一,java.io包介绍

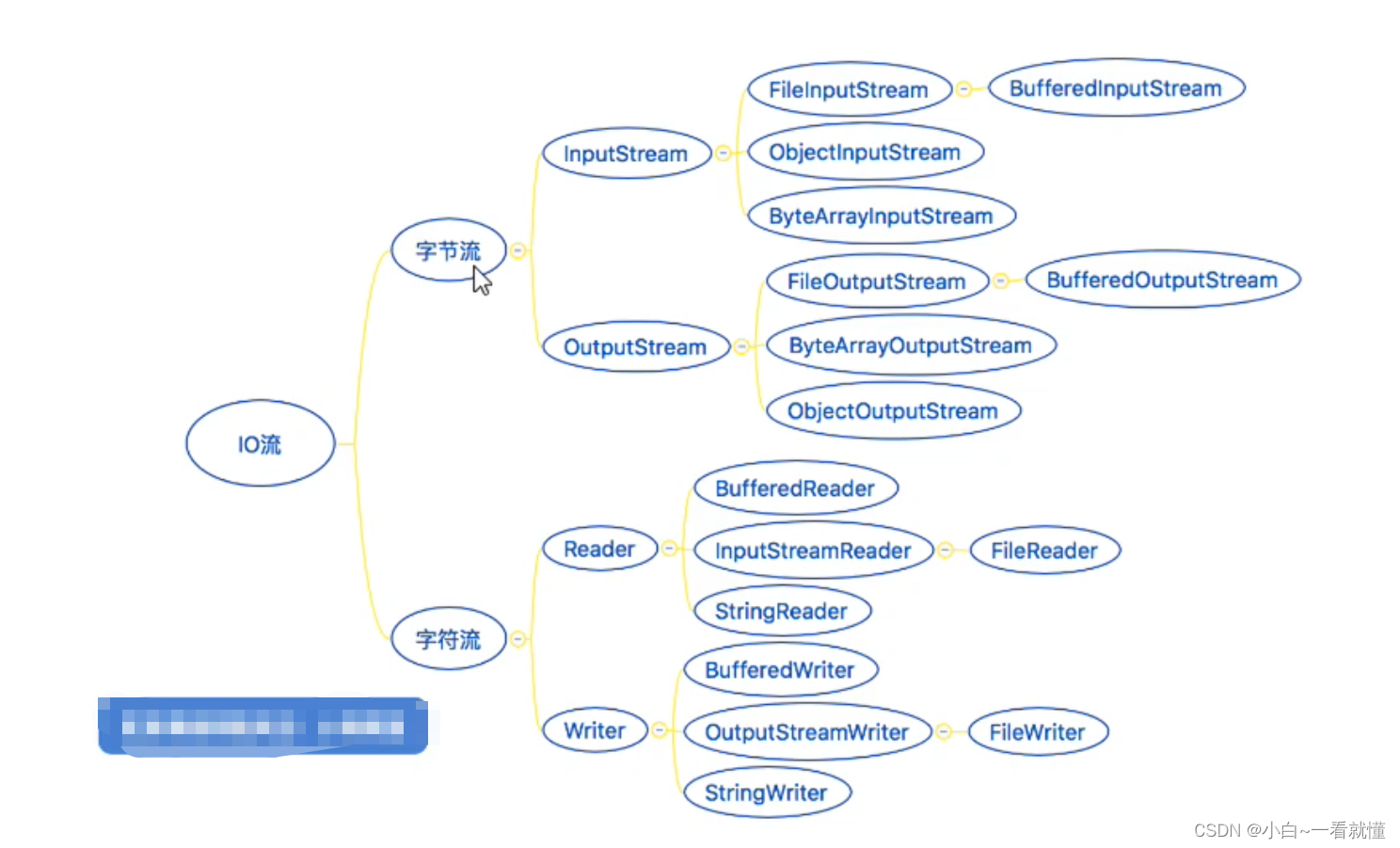
二,输入流inputStream讲解

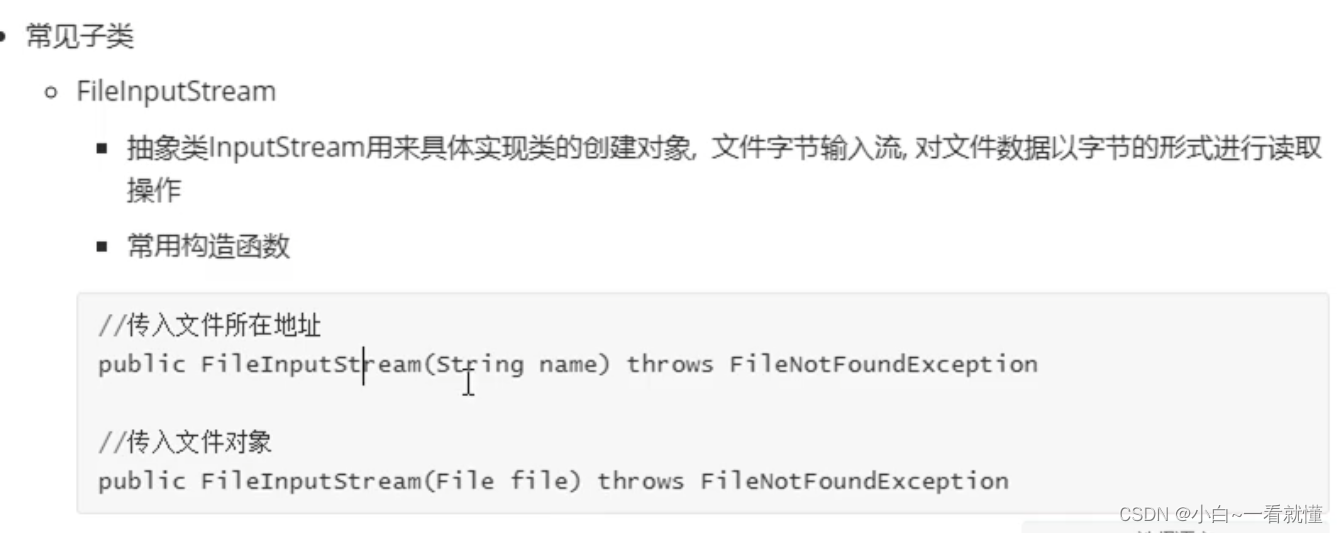

代码演示
package chapter11;
import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.policy.privateutil.PolicyUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class Main {
public static void main(String [] args)throws IOException {
String dir="C:\\Users\\联想\\Desktop";
String name="a.txt";
File file = new File(dir,name);
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// testRead(inputStream);
// testSkip(inputStream);
