JUC并发编程系列文章
http://t.csdn.cn/UgzQi
文章目录
前言

一、AQS原理
1、概述


2、自定义不可重入锁
使用 AQS加 Lock 接口实现简单的不可重入锁
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.testThread29")
public class testThread29 {
/**
* T2需要等待 T1 释放锁后才能执行
* 16:44:09 [T1] c.testThread29 - locking....
* 16:44:10 [T1] c.testThread29 - unlocking....
* 16:44:10 [T2] c.testThread29 - locking....
* 16:44:10 [T2] c.testThread29 - unlocking....
*
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLock lock = new MyLock();
new Thread(()->{
lock.lock();
//不能两次加锁,因为是不可重入锁
//lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("locking....");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking....");
lock.unlock();
}
},"T1").start();
new Thread(()->{
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("locking....");
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking....");
lock.unlock();
}
},"T2").start();
}
}
//自定义锁,继承AQS同步器,重写几个重要的方法
final class MySync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
@Override
protected boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
//判断状态,传入 1 表示尝试加锁
if (acquires == 1){
//原子加锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
//锁住当前线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//释放锁
@Override
protected boolean tryRelease(int acquires) {
//判断状态,传入 1 表示尝试加锁,这里是解锁,传入 1,直接返回 false
if(acquires == 1) {
//释放锁时,如果锁没有被当前线程占用,当前线程不能释放锁,抛出异常。
if(getState() == 0) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
return false;
}
protected Condition newCondition() {
//直接返回一个添加变量
return new ConditionObject();
}
//判断锁的状态,1为已被持有加锁,0为未加锁没有线程持有
@Override
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() == 1;
}
}
//自定义不可重入锁,使用上面AQS自定义的同步器
class MyLock implements Lock {
//创建AQS对象
static MySync sync = new MySync();
@Override
// 尝试,不成功,进入等待队列
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
@Override
// 尝试,不成功,进入等待队列,可打断
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
@Override
// 尝试一次,不成功返回,不进入队列
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryAcquire(1);
}
@Override
// 尝试,不成功,进入等待队列,有时限
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(time));
}
@Override
// 释放锁
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
@Override
// 生成条件变量
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
}
3、心得
早期程序员会自己通过一种同步器去实现另一种相近的同步器,例如用可重入锁去实现信号量,或反之。这显然不够优雅,于是在 JSR166(java 规范提案)中创建了 AQS,提供了这种通用的同步器机制。
AQS 要实现的功能目标
● 阻塞版本获取锁 acquire 和非阻塞的版本尝试获取锁 tryAcquire
● 获取锁超时机制
● 通过打断取消机制
● 独占机制及共享机制
● 条件不满足时的等待机制
AQS的设计思想其实很简单
获取锁的逻辑
while(state 状态不允许获取) {
if(队列中还没有此线程) {
入队并阻塞
}
}
当前线程出队
释放锁的逻辑
if(state 状态允许了) {
恢复阻塞的线程(s)
}
要点
● 原子维护 state 状态
● 阻塞及恢复线程
● 维护队列
主要用到 AQS 的并发工具类
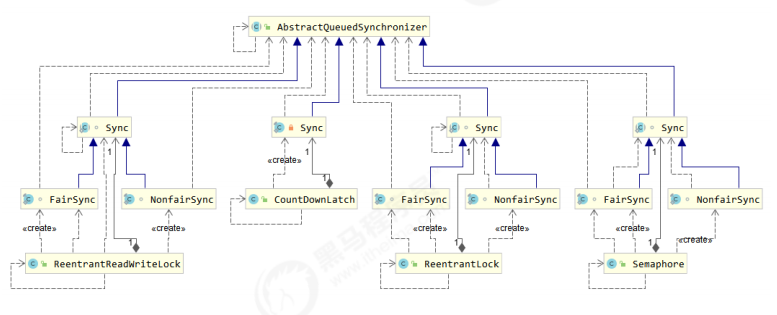
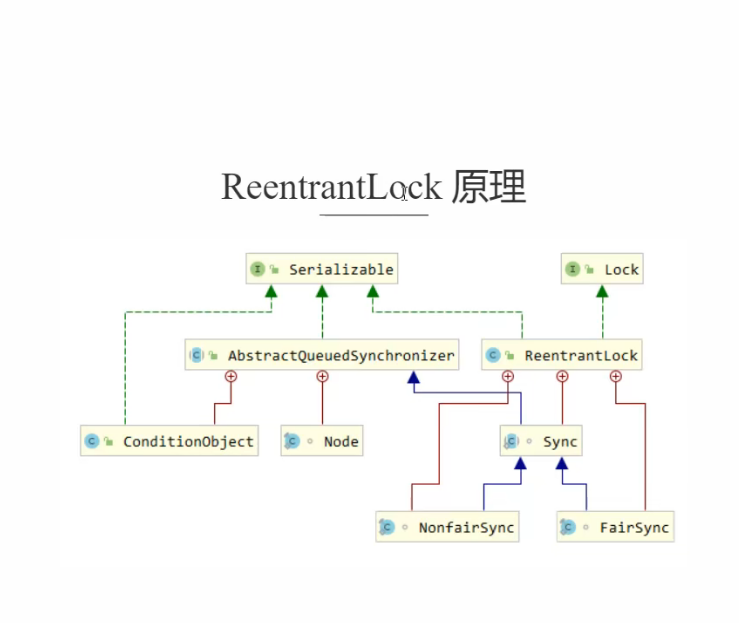
二、ReentrantLock原理
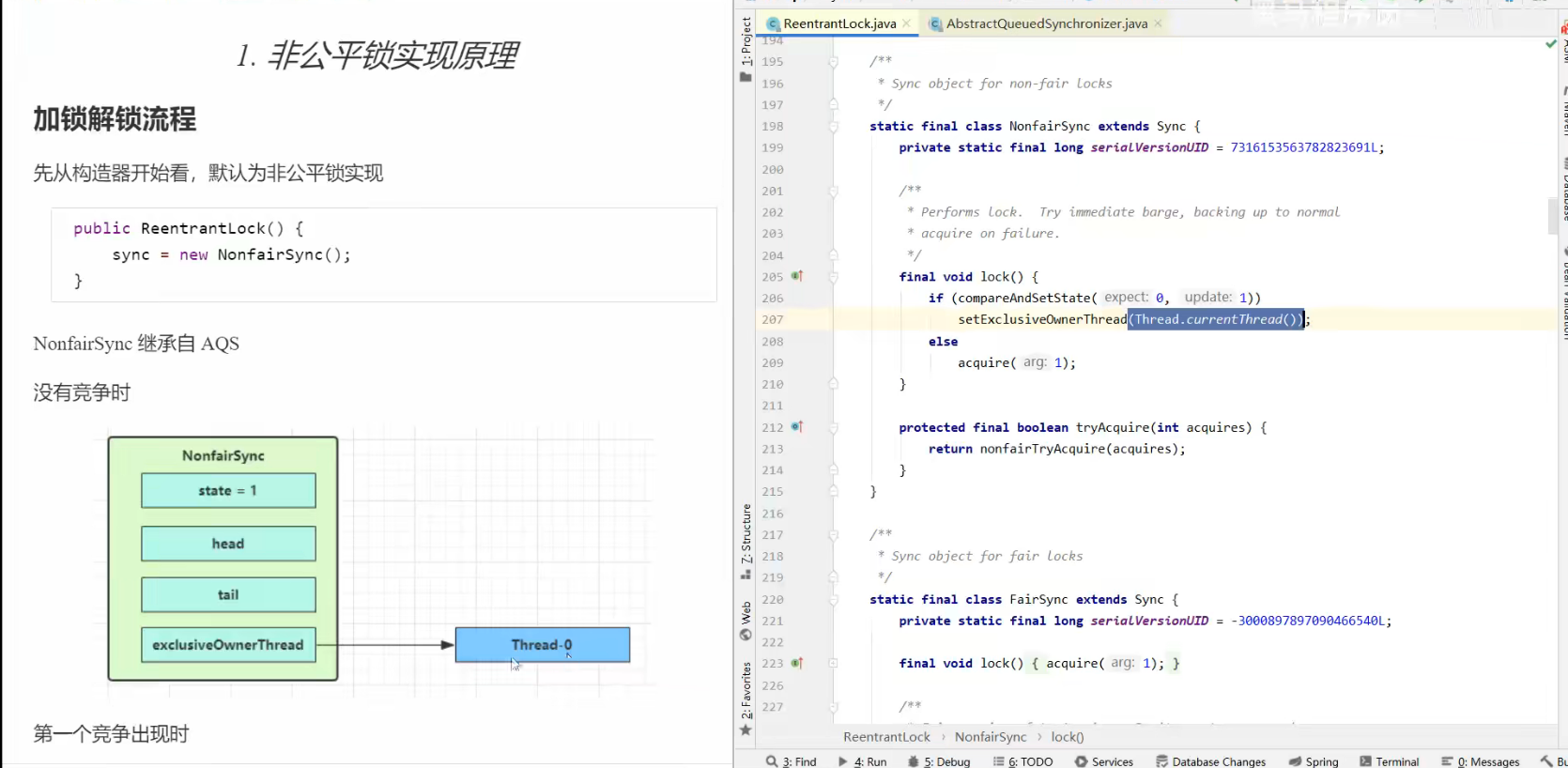
1、非公平锁实现原理
加锁解锁流程 P239
没有竞争时(占有锁)
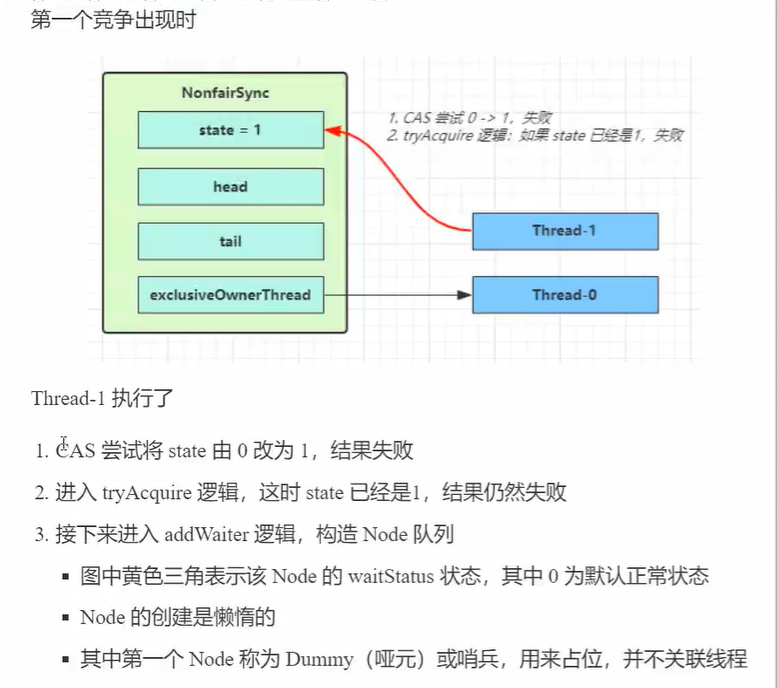
第一个竞争出现时(发生排队)
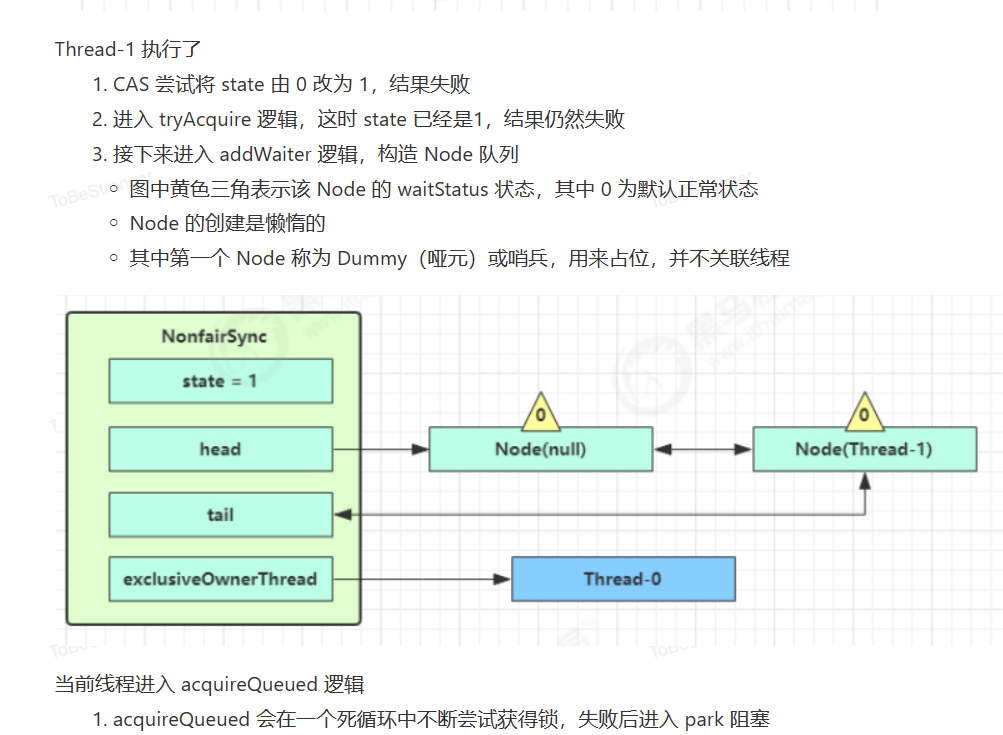
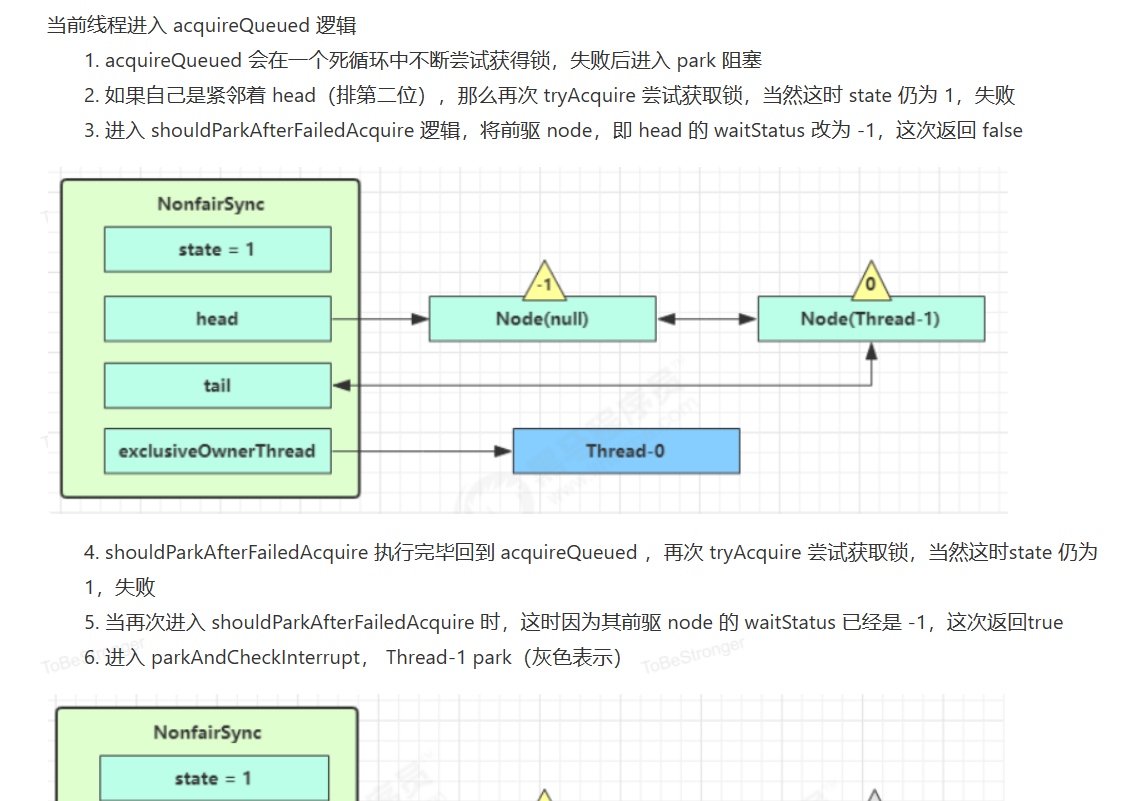
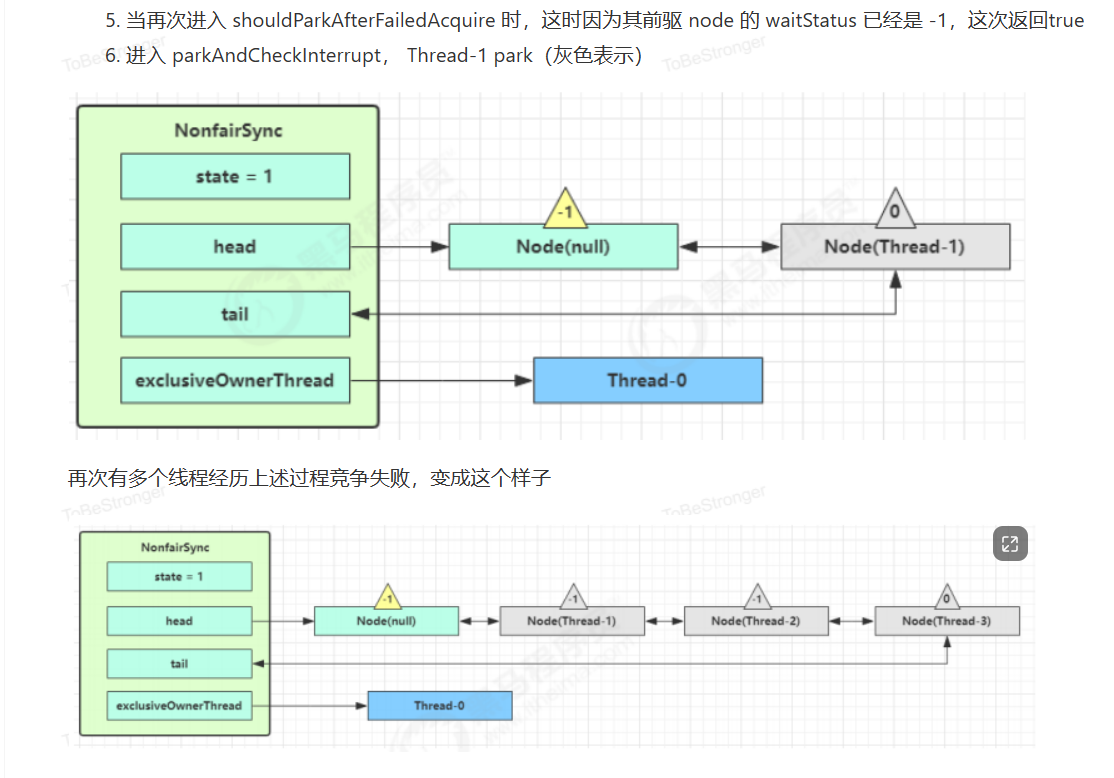
原OwnerThread释放锁时
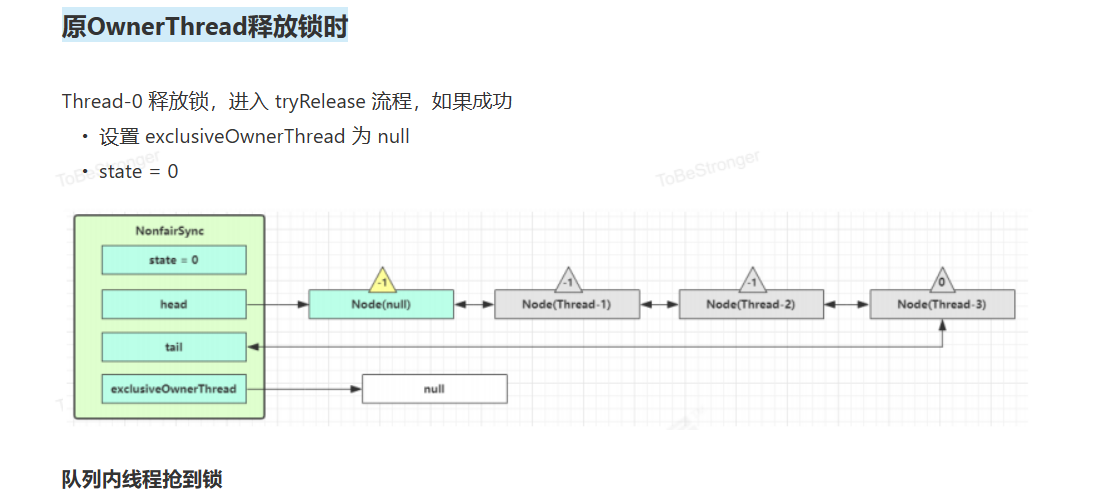
队列内线程抢到锁

