import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
import matplotlib.animation as animation
class Dijkstra:
def __init__(self, nums: int):
self.fig, self.ax = plt.subplots() # 初始画布
self.nums = nums # 随机点个数
self.points, self.nearPs = self.genPoints((1, 1000), (1, 1000)) # 生成点集
print(f"Points:{self.nearPs}")
self.startP, self.endP = self.findStartEndPoints() # 随机起终点
print(f"Start Point:{self.startP}\tEnd Point:{self.endP}")
self.wayList = self.dijkstra() # 获取路径
plt.gca().axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False) # 隐藏x轴
plt.gca().axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) # 隐藏y轴
# 点与点距离
def lengthP2P(self, p1, p2):
return int(math.sqrt(abs(p2[0] - p1[0]) ** 2 + abs(p2[1] - p1[1]) ** 2))
# 生成随机点与点关系
def genPoints(self, x, y):
points = []
nearPs = {}
x = [random.randint(x[0], x[1]) for i in range(self.nums)]
y = [random.randint(y[0], y[1]) for i in range(self.nums)]
for i in range(len(x)):
points.append((x[i], y[i]))
for p in points:
m = random.randint(1, int(math.sqrt(self.nums)))
nearPs[p] = {}
for i in range(m):
n = random.randint(0, len(points) - 1)
if p != points[n]:
nearPs[p][points[n]] = self.lengthP2P(p, points[n])
for p in nearPs.keys():
for k, v in nearPs.items():
if p == k:
pass
if p in v:
nearPs[p][k] = self.lengthP2P(p, k)
return points, nearPs
# 生成随机起点和终点
def findStartEndPoints(self):
start = random.choice(self.points)
end = random.choice(self.points)
if start == end:
start, end = self.findStartEndPoints()
return start, end
# 画初始图像点线图
def drawMap(self):
for p in self.points:
plt.scatter(p[0], p[1])
plt.annotate(text=(p[0], p[1]), xy=(p[0], p[1]))
for p, ps in self.nearPs.items():
