给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:

输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 输出:6 解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height)
{
if(height.size() <= 2) return 0;
stack<int> myst;
myst.push(0);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1 ; i < height.size() ; i ++)
{
if(height[i] <= height[myst.top()])
{
myst.push(i);
}
else
{
while(!myst.empty() && height[i] > height[myst.top()])
{
int mid = myst.top();
myst.pop();
if(!myst.empty())
{
int h = min(height[myst.top()],height[i]) - height[mid];
int w = i - myst.top() - 1;
res += h*w;
}
}
myst.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
};给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
示例 1:
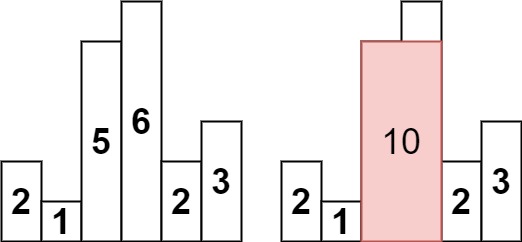
输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] 输出:10 解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights)
{
int res = 0;
stack<int> myst;
heights.insert(heights.begin(),0);
heights.push_back(0);
myst.push(0);
for(int i = 1 ;i < heights.size() ; i ++)
{
if(heights[i] >= heights[myst.top()])
{
myst.push(i);
}
else
{
while(!myst.empty() && heights[i] < heights[myst.top()])
{
int mid = myst.top();
myst.pop();
if(!myst.empty())
{
int left = myst.top();
int right = i;
int w = right - left - 1;
int h = heights[mid];
res = max(res,h*w);
}
}
myst.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
};给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 nums ,表示一些石块的初始位置。再给你两个长度 相等 下标从 0 开始的整数数组 moveFrom 和 moveTo 。
在 moveFrom.length 次操作内,你可以改变石块的位置。在第 i 次操作中,你将位置在 moveFrom[i] 的所有石块移到位置 moveTo[i] 。
完成这些操作后,请你按升序返回所有 有 石块的位置。
注意:
- 如果一个位置至少有一个石块,我们称这个位置 有 石块。
- 一个位置可能会有多个石块。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,6,7,8], moveFrom = [1,7,2], moveTo = [2,9,5] 输出:[5,6,8,9] 解释:一开始,石块在位置 1,6,7,8 。 第 i = 0 步操作中,我们将位置 1 处的石块移到位置 2 处,位置 2,6,7,8 有石块。 第 i = 1 步操作中,我们将位置 7 处的石块移到位置 9 处,位置 2,6,8,9 有石块。 第 i = 2 步操作中,我们将位置 2 处的石块移到位置 5 处,位置 5,6,8,9 有石块。 最后,至少有一个石块的位置为 [5,6,8,9] 。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> relocateMarbles(vector<int>& nums, vector<int>& moveFrom, vector<int>& moveTo)
{
unordered_map<int,int> mymap;
vector<int> res;
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.size() ; ++i)
{
mymap[nums[i]]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < moveFrom.size() ; ++i)
{
if(moveFrom[i] == moveTo[i]) continue;
else
{
if(!mymap.count(moveFrom[i])) continue;
mymap[moveTo[i]] += mymap[moveFrom[i]];
mymap.erase(moveFrom[i]);
}
}
for(auto i : mymap)
{
res.push_back(i.first);
}
sort(res.begin(),res.end());
return res;
}
};




















 47
47

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








