目录
前言
最近有人问我相关这个迷宫实现最短路径的代码怎么写,然后我听说这个好像也是大学时一些算法设计与分析的课设题目,然后老师要求一定要用一个已成熟的算法实现求取最短路径,那么我在这个文章里所使用的算法是A*算法。
那么A*算法呢,简单介绍下,
A*(A-Star)算法是一种静态路网中求解最短路径最有效的直接搜索方法,也是许多其他问题的常用启发式算法。
同时它也是最有效的直接搜索算法,之后涌现了很多预处理算法(如CH),在线查询效率是A*算法的数千甚至上万倍。
公式表示为: f*(n)=g*(n)+h*(n)。
其中, f*(n) 是从初始状态经由状态n到目标状态的最小代价估计;
g*(n) 是在状态空间中从初始状态到状态n的最小代价;
h*(n) 是从状态n到目标状态的路径的最小估计代价;
真实h(n)的选取:
保证找到最短路径(最优解的)条件,关键在于估价函数f(n)的选取(或者说h(n)的选取)。
以h(n)表达状态n到目标状态估计的距离,那么h(n)的选取大致有如下三种情况:
(1)如果h(n)< h*(n),这种情况下,搜索的点数多,搜索范围大,效率低。但能得到最优解。
(2)如果h(n)=h*(n),此时的搜索效率是最高的。
(3)如果 h(n)>h*(n),搜索的点数少,搜索范围小,效率高,但不能保证得到最优解。
一,需求分析
1,需求
以下是这个迷宫设计方面的要求(你可以理解为万恶的甲方提出的功能需求):
程序开始运行时显示一个迷宫地图,迷宫中央有一只老鼠,迷宫的右下方有一个粮仓.游戏的任务是使用键盘上的方向键操纵老鼠在规定的时间内走到粮仓处。而在本次项目中,系统内部的功能要求如下:
- 老鼠形象可辨认,可用键盘操纵老鼠上下左右移动;
- 迷宫的墙足够结实,老鼠不能穿墙而过;
- 正确检测结果,若老鼠在规定时间内走到粮仓处,提示成功,否则提示失败;
- 添加编辑迷宫功能,可修改当前迷宫,修改内容:墙变路,路变墙;
- 找出走出迷宫的所有路径,以及最短路径;
- 利用序列化功能实现迷宫地图文件的存盘和读出等功能。
相应的限制条件如下:
- 建立可编辑窗口,并实现窗口内贴图及覆盖;
- 老鼠移动坐标时需根据目标坐标下是否为墙来决定行为是否被准许;
- 以时间和抵达终点为双重通关结束信号,需将老鼠移动并显示窗口和时间计时器动态并发,并设立相应结束响应器,一方结束则另一方立即终止;
- 添加编辑迷宫功能,可修改当前迷宫,修改内容:墙变路,路变墙;
- 可显示最优解答案;
- 对游戏数据加以文件处理(保存和读取)。
2,分析
(1)贴图诉求
首先呢,我是用easyx库建立的窗口,并直接在原窗口上进行贴背景图以及选项鼠标响应后仍然以贴图实现载入地图资源的(这里说明一下,我所有的图都是从百度网上直接免费下载来的,如有侵权,麻烦告知我一声,立马删,谢谢)
那么保护措施已经上了,废话不多说,直接上图,封面如下:

然后这个墙体和路我用的是这两张图:


然后是老鼠和猫的图:



(2)算法流程图
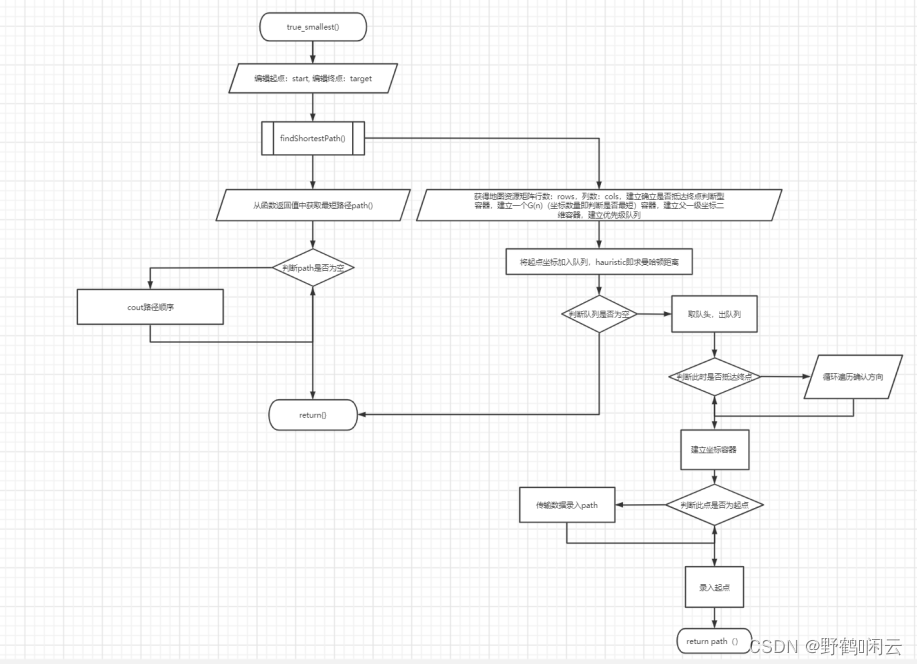
二,具体框架
1,所需全局变量
(1)地图资源:二维数组(矩阵)
在这里,作者采用的是将地图矩阵录入到vector容器里面,其中数字1代表墙体,0代表通路,2和3代表猫。
vector<vector<int>> Map = {
{ 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,3,1 },
{ 1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,1 },
{ 1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1 },
{ 1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,1 },
{ 1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1 },
{ 1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,1 },
{ 1,0,1,2,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1 },
