
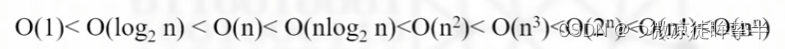
数据结构与算法
主要是由连续或跳转或者连续加跳转构成的。即线性和非线性
基本数据结构
- 数组:便于寻址,不便于增删数据
- 链表:便于增删数据,不便于寻址
位移运算
负数二进制整数二进制取反加一。
相反数原数取反加一。
int的最小值取反和取反加一后与原数一样
package day8_位移运算;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// int num = 12138;
// int num2=~num;//取反
// print(num);
// print(num2);
int num3=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
print(num3);
print(num3>>1);//带符号右移
print(num3>>>1);//不带符号右移
}
public static void print(int num){
for (int i = 31; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print((num & (1<<i)) == 0 ? "0" : "1");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
选择排序
本质:将每次遍历后选择最小的值放在前面
每一项都依次向后进行遍历,将每一次遍历的时候最小的值和当前索引上的值进行调换。
package day1;
//选择排序
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={2,7,4,5,6,9,1,3,8};
//arr.length-1可以使得循环少执行一次
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
int minpos=i;
for (int j=i+1;j<arr.length;j++) {
// if(arr[j]<arr[minpos]){
// minpos=j;
// }
//改写三目运算符形势
minpos=arr[j] < arr[minpos] ? j :minpos;
}
swap(arr,i,minpos);
//交换数值也被分装成一个方法
// int temp=arr[i];
// arr[i]=arr[minpos];
// arr[minpos]=temp;