队列外线程抢到锁

加锁源码
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
// 加锁实现
final void lock() {
// 首先用 cas 尝试(仅尝试一次)将 state 从 0 改为 1, 如果成功表示获得了独占锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
// 如果尝试失败,进入 ㈠
acquire(1);
}
// ㈠ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// ㈡ tryAcquire
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
// 当 tryAcquire 返回为 false 时, 先调用 addWaiter ㈣, 接着 acquireQueued ㈤
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// ㈡ 进入 ㈢
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
// ㈢ Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 如果还没有获得锁
if (c == 0) {
// 尝试用 cas 获得, 这里体现了非公平性: 不去检查 AQS 队列
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 如果已经获得了锁, 线程还是当前线程, 表示发生了锁重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// state++
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
// 获取失败, 回到调用处
return false;
}
// ㈣ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 将当前线程关联到一个 Node 对象上, 模式为独占模式
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 如果 tail 不为 null, cas 尝试将 Node 对象加入 AQS 队列尾部
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
// 双向链表
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 尝试将 Node 加入 AQS, 进入 ㈥
enq(node);
return node;
}
// ㈥ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
// 还没有, 设置 head 为哨兵节点(不对应线程,状态为 0)
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) {
tail = head;
}
} else {
// cas 尝试将 Node 对象加入 AQS 队列尾部
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
// ㈤ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 上一个节点是 head, 表示轮到自己(当前线程对应的 node)了, 尝试获取
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 获取成功, 设置自己(当前线程对应的 node)为 head
setHead(node);
// 上一个节点 help GC
p.next = null;
failed = false;
// 返回中断标记 false
return interrupted;
}
if (
// 判断是否应当 park, 进入 ㈦
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
// park 等待, 此时 Node 的状态被置为 Node.SIGNAL ㈧
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// ㈦ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 获取上一个节点的状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
// 上一个节点都在阻塞, 那么自己也阻塞好了
return true;
}
// > 0 表示取消状态
if (ws > 0) {
// 上一个节点取消, 那么重构删除前面所有取消的节点, 返回到外层循环重试
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
// 这次还没有阻塞
// 但下次如果重试不成功, 则需要阻塞,这时需要设置上一个节点状态为 Node.SIGNAL
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
// ㈧ 阻塞当前线程
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
}
注意
● 是否需要 unpark 是由当前节点的前驱节点的 waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 来决定,而不是本节点的 waitStatus 决定
解锁源码
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// 解锁实现
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 尝试释放锁, 进入 ㈠
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 队列头节点 unpark
Node h = head;
if (
// 队列不为 null
h != null &&
// waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 才需要 unpark
h.waitStatus != 0
) {
// unpark AQS 中等待的线程, 进入 ㈡
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ㈠ Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// state--
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 支持锁重入, 只有 state 减为 0, 才释放成功
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
// ㈡ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// 如果状态为 Node.SIGNAL 尝试重置状态为 0
// 不成功也可以
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0) {
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
}
// 找到需要 unpark 的节点, 但本节点从 AQS 队列中脱离, 是由唤醒节点完成的
Node s = node.next;
// 不考虑已取消的节点, 从 AQS 队列从后至前找到队列最前面需要 unpark 的节点
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
}
2、可重入原理