{ 1,0,1,1,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1 },
{ 1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1 },
{ 1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,2,0,0,0,1 },
{ 1,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1 },
{ 1,0,1,0,1,0,0,1,1,0,1,1,1,1,0,0,1,0,3,1 },
{ 1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1 },
{ 1,2,1,0,1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1 },
{ 1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1 },
};(2)线程相关构造
typedef void (*func)();
bool game_over = false;2,多线程并发执行
首先,在上述代码中,先建立一个空的、无参的函数指针func,然后将你所需要并发执行的函数地址放入vector<func>容器下,在引入thread头文件后利用C11函数调用emplace_back将这两个函数放入多线程队列中去,最后调用join将子线程加入等待队列(此时线程实体已结束)。
vector<func> func_vec = { &work, &time };
vector<std::thread> thread_vec;
for (func& f : func_vec)
thread_vec.emplace_back(std::thread(f));
for (std::thread& t : thread_vec)
t.join();三,函数封装
1,算法.cpp
(1)引入头文件
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <limits>(2)节点结构体
struct Node {
int row;
int col;
int gScore;
int fScore;
//构造函数
Node(int r, int c, int g, int f) : row(r), col(c), gScore(g), fScore(f) {}
};(3)路径计算结构体(后面建立优先级队列用)
struct CompareNodes {
bool operator()(const Node& node1, const Node& node2) {
return node1.fScore > node2.fScore;
}
};(4)方向性操作
//方向性操作
vector<pair<int, int>> neighbor_direction = { {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0} };(5)是否超出边框
//是否超出边框
bool isValid(int row, int col, int rows, int cols) {
return (row >= 0 && row < rows && col >= 0 && col < cols);
}(6)曼哈顿距离
//曼哈顿距离
int heuristic(const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b) {
return abs(a.first - b.first) + abs(a.second - b.second);
}(7)找寻最短路径
vector<pair<int, int>> findShortestPath(const vector<vector<int>>& matrix, const pair<int, int>& start, const pair<int, int>& target) {
int rows = matrix.size();
int cols = matrix[0].size();
//建立确立是否抵达终点判断型容器
