搜索问题与技术
1
A A BCD
2
def PlayMazz(mazz, start, end):
'''
走迷宫,从start走到end
:param mazz: 图
:param start: 图的起点
:param end: 图的出口
'''
# queue为队列,当队列为空或者当前地点为终点时搜索结束
queue =list()
closed=set()
queue.append(start)
#********* Begin *********#
while(queue!=0):
closed.add(queue[0])
if queue[0]==end:
print(end,end='')
break
else:
print(queue[0],end='')
for i in mazz[queue[0]]:
if i in closed:
pass
else:
queue.append( i )
queue.remove(queue[0])
#********* End *********#
3
from a_star_utils import Node
def A_star(map, mapSize, start, end):
'''
A*算法,从start走到end
:param map:地图
:param mapSize:地图大小,例如[10,10]表示地图长10宽10
:param start:表示出发地,类型为列表,如[1,2]表示出发地为地图中的第1行第2列的方块
:param end:表示目的地,类型为列表,如[1,2]表示目的地为地图中的第1行第2列的方块
:return:从出发地到目的地的路径
'''
openedList = []
#********* Begin *********#
# 获得出发地方块的信息,并将信息保存为node变量
node = map[start[0]][start[1]]
#********* End *********#
node.distanceFromOri = 0
node.allDistance = 0
#********* Begin *********#
# 将当前方块存到开启列表中
openedList.append (node)
node.added = True
#********* End *********#
while len(openedList) != 0:
node = openedList.pop(0)
node.closed = True
if node.y == end[0] and node.x == end[1]:
finalListNeedReverse = []
while node != None:
finalListNeedReverse.append(node)
node = node.parent
finalListNeedReverse.reverse()
return finalListNeedReverse
neighboursList = []
y = node.y
x = node.x
parentDistanceFromOri = node.distanceFromOri
for needNodey in (y + 1, y, y - 1):
if needNodey < 0 or needNodey >= mapSize[0]:
continue
for needNodex in (x + 1, x, x - 1):
if needNodex < 0 or needNodex >= mapSize[1]:
continue
needNode = map[needNodey][needNodex]
if needNode.unable == True or needNode.closed == True or needNode.added == True:
continue
yOffset = needNodey - y
xOffset = needNodex - x
allOffset = yOffset + xOffset
if allOffset == 1 or allOffset == -1:
distanceFromOri = parentDistanceFromOri + 1
else:
distanceFromOri = parentDistanceFromOri + 1.4