static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ...
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 如果已经获得了锁, 线程还是当前线程, 表示发生了锁重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// state++
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// state--
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 支持锁重入, 只有 state 减为 0, 才释放成功
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
}
3、可打断原理
(默认)不可打断模式
在此模式下,即使它被打断,仍会驻留在 AQS 队列中,一直要等到获得锁后方能得知自己被打断了
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ...
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 如果打断标记已经是 true, 则 park 会失效
LockSupport.park(this);
// interrupted 会清除打断标记
return Thread.interrupted();
}
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null;
failed = false;
// 还是需要获得锁后, 才能返回打断状态
return interrupted;
}
if (
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
) {
// 如果是因为 interrupt 被唤醒, 返回打断状态为 true
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
// 如果打断状态为 true
selfInterrupt();
}
}
static void selfInterrupt() {
// 重新产生一次中断
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
可打断模式:直接抛出异常
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 如果没有获得到锁, 进入 ㈠
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
// ㈠ 可打断的获取锁流程
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt()) {
// 在 park 过程中如果被 interrupt 会进入此
// 这时候抛出异常, 而不会再次进入 for (;;)
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
}
4、公平锁实现原理
非公平锁不会检查阻塞队列,而是直接和队列的老二进行竞争,而公平锁会检查队列的老二是不是自己或者队列有没有其他线程,如果有会先执行队列中的线程
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// 与非公平锁主要区别在于 tryAcquire 方法的实现
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// 先检查 AQS 队列中是否有前驱节点, 没有才去竞争
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ㈠ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
// h != t 时表示队列中有 Node
return h != t &&
(
// (s = h.next) == null 表示队列中还有没有老二
(s = h.next) == null ||
// 或者队列中老二线程不是此线程
s.thread != Thread.currentThread()
);
}
}
5、条件变量实现原理
await 流程
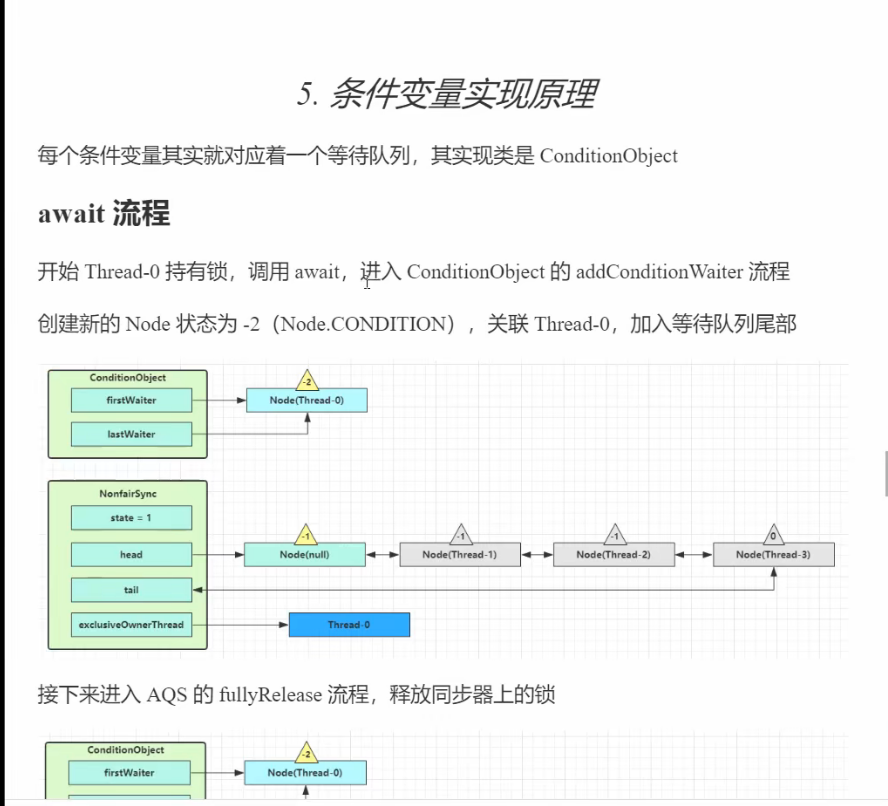
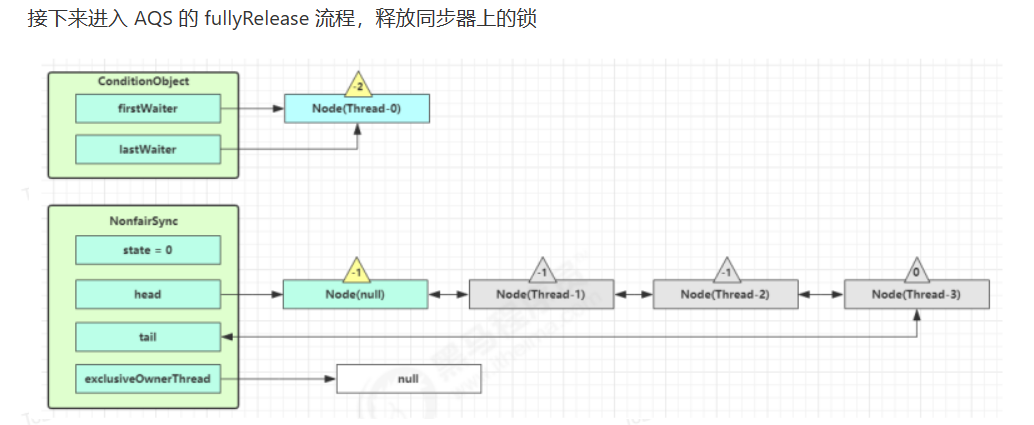
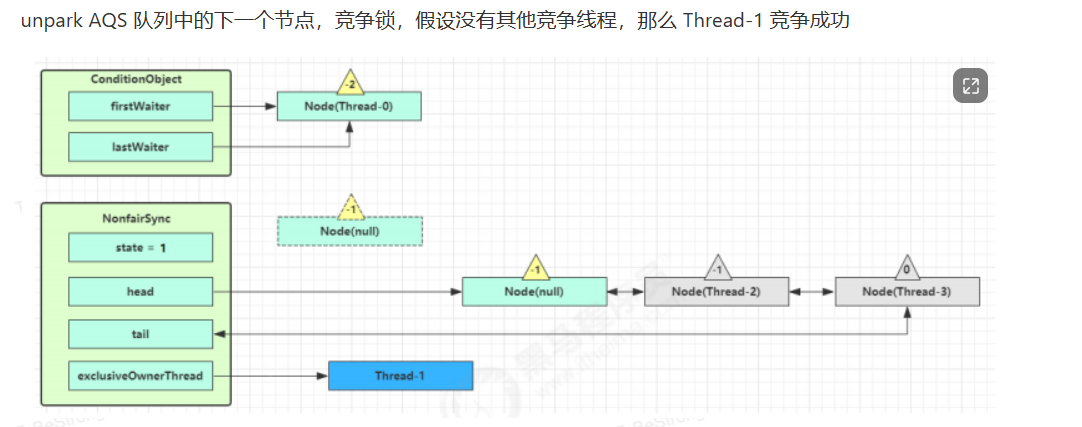
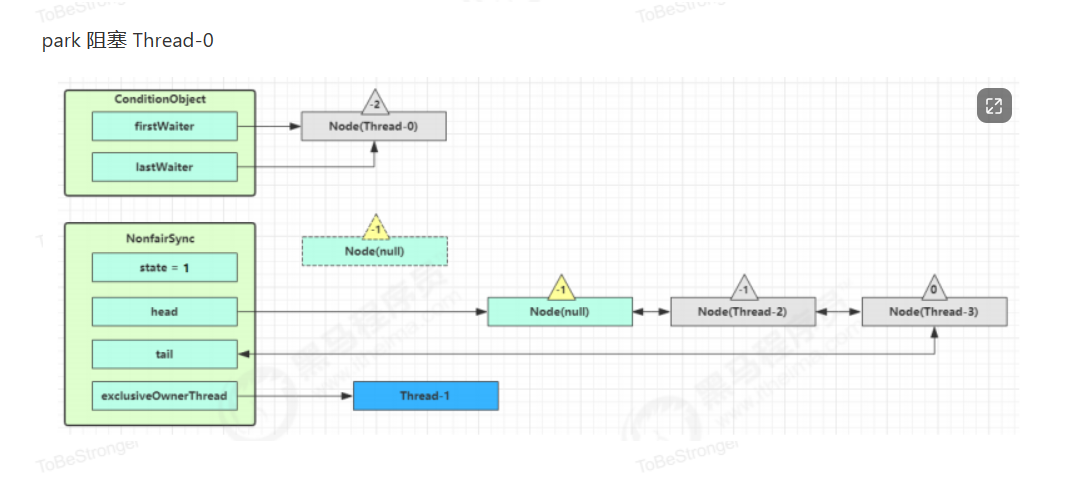
signal 流程