vector<vector<bool>> visited(rows, vector<bool>(cols, false));
//建立一个G(n)(坐标数量即判断是否最短)容器
vector<vector<int>> gScores(rows, vector<int>(cols, numeric_limits<int>::max()));
//建立父一级坐标二维容器
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> parents(rows, vector<pair<int, int>>(cols));
//建立优先级队列
priority_queue<Node, vector<Node>, CompareNodes> openList;
gScores[start.first][start.second] = 0;
//加入队列,hauristic即求曼哈顿距离
openList.push(Node(start.first, start.second, 0, heuristic(start, target)));
while (!openList.empty()) {
//取队头
Node current = openList.top();
//出队列
openList.pop();
int row = current.row;
int col = current.col;
if (make_pair(row, col) == target) {//抵达终点
//建立坐标容器
vector<pair<int, int>> path;
while (make_pair(row, col) != start) {
//将当前坐标录入path容器
path.push_back(make_pair(row, col));
//父坐标回弹至上一级
pair<int, int> parent = parents[row][col];
row = parent.first;
col = parent.second;
}
//录入起点
path.push_back(start);
//翻转path容器内部顺序,由于是反向获取的坐标路径
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
return path;
}
//未抵达终点
visited[row][col] = true;
//循环遍历确认方向算法(核心算法)
for (const auto& dir : neighbor_direction) {
//建立新坐标(默认先向右)
int newRow = row + dir.first;
int newCol = col + dir.second;
//判断新坐标是否越界,判断是否撞墙,判断还未抵达终点
if (isValid(newRow, newCol, rows, cols) && matrix[newRow][newCol] == 0 && !visited[newRow][newCol]) {
//计算新的G(n)值,并将之与旧值比对
int gScore = gScores[row][col] + heuristic(make_pair(row, col), make_pair(newRow, newCol));
if (gScore < gScores[newRow][newCol]) {
gScores[newRow][newCol] = gScore;
parents[newRow][newCol] = make_pair(row, col);
int fScore = gScore + heuristic(make_pair(newRow, newCol), target);
//将新坐标入队
openList.push(Node(newRow, newCol, gScore, fScore));
}
}
}
}
return {}; // No path found
}(8)整体调用函数
void true_smallest() {
//确立起终点
pair<int, int> start = make_pair(1, 1);
pair<int, int> target = make_pair(14, 18);
//调用A*算法确立最短路径