if needNode in neighboursList:
# 若新的G值比老的G值低,则更新成老的G值
if distanceFromOri < needNode.distanceFromOri:
needNode.distanceFromOri = distanceFromOri
else:
needNode.distanceFromOri = distanceFromOri
neighboursList.append(needNode)
for needNode in neighboursList:
needNode.parent = node
# 更新F值
needNode.allDistance = needNode.distanceFromOri + needNode.distanceFromDes
needNode.added = True
openedList.append(needNode)
openedList.sort(key=lambda x: x.allDistance)
return None
4
def make(mark):
'''
标记皇后的位置,例如mark[0] = 2, 表示第1行皇后放在第3列的位置
:param mark: 皇后的位置信息
:return: 拼接好的结果
'''
#初始化数组
r = [['X' for _ in range(len(mark))] for _ in range(len(mark))]
#将每一行中皇后的位置用‘Q’代替
for i in mark:
r[i][mark[i]] = 'Q'
#枚举,将原来散的元素连接成字符串
for k, v in enumerate(r):
r[k] = ''.join(v)
return r
def FourQueens(mark, cur, ret):
'''
深度优先搜索的方式求解四皇后问题
:param mark:表示皇后的位置信息,例如[0,1,3,2]表示棋盘的第1行第1列,第2行第2列,第3行第4列,第4行第3列放置了皇后。例如[1, None, None, None]表示第1行第2列放置了皇后,其他行没有放置皇后。初始值为[None,None,None,None]
:param cur:表示当前准备在第几行放置皇后,例如`cur=1`时,表示准备在第`2`行放置皇后。初始值为0
:param ret:表示存放皇后摆放结果的列表,类型为列表。初始值为[]
:return:无
'''
if cur == len(mark):
#********* Begin *********#
# 如果当前行是最后一行,记录一个解,并返回结束此次搜索
ret.append(make(mark))
return
#********* End *********#
#试探处理,将当前行的皇后应该在的位置遍历每一列,如果满足条件,递归调用处理下一行
for i in range(len(mark)):
mark[cur], down = i, True
for j in range(cur):
# 当想在当前位置放皇后会与其他皇后冲突时不放置皇后
if mark[j] == i or abs(i-mark[j]) == cur - j:
down = False
break
if down:
# 准备在下一行找能放置换后的位置
FourQueens(mark, cur+1, ret)
确定性推理
1
对 D ABC ABCD C ABCD
2
C F
3
对 对 对
4
S = [] # 以列表形式存储子句集S
""" 读取子句集文件中子句,并存放在S列表中 - 每个子句也是以列表形式存储 - 以析取式分割 - 例如:~p ∨ ~q ∨ r 存储形式为 ['~p', '~q', 'r'] """
def readClauseSet(filePath):
global S
for line in open(filePath, mode='r', encoding='utf-8'):
line = line.replace(' ', '').strip()
line = line.split('∨')
S.append(line)
""" - 为正文字,则返回其负文字 - 为负文字,则返回其正文字 """
def opposite(clause):
