1. 创建项目
创建maven项目。
引入依赖(mysql connector和servlet):
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.49</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/javax.servlet/javax.servlet-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
创建目录结构:
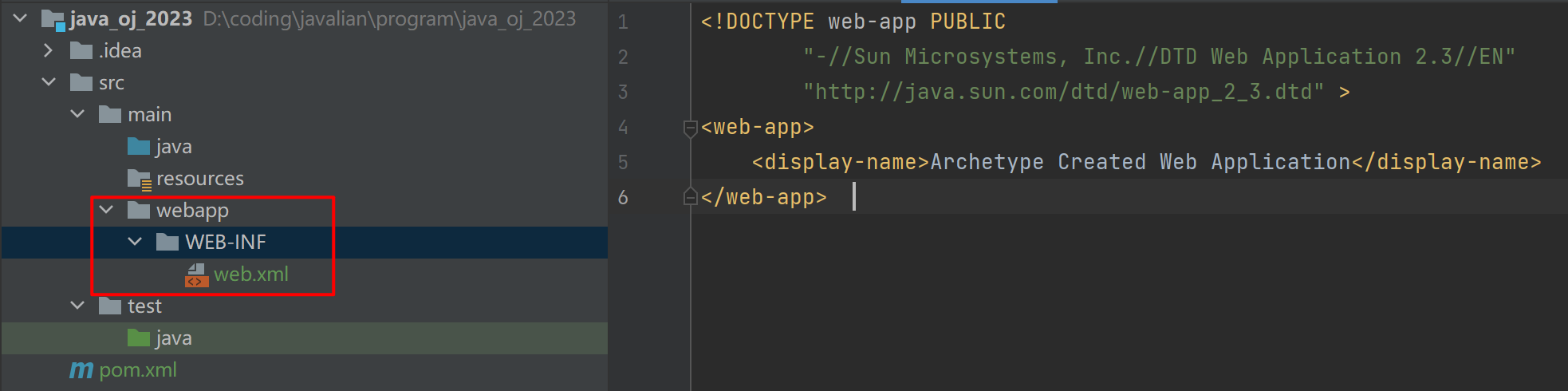
编写web.xml
往 web.xml 中拷贝以下代码. 具体细节内容我们暂时不关注.
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
</web-app>
2. 多进程编程
用户提交的代码,其实也是一个独立的逻辑。这个逻辑是使用多线程执行好,还是多进程呢?
对于这里用户提交的代码,一定是要通过“多进程”的方式来执行的。因为我们无法控制用户到底提交了啥代码。代码很可能是存在问题的,很可能一运行就崩溃的。如果使用多线程,就会导致用户代码直接把整个服务器进程都给带走了的糟糕情况。操作系统上,同一时刻运行着很多个进程如果某个进程挂了,不会影响到其他进程.(每个进程有各自的地址空间)
而在Java 中对系统提供的这些进程操作进行了限制,最终给用户只提供了两个操作:
- 进程创建
通过 Runtime.exec 方法创建多进程。
- 进程等待
通过 Process 类的 waitFor 方法来实现进程的等待.
public class TestExec {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// Runtime 在 JVM 中是一个单例
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
// Process 就表示 "进程"
Process process = runtime.exec("javac");
// 获取到子进程的标准输出和标准错误, 把这里的内容写入到两个文件中.
// 获取标准输出, 从这个文件对象中读, 就能把子进程的标准输出给读出来!
try (InputStream stdoutFrom = process.getInputStream();
OutputStream stdoutTo = new FileOutputStream("stdout.txt")){
while (true){
int ch = stdoutFrom.read();
if (ch == -1){
break;
}
stdoutTo.write(ch);
}
}
// 获取标准错误, 从这个文件对象中读, 就能把子进程的标准错误给读出来!
try (InputStream stderrFrom = process.getErrorStream();
OutputStream stderrTo = new FileOutputStream("stderr.txt")){
while (true){
int ch = stderrFrom.read();
if (ch == -1){
break;
}
stderrTo.write(ch);
}
}
// 通过 Process 类的 waitFor 方法来实现进程的等待.
// 父进程执行到 waitFor 的时候, 就会阻塞. 一直阻塞到子进程执行完毕为止.
// (和 Thread.join 是非常类似的)
// 返回值,这个退出码 就表示子进程的执行结果是否 ok. 如果子进程是代码执行完了正常退出, 此时返回的退出码就是 0.
// 如果子进程代码执行了一半异常退出(抛异常), 此时返回的退出码就非 0.
int exitCode = process.waitFor();
System.out.println(exitCode);
}
}
3. 编译运行模块
1. 实现通过命令行调用程序
通过上面的多进程方法,来封装成一个类:
public class CommandUtil {
// 1. 通过 Runtime 类得到 Runtime 实例, 执行 exec 方法
// 2. 获取到标准输出, 并写入到指定文件中.
// 3. 获取到标准错误, 并写入到指定文件中.
// 4. 等待子进程结束, 拿到子进程的状态码, 并返回.
public static int run(String cmd,String stdoutFile,String stderrFile) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 1. 通过 Runtime 类得到 Runtime 实例, 执行 exec 方法
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
// 2. 获取到标准输出, 并写入到指定文件中.
if (stdoutFile != null){
try (InputStream stdoutFrom = process.getInputStream();
OutputStream stdoutTo = new FileOutputStream(stdoutFile)){
while (true){
int ch = stdoutFrom.read();
if (ch == -1){
break;
}
stdoutTo.write(ch);
}
}
}
// 3. 获取到标准错误, 并写入到指定文件中.
if (stderrFile != null){
try (InputStream stderrFrom = process.getErrorStream();
OutputStream stderrTo = new FileOutputStream(stderrFile)){
while (true){
int ch = stderrFrom.read();
if (ch == -1){
break;
}
stderrTo.write(ch);
}
}
}
// 4. 等待子进程结束, 拿到子进程的状态码, 并返回.
int exitCode = process.waitFor();
return exitCode;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
CommandUtil.run("javac","stdout.txt","stderr.txt");
}
}
2. 搭建Task类的框架
每次的 “编译+运行” 这个过程, 就称为是一个 Task
这个 Task 类提供的核心方法, 就叫做 compileAndRun, 编译+运行 的意思.