vector<pair<int, int>> path = findShortestPath(Map, start, target);
//这里我选择用方向来表示,我觉得这样比较清晰简单明了
vector<string> arrow_symbols = { "→", "←", "↓", "↑" };
if (!path.empty()) {
cout << "最短路径如下:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < path.size() - 1; i++) {
const auto& current = path[i];
const auto& next = path[i + 1];
int dx = next.first - current.first;
int dy = next.second - current.second;
string arrow;
if (dx == 1 && dy == 0)
arrow = arrow_symbols[2];
// ↓
else if (dx == -1 && dy == 0)
arrow = arrow_symbols[3];
// ↑
else if (dx == 0 && dy == 1)
arrow = arrow_symbols[0];
// →
else if (dx == 0 && dy == -1)
arrow = arrow_symbols[1];
// ←
//cout << "(" << current.first << ", " << current.second << ") " << arrow << " ";
cout << arrow << " ";
}
//cout << "(" << path.back().first << ", " << path.back().second << ")" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "未找到最短路径!" << endl;
}
}2,easy.cpp
(1)引入头文件
#include <time.h>
#include<Windows.h>
#include<graphics.h>//调用EasyX图形库函数
#include<conio.h>//用于调用getch()函数
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <thread> (2) 引入相关全局变量
extern vector<vector<int>> Map;
extern void true_smallest();(3)设置计时器函数
void time()
{
int hour = 0, min = 0, sec = 60;
time_t time_sec = 0; //time_t相当于long int
time_t old_sec = 0;
old_sec = time_sec; //更新旧的秒数
while (hour > 0 || min > 0 || sec > 0)
{
if (game_over) {
return;
}
time(&time_sec); //获取当前秒数(1970-1-1 00:00:00到现在),然后将秒数保存到time_t变量
if (time_sec != old_sec) //如果秒数改变(计时达到1秒)
{
old_sec = time_sec; //更新旧的秒数
if (sec > 0)
sec--; //计时秒数减1
else
{
sec = 59; //如果原秒数为0,则变为59
if (min > 0)
min--; //计时分钟减1
else
{
min = 59; //如果分钟数为0,则变为59
hour--; //计时小时数减1
}
}
cout << "还有多久就会被猫捉住:" << endl;
cout << "倒计时——" << hour << "时:" << min << "分:" << sec << "秒..." << endl;
}
}
game_over = true;
MessageBox(NULL, "很抱歉,您已超时,游戏结束!", "失败", MB_OK | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