if '~' in clause:
return clause.replace('~', '')
else:
return '~' + clause
""" 归结 """
def resolution():
global S
end = False
while True:
if end: break
father = S.pop()
for i in father[:]:
if end: break
for mother in S[:]:
if end: break
j = list(filter(lambda x: x == opposite(i), mother))
if j == []:
continue
else:
print('\n亲本子句:' + ' ∨ '.join(father) + ' 和 ' + ' ∨ '.join(mother))
father.remove(i)
mother.remove(j[0])
#********** Begin **********#
if father == [] and mother == []:
print('归结式:NIL')
end = True
elif father == []:
print('归结式:' + ' ∨ '.join(mother))
elif mother == []:
print('归结式:' + ' ∨ '.join(father))
else:
print('归结式:' + ' ∨ '.join(father) + ' ∨ ' + ' ∨ '.join(mother))
#********** End **********#
产生式系统实验
# 动物识别系统
# 自定义函数,判断有无重复元素
def judge_repeat(value, list=[]):
for i in range(0, len(list)):
if (list[i] == value):
return 1
else:
if (i != len(list) - 1):
continue
else:
return 0
# 自定义函数,对已经整理好的综合数据库real_list进行最终的结果判断
def judge_last(list):
for i in list:
if i == '23': # 食肉类
for i in list:
if i == '12': # 黄褐色
for i in list:
if i == '21': # 哺乳类
for i in list:
if i == '13': # 有斑点
print("黄褐色,有斑点,哺乳类,食肉类->金钱豹\n")
print("所识别的动物为金钱豹")
return 0
elif i == '14': # 有黑色条纹
print("黄褐色,有黑色条纹,哺乳类,食肉类->虎\n")
print("所识别的动物为虎")
return 0
elif (i == '14'): # 有黑色条纹
for i in list:
if i == '24': # 蹄类
print("有黑色条纹,蹄类->斑马\n")
print("所识别的动物为斑马")
return 0
elif i == '24': # 蹄类
for i in list:
if i == '13': # 有斑点
for i in list:
if i == '15': # 长脖
for i in list:
if i == '16': # 长腿
print("有斑点,有黑色条纹,长脖,蹄类->长颈鹿\n")
print("所识别的动物为长颈鹿")
return 0
########## Begin ##########
# 根据右侧规则库完成信天翁的判断
elif i == '20': # 善飞
for i in list:
if i == '22': # 鸟类
print("善飞,鸟类->信天翁\n")
print("所识别的动物为信天翁")
return 0
########## End ##########
elif i == '22': # 鸟类
for i in list:
if i == '4': # 不会飞
for i in list:
if i == '15': # 长脖
for i in list:
if i == '16': # 长腿
print("不会飞,长脖,长腿,鸟类->鸵鸟\n")