for point in ps:
plt.plot((p[0], point[0]), (p[1], point[1]))
self.ax.scatter(self.startP[0], self.startP[1], s=250, c="green", marker="*")
self.ax.annotate((self.startP[0], self.startP[1]), xy=(self.startP[0], self.startP[1]))
self.ax.scatter(self.endP[0], self.endP[1], s=250, c="red", marker="*")
self.ax.annotate((self.endP[0], self.endP[1]), xy=(self.endP[0], self.endP[1]))
plt.pause(1)
plt.ioff()
plt.savefig("map", dpi=300)
# 算法
def dijkstra(self):
shortest_paths = {self.startP: (None, 0)}
current_node = self.startP
visited = set()
while current_node != self.endP:
visited.add(current_node)
destinations = self.nearPs[current_node]
weight_to_current_node = shortest_paths[current_node][1]
for next_node in destinations:
weight = self.nearPs[current_node][next_node] + weight_to_current_node
if next_node not in shortest_paths:
shortest_paths[next_node] = (current_node, weight)
else:
current_shortest_weight = shortest_paths[next_node][1]
if current_shortest_weight > weight:
shortest_paths[next_node] = (current_node, weight)
next_destinations = {node: shortest_paths[node] for node in shortest_paths if node not in visited}
if not next_destinations:
return "Route Not Possible"
current_node = min(next_destinations, key=lambda k: next_destinations[k][1])
path = []
while current_node is not None:
path.append(current_node)
next_node = shortest_paths[current_node][0]
current_node = next_node
path = path[::-1]
return path
# 画路径图
def drawFig(self):
print("Shortest Path:", self.wayList)
if type(self.wayList) == str:
return
for i in range(1, len(self.wayList)):
self.ax.plot((self.wayList[i - 1][0], self.wayList[i][0]), (self.wayList[i - 1][1], self.wayList[i][1]),