- 参数: 要编译运行的 java 源代码.
- 返回值: 表示编译运行的结果. 编译出错/运行出错/运行正确…
compileAndRun方法的执行步骤:
- 把 question 中的 code 写入到一个 compile.Solution.java 文件中.
- 创建子进程, 调用 javac 进行编译. 注意! 编译的时候, 需要有一个 .java 文件.
如果编译出错, javac 就会把错误信息给写入到 stderr 里. 就可以用一个专门的文件来保存. compileError.txt - 创建子进程, 调用 java 命令并执行
运行程序的时候, 也会把 java 子进程的标准输出和标准错误获取到. stdout.txt, stderr.txt - 父进程获取到刚才的编译执行的结果, 并打包成 compile.Answer 对象
编译执行的结果, 就通过刚才约定的这几个文件来进行获取即可.
先创建Teak的输入内容和返回参数
// 用这个类来表示一个 task 的输入内容
// 会包含要编译的代码
public class Question {
private String code;
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
// 表示一个 compile.Task 的执行结果
public class Answer {
// 错误码. 约定 error 为 0 表示编译运行都 ok, 为 1 表示编译出错, 为 2 表示运行出错(抛异常).
private int error;
// 出错的提示信息. 如果 error 为 1, 编译出错了, reason 中就放编译的错误信息, 如果 error 为 2, 运行异常了, reason 就放异常信息
private String reason;
// 运行程序得到的标准输出的结果.
private String stdout;
// 运行程序得到的标准错误的结果.
private String stderr;
//Getter and Setter ……
@Override
public String toString() {
return "compile.Answer{" +
"error=" + error +
", reason='" + reason + '\'' +
", stdout='" + stdout + '\'' +
", stderr='" + stderr + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
创建Task类:
public class Task {
public Answer compileAndRun(Question question){
}
}
3. 约定临时文件名
public class Task {
// 通过一组常量来约定临时文件的名字.
// 这个表示所有临时文件所在的目录
private static final String WORK_DIR = "./tmp/" ;
// 约定代码的类名
private static final String CLASS = "Solution";
// 约定要编译的代码文件名.
private static final String CODE = WORK_DIR + "Solution.java";
// 约定存放编译错误信息的文件名
private static final String COMPILE_ERROR = WORK_DIR + "compileError.txt";
// 约定存放运行时的标准输出的文件名
private static final String STDOUT = WORK_DIR + "stdout.txt";
// 约定存放运行时的标准错误的文件名
private static final String STDERR = WORK_DIR + "stderr.txt";
//……
}
为啥要搞这么多临时文件呢?
最主要的目的,就是为了进行“进程间通信。进程和进程之间,是存在独立性的一个进程很难影响到其他进程。
Linux 系统,提供的进程间通信的手段有很多种:管道,消息队列,信号量,信号,socket, 文件…
只要某个东西,可以被多个进程同时访问到,就可以用来进行进程间通信。虽然实际开发中最常见的进程间通信手段是 socket (网络编程)。但是由于javac 和java 这俩进程的代码,都是别人写好的,咱们控制不了。此处也就只能通过 文件 的方式来进程间通信。
此处的临时文件也对于后面的测试,调试,起到关键的作用。
4. 对读写文件的操作进一步封装.
虽然 Java 本身已经提供了不少文件读写操作。但是用起来微麻烦一些。现在封装一下,搞一个类,提供两个方法。让这俩方法,一个负责读取整个文件内容,返回一个字符串。另一个方法负责写入整个字符串到文件中。
对于文本文件来说,字节流和字符流都可以进行。读写字符流会省事很多,字节流可能会比较麻烦.(手动的处理编码格式,尤其是文件中包含中文的时候)。后续需要读写的这些文件,都是文本文件,因此使用字符流更合适一些。
public class FileUtil {
// 负责把 filePath 对应的文件的内容读取出来, 放到返回值中.
public static String readFile(String filePath){
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
try (Reader reader = new FileReader(filePath)){
while (true){
int ch = reader.read();
if (ch == -1){
break;
}
result.append((char) ch);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result.toString();
}
// 负责把 content 写入到 filePath 对应的文件中
public static void writFile(String filePath,String content){
try (Writer writer = new FileWriter(filePath)){
writer.write(content);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileUtil.writFile("./test.txt","hello world");
String content = FileUtil.readFile("./test.txt");
System.out.println(content);
}
}
5. 实现保存源代码文件
// 每次的 "编译+运行" 这个过程, 就称为是一个 Task
public class Task {
// .....
public Answer compileAndRun(Question question){
Answer answer = new Answer();
//准备好要存放临时文件目录
File workDir = new File(WORK_DIR);
if (!workDir.exists()){
//创建多级目录
workDir.mkdirs();
}
// 1. 把 question 中的 code 写入到一个 Solution.java 文件中.
FileUtil.writFile(CODE,question.getCode());
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Task task = new Task();
Question question = new Question();
question.setCode("public class Solution {\n" +
" public static void main(String[] args) {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"hello world\");\n" +
" }\n" +
"}");
Answer answer = task.compileAndRun(question);
System.out.println(answer);
}
}
6. 实现编译功能
// 每次的 "编译+运行" 这个过程, 就称为是一个 Task
public class Task {
// .....
public Answer compileAndRun(Question question) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//……
// 2. 创建子进程, 调用 javac 进行编译. 注意! 编译的时候, 需要有一个 .java 文件.