print("所识别的动物为鸵鸟")
return 0
elif (i == '4'): # 不会飞
for i in list:
if (i == '22'): # 鸟类
for i in list:
if (i == '18'): # 会游泳
for i in list:
if (i == '19'): # 黑白二色
print("不会飞,会游泳,黑白二色,鸟类->企鹅\n")
print("所识别的动物企鹅")
return 0
else:
if (list.index(i) != len(list) - 1):
continue
else:
print("\n根据所给条件无法判断为何种动物")
dict_before = {'1': '有毛发', '2': '产奶', '3': '有羽毛', '4': '不会飞', '5': '会下蛋', '6': '吃肉', '7': '有犬齿',
'8': '有爪', '9': '眼盯前方', '10': '有蹄', '11': '反刍', '12': '黄褐色', '13': '有斑点', '14': '有黑色条纹',
'15': '长脖', '16': '长腿', '17': '不会飞', '18': '会游泳', '19': '黑白二色', '20': '善飞', '21': '哺乳类',
'22': '鸟类', '23': '食肉类', '24': '蹄类', '25': '金钱豹', '26': '虎', '27': '长颈鹿', '28': '斑马',
'29': '鸵鸟', '30': '企鹅', '31': '信天翁'}
print("""输入对应条件前面的数字:
*******************************************************
*1:有毛发 2:产奶 3:有羽毛 4:不会飞 5:会下蛋 *
*6:吃肉 7:有犬齿 8:有爪 9:眼盯前方 10:有蹄 *
*11:反刍 12:黄褐色 13:有斑点 14:有黑色条纹 15:长脖 *
*16:长腿 17:不会飞 18:会游泳 19:黑白二色 20:善飞 *
*21:哺乳类 22:鸟类 23:食肉类 24:蹄类 *
*******************************************************
*******************当输入数字0时!程序结束***************
""")
# 综合数据库
list_real = []
while (1):
# 循环输入前提条件所对应的字典中的键
num_real = input("请输入:")
print(num_real)
list_real.append(num_real)
if (num_real == '0'):
break
print("\n")
print("前提条件为:")
# 输出前提条件
for i in range(0, len(list_real) - 1):
print(dict_before[list_real[i]], end=" ")
print("\n")
print("推理过程如下:")
# 遍历综合数据库list_real中的前提条件
for i in list_real:
if i == '1':
if judge_repeat('21', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('21')
print("有毛发->哺乳类")
elif i == '2':
if judge_repeat('21', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('21')
print("产奶->哺乳类")
elif i == '3':
if judge_repeat('22', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('22')
print("有羽毛->鸟类")
else:
if list_real.index(i) != len(list_real) - 1:
continue
else:
break
for i in list_real:
if i == '4':
for i in list_real:
if i == '5':
if judge_repeat('22', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('22')
print("不会飞,会下蛋->鸟类")
elif i == '6':
for i in list_real:
if i == '21':
if judge_repeat('21', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('21')
print("食肉->哺乳类")
########## Begin ##########
# 根据右侧规则库完成食肉类的判断
elif i == '7':
for i in list_real:
if i == '8':
for i in list_real:
if i == '9':
if judge_repeat('23', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('23')
print("有犬齿,有爪,眼盯前方->食肉类")
# 根据右侧规则库完成蹄类的判断
elif i == '10':
for i in list_real:
if i == '21':
if judge_repeat('24', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('24')
print("有蹄,哺乳类->蹄类")
########## End ##########
elif i == '11':
for i in list_real:
if i == '21':
if judge_repeat('24', list_real) == 0:
list_real.append('24')
print("反刍,哺乳类->哺乳类")
else:
if i != len(list_real) - 1:
continue
else:
break
judge_last(list_real)
不确定性推理


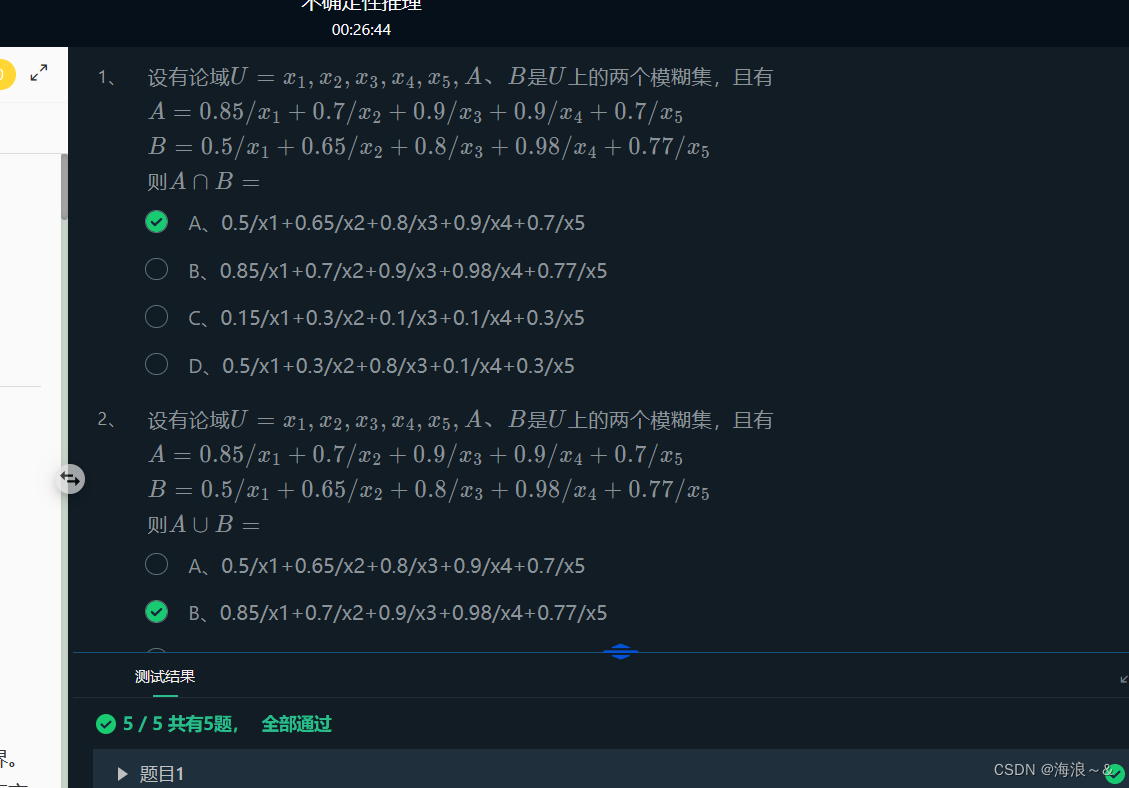


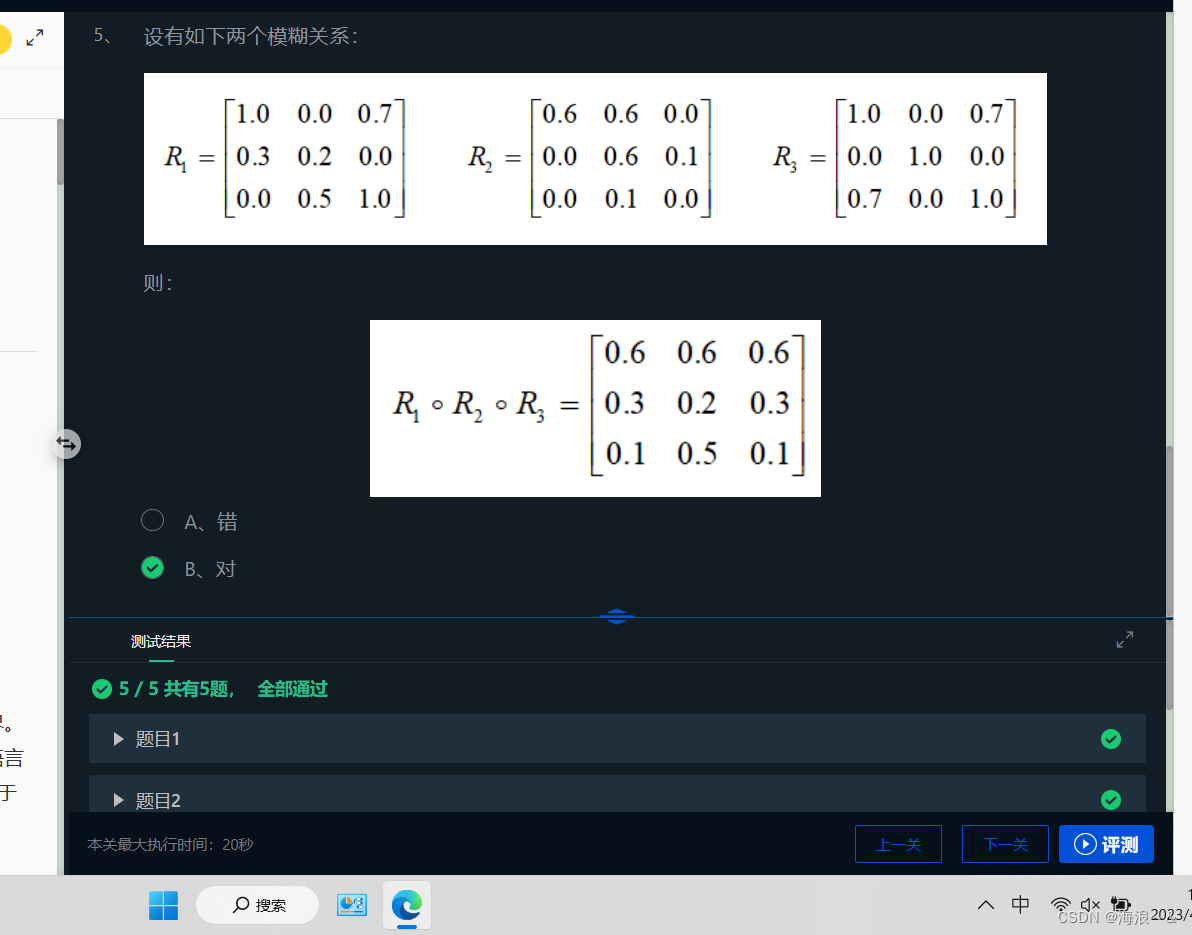
OIL=100.0#定义油渍论域
Stain=100.0#定义污渍论域
def ruleMD(stain):
if stain < 0 or stain > 100:
return 0.0
else: # 当传入的参数在0-100之间时,该处有两种情况
# 计算MD的结果,并且和同参数下的SD结果相比较,得出一个结果
if stain >= 0 and stain <= 50:
return stain / 50.0
else:
# 同上的操作,得出结果和同参数下的LD相比较
return (100 - stain) / 50.0
def ruleSD(stain):
# SD部分的rule
# 当输入的参数0 <= x <= 50, 执行该方法
result = (50 - stain) / 50.0
returnMDresult = ruleMD(stain)
# 传参数到MD中,计算,并比较
# 1、相同,则返回结果为SD,2、SD的结果大,则返回SD,3、MD的结果大,则返回MD的返回值
if result < returnMDresult:
return 2.0
else:
return 1.0
def ruleLD(stain):
# LD部分的rule
# 当输入的参数在50 - 100之间时,执行
result = (stain - 50) / 50
returnMDresult = ruleMD(stain)
# 同时将参数传入给MD,同时比较MD方法传回来的参数和该方法求出的值相比较,求出最后的最适合的预测值
# ********** Begin **********#
if result < returnMDresult:
return 2.0
else:
return 3.0
# ********** End **********#
def ruleMG(oil):
# 当传入的参数在0 - 100之间时,该处有两种情况
if oil < 0 or oil > 100:
return 0 # 当在论域之外时,直接返回无结果
