val == key){
head = head.next;
return;
}
// 如果key在head之后的节点上
Node cur = findPreKey(key);
if(cur == null){
return;
}
Node del = cur.next; // 要删除的节点
cur.next = del.next;
}
// 找到key的前一个节点
private Node findPreKey(int key){
if(head == null){
return null;
}
Node tmp = head;
while (tmp.next != null){ // 这个地方要着重 理解 !!!!!!!!!!!!!!
if(tmp.next.val == key){ // 这个地方要着重 理解 !!!!!!!!!!!!
return tmp;
}
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return null; // 没有要删除的节点
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
// 如果链表为空,退出
if(head == null){
return;
}
// 定义两个指针
Node pre = head;
Node cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val == key){
head = head.next;
}
}
// 清空 链表
public void clear() {
head = null;
}
}
抛出异常:
package dataStructLinkedList;
public class ListIndexOutOfException extends RuntimeException{
public ListIndexOutOfException() {
}
public ListIndexOutOfException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
LinkedList的使用
1.LinkedList的构造

2.LinkedList的常用方法

代码案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedLis
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list);
// 在起始位置插入0
list.add(0, 0); // add(index, elem): 在index位置插入元素elem
System.out.println(list);
list.remove(); // remove(): 删除第一个元素,内部调用的是removeFirst()
list.removeFirst(); // removeFirst(): 删除第一个元素
list.removeLast(); // removeLast(): 删除最后元素
list.remove(1); // remove(index): 删除index位置的元素
System.out.println(list);
// contains(elem): 检测elem元素是否存在,如果存在返回true,否则返回false
if(!list.contains(1)){
list.add(0, 1);
}
list.add(1);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(list.indexOf(1)); // indexOf(elem): 从前往后找到第一个elem的位置
System.out.println(list.lastIndexOf(1)); // lastIndexOf(elem): 从后往前找第一个1的位置
int elem = list.get(0); // get(index): 获取指定位置元素
list.set(0, 100); // set(index, elem): 将index位置的元素设置为elem
System.out.println(list);
// subList(from, to): 用list中[from, to)之间的元素构造一个新的LinkedList返回
List<Integer> copy = list.subList(0, 3);
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println(copy);
list.clear(); // 将list中元素清空
System.out.println(list.size());
}链表的遍历
for循环遍历
foreach遍历