}(4)创建初始化窗口
void start() {
//SHOWCONSOLE 展示控制台 NOCLOSE 不能点x关闭 NOMNOMINIMIZE 不能最小化
initgraph(1000, 800, SHOWCONSOLE | NOCLOSE);//建立图形化窗口(单位:像素)
HWND h = GetHWnd();//获得窗口权柄
SetWindowText(h, "猫和老鼠");//修改窗口标题
setbkcolor(WHITE);//setbkcolor(RGB(0, 0, 0));
cleardevice();//清除原本的背影屏幕颜色(必须先进行设置背景色,再进行清除)
IMAGE fengmian;
loadimage(&fengmian, "封面.jpg", 1000, 800, true);
putimage(0, 0, &fengmian);
setfillcolor(RED);//设置填充色为RED
setlinecolor(YELLOW);//设置线条颜色
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 5);//设置线条风格,宽度
//画圆 circle(x, y, 半径) 自带边框填充fillcircle(x, y, 半径)
fillcircle(0, 0, 50);
setfillcolor(WHITE);//设置填充色
setlinecolor(BLUE);//设置线条颜色
setlinestyle(PS_SOLID, 3);//设置线条风格,宽度
settextcolor(BLACK);//设置文字颜色
settextstyle(30, 10, "楷体");//设置文字大小
setbkmode(TRANSPARENT);//设置文字透明背景
//矩形(多用于按钮) rectangle(起点x, 起点y, 终点x, 终点y) 自带边框填充fillrectangle(同上)无边框填充solidrectangle()
//设置文字居中
RECT rect1 = { 50, 570, 150, 600 };
fillrectangle(50, 570, 150, 600);
drawtext("开始游戏", &rect1, DT_CENTER | DT_VCENTER | DT_SINGLELINE);
RECT rect2 = { 50, 620, 150, 650 };
fillrectangle(50, 620, 150, 650);
drawtext("编辑地图", &rect2, DT_CENTER | DT_VCENTER | DT_SINGLELINE);
RECT rect3 = { 50, 670, 150, 700 };
fillrectangle(50, 670, 150, 700);
drawtext("最短路径", &rect3, DT_CENTER | DT_VCENTER | DT_SINGLELINE);
//鼠标事件监听 左键 右键
while (true) {
MOUSEMSG msg = GetMouseMsg();
//鼠标操作
if (msg.x >= 50 && msg.x <= 150 && msg.y >= 570 && msg.y <= 600 && msg.uMsg == WM_LBUTTONDOWN) {
int a = MessageBox(NULL, "是否开始游戏?", "老鼠出迷宫", MB_YESNO | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
if (a == 6) {
break;
}
else {
continue;
}
}
if (msg.x >= 50 && msg.x <= 150 && msg.y >= 620 && msg.y <= 650 && msg.uMsg == WM_LBUTTONDOWN) {
int a = MessageBox(NULL, "是否编辑地图?", "老鼠出迷宫", MB_YESNO | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
if (a == 6) {
change_Map();
}
continue;
}