源码
public class ConditionObject implements Condition, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1173984872572414699L;
// 第一个等待节点
private transient Node firstWaiter;
// 最后一个等待节点
private transient Node lastWaiter;
public ConditionObject() { }
// ㈠ 添加一个 Node 至等待队列
private Node addConditionWaiter() {
Node t = lastWaiter;
// 所有已取消的 Node 从队列链表删除, 见 ㈡
if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
t = lastWaiter;
}
// 创建一个关联当前线程的新 Node, 添加至队列尾部
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);
if (t == null)
firstWaiter = node;
else
t.nextWaiter = node;
lastWaiter = node;
return node;
}
// 唤醒 - 将没取消的第一个节点转移至 AQS 队列
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
// 已经是尾节点了
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null) {
lastWaiter = null;
}
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (
// 将等待队列中的 Node 转移至 AQS 队列, 不成功且还有节点则继续循环 ㈢
!transferForSignal(first) &&
// 队列还有节点
(first = firstWaiter) != null
);
}
// 外部类方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
// ㈢ 如果节点状态是取消, 返回 false 表示转移失败, 否则转移成功
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
// 如果状态已经不是 Node.CONDITION, 说明被取消了
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
// 加入 AQS 队列尾部
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (
// 上一个节点被取消
ws > 0 ||
// 上一个节点不能设置状态为 Node.SIGNAL
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL)
) {
// unpark 取消阻塞, 让线程重新同步状态
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
}
return true;
}
// 全部唤醒 - 等待队列的所有节点转移至 AQS 队列
private void doSignalAll(Node first) {
lastWaiter = firstWaiter = null;
do {
Node next = first.nextWaiter;
first.nextWaiter = null;
transferForSignal(first);
first = next;
} while (first != null);
}
// ㈡
private void unlinkCancelledWaiters() {
// ...
}
// 唤醒 - 必须持有锁才能唤醒, 因此 doSignal 内无需考虑加锁
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
// 全部唤醒 - 必须持有锁才能唤醒, 因此 doSignalAll 内无需考虑加锁
public final void signalAll() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignalAll(first);
}
// 不可打断等待 - 直到被唤醒
public final void awaitUninterruptibly() {
// 添加一个 Node 至等待队列, 见 ㈠
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// 释放节点持有的锁, 见 ㈣
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
boolean interrupted = false;
// 如果该节点还没有转移至 AQS 队列, 阻塞
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// park 阻塞
LockSupport.park(this);
// 如果被打断, 仅设置打断状态
if (Thread.interrupted())
interrupted = true;
}
// 唤醒后, 尝试竞争锁, 如果失败进入 AQS 队列
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) || interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
}
// 外部类方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
// ㈣ 因为某线程可能重入,需要将 state 全部释放
final int fullyRelease(Node node) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
int savedState = getState();
if (release(savedState)) {
failed = false;
return savedState;
} else {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
}
}
// 打断模式 - 在退出等待时重新设置打断状态
private static final int REINTERRUPT = 1;
// 打断模式 - 在退出等待时抛出异常
private static final int THROW_IE = -1;
// 判断打断模式
private int checkInterruptWhileWaiting(Node node) {
return Thread.interrupted() ?
(transferAfterCancelledWait(node) ? THROW_IE : REINTERRUPT) :
0;
}
// ㈤ 应用打断模式
private void reportInterruptAfterWait(int interruptMode)
throws InterruptedException {
if (interruptMode == THROW_IE)
throw new InterruptedException();
else if (interruptMode == REINTERRUPT)
selfInterrupt();
}
// 等待 - 直到被唤醒或打断
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 添加一个 Node 至等待队列, 见 ㈠
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// 释放节点持有的锁
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
// 如果该节点还没有转移至 AQS 队列, 阻塞
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// park 阻塞
LockSupport.park(this);
// 如果被打断, 退出等待队列
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
// 退出等待队列后, 还需要获得 AQS 队列的锁
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
// 所有已取消的 Node 从队列链表删除, 见 ㈡
if (node.nextWaiter != null)
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 应用打断模式, 见 ㈤
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
// 等待 - 直到被唤醒或打断或超时
public final long awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 添加一个 Node 至等待队列, 见 ㈠
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// 释放节点持有的锁
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
// 获得最后期限
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
int interruptMode = 0;
// 如果该节点还没有转移至 AQS 队列, 阻塞
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// 已超时, 退出等待队列
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L) {
transferAfterCancelledWait(node);
break;
}
// park 阻塞一定时间, spinForTimeoutThreshold 为 1000 ns
if (nanosTimeout >= spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
// 如果被打断, 退出等待队列
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
// 退出等待队列后, 还需要获得 AQS 队列的锁
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
// 所有已取消的 Node 从队列链表删除, 见 ㈡
if (node.nextWaiter != null)
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 应用打断模式, 见 ㈤
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
return deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
// 等待 - 直到被唤醒或打断或超时, 逻辑类似于 awaitNanos
public final boolean awaitUntil(Date deadline) throws InterruptedException {
// ...
}
// 等待 - 直到被唤醒或打断或超时, 逻辑类似于 awaitNanos
public final boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// ...
}
// 工具方法 省略 ...
}
三、读写锁: 读时共享,写时互斥
1、ReentrantReadWriteLock
当读操作远远高于写操作时,这时候使用 读写锁 让 读-读 可以并发,提高性能。
类似于数据库中的 select … from … lock in share mode
示例
提供一个 数据容器类 内部分别使用读锁保护数据的 read() 方法,写锁保护数据的 write() 方法
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
public class testThread30 {
/** 两个线程都读时,等于没有加锁
* 13:16:54 [t2] c.DataContainer - 获取读锁...
* 13:16:54 [t1] c.DataContainer - 获取读锁...
* 13:16:54 [t1] c.DataContainer - 读取
* 13:16:54 [t2] c.DataContainer - 读取
* 13:16:55 [t2] c.DataContainer - 释放读锁...
* 13:16:55 [t1] c.DataContainer - 释放读锁...
* @param args
*/
/** 一个线程读一个线程 写,就会产生互斥,如果都去写也会互斥
* 13:19:57 [t1] c.DataContainer - 获取读锁...
* 13:19:57 [t1] c.DataContainer - 读取
* 13:19:57 [t2] c.DataContainer - 获取写锁...
* 13:19:58 [t1] c.DataContainer - 释放读锁...
* 13:19:58 [t2] c.DataContainer - 写入
* 13:19:59 [t2] c.DataContainer - 释放写锁...
* @param args
*/
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataContainer dataContainer = new DataContainer();
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.read();
}, "t1").start();
Thread.sleep(100);
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.write();
}, "t2").start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.DataContainer")
class DataContainer {
private Object data;
private ReentrantReadWriteLock rw = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock r = rw.readLock();
private ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock w = rw.writeLock();
@SneakyThrows
public Object read() {
log.debug("获取读锁...");
r.lock();
try {
log.debug("读取");
Thread.sleep(1000);
return data;
} finally {
log.debug("释放读锁...");
r.unlock();
}
}
@SneakyThrows
public void write() {
log.debug("获取写锁...");
w.lock();
try {
log.debug("写入");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} finally {
log.debug("释放写锁...");
w.unlock();
}
}
}
注意事项


class CachedData {
Object data;
// 是否有效,如果失效,需要重新计算 data
volatile boolean cacheValid;
final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
void processCachedData() {
rwl.readLock().lock();
if (!cacheValid) {
// 获取写锁前必须释放读锁
rwl.readLock().unlock();
rwl.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 判断是否有其它线程已经获取了写锁、更新了缓存, 避免重复更新
if (!cacheValid) {
data = ...
cacheValid = true;
}
// 降级为读锁, 释放写锁, 这样能够让其它线程读取缓存
rwl.readLock().lock();
} finally {
rwl.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
// 自己用完数据, 释放读锁
try {
use(data);
} finally {
rwl.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
应用之缓存
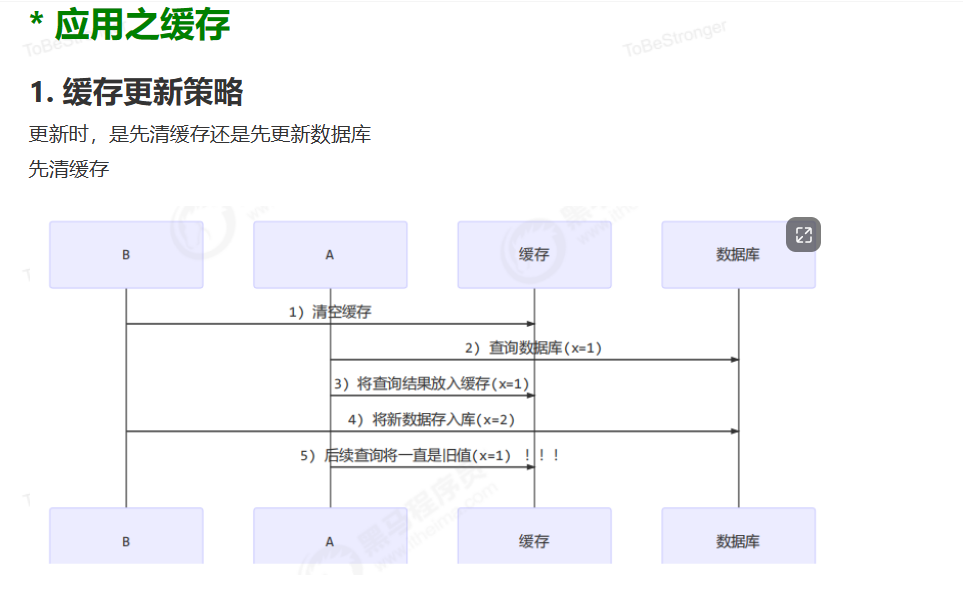
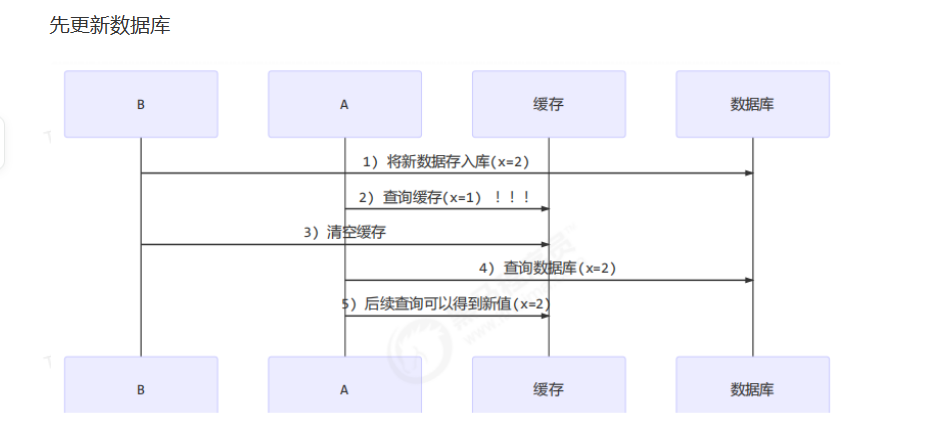

读写锁实现一致性缓存
使用读写锁实现一个简单的按需加载缓存
class GenericCachedDao<T> {
// HashMap 作为缓存非线程安全, 需要保护
HashMap<SqlPair, T> map = new HashMap<>();
ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
GenericDao genericDao = new GenericDao();
public int update(String sql, Object... params) {
SqlPair key = new SqlPair(sql, params);
// 加写锁, 防止其它线程对缓存读取和更改
lock.writeLock().lock();
try {
int rows = genericDao.update(sql, params);
map.clear();
return rows;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
public T queryOne(Class<T> beanClass, String sql, Object... params) {
SqlPair key = new SqlPair(sql, params);
// 加读锁, 防止其它线程对缓存更改
lock.readLock().lock();
try {
T value = map.get(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
} finally {
lock.readLock().unlock();
}
// 加写锁, 防止其它线程对缓存读取和更改
lock.writeLock().lock();
try {
// get 方法上面部分是可能多个线程进来的, 可能已经向缓存填充了数据
// 为防止重复查询数据库, 再次验证
T value = map.get(key);
if (value == null) {
// 如果没有, 查询数据库
value = genericDao.queryOne(beanClass, sql, params);
map.put(key, value);
}
return value;
} finally {
lock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
// 作为 key 保证其是不可变的
class SqlPair {
private String sql;
private Object[] params;
public SqlPair(String sql, Object[] params) {
this.sql = sql;
this.params = params;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
SqlPair sqlPair = (SqlPair) o;
return sql.equals(sqlPair.sql) &&
Arrays.equals(params, sqlPair.params);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = Objects.hash(sql);
result = 31 * result + Arrays.hashCode(params);
return result;
}
}
}
注意
● 以上实现体现的是读写锁的应用,保证缓存和数据库的一致性,但有下面的问题没有考虑
○ 适合读多写少,如果写操作比较频繁,以上实现性能低
○ 没有考虑缓存容量
○ 没有考虑缓存过期
○ 只适合单机
○ 并发性还是低,目前只会用一把锁
○ 更新方法太过简单粗暴,清空了所有 key(考虑按类型分区或重新设计 key)
● 乐观锁实现:用 CAS 去更新
读写锁原理 🔞