// 如果编译出错, javac 就会把错误信息给写入到 stderr 里. 就可以用一个专门的文件来保存. compileError.txt
//需要先把编译命令给构造出来
String compileCmd = String.format("javac -encoding utf8 %s -d %s",CODE,WORK_DIR);
System.out.println("编译命令:" + compileCmd);
CommandUtil.run(compileCmd,null,COMPILE_ERROR);
// 如果编译出错了, 错误信息就被记录到 COMPILE_ERROR 这个文件中了. 如果没有编译出错, 这个文件是空文件.
String compileError = FileUtil.readFile(COMPILE_ERROR);
if (!compileError.equals("")){//编译出错
//直接返回Answer,让Answer中记录编译的错误信息
System.out.println("编译出错");
answer.setError(1);
answer.setReason(compileError);
return answer;
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Task task = new Task();
Question question = new Question();
question.setCode("public class Solution {\n" +
" public static void main(String[] args) {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"hello world\");\n" +
" }\n" +
"}");
Answer answer = task.compileAndRun(question);
System.out.println(answer);
}
}
7. 实现运行代码
// 每次的 "编译+运行" 这个过程, 就称为是一个 Task
public class Task {
//……
public Answer compileAndRun(Question question) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//……
// 3. 创建子进程, 调用 java 命令并执行
// 运行程序的时候, 也会把 java 子进程的标准输出和标准错误获取到. stdout.txt, stderr.txt
String runCmd = String.format("java -classpath %s %s",WORK_DIR,CLASS);
System.out.println("运行命令 " + runCmd);
CommandUtil.run(runCmd,STDOUT,STDERR);
String runError = FileUtil.readFile(STDERR);
if (!runError.equals("")){
System.out.println("运行出错");
answer.setError(2);
answer.setReason(runError);
return answer;
}
// 4. 父进程获取到刚才的编译执行的结果, 并打包成 compile.Answer 对象
// 编译执行的结果, 就通过刚才约定的这几个文件来进行获取即可.
answer.setError(0);
answer.setStdout(FileUtil.readFile(STDOUT));
return answer;
}
}
4. 题目管理模块
把当前的题目的信息给保存到数据库中。
create database if not exists oj_databases charset utf8;
use oj_databases;
drop table if exists oj_table;
create table oj_table(
id int primary key auto_increment,
title varchar(50),
level varchar(50),
description varchar(4098), -- 题干
templateCode varchar(4098), -- 代码模板
testCode text -- 测试用例
);
1. 封装DBUtil
public class DBUtil {
//使用单例模式(懒汉)进行封装数据与数据库之间的连接
private static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/oj_database?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false";
private static final String USERNAME = "root";
private static final String PASSWORD = "abc123";
private static volatile DataSource dataSource = null;//volatile避免出现内存可见性问题
private static DataSource getDataSource() {
if (dataSource == null) {//判断是否需要加锁
synchronized (DBUtil.class) {
if (dataSource == null) {//判断是否需要实例化
MysqlDataSource mysqlDataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
mysqlDataSource.setURL(URL);
mysqlDataSource.setUser(USERNAME);
mysqlDataSource.setPassword(PASSWORD);
dataSource = mysqlDataSource;
}
}
}
return dataSource;
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return getDataSource().getConnection();
}
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. 封装题目表操作
创建problem实体类,一个 Problem 对象,就对应着表中的一条记录:
public class Problem {
private int id;
private String title;
private String level;
private String description;
private String templateCode;
private String testCode;
//Getter and Setter …… toString()
}
还需要针对这个表进行“增删改查”.创建一个ProblemDAO来负责进行增删改查操作.
通过这个类封装了针对 Problem 的增删改查.
- 新增题目
- 删除题目
- 查询题目列表
- 查询题目详情
public class ProblemDAO {
//新增题目
public void insert(Problem problem){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
//建立数据库连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//构造sql语句
String sql = "insert into oj_table values(null,?,?,?,?,?)";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,problem.getTitle());
statement.setString(2,problem.getLevel());
statement.setString(3,problem.getDescription());
statement.setString(4,problem.getTemplateCode());
statement.setString(5,problem.getTestCode());
//执行sql
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
if (ret == -1){
System.out.println("新增题目失败");
}else {
System.out.println("新增题目");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
//删除题目
public void delete(int id){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
try {
//建立数据库连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//构造sql语句
String sql = "delete from oj_table while id = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id);
//执行sql
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
if (ret == -1){
System.out.println("删除题目失败!");
}else {
System.out.println("删除题目成功");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,null);
}
}
// 这个操作是把当前题目列表中的所有题都查出来了
// 万一数据库中的题目特别多, 咋办? 只要实现 "分页查询" 即可. 后台实现分页查询, 非常容易.
// 前端传过来一个当前的 "页码" , 根据页码算一下, 依据 sql limit offset 语句, 要算出来 offset 是 几
// 但是前端这里实现一个分页器稍微麻烦一些(比后端要麻烦很多). 此处暂时不考虑分页功能.