if (msg.x >= 50 && msg.x <= 150 && msg.y >= 670 && msg.y <= 700 && msg.uMsg == WM_LBUTTONDOWN) {
int a = MessageBox(NULL, "是否显示当前最短路径?", "老鼠出迷宫", MB_YESNO | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
if (a == 6) {
true_smallest();
}
continue;
}
}
cleardevice();//清屏
}(5) 初始化地图
void InitMap() {
IMAGE tom_l, tom_r, rode, wall, end;
loadimage(&tom_l, "汤姆左.jpg", 50, 50);
loadimage(&tom_r, "汤姆右.jpg", 50, 50);
loadimage(&rode, "可落脚.jpg", 50, 50);
loadimage(&wall, "墙体.jpg", 50, 50);
loadimage(&end, "出口.jpg", 50, 50);
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
if (Map[i][j] == 0) {
putimage(j * 50, i * 50, &rode);
}
else if (Map[i][j] == 1) {
putimage(j * 50,i * 50, &wall);
}
else if (Map[i][j] == 2) {
putimage(j * 50, i * 50, &tom_l);
}
else {
putimage(j * 50, i * 50, &tom_r);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
putimage(900, 700, &end);
}(6) 动态贴图
void work() {
int x = 50, y = 50;
IMAGE jierui,rode, fail;
loadimage(&jierui, "杰瑞.jpg", 50, 50);
loadimage(&rode, "可落脚.jpg", 50, 50);
loadimage(&fail, "闯关失败.jpg", 1000, 800);
while (1) {
if (game_over) {
return;
}
putimage(x, y, &jierui);
char c = _getch();
switch (c) {
case 72:
if (Map[y / 50 - 1][x / 50] == 0) {
putimage(x, y, &rode);
y -= 50;
break;
}
else if (Map[y / 50 - 1][x / 50] == 1) {
break;
}
else if (Map[y / 50 - 1][x / 50] == 2 || Map[y / 50 - 1][x / 50] == 3) {
putimage(0, 0, &fail);
game_over = true;
MessageBox(NULL, "很抱歉,你被汤姆猫抓住了,游戏结束!", "失败", MB_OK | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
return;
}
case 80:
if (Map[y / 50 + 1][x / 50] == 0) {
putimage(x, y, &rode);
y += 50;
break;
}
else if (Map[y / 50 + 1][x / 50] == 1) {
break;
}
else if (Map[y / 50 + 1][x / 50] == 2 || Map[y / 50 + 1][x / 50] == 3) {
putimage(0, 0, &fail);
game_over = true;
MessageBox(NULL, "很抱歉,你被汤姆猫抓住了,游戏结束!", "失败", MB_OK | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