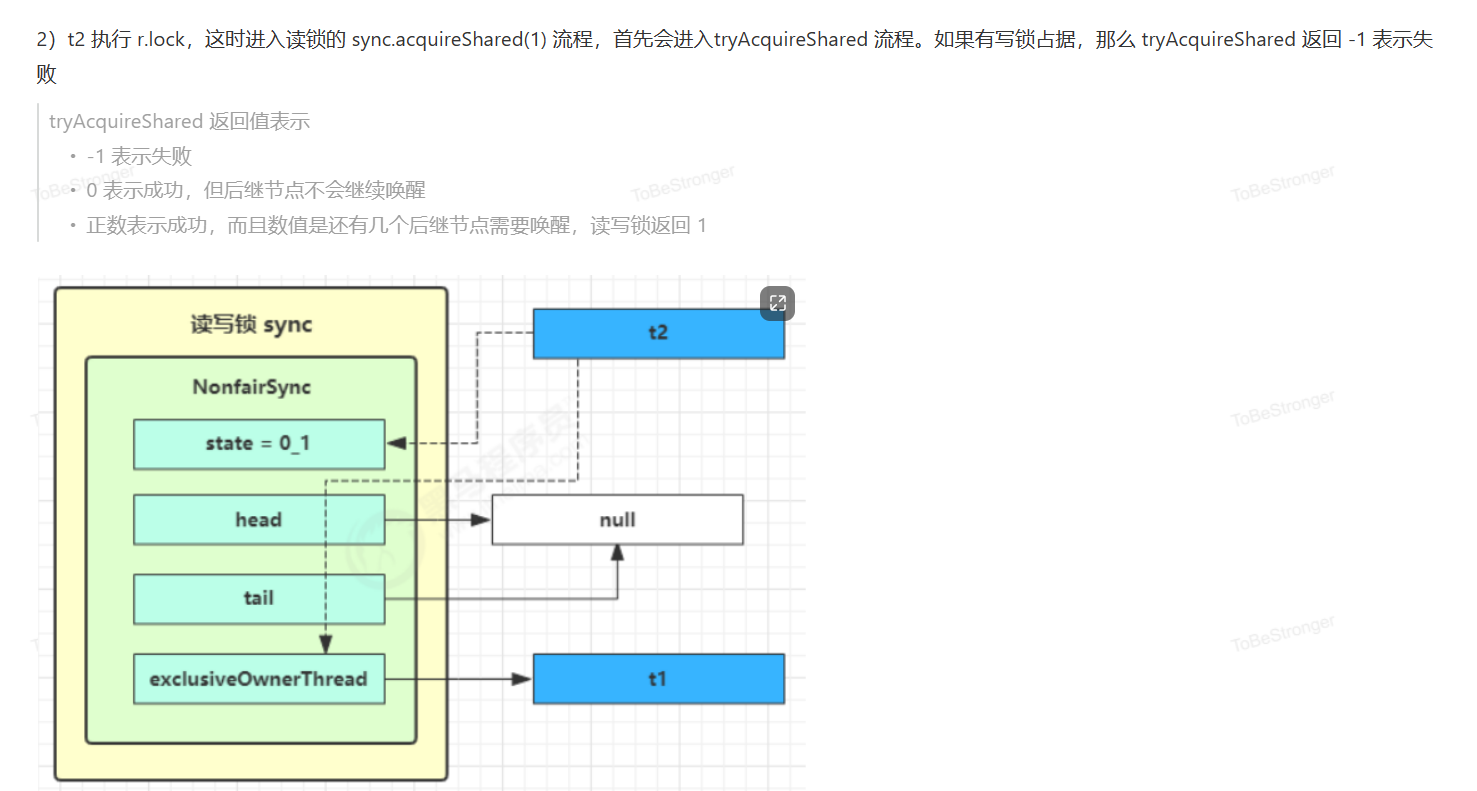


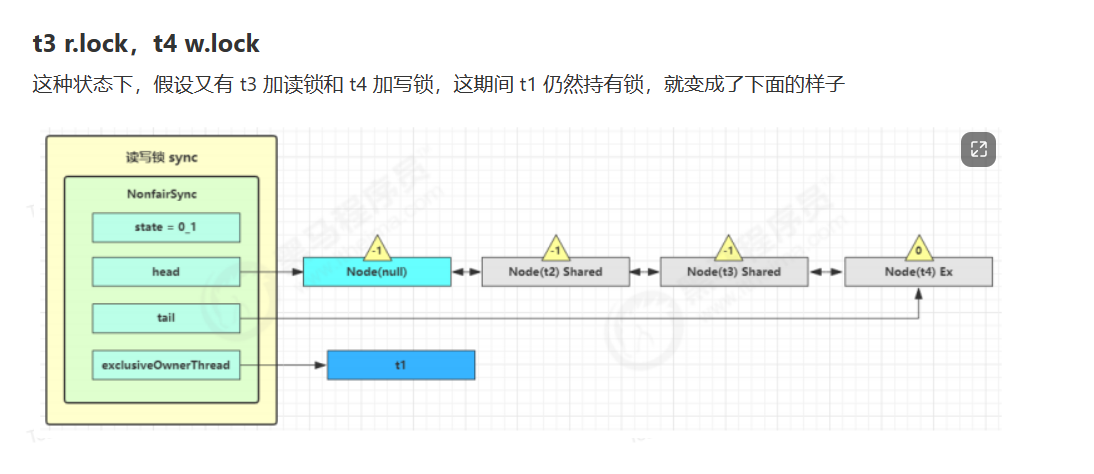
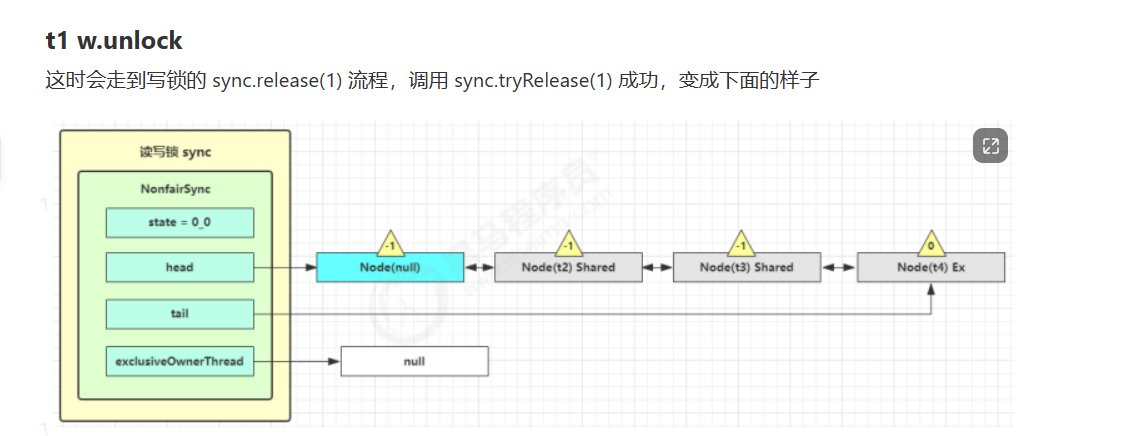
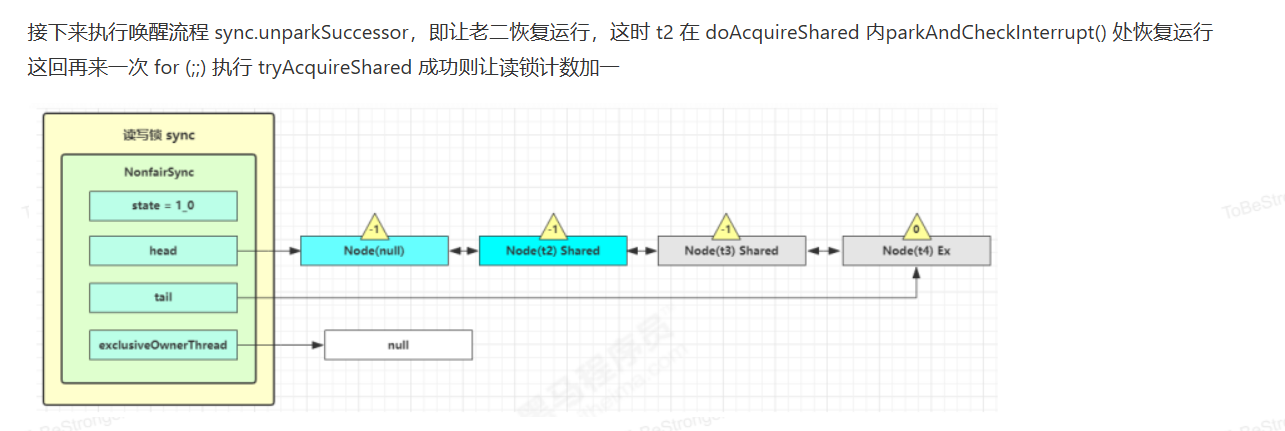
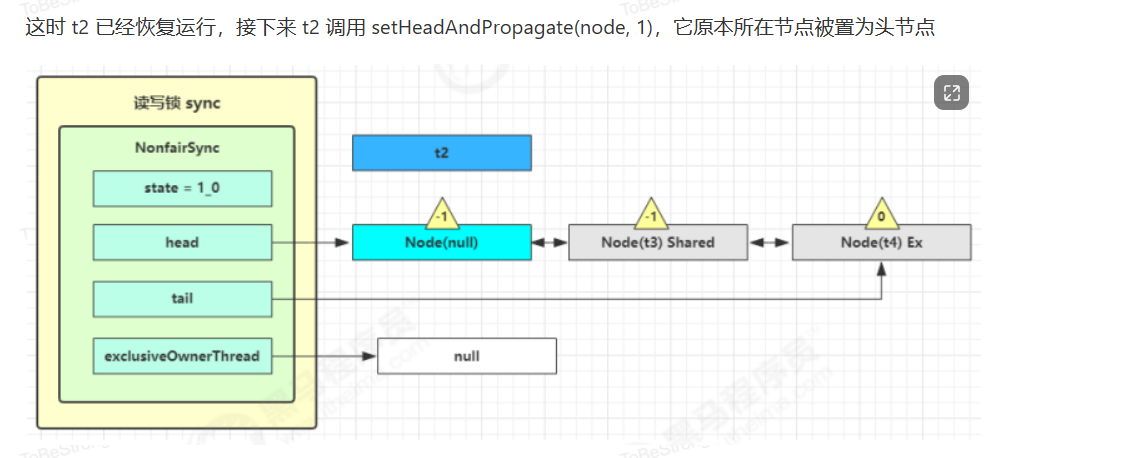
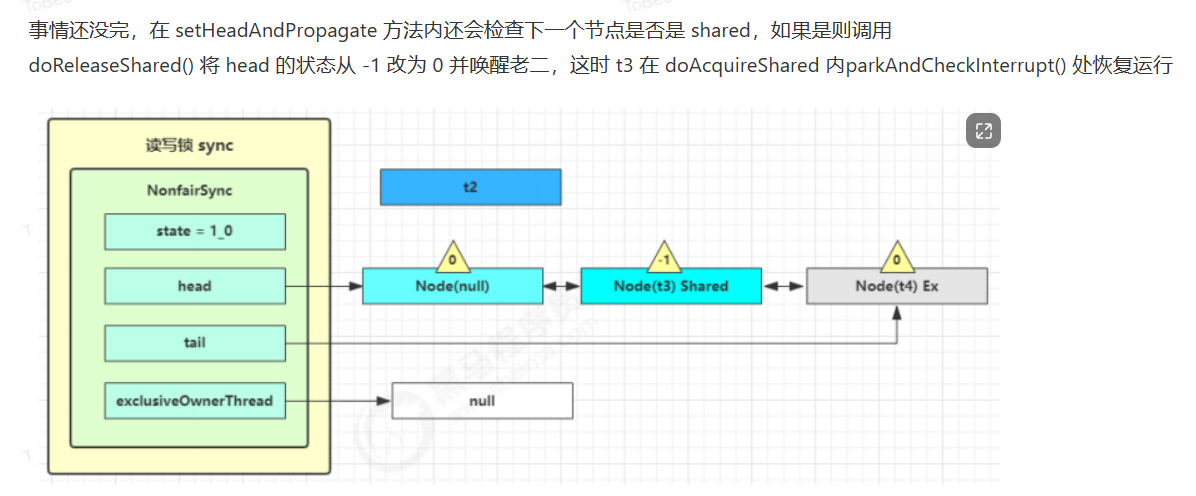
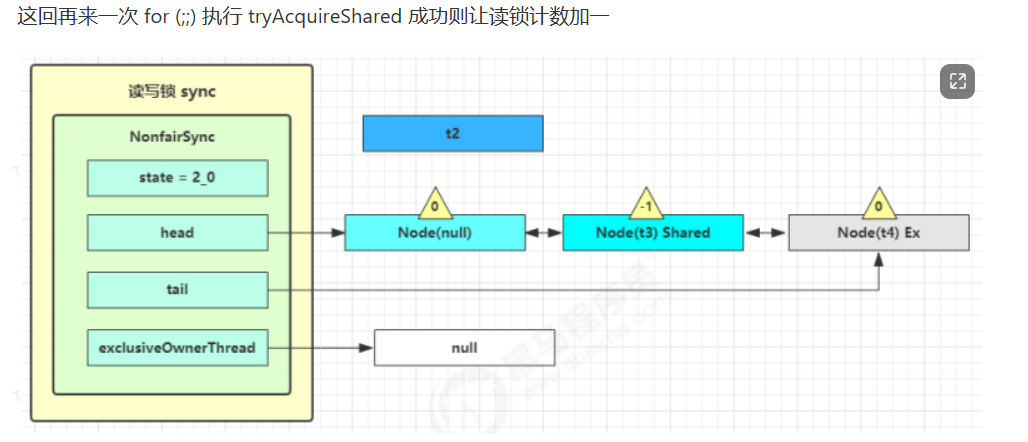
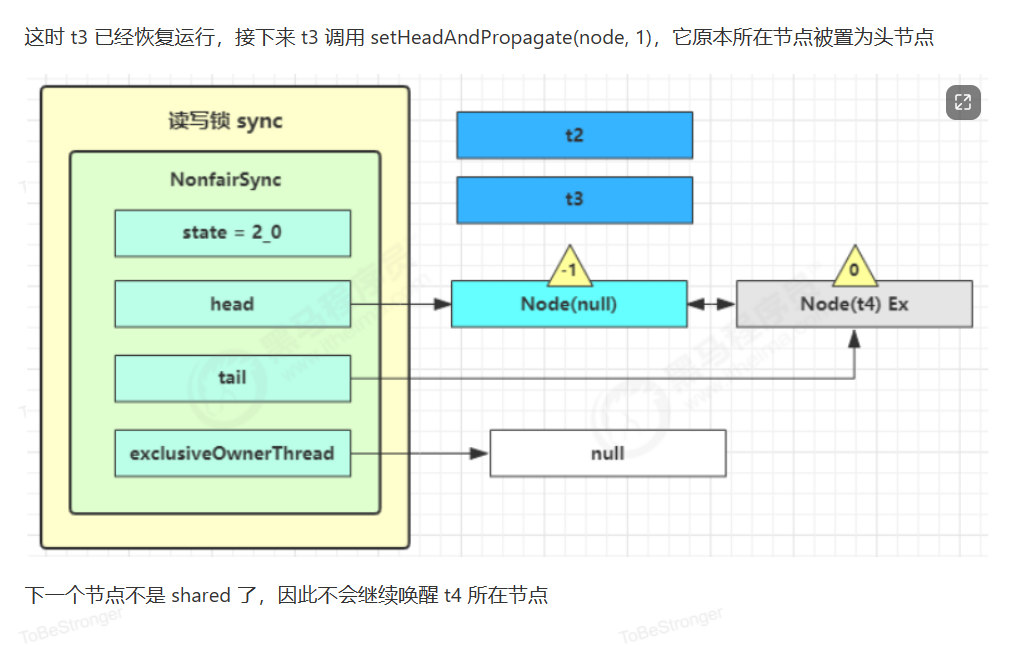
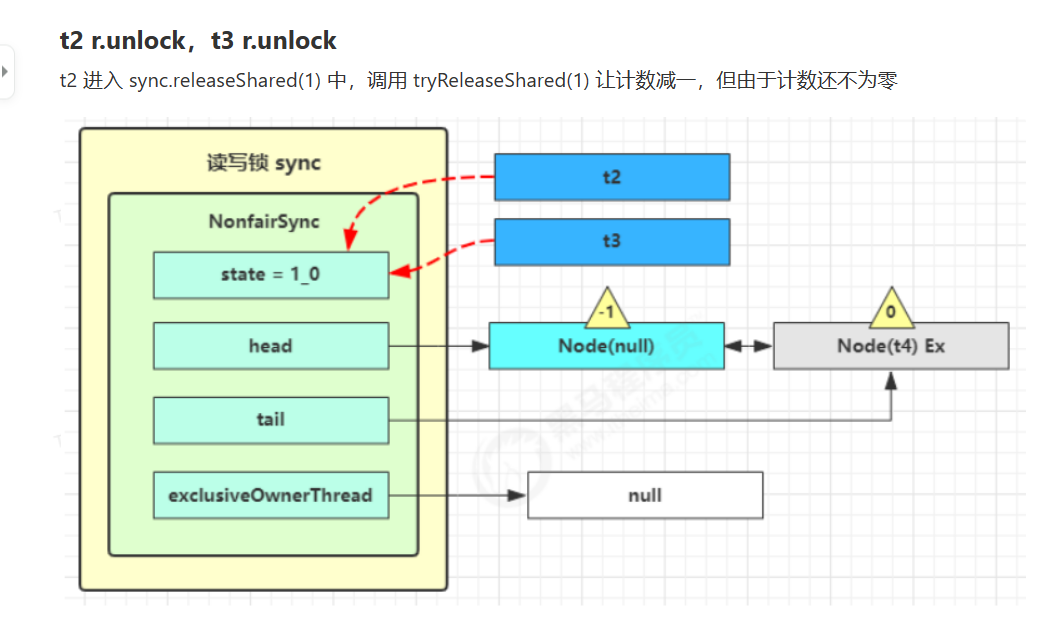
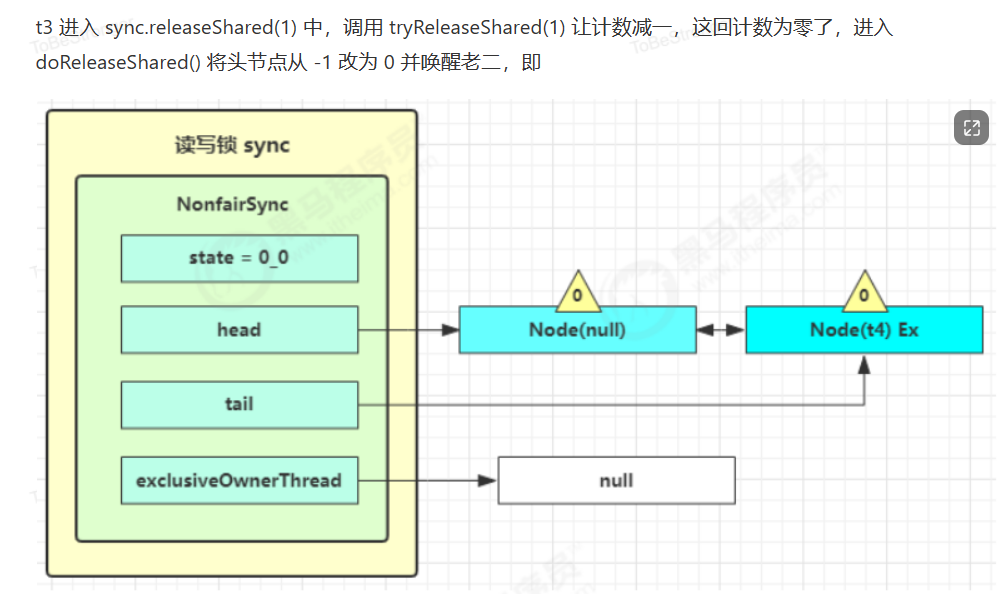
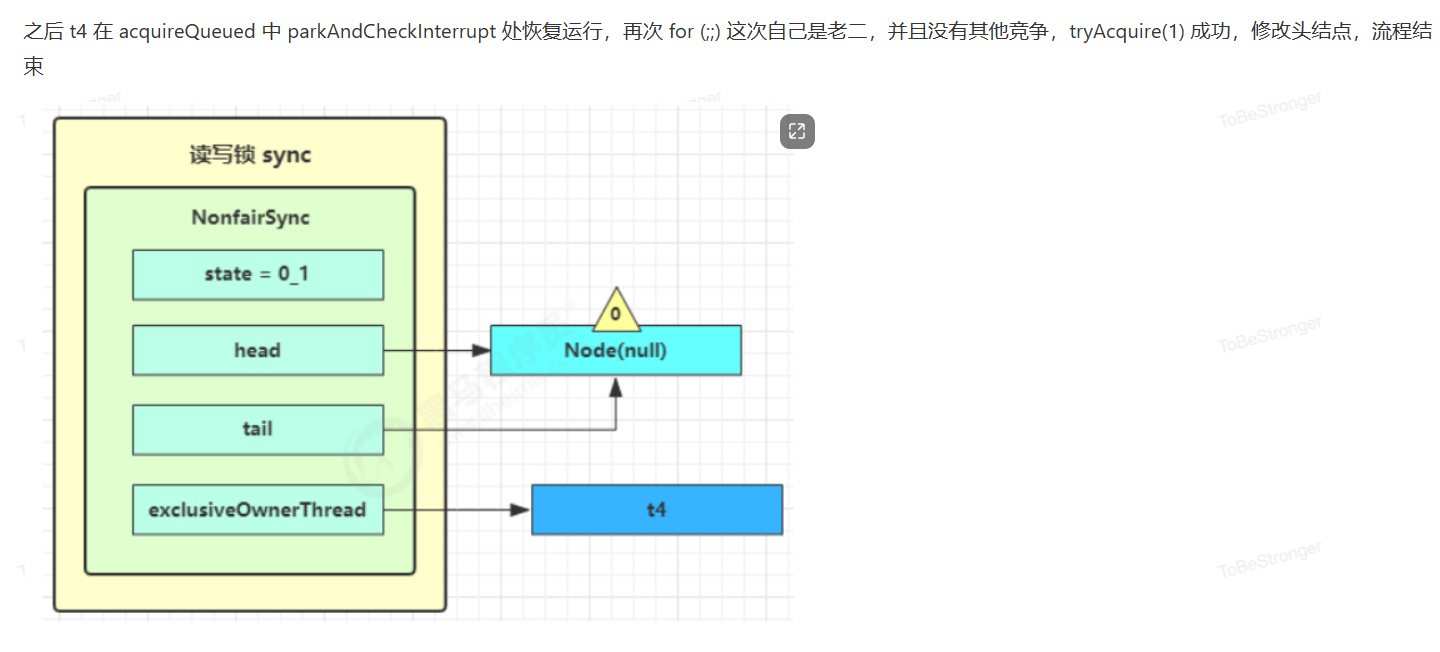
读写锁源码分析
写锁上锁流程
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ... 省略无关代码
// 外部类 WriteLock 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (
// 尝试获得写锁失败
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
// 将当前线程关联到一个 Node 对象上, 模式为独占模式
// 进入 AQS 队列阻塞
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
// 获得低 16 位, 代表写锁的 state 计数
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
if (c != 0) {
if (
// c != 0 and w == 0 表示有读锁, 或者
w == 0 ||
// 如果 exclusiveOwnerThread 不是自己
current != getExclusiveOwnerThread()
) {
// 获得锁失败
return false;
}
// 写锁计数超过低 16 位, 报异常
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// 写锁重入, 获得锁成功
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
}
if (
// 判断写锁是否该阻塞, 或者
writerShouldBlock() ||
// 尝试更改计数失败
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires)
) {
// 获得锁失败
return false;
}
// 获得锁成功
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
// 非公平锁 writerShouldBlock 总是返回 false, 无需阻塞
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return false;
}
}
写锁释放流程
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ... 省略无关代码
// WriteLock 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 尝试释放写锁成功
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// unpark AQS 中等待的线程
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
int nextc = getState() - releases;
// 因为可重入的原因, 写锁计数为 0, 才算释放成功
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
if (free) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(nextc);
return free;
}
}
读锁上锁流程
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ReadLock 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
// tryAcquireShared 返回负数, 表示获取读锁失败
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) {
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 如果是其它线程持有写锁, 获取读锁失败
if (
exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current
) {
return -1;
}
int r = sharedCount(c);
if (
// 读锁不该阻塞(如果老二是写锁,读锁该阻塞), 并且
!readerShouldBlock() &&
// 小于读锁计数, 并且
r < MAX_COUNT &&
// 尝试增加计数成功
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)
) {
// ... 省略不重要的代码
return 1;
}
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}
// 非公平锁 readerShouldBlock 看 AQS 队列中第一个节点是否是写锁
// true 则该阻塞, false 则不阻塞
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {
return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive();
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
// 与 tryAcquireShared 功能类似, 但会不断尝试 for (;;) 获取读锁, 执行过程中无阻塞
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {
// ... 省略不重要的代码
}
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
// ... 省略不重要的代码
return 1;
}
}
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
// 将当前线程关联到一个 Node 对象上, 模式为共享模式
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
// 再一次尝试获取读锁
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
// 成功
if (r >= 0) {
// ㈠
// r 表示可用资源数, 在这里总是 1 允许传播
//(唤醒 AQS 中下一个 Share 节点)
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (
// 是否在获取读锁失败时阻塞(前一个阶段 waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL)
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
// park 当前线程
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// ㈠ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head; // Record old head for check below
// 设置自己为 head
setHead(node);
// propagate 表示有共享资源(例如共享读锁或信号量)
// 原 head waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 或 Node.PROPAGATE
// 现在 head waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 或 Node.PROPAGATE
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
// 如果是最后一个节点或者是等待共享读锁的节点
if (s == null || s.isShared()) {
// 进入 ㈡
doReleaseShared();
}
}
}
// ㈡ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void doReleaseShared() {
// 如果 head.waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL ==> 0 成功, 下一个节点 unpark
// 如果 head.waitStatus == 0 ==> Node.PROPAGATE, 为了解决 bug, 见后面分析
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
// 队列还有节点
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
// 下一个节点 unpark 如果成功获取读锁
// 并且下下个节点还是 shared, 继续 doReleaseShared
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
}
读锁释放流程
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ReadLock 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
// ... 省略不重要的代码
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) {
// 读锁的计数不会影响其它获取读锁线程, 但会影响其它获取写锁线程
// 计数为 0 才是真正释放
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void doReleaseShared() {
// 如果 head.waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL ==> 0 成功, 下一个节点 unpark
// 如果 head.waitStatus == 0 ==> Node.PROPAGATE
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
// 如果有其它线程也在释放读锁,那么需要将 waitStatus 先改为 0
// 防止 unparkSuccessor 被多次执行
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
// 如果已经是 0 了,改为 -3,用来解决传播性,见后文信号量 bug 分析
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
}
2、StampedLock
虽然ReentrantReadWriteLock读写锁,在多个线程进行读操作时,性能已经很不错了,但是每个线程在读的时候还是会进行AQS同步器和CAS的方式去修改读锁的高十六位的状态,很显然性能没有拉到极致,这时就可以使用 StampedLock,在多线程都去读的情况下,先获取一个 戳 当戳没有被别的线程修改,可以在不加锁的情况下让所有线程都乐观读,一旦戳被修改,就对锁进行升级,从乐观读升级到读锁,读锁又与写锁产生互斥。