for( : ) 冒号左边是遍历的元素的数据类型,冒号右边是要遍历的集合
通过迭代器遍历
通过反向迭代器遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.add(1); // add(elem): 表示尾插
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.add(6);
list.add(7);
System.out.println(list.size());
// foreach遍历
for (int e:list) {
System.out.print(e + " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 使用迭代器遍历---正向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next()+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
// 使用反向迭代器---反向遍历
ListIterator<Integer> rit = list.listIterator(list.size());
while (rit.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(rit.previous() +" ");
}
System.out.println();
}链表算法题
1.删除链表中某个值的所有元素
思路:
定义两个指针,pre,cur。 如果cur的值 是要删的值,则pre.next = cur.next,完成删除操作
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
ListNode pre = head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null){
if (cur.val == val){
pre.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else{
pre = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val == val){
head = head.next;
}
return head;
}
}2. 反转一个单链表
使用头插法。
运用 tou , wei , head三个指针
tou保持不变,head不断往前移一位,wei往后走并且左边一直是tou
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
// 反转链表,可以用头插法
ListNode tou = head;
ListNode wei = head.next;
while (wei != null){
tou.next = wei.next;
wei.next = head;
head =wei;
wei = tou.next;
}
return head;
}
}
3.找中间结点
思路:
使用快慢指针,fast比slow快两倍,fast到达尽头时,slow的位置恰好就在中间
这道题说明了至少有一个结点,因此不用考虑链表为null 的情况。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}4.输出链表中倒数第k个结点
链表中倒数第k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
使用快慢指针,倒数第K个,则fast先走K-1步(画图理解)
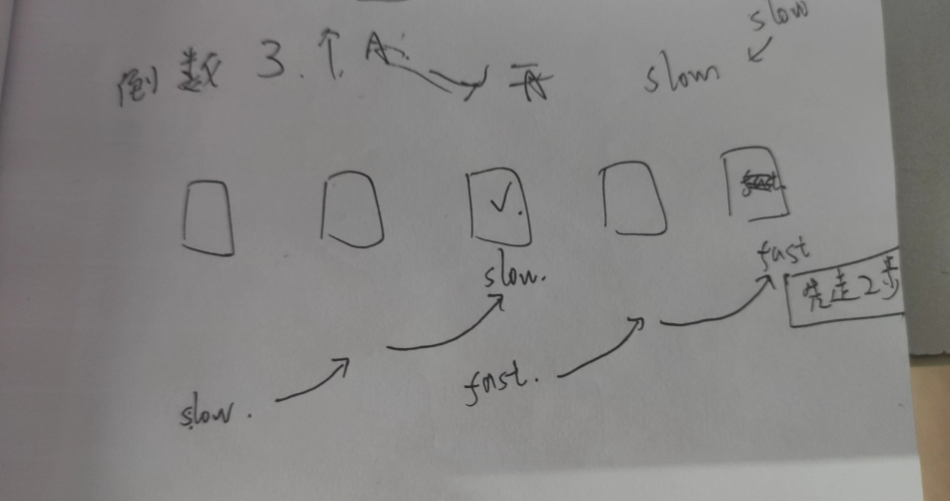
然后再让快慢指针一起一步步走,直到fast到尽头
此时slow指针的位置就是所求的倒数第K个的结点
难点:
1.要考虑到 链表为null 时的情况
2.考虑k的范围
当k的值大于链表的长度的时候,可以在fast先走的这一步判断,K大于链表长度时,fast走K-1步必定超出了链表的范围了,为null (画图理解)

import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head, int k) {
// 判断 k 是否符合范围
if (k <= 0 || head == null) {
return null;
}
// 快慢指针
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
// 倒数第K个
// 则fast先走k-1步,然后再快慢指针一起走,直到终点。
// 此时的slow指针 就是所求的倒数第K个结点
while (k - 1 != 0) {
fast = fast.next;
if (fast == null) {
return null;
}
k--;
}
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
5.合并两个有序链表
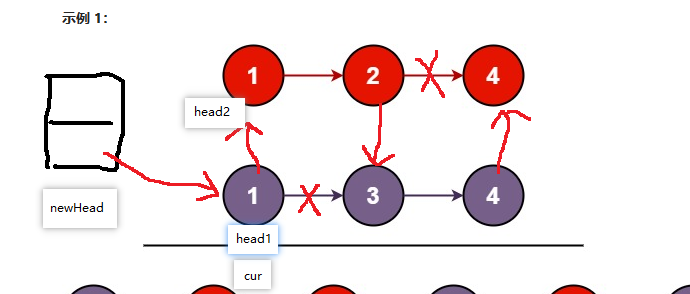
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode head1 = list1;
ListNode head2 = list2;
if(head1 == null){
return head2;
}
if(head2 == null){
return head1;
}
ListNode cur = new ListNode();
ListNode newHead = cur;
while (head1 != null && head2 != null){
if(head1.val <= head2.val){
cur.next= head1;
head1 = head1.next;
cur = cur.next;
}else {
cur.next = head2;
head2 = head2.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head1 == null){
cur.next = head2;
}
if(head2 == null){
cur.next = head1;
}
return newHead.next;
}
}6.给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
思路:
将链表分成两部分,一边的小于定值,另一边的大等于定值,再将两边.next连接到一起即可
定义三个指针 cur,one,two
cur 遍历链表,每走一步就判断当前值的大小
one 接收小于定值的结点
two 接收不小于定值的结点
难点:
1.要判断 twoEnd.next 需不需要置空,因为如果恰好是链表的最后一个就不用专门置空,如果不是就要记得置空。
2.要考虑到 oneHead 或 twoHead 为null 时的情况,因为有可能链表恰好所有元素都大于定值,或者恰好都小于定值。
// write code here
if(pHead == null){
return null;
}
ListNode oneHead = null;
ListNode oneEnd = null;
ListNode twoHead = null;
ListNode twoEnd = null;
ListNode cur = pHead;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.val < x){
if(oneHead == null){
oneHead = cur;
oneEnd = oneHead;
}else{
oneEnd.next = cur;
oneEnd = oneEnd.next;
}
}else {
if(twoHead == null){
twoHead = cur;
twoEnd = twoHead;
}else {
twoEnd.next = cur;
twoEnd = twoEnd.next;
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
if(oneHead == null){
return twoHead;
}
oneEnd.next = twoHead;
if(twoHead != null){
twoEnd.next = null;
}
return oneHead;7.链表的回文结构 (重点)
链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
思路:
回文结构要考虑两种情况,链表节点为 偶数 和 奇数 两种情况(先分析奇数情况)
采用 快慢指针,快指针走到最后时,慢指针正好处于链表正中间。
然后slow指针继续往后走的同时,将后一半的链表翻转。
最后slow从后往前走,head从前往后走,并同时比较大小是否相等,直到相遇。
都相等,即为回文结构。
难点1: 再找中间节点时,循环条件为什么是while (fast != null && fast.next != null) ?
如果fast.next 为null 的话,那么下面这行代码 >>>![]()
就等于 fast = null.next 了, null 怎么会有.next呢 ? 直接报错 。
难点2: 如果链表为偶数个怎么办 ?