public List<Problem> selectAll(){
List<Problem> problems = new ArrayList<>();
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//建立数据库连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//构造sql语句
String sql = "select id,title,level from oj_table";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//执行sql
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//遍历resultSet
while (resultSet.next()){
//每一行都是一个Problem对象
Problem problem = new Problem();
problem.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
problem.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
problem.setLevel(resultSet.getString("level"));
problems.add(problem);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
return problems;
}
//查看题目详情
public Problem selectOne(int id){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//建立数据库连接
connection = DBUtil.getConnection();
//构造sql语句
String sql = "select * from oj_table where id = ?";
statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setInt(1,id);
//执行sql
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//遍历resultSet
while (resultSet.next()){
//每一行都是一个Problem对象
Problem problem = new Problem();
problem.setId(resultSet.getInt("id"));
problem.setTitle(resultSet.getString("title"));
problem.setLevel(resultSet.getString("level"));
problem.setDescription(resultSet.getString("description"));
problem.setTemplateCode(resultSet.getString("templateCode"));
problem.setTestCode(resultSet.getString("testCode"));
return problem;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBUtil.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
}
System.out.println("查询题目详情失败");
return null;
}
}
3. 对封装的题目表进行测试
测试用例代码,就是一个 main 方法。在这个 main 方法里面,会创建 Solution 的实例,并目调用 里面提供的 核心方法(twoSum)。调用核心方法的时候,传入不同的参数,并针对返回结果进行不同的判定。如果返回结果符合预期,就打印"Test OK”如果不符合预期,就打印“Test failed",同时打印出出错的详情。
public class ProblemDAO {
//……
private static void testInsert(){
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
Problem problem = new Problem();
problem.setTitle("两数之和");
problem.setLevel("简单");
problem.setDescription("给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。\n" +
"\n" +
"你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。\n" +
"\n" +
"你可以按任意顺序返回答案。\n" +
"\n" +
" \n" +
"\n" +
"示例 1:\n" +
"\n" +
"输入:nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9\n" +
"输出:[0,1]\n" +
"解释:因为 nums[0] + nums[1] == 9 ,返回 [0, 1] 。\n" +
"示例 2:\n" +
"\n" +
"输入:nums = [3,2,4], target = 6\n" +
"输出:[1,2]\n" +
"示例 3:\n" +
"\n" +
"输入:nums = [3,3], target = 6\n" +
"输出:[0,1]\n" +
" \n" +
"\n" +
"提示:\n" +
"\n" +
"2 <= nums.length <= 104\n" +
"-109 <= nums[i] <= 109\n" +
"-109 <= target <= 109\n" +
"只会存在一个有效答案\n" +
" \n" +
"\n" +
"进阶:你可以想出一个时间复杂度小于 O(n2) 的算法吗?");
problem.setTemplateCode("class Solution {\n" +
" public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {\n" +
"\n" +
" }\n" +
"}");
problem.setTestCode(" public static void main(String[] args) {\n" +
" Solution solution = new Solution();\n" +
" //testcase1\n" +
" int[] nums = {2,7,11,15};\n" +
" int target = 9;\n" +
" int[] result = solution.twoSum(nums,target);\n" +
" if (result.length == 2 && result[0] == 0 && result[1] == 1){\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase1 ok\");\n" +
" }else {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase1 failed\");\n" +
" }\n" +
" //testcase2\n" +
" int[] nums2 = {3,2,4};\n" +
" int target2 = 6;\n" +
" int[] result2 = solution.twoSum(nums2,target2);\n" +
" if (result.length == 2 && result[0] == 1 && result[1] == 2){\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase2 ok\");\n" +
" }else {\n" +
" System.out.println(\"testcase2 failed\");\n" +
" }\n" +
" }");
problemDAO.insert(problem);
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
private static void testSelectAll(){
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
List<Problem> problems = problemDAO.selectAll();
System.out.println(problems);
}
private static void testSelectOne(){
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
Problem problem = problemDAO.selectOne(1);
System.out.println(problem);
}
private static void testDelete(){
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
problemDAO.delete(1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//testInsert();
//testSelectAll();
//testSelectOne();
testDelete();
}
}
5. API模块
当前已经把数据库的相关操作封装好了。接下来可以设计服务器提供的 API。这是一些 HTTP 风格的接口.通过这些接口和网页前端进行交互。
a)题目列表页:功能就是展示当前题目的列表。向服务器请求,题目的列表。
b) 题目详情页:
- 功能一: 展示题目的详细要求 => 向服务器请求,获取指定题目的详细信息
- 功能二: 能够有一个代码编辑框,让用户来编写代码.(这个过程不需要和服务器交互,纯前端实现)
- 功能三: 有一个提交按钮点击提交按钮,就能把用户编辑的代码给发到服务器上.服器进行编译和运行,并返回结果. => 向服务器发送用户当前编写的代码,并且获取到结果.
上面这是两个最核心的页面。除此之外,还可以提供一个 题目管理页(给管理员使用,不开放给普通用户)
- 管理员通过这个页面来 新增题目/删除题目
- 向服务器提交新增题目的请求。
- 向服务器提交一个删除题目的请求
咱们现在比较流行的前后端交互的方式,主要是通过JSON 格式来组织的。由于JSON 格式的解析,其实还挺麻烦的。需要引入第三方库,帮我们完成.Java 圈子中,处理JSON 的第三方库有很多Jackson 。
引入jackson依赖:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-databind -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.14.1</version>
</dependency>
1. 获取题目列表
@WebServlet("/problem")
public class ProblemServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setStatus(200);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
List<Problem> problems = problemDAO.selectAll();
String respString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(problems);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
}
}
2. 获取题目详细信息
@WebServlet("/problem")
public class ProblemServlet extends HttpServlet {
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setStatus(200);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
//获取id字段,如果能获取到->题目详情页。不能获取到->题目列表页
String idString = req.getParameter("id");
if (idString == null || idString.equals("")){
//没有获取到id字段,查询题目列表
List<Problem> problems = problemDAO.selectAll();
String respString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(problems);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
}else {
//题目列表页
Problem problem = problemDAO.selectOne(Integer.valueOf(idString));
String respString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(problem);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
}
}
}
3. 实现在线编译运行的思路
思路:
-
先读取请求的正文. 先按照 JSON 格式进行解析
-
根据 id 从数据库中查找到题目的详情 => 得到测试用例代码
-
把用户提交的代码和测试用例代码, 给拼接成一个完整的代码.
-
创建一个 Task 实例, 调用里面的 compileAndRun 来进行编译运行.