示例
提供一个 数据容器类 内部分别使用读锁保护数据的 read() 方法,写锁保护数据的 write() 方法
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.StampedLock;
public class testThread30 {
@SneakyThrows
public static void main(String[] args) {
DataContainerStamped dataContainer = new DataContainerStamped(1);
/**
* 测试 读-读 可以优化
*/
// new Thread(() -> {
// dataContainer.read(1);
// }, "t1").start();
//
// Thread.sleep(500);
// new Thread(() -> {
// dataContainer.read(0);
// }, "t2").start();
/**
* 测试 读-写 时优化读补加读锁
* 16:41:45 [t1] c.DataContainerStamped - optimistic read locking...256
* 16:41:45 [t1] c.DataContainerStamped - read finish...256, data:1
* 16:41:45 [t2] c.DataContainerStamped - write lock 384
* 16:41:47 [t2] c.DataContainerStamped - write unlock 384
*/
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.read(1);
}, "t1").start();
Thread.sleep(500);
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.write(100);
}, "t2").start();
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.DataContainerStamped")
class DataContainerStamped {
private int data;
private final StampedLock lock = new StampedLock();
public DataContainerStamped(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
@SneakyThrows
public int read(int readTime) {
long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead();
log.debug("optimistic read locking...{}", stamp);
Thread.sleep(readTime);
if (lock.validate(stamp)) {
log.debug("read finish...{}, data:{}", stamp, data);
return data;
}
// 锁升级 - 读锁
log.debug("updating to read lock... {}", stamp);
try {
stamp = lock.readLock();
log.debug("read lock {}", stamp);
Thread.sleep(readTime);
log.debug("read finish...{}, data:{}", stamp, data);
return data;
} finally {
log.debug("read unlock {}", stamp);
lock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
@SneakyThrows
public void write(int newData) {
long stamp = lock.writeLock();
log.debug("write lock {}", stamp);
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
this.data = newData;
} finally {
log.debug("write unlock {}", stamp);
lock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
}
}
注意 StampedLock 不支持条件变量 StampedLock 不支持锁重入
四、信号量 Semaphore

使用 Semaphore 限制线程的运行数量
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.testThread31")
public class testThread31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 创建 semaphore 对象
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);
// 2. 10个线程同时运行
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
// 3. 获取许可
try {
semaphore.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
log.debug("running...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("end...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4. 释放许可
semaphore.release();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
Semaphore的应用: 改进连接池