这一步解决。
import java.util.*;
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class PalindromeList {
public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {
// write code here
if(A == null){
return false;
}
if(A.next == null){
return true;
}
ListNode fast = A;
ListNode slow = A;
// 第一步 找出中间节点
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 第二步 翻转
ListNode cur = slow.next;
while (cur != null){
ListNode curNext = cur.next;
cur.next = slow;
slow = cur;
cur = curNext;
}
// 第三步 比较大小是否相等
while (A != slow){
if(A.val != slow.val){
return false;
}
if(A.next == slow){
return true;
}
A = A.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
}8.输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
思路:
先遍历两个链表,找出它们的长度差
长的链表先走(长度差)步,然后长短链表再一起走,直到指针相等。
难点:
指针相等的情况,也有可能两者根本没相交,比如两者都为null 也是相等。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int lenA = 0;
int lenB = 0;
int len = 0;
// 假设A链表 更长
ListNode longList = headA;
ListNode shotList = headB;
while (longList != null){
longList = longList.next;
lenA++;
}
while (shotList != null){
shotList = shotList.next;
lenB++;
}
longList = headA;
shotList = headB;
// 假设A链表 更长
len = lenA - lenB;
// 不是再变为 B
if(len < 0){
len = lenB - lenA;
longList = headB;
shotList = headA;
}
while (len != 0){
longList = longList.next;
len--;
}
while (longList != shotList){
longList = longList.next;
shotList = shotList.next;
}
if(longList == null || shotList == null){
return null;
}
return longList;
}
}9. 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
思路:
快慢指针
快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,在环中两指针一定会相遇,其中慢指针在环中的路程不会超过一圈
问题:
1.为什么快指针走两步,慢指针走一步就可以?
2.快指针走三步 行不行 ?

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return false;
}
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}10. 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点(重点)
思路:
要找环的第一个结点,记结论: 一个指针从head开始走(x段),一个指针从相遇点开始走(y段),当两个指针相同时,所处的结点就是入环点。
如下图的推导过程,C是一整圈,不影响结论,带入C=1,即可 得 X = Y。

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow){
break;
}
}
if(fast == null || fast.next == null){
return null;
}
slow = head;
while (slow != fast){
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}





















 525
525











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