-
根据 Task 运行的结果, 包装成一个 HTTP 响应
@WebServlet("/compile")
public class CompileServlet extends HttpServlet {
static class CompileRequest{//对应req的json值
public int id;
public String code;
}
static class CompileResponse{//对应resp的json值
//0 表示编译运行 ok,1 表示编译出错,2 表示运行出错(抛异常)
public int error;
//出错的详细原因
public String reason;
//测试用例的输出情况,包含了通过几个用例这样的信息
public String stdout;
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
}
4. 实现读取请求正文
@WebServlet("/compile")
public class CompileServlet extends HttpServlet {
//……
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. 先读取请求的正文. 先按照 JSON 格式进行解析
String body = readBody(req);
CompileRequest compileRequest = objectMapper.readValue(body,CompileRequest.class);
}
private String readBody(HttpServletRequest req) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//1.获取body的长度
int contentLength = req.getContentLength();
//2.准备一个byte[]
byte[] buffer = new byte[contentLength];
//3.获取body中的流对象
try (InputStream inputStream = req.getInputStream()){
//4.将流对象的内容放到byte[]中
inputStream.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//将byte[]中的内容构造成字符串,从二进制变成文本文件,我们应该注意的一个问题是:几个字节算一个字符集
//为了解决这个问题我们指定UTF8为指定字符集
return new String(buffer,"UTF8");
}
}
5. 实现代码拼接
所谓的"合并",其实就是把 testCode 的这个 main方法,给嵌入到 requestCode 里面。做法就是把 testCode 给放到 Solution 的最后一个}的前面即可。
@WebServlet("/compile")
public class CompileServlet extends HttpServlet {
//……
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//……
//2.根据 id 从数据库中查找到题目的详情 => 得到测试用例代码
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
Problem problem = problemDAO.selectOne(compileRequest.id);
// 3. 把用户提交的代码和测试用例代码, 给拼接成一个完整的代码.
//testCode是测试用例代码
String testCode = problem.getTestCode();
//finalCode是用户提交代码
String requestCode = compileRequest.code;
//finalCode是最终代码
String finalCode = mergeCode(testCode,requestCode);
System.out.println(finalCode);
}
private String mergeCode(String testCode, String requestCode) {
//1.查找requestCode中的最后一个}
int pos = requestCode.lastIndexOf("}");
if (pos == -1){
//说明这个代码没有},是个非法代码
return null;
}
//2.根据这个位置进行字符串截取
String subStr = requestCode.substring(0,pos);
//3.进行拼接
return subStr + testCode + "\n}";
}
}
写完代码后进行验证,可以用postman进行发送post请求。post请求的body部分为json字符串:
{
"id": 2,
"code": "class Solution {\n public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {\n int[] a = {0,1};\n return a;\n }\n}"
}
从idea控制台能输出完整的拼接代码说明拼接没问题。
6. 调用Task完成编译和运行
@WebServlet("/compile")
public class CompileServlet extends HttpServlet {
//……
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
//……
// 4. 创建一个 Task 实例, 调用里面的 compileAndRun 来进行编译运行.
Task task = new Task();
Question question = new Question();
question.setCode(finalCode);
Answer answer = null;
try {
answer = task.compileAndRun(question);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 5. 根据 Task 运行的结果, 包装成一个 HTTP 响应
resp.setStatus(200);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
CompileResponse compileResponse = new CompileResponse();
compileResponse.error = answer.getError();
compileResponse.reason = answer.getReason();
compileResponse.stdout = answer.getStdout();
String respString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(compileResponse);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
}
//……
}
写完代码后进行验证,可以用postman进行发送post请求。post请求的body部分为json字符串:
{
"id": 2,
"code": "class Solution {\n public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {\n int[] a = {0,1};\n return a;\n }\n}"
}
postman正常返回:
{
"error": 0,
"reason": null,
"stdout": "testcase1 ok\r\ntestcase2 failed\r\n"
}
7. 处理异常请求
当传输的数据id不存在,或者code不合法,会直返回状态码500(异常)。我们需要一个更温和的处理提高我们的代码的容错能力,返回给用户一个错误提示。
//题目未找到异常
public class ProblemNotFoundException extends Exception{
}
//code非法异常
public class CodeInValidException extends Exception{
}
@WebServlet("/compile")
public class CompileServlet extends HttpServlet {
//……
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
CompileRequest compileRequest = null;
CompileResponse compileResponse = new CompileResponse();
try {
resp.setStatus(200);
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf8");
//1. 先读取请求的正文. 先按照 JSON 格式进行解析
String body = readBody(req);
compileRequest = objectMapper.readValue(body, CompileRequest.class);
//2.根据 id 从数据库中查找到题目的详情 => 得到测试用例代码
ProblemDAO problemDAO = new ProblemDAO();
Problem problem = problemDAO.selectOne(compileRequest.id);
if (problem == null){
//为了同意处理错误,在这个地方抛出异常
throw new ProblemNotFoundException();
}
// 3. 把用户提交的代码和测试用例代码, 给拼接成一个完整的代码.
//testCode是测试用例代码
String testCode = problem.getTestCode();
//finalCode是用户提交代码
String requestCode = compileRequest.code;
//finalCode是最终代码
String finalCode = mergeCode(testCode,requestCode);
if (finalCode == null){
//code不合法异常
throw new CodeInValidException();
}
//System.out.println(finalCode);
// 4. 创建一个 Task 实例, 调用里面的 compileAndRun 来进行编译运行.