testReadByteArr(inputStream);
}
public static void testReadByteArr(InputStream inputStream)throws IOException{
//如果buf的长度为0。则不读取任何字节并返回0;每次读取的字节最多等于buf的长度
//byte [] buf=new byte[2];
byte [] buf=new byte[inputStream.available()];
int length;
//循环读取文件内容,输入流中最多讲buf.length个字节数据读入一个buf数据中,返回类型是读取到的字节数
//如果这个缓冲区没有满的话,则返回真实的字节数
while((length=inputStream.read(buf))!=-1){
//中文乱码问题,焕成GBK,或者UTF-8
// System.out.println(new String(buf,0,length,"UTF-8"));
// System.out.print(new String(buf,0,length));
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,length));
}
}
public static void testRead(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException{
//对于汉字等 unicode中的字符不能正常读取,只能以乱码的形势显示
int read=inputStream.read();
System.out.println(read);
System.out.println((char)read);
}
public static void testSkip(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException{
long sikpSize=inputStream.skip(2);
int read = inputStream.read();
System.out.println(read);
System.out.println((char)read);
}
}
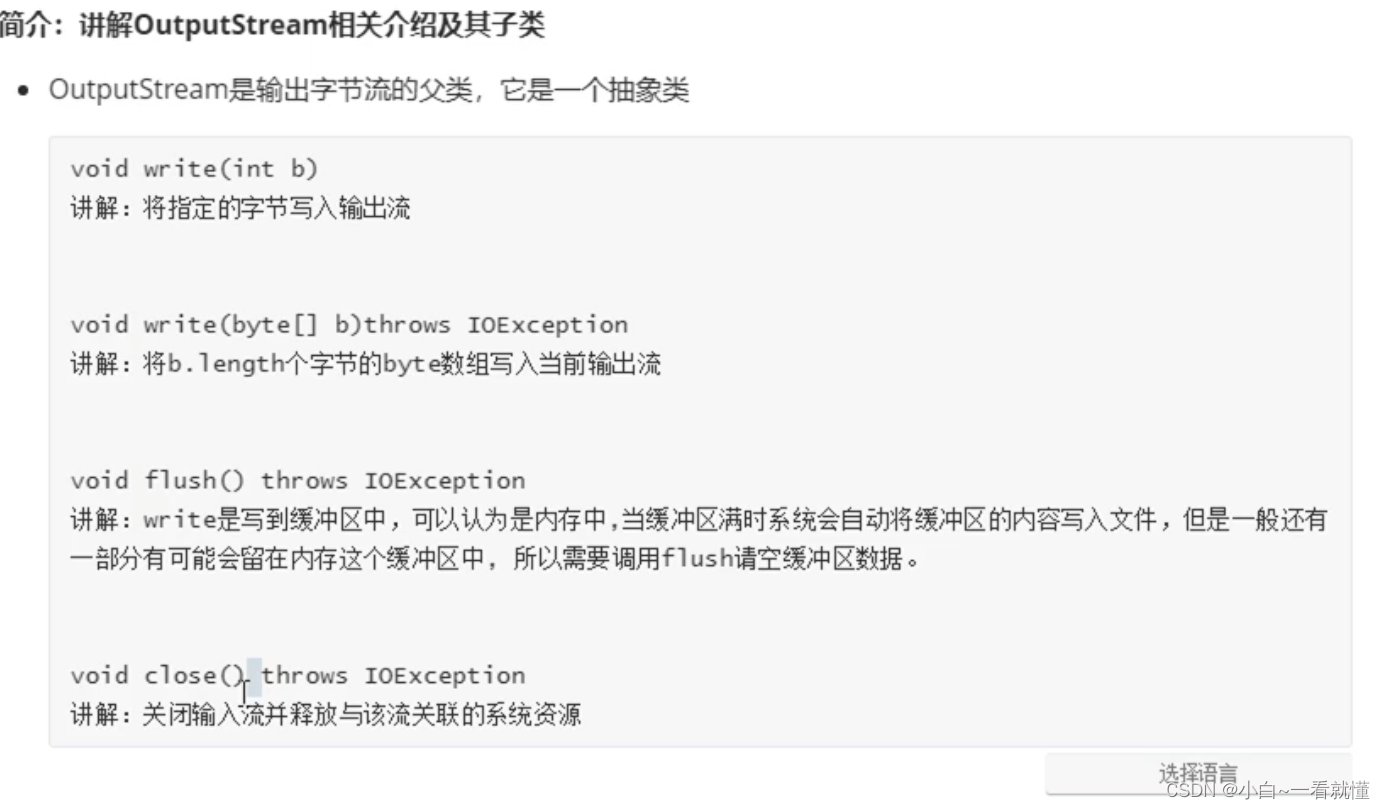
三,java输出流OutputStream讲解
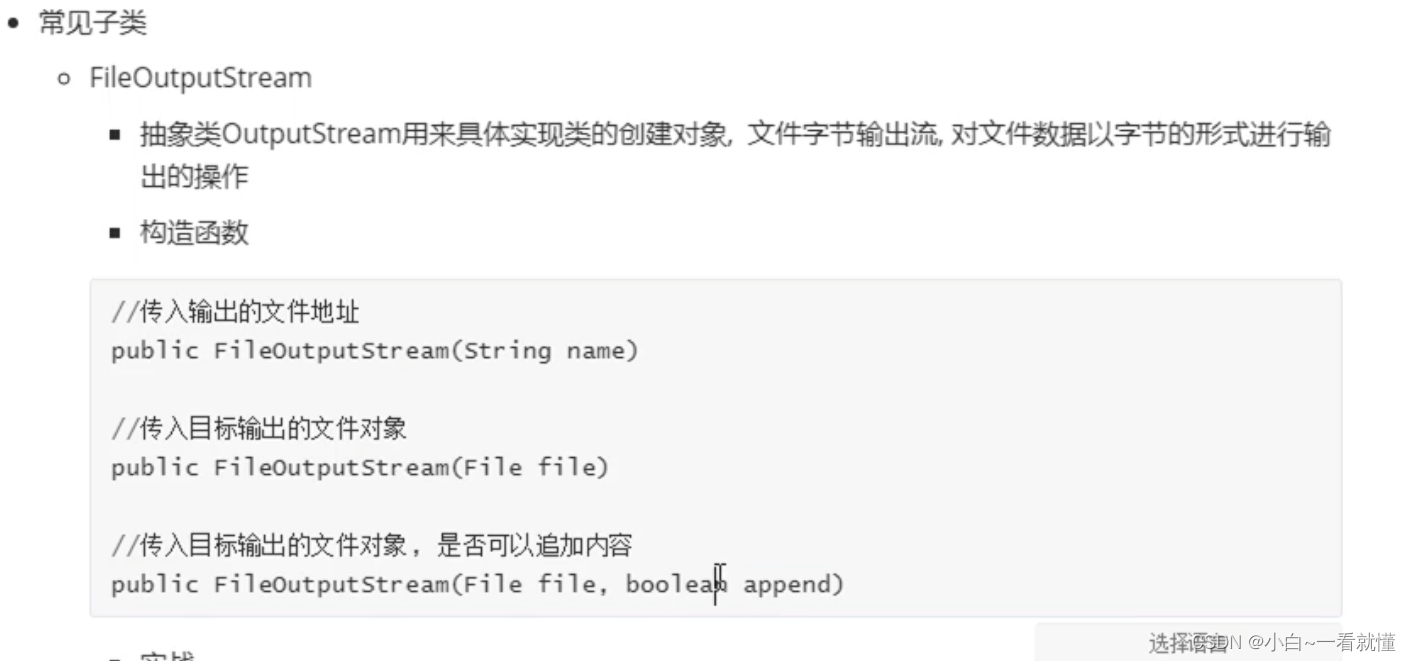