import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;
/**
* 自定义连接池,使用信号量
*/
public class testThread26 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
pool pool= new pool(2);
for (int i = 1; i <= 5;i++){
new Thread(()->{
//借出连接
Connection borrow = pool.borrow();
try {
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//归还连接
pool.still(borrow);
}
}).start();
}
}
}
@Slf4j(topic = "c.pool")
class pool{
//连接池大小
private final int poolSize;
//连接池数组
private Connection[] connections;
//连接池数组状态 为了防止多线程同时修改连接状态需要使用原子数组
private AtomicIntegerArray states;
//使用信号量改善连接
private Semaphore semaphore;
//初始化连接池
public pool(int poolSize) {
this.poolSize = poolSize;
this.connections = new Connection[poolSize];
//使用信号量改善连接
this.semaphore = new Semaphore(poolSize);
this.states = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[poolSize]);
//创建连接池
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++) {
connections[i] = new MyConnection("连接" + (i+1));
}
}
//借出连接
public Connection borrow(){
//检查连接是否空闲
try {
//获取许可
semaphore.acquire();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < poolSize; i++){
if(states.get(i) == 0){
//表示连接空闲
//修改连接状态
boolean b = states.compareAndSet(i, 0, 1);
if (b){
log.debug("借出连接"+ (i+1));
return connections[i];
}
}
}
//这里永远执行不到
return null;
}
//归还连接
public void still(Connection connection){
//判断归还的连接是否合法
for (int i = 0; i < connections.length; i++) {
if (connections[i] == connection) {
log.debug("归还连接"+ (i+1));
states.set(i,0);
//释放许可
semaphore.release();
break;
}
}
}
}
class MyConnection implements Connection{
private String name;
public MyConnection(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyConnection{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
Semaphore 原理
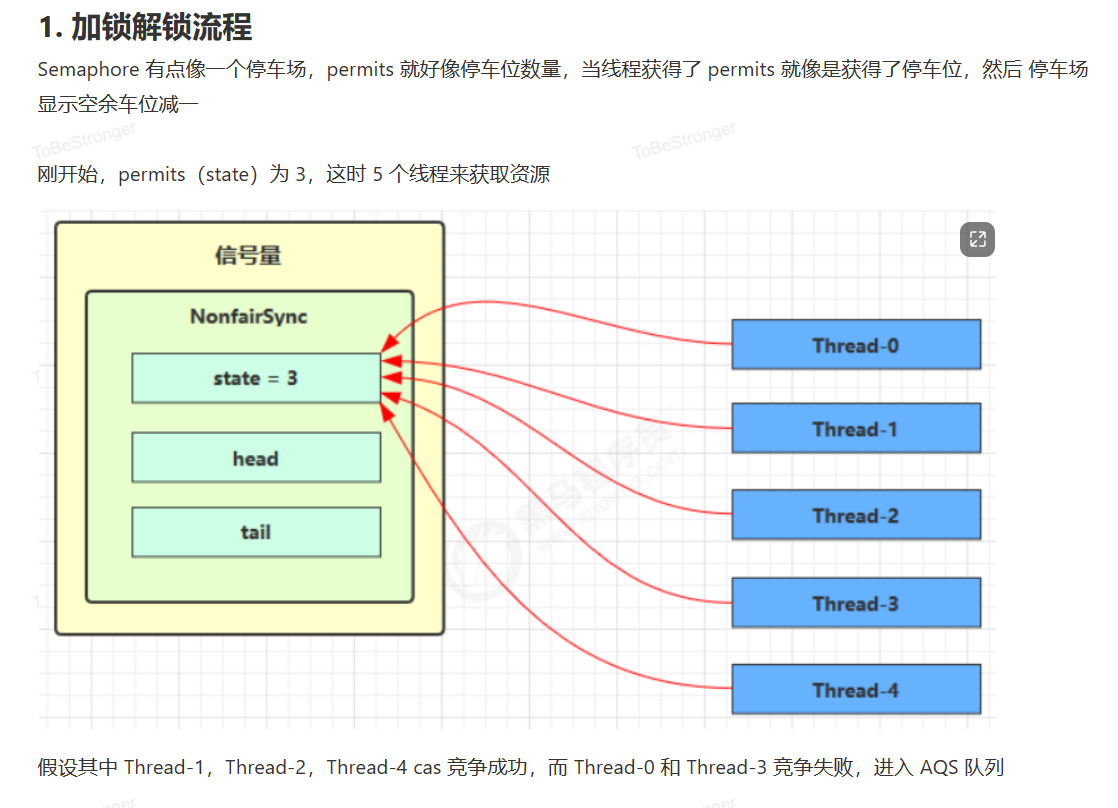
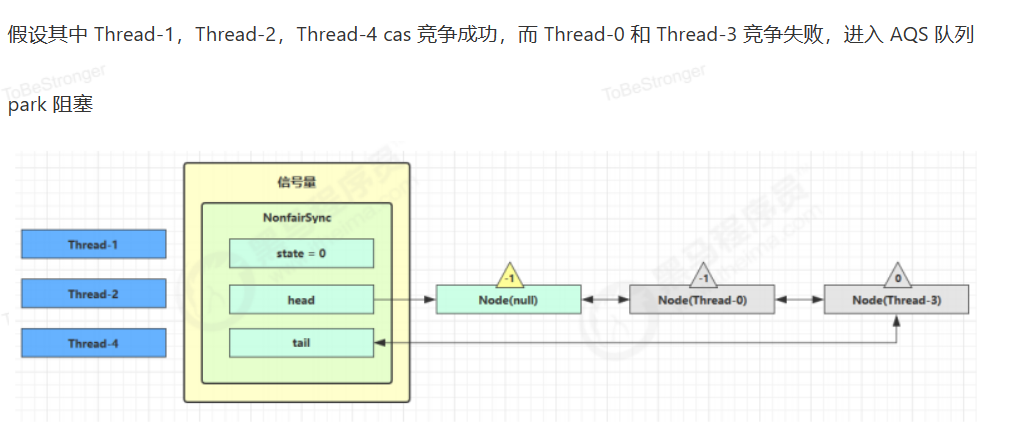
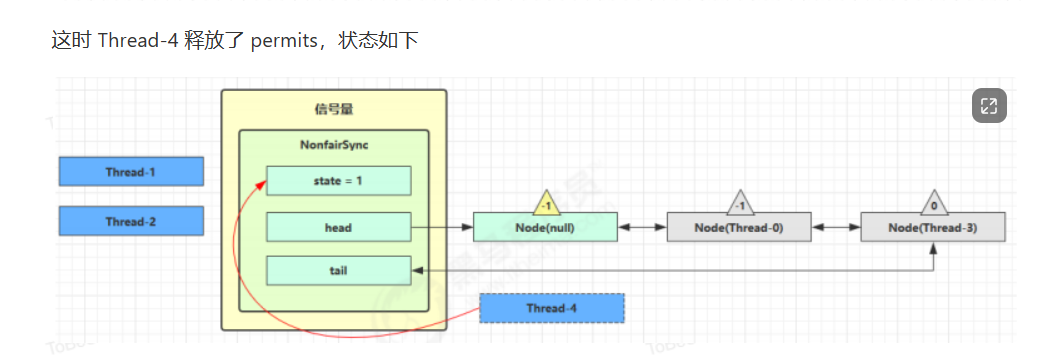
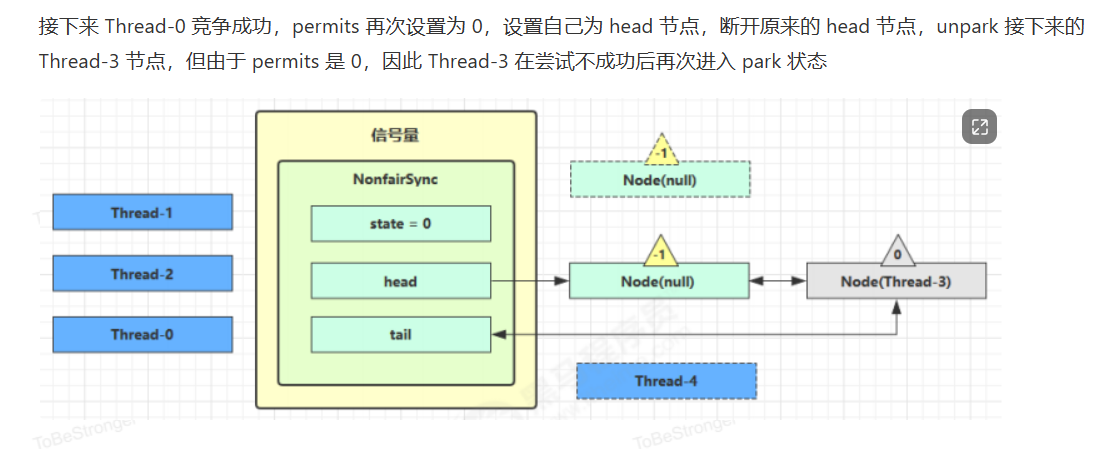
源码分析
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2694183684443567898L;
NonfairSync(int permits) {
// permits 即 state
super(permits);
}
// Semaphore 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void acquire() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
// 尝试获得共享锁
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (
// 如果许可已经用完, 返回负数, 表示获取失败, 进入 doAcquireSharedInterruptibly
remaining < 0 ||
// 如果 cas 重试成功, 返回正数, 表示获取成功
compareAndSetState(available, remaining)
) {
return remaining;
}
}
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
// 再次尝试获取许可
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
// 成功后本线程出队(AQS), 所在 Node设置为 head
// 如果 head.waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL ==> 0 成功, 下一个节点 unpark
// 如果 head.waitStatus == 0 ==> Node.PROPAGATE
// r 表示可用资源数, 为 0 则不会继续传播
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
}
// 不成功, 设置上一个节点 waitStatus = Node.SIGNAL, 下轮进入 park 阻塞
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// Semaphore 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void release() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current + releases;
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
}
五、 CountdownLatch 倒计时调度线程
用来进行线程同步协作,等待所有线程完成倒计时。
其中构造参数用来初始化等待计数值,await() 用来等待计数归零,countDown() 用来让计数减一,
那么肯定会有人说用 join 不行吗?当然 join 也是可以的,只不过比较底层,而且我们以后获取线程都是从线程池中获取,线程池中的线程都是一直在运行的,再使用 join 肯定是不行的了。
基本使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(1);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(2);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
sleep(1.5);
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
}).start();
log.debug("waiting...");
latch.await();
log.debug("wait end...");
}
输出
18:44:00.778 c.TestCountDownLatch [main] - waiting...
18:44:00.778 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-2] - begin...
18:44:00.778 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-0] - begin...
18:44:00.778 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-1] - begin...
18:44:01.782 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-0] - end...2
18:44:02.283 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-2] - end...1
18:44:02.782 c.TestCountDownLatch [Thread-1] - end...0
18:44:02.782 c.TestCountDownLatch [main] - wait end...
改进,添加线程池
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.testThread31")
public class testThread31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(() -> {
log.debug("begin...");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
latch.countDown();
log.debug("end...{}", latch.getCount());
});
service.submit(()->{
try {
log.debug("waiting...");
latch.await();
log.debug("wait end...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
应用之同步等待多线程准备完毕
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.testThread31")
public class testThread31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10, (r) -> {
return new Thread(r, "t" + num.getAndIncrement());
});
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);
String[] all = new String[10];
Random r = new Random();
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
int x = j;
service.submit(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
all[x] = Thread.currentThread().getName() + "(" + (i + "%") + ")";
System.out.print("\r" + Arrays.toString(all));
}
//计数减一
latch.countDown();
});
}
try {
//等待所有线程执行完毕
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("\n游戏开始...");
service.shutdown();
}
}
输出
[t0(100%), t1(100%), t2(100%), t3(100%), t4(100%), t5(100%), t6(100%), t7(100%), t8(100%), t9(100%)]
游戏开始...
rest 远程调用 P270
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.testThread31")
public class testThread31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
log.debug("begin");
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(4);
Future<Map<String,Object>> f1 = service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> r =
restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/order/{1}", Map.class, 1);
return r;
});
Future<Map<String, Object>> f2 = service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> r =
restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/product/{1}", Map.class, 1);
return r;
});
Future<Map<String, Object>> f3 = service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> r =
restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/product/{1}", Map.class, 2);
return r;
});
Future<Map<String, Object>> f4 = service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> r =
restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/logistics/{1}", Map.class, 1);
return r;
});
System.out.println(f1.get());
System.out.println(f2.get());
System.out.println(f3.get());
System.out.println(f4.get());
log.debug("执行完毕");
service.shutdown();
}
}
六、CyclicBarrier
CyclicBarrier 和 CountdownLatch 最大的不同就是,CountdownLatch的倒计时数只能设置不能更改,而CyclicBarrier 是可以更改的,如果 CyclicBarrier的计数标记为 0 时,再次调用 await 计数就会恢复一开始的计数标记。在一些特殊的应用场景下 可以大显身手。
注意 CyclicBarrier 与 CountDownLatch 的主要区别在于 CyclicBarrier 是可以重用的 CyclicBarrier 可以被比喻为『人满发车』

一定要注意线程数和 CyclicBarrier 计数标记一定要一致,不然会有问题。
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.testThread31")
public class testThread31 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CyclicBarrier cb = new CyclicBarrier(2,()->{
//对结果进行汇总,但只能获得 cb.await(); 之前的结果
log.debug("线程1 和 线程2 运行完了");
}); // 个数为2时才会继续执行
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
executorService.submit(()->{
System.out.println("线程1开始.."+new Date());
try {
cb.await(); // 当个数不足时,等待 2 - 1 = 1
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程1继续向下运行..."+new Date());
});
executorService.submit(()->{
System.out.println("线程2开始.."+new Date());
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
try {
cb.await(); // 2 秒后,线程个数够2,继续运行 1 - 1 = 0,条件满足
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程2继续向下运行..."+new Date());
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
输出
线程1开始..Wed Apr 05 20:51:44 CST 2023
线程2开始..Wed Apr 05 20:51:44 CST 2023
20:51:46 [pool-1-thread-2] c.testThread31 - 线程1 和 线程2 运行完了
线程2继续向下运行...Wed Apr 05 20:51:46 CST 2023
线程1继续向下运行...Wed Apr 05 20:51:46 CST 2023
线程1开始..Wed Apr 05 20:51:46 CST 2023
线程2开始..Wed Apr 05 20:51:46 CST 2023
20:51:48 [pool-1-thread-1] c.testThread31 - 线程1 和 线程2 运行完了
线程2继续向下运行...Wed Apr 05 20:51:48 CST 2023
线程1继续向下运行...Wed Apr 05 20:51:48 CST 2023
线程1开始..Wed Apr 05 20:51:48 CST 2023
线程2开始..Wed Apr 05 20:51:48 CST 2023
20:51:50 [pool-1-thread-2] c.testThread31 - 线程1 和 线程2 运行完了
线程2继续向下运行...Wed Apr 05 20:51:50 CST 2023
线程1继续向下运行...Wed Apr 05 20:51:50 CST 2023






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