Task task = new Task();
Question question = new Question();
question.setCode(finalCode);
Answer answer = task.compileAndRun(question);
// 5. 根据 Task 运行的结果, 包装成一个 HTTP 响应
compileResponse = new CompileResponse();
compileResponse.error = answer.getError();
compileResponse.reason = answer.getReason();
compileResponse.stdout = answer.getStdout();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ProblemNotFoundException e) {
//处理题目未找到异常
compileResponse.error = 3;
compileResponse.reason = "没有找打指定题目!id = " + compileRequest.id;
} catch (CodeInValidException e) {
//处理code不合法异常
compileResponse.error = 3;
compileResponse.reason = "提交的代码不符合要求!";
}finally {
String respString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(compileResponse);
resp.getWriter().write(respString);
}
}
//……
}
8. 区分不提供请求的工作目录
每次有一个请求过来,都需要生成这样的一组临时文件。如果同一时刻,有N个请求一起过来了。这些请求的临时文件的名字和所在的目录都是一样的。此时多个请求之间就会出现“相互干扰”的情况.(非常类似于线程安全问题)
如果采用加锁的方式解决这个问题会发生类似于线程等待,一个用户在提交 代码其他用户不能进行提交代码。更好的办法,就是让每个请求,有一个自己的目录来生成这些临时文件。这样的话相互之间就不再干扰了。
因此,咱们要做的事情就是让每个请求创建的 WORK_DIR 目录都不相同。如果使用类似以mysq的自增主键,我们需要用一个全局变量来存储这个自增值,但是如果重新部署程序的话会导致变量重新自增会有重复的出现 。更好的解决方案是用UUID生成全世界唯一的ID。我们一直提交时间长了文件会变得越来越大,我们可以采取定时清除的办法(每天一清除,保留三天的文件)。
public class Task {
// 之前这里的名字都是静态常量. 但是现在要实现针对每个请求都有不同的临时目录, 就不能使用静态常量了
// 这个表示所有临时文件所在的目录
private String WORK_DIR = null ;
// 约定代码的类名
private String CLASS = null;
// 约定要编译的代码文件名.
private String CODE = null;
// 约定存放编译错误信息的文件名
private String COMPILE_ERROR = null;
// 约定存放运行时的标准输出的文件名
private String STDOUT = null;
// 约定存放运行时的标准错误的文件名
private String STDERR = null;
public Task(){
// 在 Java 中使用 UUID 这个类就能生成一个 UUID 了
WORK_DIR = "./tmp/" + UUID.randomUUID().toString() +"/";
CLASS = "Solution";
CODE = WORK_DIR + "Solution.java";
COMPILE_ERROR = WORK_DIR + "compileError.txt";
STDOUT = WORK_DIR + "stdout.txt";
STDERR = WORK_DIR + "stderr.txt";
}
//……
}
我们在idea上运行生成的相对路径和通过tomcat运行生成的相对路径是不同的,可以通过一行代码打印出当前运行状态下的相对路径:
//获取到 工作目录
System.out.println("用户的当前工作目录: "+System.getProperty("user.dir"));
6. 前端模块
将上面的前端模版进行修改:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Charcoal - Free Bootstrap 4 UI Kit</title>
<meta name="description" content="Charcoal is a free Bootstrap 4 UI kit build by @attacomsian at Wired Dots." />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<!--Bootstrap 4-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-md navbar-dark fixed-top sticky-navigation">
<a class="navbar-brand font-weight-bold" href="#">我的oj系统</a>
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-toggle="collapse" data-target="#topMenu" aria-controls="navbarSupportedContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="topMenu">
<ul class="navbar-nav ml-auto">
</ul>
</div>
</nav>
<!--hero section-->
<section class="bg-hero">
<div class="container">
<div class="row vh-100">
<div class="col-sm-12 my-auto text-center">
<h1>我的oj平台</h1>
<p class="lead text-capitalize my-4">
基于java Servlet 的oj平台
</p>
<a href="https://gitee.com/dalinya/javalian/tree/master/program/java_oj_2023" class="btn btn-outline-light btn-radius btn-lg">项目链接</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</section>
<!--components-->
<section class="my-5 pt-5">
<div class="container">
<!-- Tables -->
<div class="row mb-5" id="tables">
<div class="col-sm-12">
<h1>Tables</h1>
<div class="mt-3 mb-5">
<h3>Table striped</h3>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Header 1</th>
<th>Header 2</th>
<th>Header 3</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<th>Footer 1</th>
<th>Footer 2</th>
<th>Footer 3</th>
</tr>
</tfoot>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>Cell</td>
<td>Cell</td>
<td>Cell</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell</td>
<td>Cell</td>
<td>Cell</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell</td>
<td>Cell</td>
<td>Cell</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!--footer-->
<section class="py-5 bg-dark">
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6 offset-md-3 col-sm-8 offset-sm-2 col-xs-12 text-center">
<p class="pt-2 text-muted">
© by yb_Account
</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</section>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.1.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.12.3/umd/popper.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.staticfile.org/twitter-bootstrap/4.3.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<script src="js/app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
1. 实现题目列表页
当前是通过写死页面的方式,来展现题目的真实的情况是需要通过让页面通过 ajax 的方式从服务器来获取到数据.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<!--和上面一样-->
</head>
<body>
<!--hero section-->
<!--和上面一样-->
<!--components-->
<section class="my-5 pt-5">
<div class="container">
<!-- Tables -->
<div class="row mb-5" id="tables">
<div class="col-sm-12">
<div class="mt-3 mb-5">
<h3>题目列表</h3>
<table class="table table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号</th>
<th>标题</th>
<th>难度</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<!--注意要添加id="problemTable"-->
<tbody id = "problemTable">
<!-- <tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>
<a href="#">两数之和</a>
</td>
<td>简答</td>
</tr> -->
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!--footer--><!--和上面一样-->
<script>
// 在页面加载的时候, 尝试从服务器获取题目列表. 通过 ajax 的方式来进行获取
function getProblems(){
// 1. 先通过 ajax 从服务器获取到题目列表.