return;
}
case 75:
if (Map[y / 50][x / 50 - 1] == 0) {
putimage(x, y, &rode);
x -= 50;
break;
}
else if (Map[y / 50][x / 50 - 1] == 1) {
break;
}
else if (Map[y / 50][x / 50 - 1] == 2 || Map[y / 50][x / 50 - 1] == 3) {
putimage(0, 0, &fail);
game_over = true;
MessageBox(NULL, "很抱歉,你被汤姆猫抓住了,游戏结束!", "失败", MB_OK | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
return;
}
case 77:
if (Map[y / 50][x / 50 + 1] == 0) {
putimage(x, y, &rode);
x += 50;
break;
}
else if (Map[y / 50][x / 50 + 1] == 1) {
break;
}
else if (Map[y / 50][x / 50 + 1] == 2 || Map[y / 50][x / 50 + 1] == 3) {
putimage(0, 0, &fail);
game_over = true;
MessageBox(NULL, "很抱歉,你被汤姆猫抓住了,游戏结束!", "失败", MB_OK | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
return;
}
}
if (x == 900 && y == 700) {
game_over = true;
MessageBox(NULL, "恭喜你未被猫捉住并成功到达目的地,游戏通关!", "胜利", MB_OK | MB_SETFOREGROUND);
break;
}
}
system("pause");//按任意键继续
closegraph();//关闭窗口
}(7)修改地图函数
void change_Map() {
cout << "地图资源如下:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
cout << Map[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout<< "请在所弹出输入框中输入您所想要修改的地图横纵坐标..." << endl;
//弹出输入账号窗口界面
char buff1[128] = { 0 };
InputBox(buff1, 128, "地图横坐标");
int value1 = atoi(buff1);
char buff2[128] = { 0 };
InputBox(buff2, 128, "地图纵坐标");
int value2 = atoi(buff2);
cout << "请在所弹出输入框中输入您所想要修改的地图加载资源..." << endl;
cout << "0:路 1:墙 2:猫(左) 3:猫(右)..." << endl;
char buff3[128] = { 0 };
InputBox(buff3, 128, "修改参数数值");
int value3 = atoi(buff3);
Map[value2][value1] = value3;
cout << "恭喜你,地图修改成功!" << endl;
}四,加入文件相关操作
1,前置工作
这里为代码方便使用,我是直接将文件信息数据存贮到文件里去了。
所以在这里需要你们在自己桌面上建立一个文本文档,用来存贮地图信息。
2,文件操作
(1)从文件中读取地图信息
void readData()
{
FILE* fp; //用于文件操作
int i = 0;//初始化,用于作结构体数组下标
//从文件中取出账户信息并存入当前操作系统中
/*a+:以附加方式打开可读/写的文件。若文件不存在,则会创建该文件,如果文件存在,则写入的数据会被加到文件尾后,即文件原先的内容会被保留(EOF符不保留)。*/
if ((fp = fopen("D:\\地图载入信息.txt", "a+")) == NULL)
{