else:
if oil >= 0 and oil <= 50:
return oil / 50.0 # 计算MD的结果,并且和同参数下的SD结果相比较,得出一个结果
else:
return (100 - oil) / 50 # 同上的操作,得出结果和同参数下的LD相比较
def ruleSG(oil):
if oil < 0 or oil > 50:
return 0.0
else:
# SG部分的rule
# 当输入的参数0<=x<=50,执行该方法
result = (50 - oil) / 50.0
returnMGresult = ruleMG(oil)
# 传参数到MD中,计算,并比较
# 1、相同,则返回结果为SD,2、SD的结果大,则返回SD,3、MD的结果大,则返回MD的返回值
if result < returnMGresult:
return 2.0
else:
return 1.0
def ruleLG(oil):
# LD部分的rula
# 当输入的参数在50 - 100之间时,执行
# 同时将参数传入给MG,同时比较MG方法传回来的参数和该方法求出的值相比较,求出最后的最适合的预测值
returnMGresult = ruleMG(oil)
result = (oil - 50) / 50.0
# 比较后,得到预测值
if result < returnMGresult:
return 2.0
else:
return 3.0
# F函数,总的函数,从该函数中分流到rule的三个函数中
def Function(oil, stain):
# VS: SD, SG
# S: MD, SG
# M: SD, MG MD, MG LD, SG
# L: SD, LG MD,LG LD,MG
# XL: LD, LG
# 根据规则输出最后的洗涤时间
# 需要客户的正确输入
# ********** Begin **********#
if stain >= 0 and stain <= 50:
result_D = ruleSD(stain)
else:
result_D = ruleLD(stain)
if oil >= 0 and oil <= 50:
result_G = ruleSG(oil)
else:
result_G = ruleLG(oil)
# ********** End **********#
# 比较最后的结果,返回结果控制规则表,例如VS在表格中的坐标是(1,1),S的坐标是(2,1)
if result_D == 1.0 and result_G == 1.0:
return 1 # return VS
elif result_G == 1.0 and result_D == 2.0:
return 2 # return S
elif (result_D == 1.0 and result_G == 2.0) or (result_G == 2.0 and result_D == 2.0) or (
result_G == 1.0 and result_D == 3.0):
return 3 # reutrn M
elif (result_D == 1.0 and result_G == 3.0) or (result_D == 2.0 and result_G == 3.0) or (
result_D == 3.0 and result_G == 2.0):
return 4 # return L
elif result_G == 3.0 and result_D == 3.0:
return 5 # return VL







 文章涉及了多种算法和推理方法,包括基于队列的迷宫求解,A*寻路算法,四皇后问题的深度优先搜索解决方案,逻辑推理中的归结法,以及一个简单的动物识别系统,该系统基于产生式规则进行不确定性推理。这些内容展示了计算机解决问题的不同策略和技术。
文章涉及了多种算法和推理方法,包括基于队列的迷宫求解,A*寻路算法,四皇后问题的深度优先搜索解决方案,逻辑推理中的归结法,以及一个简单的动物识别系统,该系统基于产生式规则进行不确定性推理。这些内容展示了计算机解决问题的不同策略和技术。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