$.ajax({
url:"problem",
type:"GET",
success:function(data,status){
// data 是响应的 body, status 是响应的状态码
// 2. 把得到的响应数据给构造成 HTML 片段
makeProblemTable(data);
}
});
}
function makeProblemTable(data){
// 通过这个函数来把数据转换成 HTML 页面片段
let problemTable = document.querySelector("#problemTable");
for(let problem of data){
let tr = document.createElement("tr");
let tdId = document.createElement("td");
tdId.innerHTML = problem.id;
tr.appendChild(tdId);
let tdTitle = document.createElement("td");
let a = document.createElement("a");
a.innerHTML = problem.title;
//todo:需要构造一个页面详情页。来展示题目的详情信息
a.href = 'problemDetail.html?id=' + problem.id;
tdTitle.appendChild(a);
tr.appendChild(tdTitle);
let tdLevel = document.createElement("td");
tdLevel.innerHTML = problem.level;
tr.appendChild(tdLevel);
problemTable.appendChild(tr);
}
}
getProblems();
</script>
</body>
</html>
2. 实现题目详情页
html中展示题目详情信息。代码编辑框,提交按钮,运行结果。

<section class="my-5 pt-5">
<div class="container">
<div class="row mt-4">
<div class="col-sm-12 pb-4">
<div class="jumbotron jumbotron-fluid">
<div class="container" id="problemDesc">
<!-- <h1>Container fluid size jumbotron</h1>
<p>Think BIG with a Bootstrap Jumbotron!</p> -->
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row mt-4">
<div class="col-sm-12 pb-4">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="codeEditor">代码编辑框</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="codeEditor" style="width: 100%; height: 400px;"></textarea>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" id="submitButton">提交</button>
<div class="row mt-4">
<div class="col-sm-12 pb-4">
<div class="jumbotron jumbotron-fluid">
<div class="container">
<pre id="problemResult">
</pre>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</section>
使用JQuery中的ajax来完成前后端交互。
<script>
console.log(location.search);
// 在页面加载的时候, 尝试从服务器获取题目详情. 通过 ajax 的方式来进行获取
function getProblem() {
$.ajax({
url:"problem" + location.search,
type: "get",
success: function(data,status){
makeProblemDetail(data);
}
})
}
function makeProblemDetail(problem){
// 1. 获取到 problemDesc, 把题目详情填写进去
let problemDesc = document.querySelector("#problemDesc");
let h3 = document.createElement("h3");
h3.innerHTML = problem.id + "." + problem.title + "_" + problem.level;
problemDesc.appendChild(h3);
let pre = document.createElement("pre");
let p = document.createElement("p");
p.innerHTML = problem.description;
pre.appendChild(p);
problemDesc.appendChild(pre);
// 2. 把代码的模板填写到编辑框中.
let codeEditor = document.querySelector("#codeEditor");
codeEditor.innerHTML = problem.templateCode;
// 3. 给提交按钮注册一个点击事件
let submitButton = document.querySelector("#submitButton");
submitButton.onclick = function(){
// 点击这个按钮, 就要进行提交. (把编辑框的内容给提交到服务器上)
let body = {
id: problem.id,
code: codeEditor.value,
};
$.ajax({
type:"POST",
url:"compile",
data: JSON.stringify(body),
success: function(data,status){
let problemResult = document.querySelector("#problemResult");
if(data.error == 0){
// 编译运行没有问题, 把 stdout 显示到页面中
problemResult.innerHTML= data.stdout;
}else{
// 编译运行有问题, 把 stdout 显示到页面中
problemResult.innerHTML = data.reason;
}
}
});
}
}
getProblem();
</script>
3. 引入ace.js
前面的文本编辑框中,不仅没有语法高亮,而且一按tabl不是出现水平制表符。有一个第三方库叫做 ace.js.这个就是一个前端版本的代码编辑器。安装非常简单只要在页面中引入对应的 地址 即可。
<!-- 引入 ace.js -->
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/ace/1.2.9/ace.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/ace/1.2.9/ext-language_tools.js"></script>
在代码编辑框外引入一层新的id = editor 的div:
<div class="form-group">
<label for="codeEditor">代码编辑框</label>
<div id="editor" style="min-height:400px">
<textarea class="form-control" id="codeEditor" style="width: 100%; height: 400px;"></textarea>
</div>
</div>
初始化ace:
function initAce() {
// 参数 editor 就对应到刚才在 html 里加的那个 div 的 id
let editor = ace.edit("editor");
editor.setOptions({
enableBasicAutocompletion: true,//是否支持自动补全
enableSnippets: true,//是否支持代码模版
enableLiveAutocompletion: true//是否支持代码模版的自动补全
});
editor.setTheme("ace/theme/twilight");//设置编辑器的主题
editor.session.setMode("ace/mode/java");//设置语言模式
editor.resize();//重新绘制窗口
document.getElementById('editor').style.fontSize = '20px';//设置字体
return editor;
}
let editor = initAce();
ace.js 会重新绘制页面(绘制 div#editor)。原来搞的那个 textarea 就没了。
在页面加载的时候,通过另外一个方式
editor.setValue(yourCode);
// 2. 把代码的模板填写到编辑框中.