printf("数据文件无法打开!\n");//出错预处理
exit(0);//exit函数直接结束当前进程
}
/*fscanf其功能为根据数据格式,从输入流(文件)中读入数据,存储到结构体数组中,遇到空格和换行时结束。*/
do {
fscanf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d", &Map[i][0], &Map[i][1], &Map[i][2], &Map[i][3], &Map[i][4], &Map[i][5], &Map[i][6], &Map[i][7], &Map[i][8], &Map[i][9],
&Map[i][10], &Map[i][11], &Map[i][12], &Map[i][13], &Map[i][14], &Map[i][15], &Map[i][16], &Map[i][17], &Map[i][18], &Map[i][19]);
i++;
} while (i < 16);
fclose(fp);//关闭文件
return;
}(2)将地图最终数据保存到文件中
void writeData()
{
FILE* fp; //用于文件操作
int i = 0;
//保存余额
/*w:打开只写文件,若文件存在则文件长度清为零,即该文件内容会消失;若文件不存在则创建该文件。*/
if ((fp = fopen("D:\\地图载入信息.txt", "w")) == NULL)
{
printf("数据文件无法打开!\n");
exit(0);//exit函数直接结束当前进程
}
do {
fprintf(fp, "%d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d %d\n", Map[i][0], Map[i][1], Map[i][2], Map[i][3], Map[i][4], Map[i][5], Map[i][6], Map[i][7], Map[i][8], Map[i][9],
Map[i][10], Map[i][11], Map[i][12], Map[i][13], Map[i][14], Map[i][15], Map[i][16], Map[i][17], Map[i][18], Map[i][19]);
i++;
} while (i < 16);
fclose(fp);//关闭文件
}五,main主函数
void welcome() {
readData();
start();
InitMap();
vector<func> func_vec = { &work, &time };
vector<std::thread> thread_vec;
for (func& f : func_vec)
thread_vec.emplace_back(std::thread(f));
for (std::thread& t : thread_vec)
t.join();
writeData();
}
int main() {
welcome();
return 0;
}六,运行结果截图
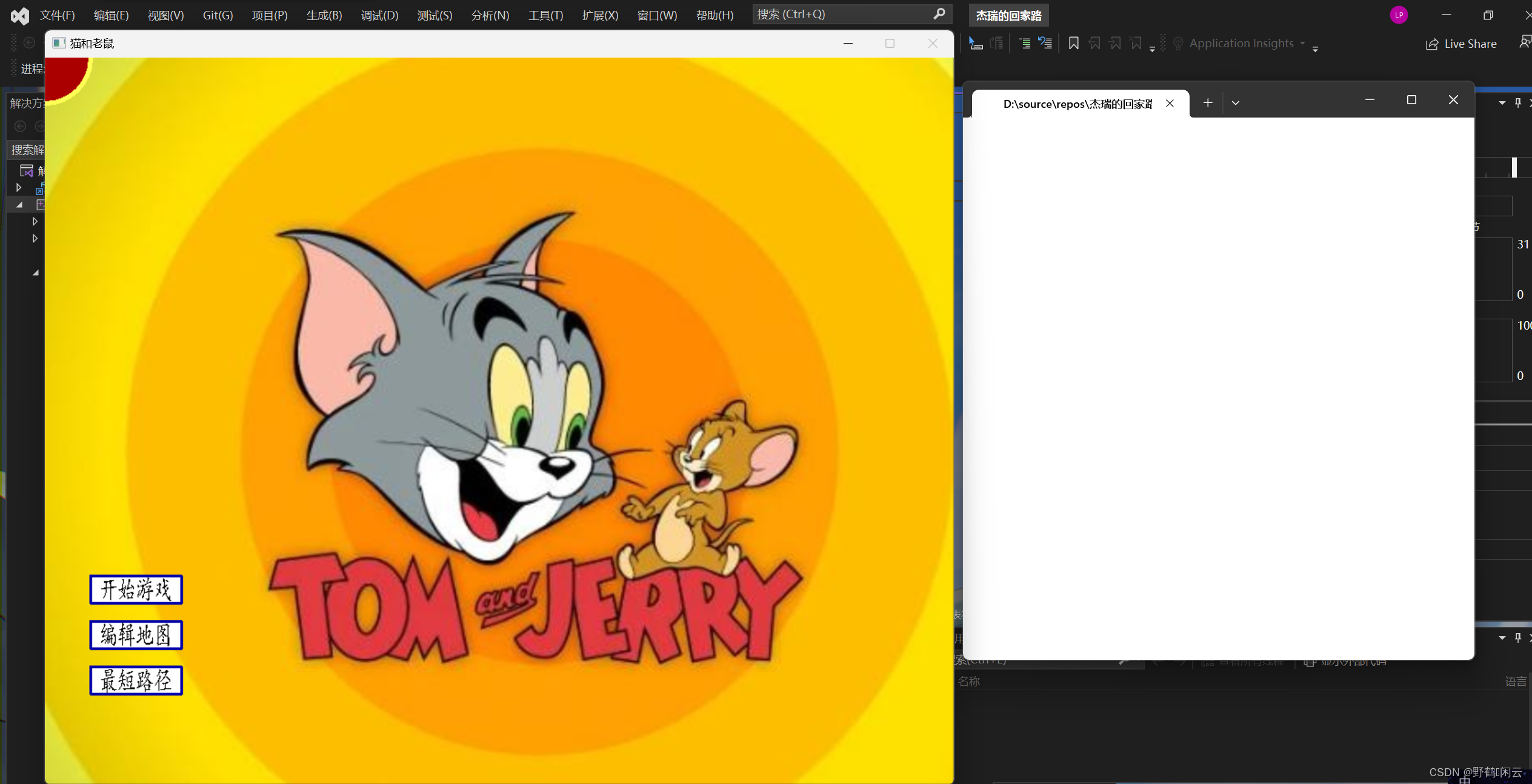
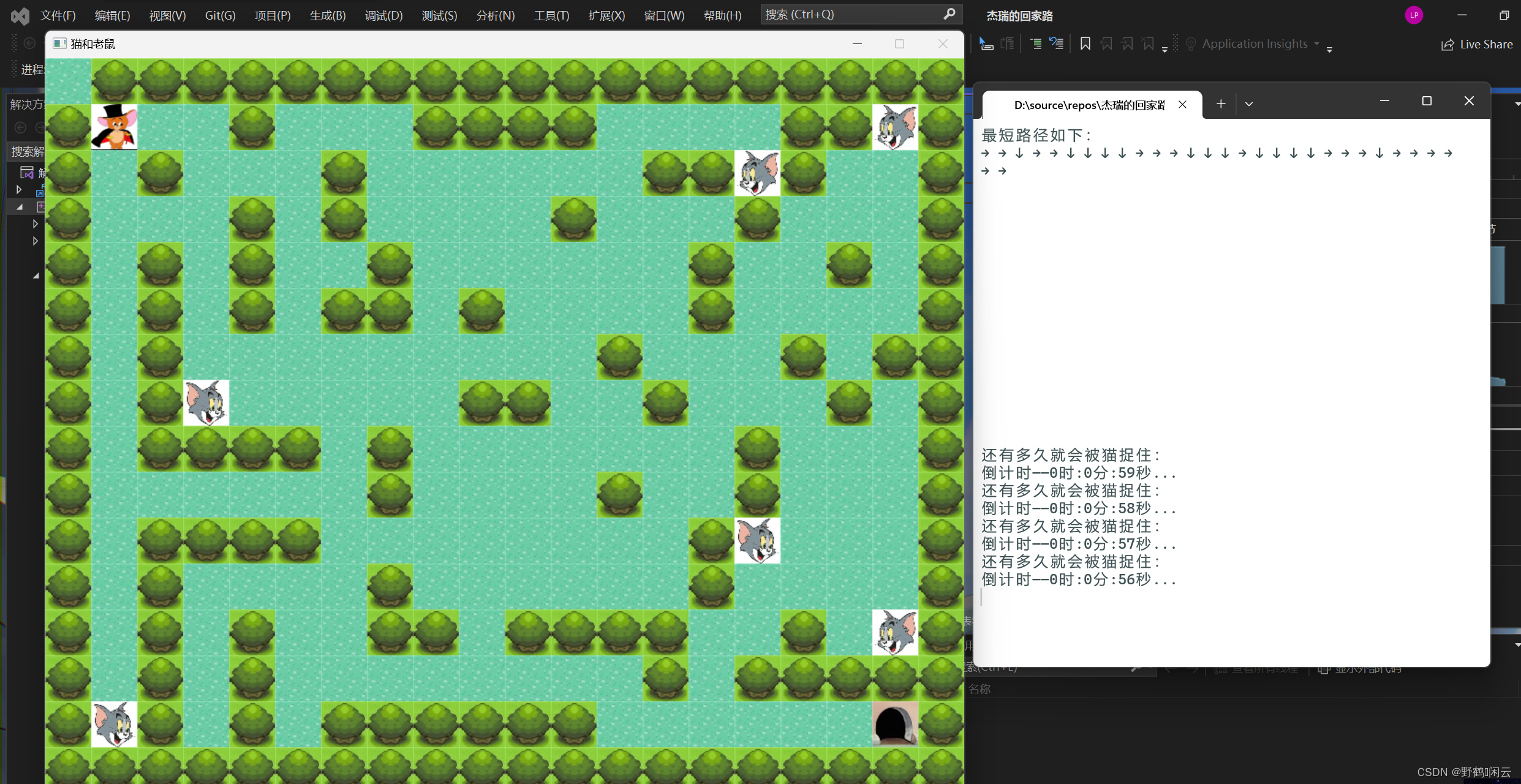
七,心得体会
作为算法课程设计的题目,我自认为我写的代码已经足够你使用去提交给老师作为课程设计,那么多线程并发和这个最短路径算法对于这门课程来说我感觉是必须掌握的知识点,然后easyx库的话如果你有把握用QT或者更好的图形化工具的话,那你也可以不用我这个easyx库。
此外,整体上来说功能模块完成的还算完整,缺点是没有展示出所有可行性路径(不过问题不大,因为我觉得游戏嘛,给出最优解就算了,给出所有通解什么的纯属扯淡,哪个游戏会直接空口白牙给出你全部的结局答案,那还叫游戏?)。
整体代码量还好,但是为了功能完整性,所以还是写了400多行![]()
![]()
![]() 。
。
最后:
(本文仅供学习时参考,如有错误,纯属作者技术不到位,不足之处请多指教,勿喷,谢谢)




















 387
387











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