package chapter11;
import com.sun.xml.internal.ws.policy.privateutil.PolicyUtils;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String dir = "C:\\Users\\联想\\Desktop";
String name = "a.txt";
String target = "b.txt";
File file = new File(dir, name);
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
// testRead(inputStream);
// testSkip(inputStream);
//testReadByteArr(inputStream);
// 会自动创建文件,但不会在多级目录下创建文件
// OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(dir + File.separator + target);
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(dir + File.separator + target,true);
//这里加上true可以多次传入数据,不删除,就是可以跟写日记一样一直写,不覆盖
//testOut(inputStream,outputStream);
testOutBuf(inputStream,outputStream);
}
public static void testOutBuf(InputStream inputStream,OutputStream outputStream)throws IOException{
byte [] buf=new byte[1024];
int length;
while((length=inputStream.read(buf))!=-1){
outputStream.write(buf,0,length);
}
//关闭流
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
//单个字节读取,中文会有问题
public static void testOut(InputStream inputStream,OutputStream outputStream)throws IOException{
int value =0;
while(value!=-1){
value = inputStream.read();
outputStream.write(value);
}
//最后记得关闭流
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
}
}
四,javaIO包之缓冲流Buffer输入输出流

常⽤用的两个⽅方法


四,缓冲输入输出流之 java文件拷贝实战


package chapter11;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class BufferTest {
public static void main(String [] args){
try{
FileInputStream fis= new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\联想\\Desktop\\test\\xdclass.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\联想\\Desktop\\test\\copy.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
int size;
byte [] buf = new byte[1024];
while((size=bis.read(buf))!=-1){
bos.write(buf,0,size);
}
//刷新此缓冲区的输出流,才可以保证数据全部输出完成
//bos.flush();
bis.close();
bos.close();//bos.close()会自动刷新
}catch(Exception e){
}
}
}
实战

package chapter11;
import java.io.*;
public class taskTest {
public static void main(String [] args) {
String dir= "C:\\Users\\联想\\Desktop\\test";
File file = new File(dir+"\\task");
File [] files=file.listFiles();
for(File from : files){
String filename=from.getName();
copy(from.getAbsolutePath(),dir+"\\task1\\"+filename);
}
}
public static void copy(String from,String to){
try{
File targetDir = new File(new File(to).getParent());
if(!targetDir.exists()){
targetDir.mkdirs();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(from);
BufferedInputStream bis= new BufferedInputStream(fis);
FileOutputStream fos= new FileOutputStream(to);
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
int size;
byte [] buf = new byte[1024];
while((size=bis.read(buf))!=-1){
bos.write( buf,0,size);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
 Java IO流详解:输入输出流与缓冲流实践
Java IO流详解:输入输出流与缓冲流实践








 本文详细介绍了Java IO包中的输入流InputStream和输出流OutputStream,通过代码实例展示了如何读取和写入文件。此外,还探讨了缓冲流BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream在文件拷贝中的应用,提供了高效的文件复制方法。
本文详细介绍了Java IO包中的输入流InputStream和输出流OutputStream,通过代码实例展示了如何读取和写入文件。此外,还探讨了缓冲流BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream在文件拷贝中的应用,提供了高效的文件复制方法。

















 2746
2746

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