//let codeEditor = document.querySelector("#codeEditor");
// codeEditor.innerHTML = problem.templateCode;
editor.setValue(problem.templateCode);
在提交代码的时候,也需要通过另一个方式获取到代码内容
let yourCode = editor.getValue();
// 点击这个按钮, 就要进行提交. (把编辑框的内容给提交到服务器上)
let body = {
id: problem.id,
//code: codeEditor.value,
code: editor.getValue(),
};
7. 部署项目
对于插入题目,输入sql语句会比较麻烦。我们可以针对ProblemDAO进行打包 。
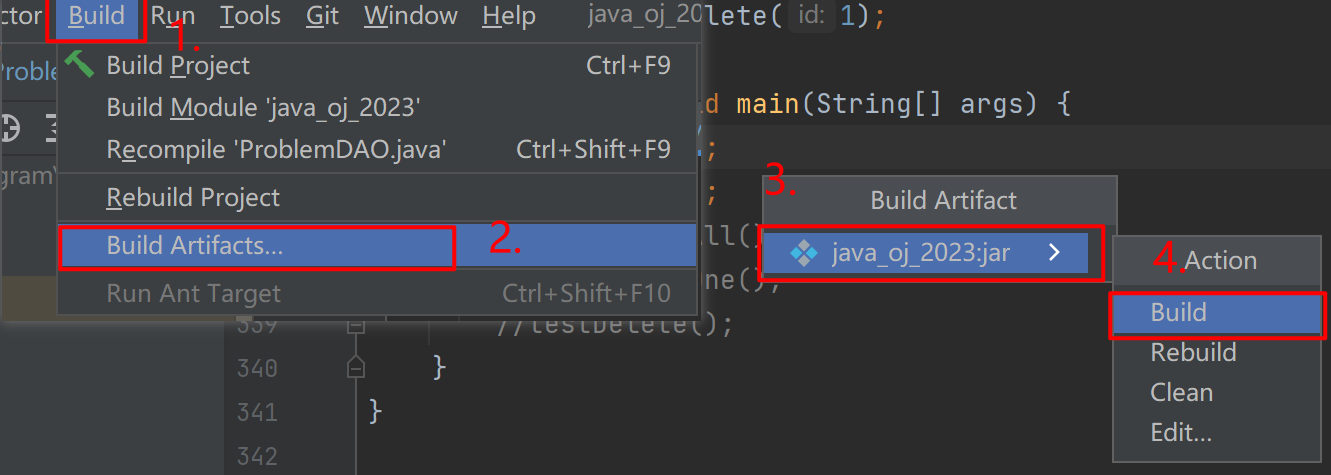
- 进行打成jar包:
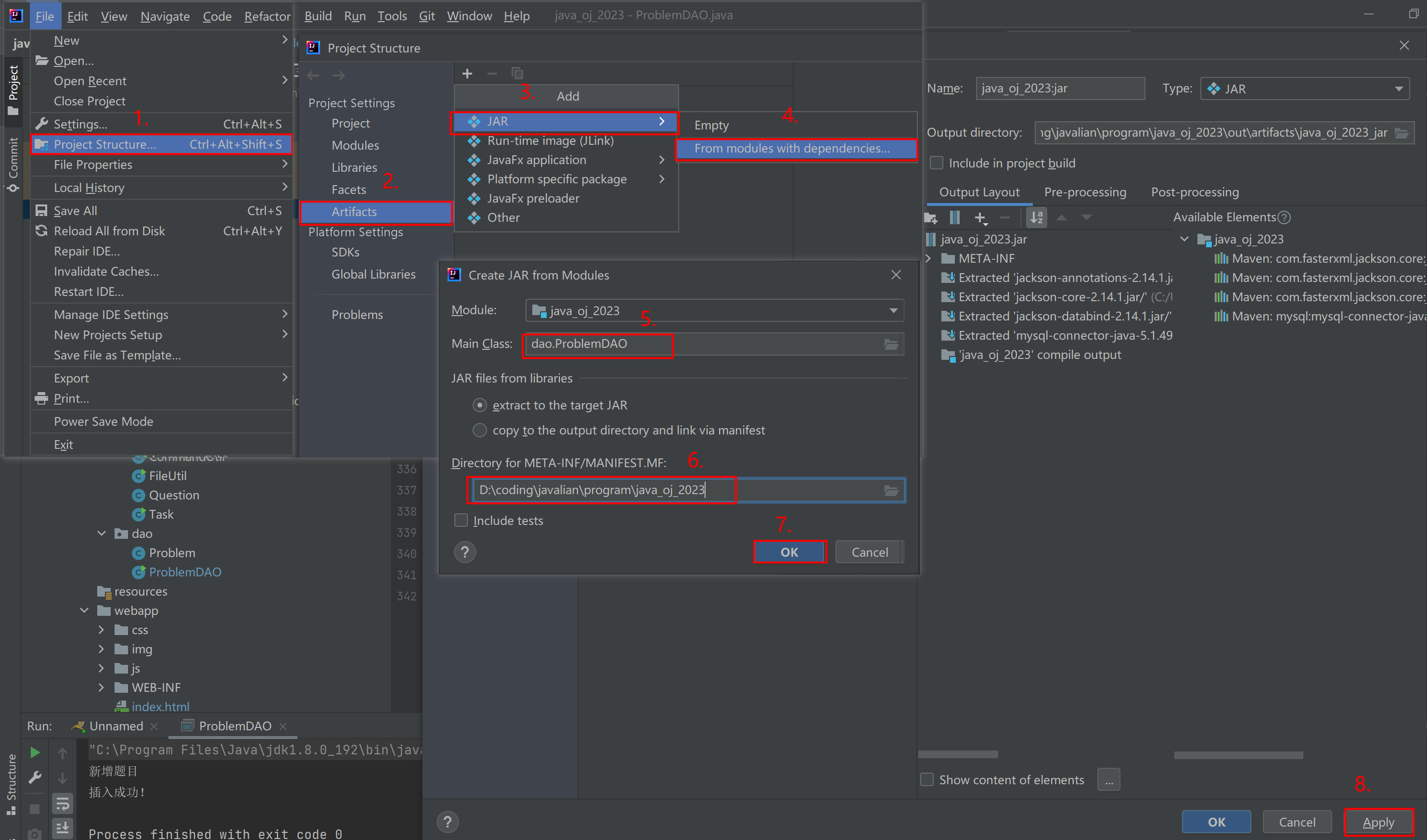
- 将jar包构造出来:





















 1476
1476











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








