
目录
前言:
最近太忙以至于很久没有更新了,接下来继续努力,一起学习
HashSet
HashSet介绍
 HashSet代码复现
HashSet代码复现
class MyHashSet {
private static final int max = 1000;
private LinkedList[] data;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyHashSet() {
data = new LinkedList[max];
for (int i = 0; i < max; ++i) {
data[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
}
public void add(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = data[h].iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer temp = iterator.next();
if (temp == key) {
return;
}
}
data[h].offerLast(key);
}
public void remove(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = data[h].iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer temp = iterator.next();
if (temp == key) {
data[h].remove(temp);
return;
}
}
}
/** Returns true if this set contains the specified element */
public boolean contains(int key) {
int h = hash(key);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = data[h].iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer temp = iterator.next();
if (temp == key) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static int hash(int key) {
return key % max;
}
}练习

class Solution {
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
for(int i:nums){
if(!set.add(i))return true;
}
return false;
}
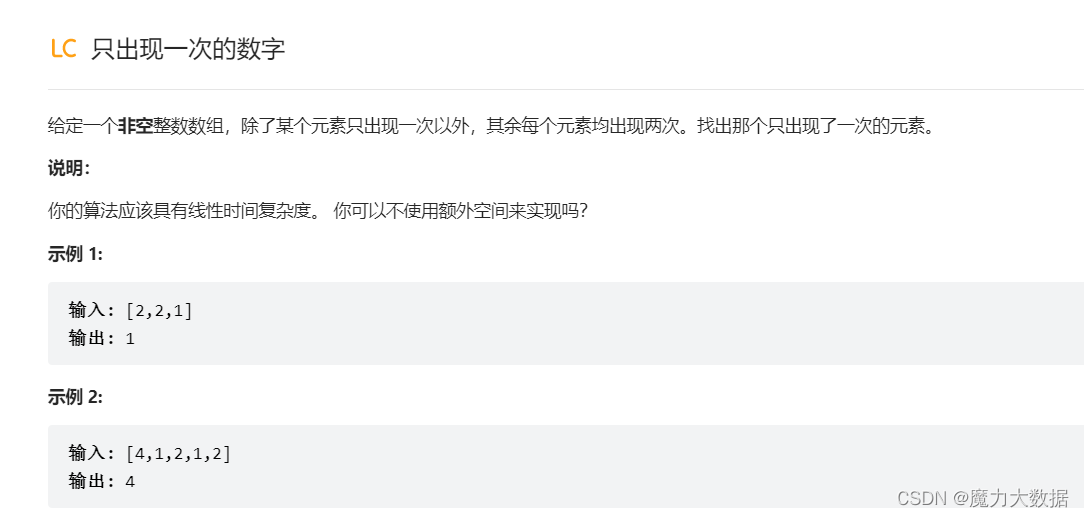
}
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set=new HashSet<>();
for(int i:nums){
if(!set.add(i))set.remove(i);
}
int result=0;
for(Integer i:set)
result=i;
return result;
}
} 两个数组的交集
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> set1=new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> set2=new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> set3=new HashSet<>();
for(int i:nums1){
if(!set1.add(i))continue;
}
for(int i:nums2){
if(!set2.add(i))continue;
}
for(Integer num:set1){
if(set2.contains(num) && !set3.contains(num))set3.add(num);
}
int i=0;
int[] num3=new int[set3.size()];
for(Integer num:set3){
num3[i]=num;
i++;
}
return num3;
}
}HashMap
HashMap代码复现
class MyHashMap {
private final int MAX_LEN = 100000; // the amount of buckets
private List<Pair<Integer, Integer>>[] map; // hash map implemented by array
/** Returns the corresponding bucket index. */
private int getIndex(int key) {
return key % MAX_LEN;
}
/** Search the key in a specific bucket. Returns -1 if the key does not existed. */
private int getPos(int key, int index) {
// Each bucket contains a list.
List<Pair<Integer, Integer>> temp = map[index];
if (temp == null) {
return -1;
}
// Iterate all the elements in the bucket to find the target key.
for (int i = 0; i < temp.size(); ++i) {
if (temp.get(i).getKey() == key) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyHashMap() {
map = (List<Pair<Integer, Integer>>[])new ArrayList[MAX_LEN];
}
/** value will always be positive. */
public void put(int key, int value) {
int index = getIndex(key);
int pos = getPos(key, index);
if (pos < 0) {
// Add new (key, value) pair if key is not existed.
if (map[index] == null) {
map[index] = new ArrayList<Pair<Integer, Integer>>();
}
map[index].add(new Pair(key, value));
} else {
// Update the value if key is existed.
map[index].set(pos, new Pair(key, value));
}
}
/** Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or -1 if this map contains no mapping for the key */
public int get(int key) {
int index = getIndex(key);
int pos = getPos(key, index);
if (pos < 0) {
return -1;
} else {
return map[index].get(pos).getValue();
}
}
/** Removes the mapping of the specified value key if this map contains a mapping for the key */
public void remove(int key) {
int index = getIndex(key);
int pos = getPos(key, index);
if (pos >= 0) {
map[index].remove(pos);
}
}
}
/**
* Your MyHashMap object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyHashMap obj = new MyHashMap();
* obj.put(key,value);
* int param_2 = obj.get(key);
* obj.remove(key);
*/练习
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(target-nums[i])){
return new int[]{map.get(target-nums[i]),i};
}else{
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
}
return new int[0];
}
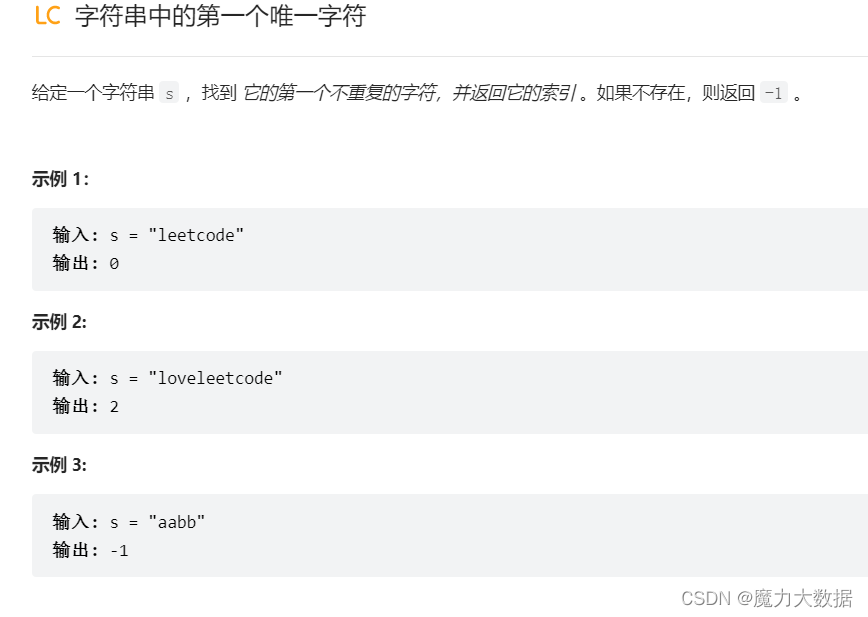
}
这一题可以课后做做,评论区讨论讨论不同算法。
掌握哈希集合和哈希映射对我们做算法题帮助很大,下一期将分享回溯算法的一些经典例题























 147
147











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