"-.",
color="black",
linewidth=3)
plt.pause(1)
plt.ioff()
plt.savefig("route.png", dpi=300)
plt.show()
# 动画更新函数
def update_ani(self, num, x, y, line):
line.set_data(x[:num], y[:num])
return line,
# 动画保存
def animate(self):
if type(self.wayList) == str:
return
xdata = [i[0] for i in self.wayList]
ydata = [i[1] for i in self.wayList]
line, = self.ax.plot(xdata, ydata, "-.",
color="black",
linewidth=3)
# 创建动画对象
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(self.fig, self.update_ani, frames=len(self.wayList) + 1,
fargs=[xdata, ydata, line],
interval=500, blit=True)
# 保存为gif
ani.save('output.gif', writer='imagemagick')
D = Dijkstra(8)
D.drawMap() # 地图
D.animate() # 动画
D.drawFig() # 展示
nearPs的示例如下:
{(823, 736): {(310, 428): 598, (400, 262): 635, (736, 534): 219},
(786, 790): {(19, 446): 840, (625, 559): 281},
(19, 446): {(400, 262): 423, (786, 790): 840, (348, 610): 367},
(400, 262): {(823, 736): 635, (310, 428): 188, (19, 446): 423},
(736, 534): {(310, 428): 438, (823, 736): 219},
(348, 610): {(19, 446): 367, (625, 559): 281, (310, 428): 185},
(310, 428): {(348, 610): 185, (823, 736): 598, (400, 262): 188, (736, 534): 438},
(625, 559): {(348, 610): 281, (786, 790): 281}}
其个数是初始化的nums大小。其格式是:{坐标A:{坐标B:AB距离},{坐标C:AC距离}}
点坐标由genPoints生成,其坐标范围可修改
代表某个点和其所有邻近点及其距离
参数可传入Dijkstra算法,获得最短路径
画图时定义起点和终点(绿⭐是起点,红⭐是终点)。
最后生成动画,其效果如下:
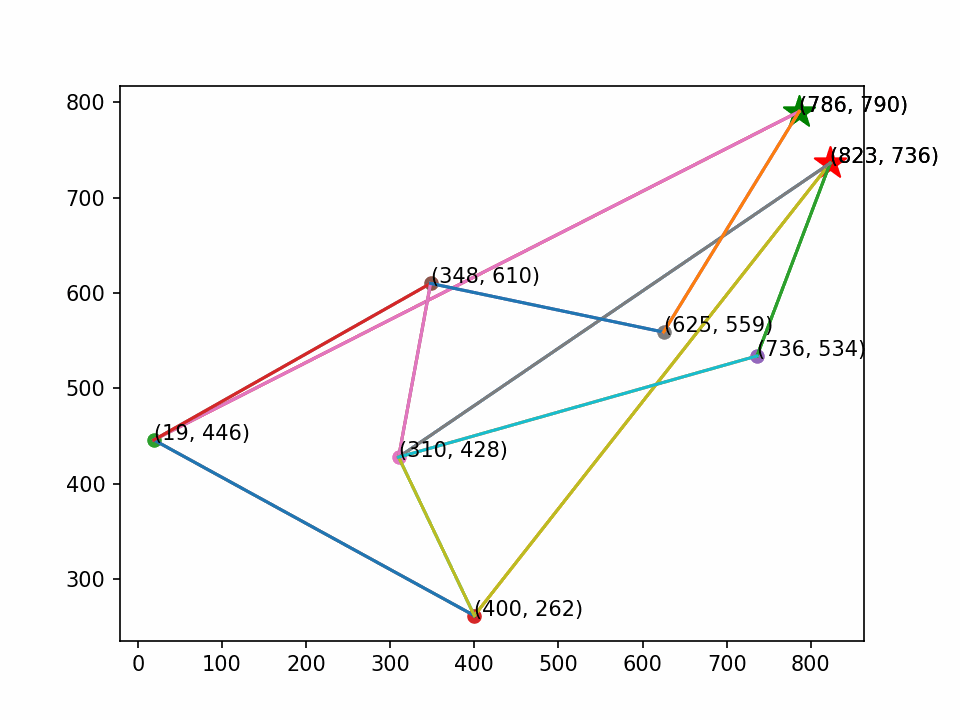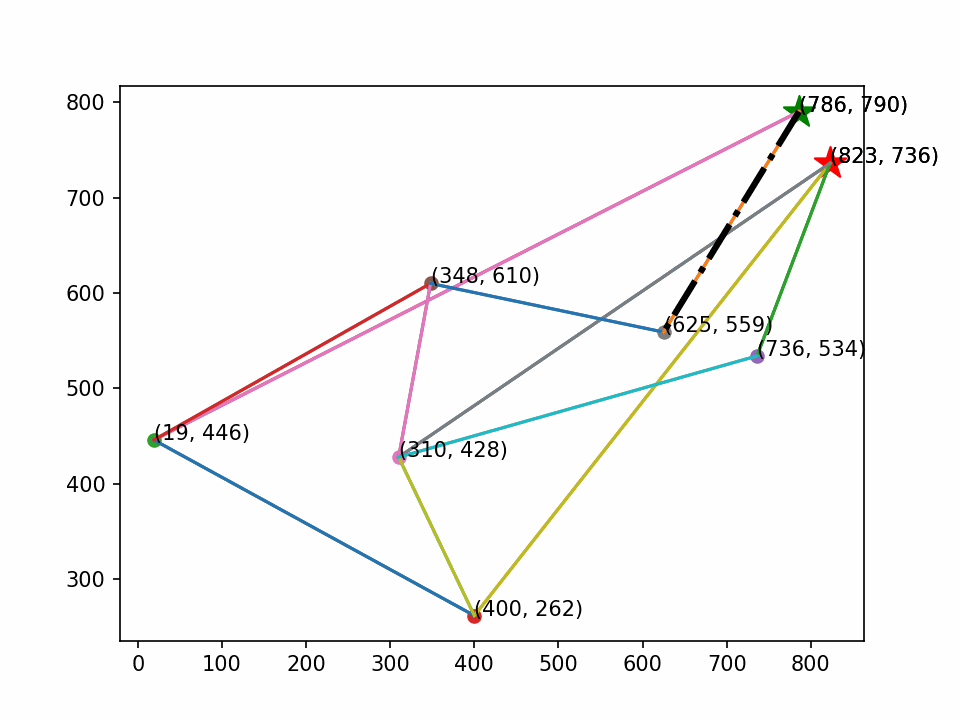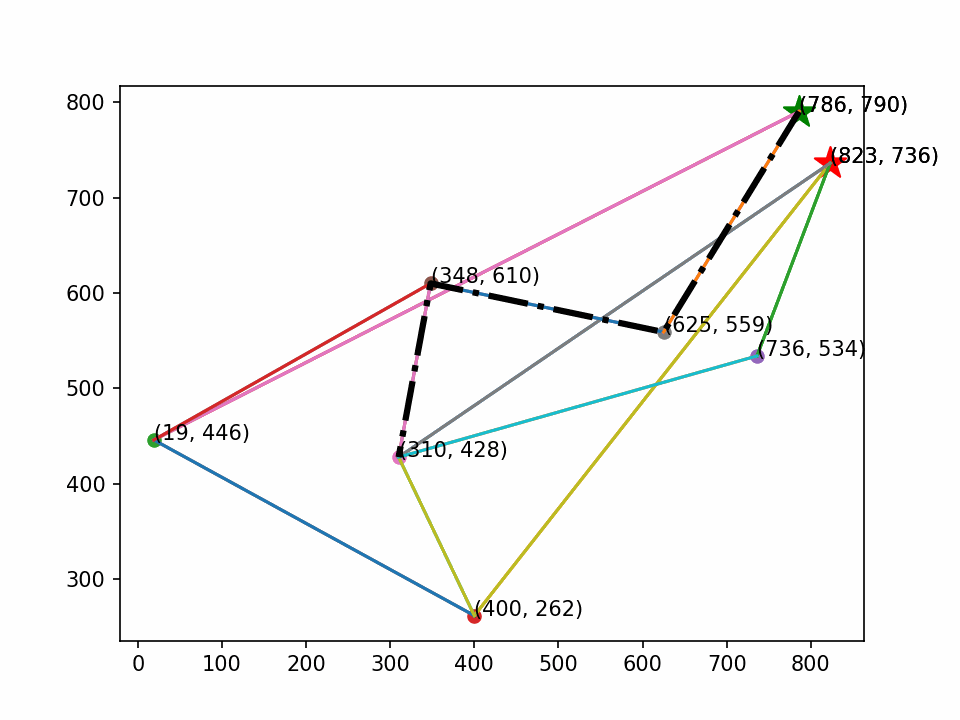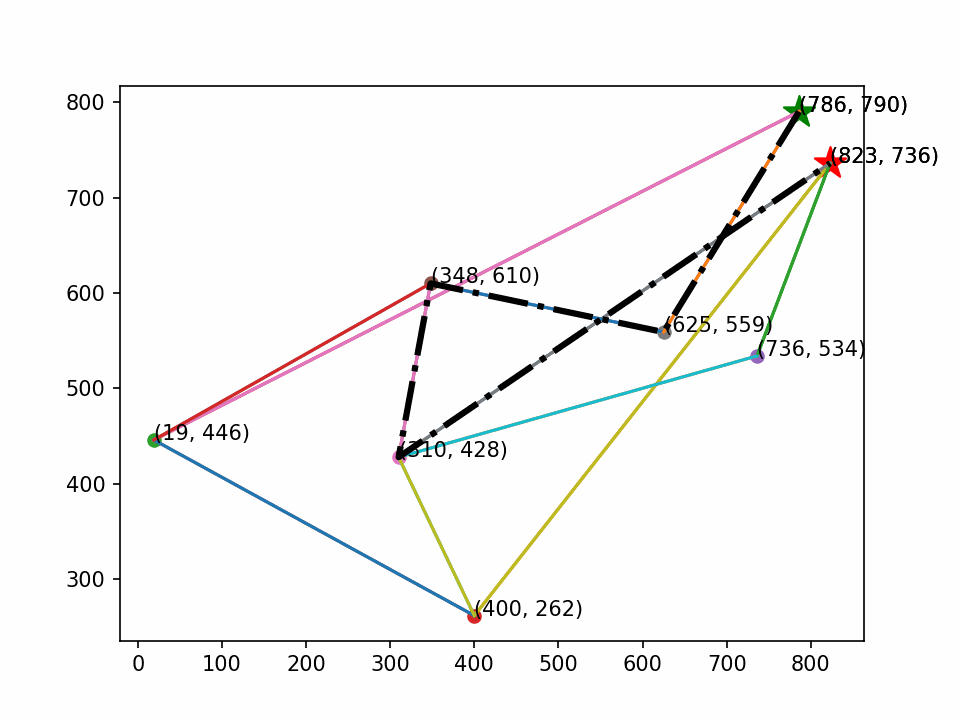























 1401
1401

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