System.out.println("经过" + i +"次:");
System.out.println("minpos="+minpos);
print(arr);
}
//被分装成一个方法
// for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
// }
}
static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int minpos){
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[minpos];
arr[minpos]=temp;
}
static void print(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
}
冒泡排序
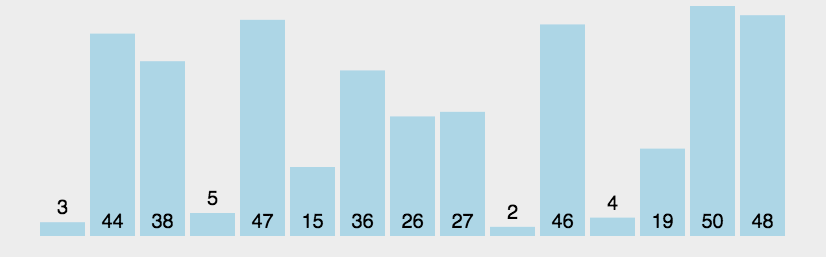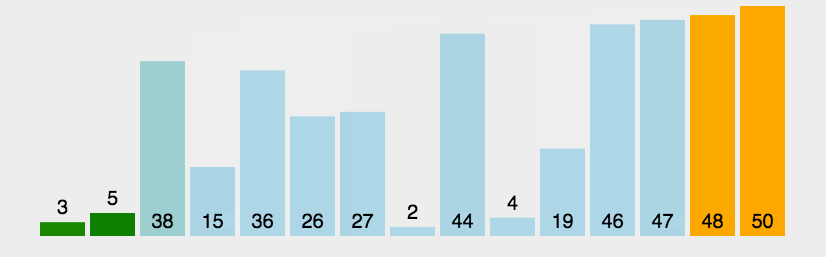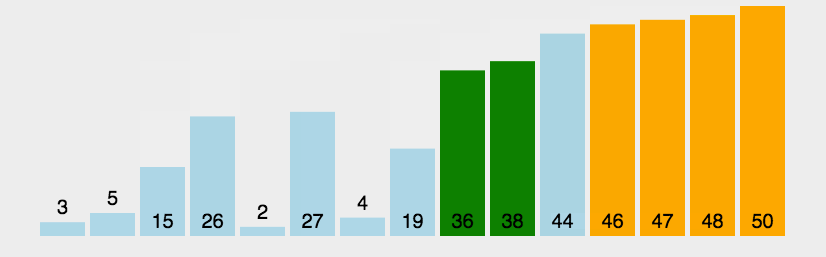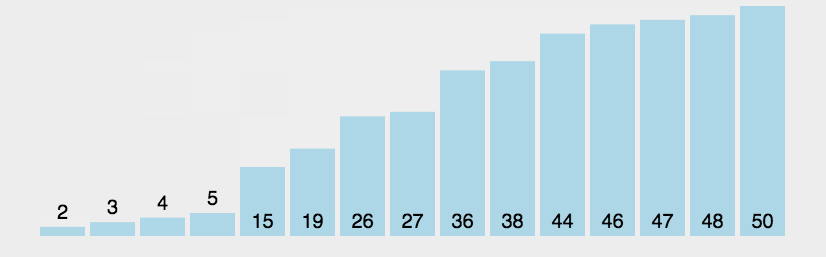
不断将大的一项向后移动
package day2;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
//冒泡排序
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,5,6,4,7,8,9,2,3};
sort(arr);
print(arr);
}
static void swap(int[] arr ,int i, int j){
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
static void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
//代码核心:
static void sort(int[] arr ){
for(int k=arr.length-1;k>0;k--){
for (int i = 0; i <k; i++) {
if(arr[i]>arr[i+1]){
swap(arr,i,i+1);
}
}
}
}
}
插入排序
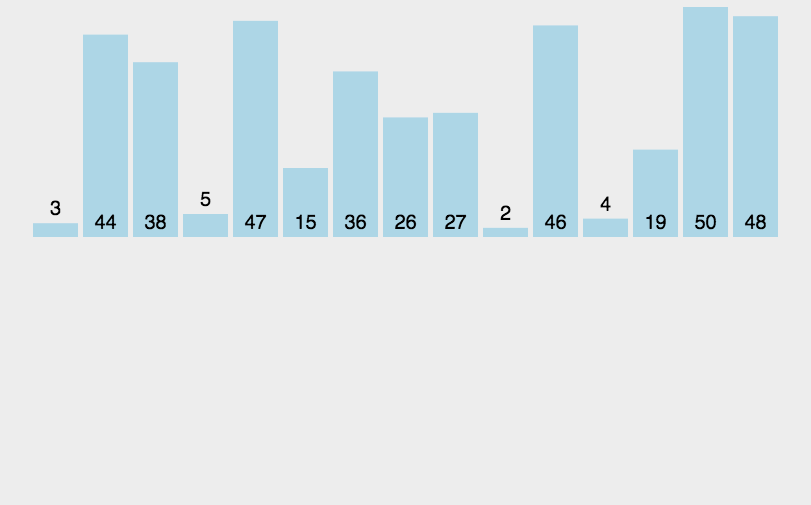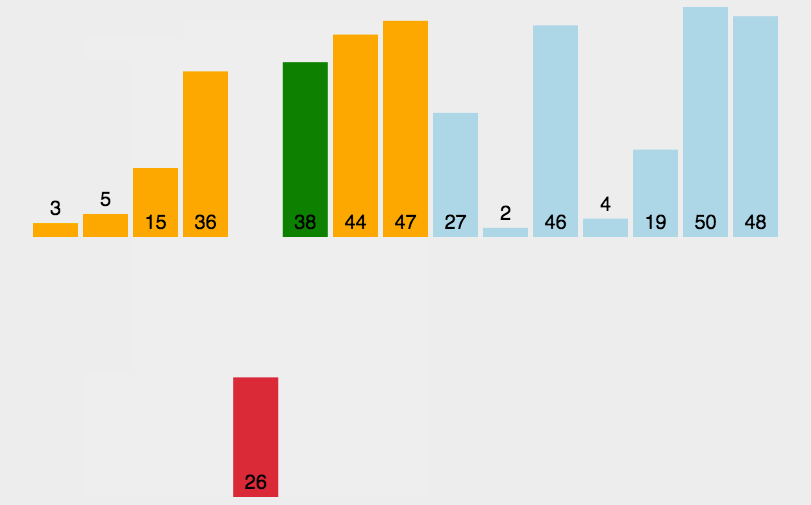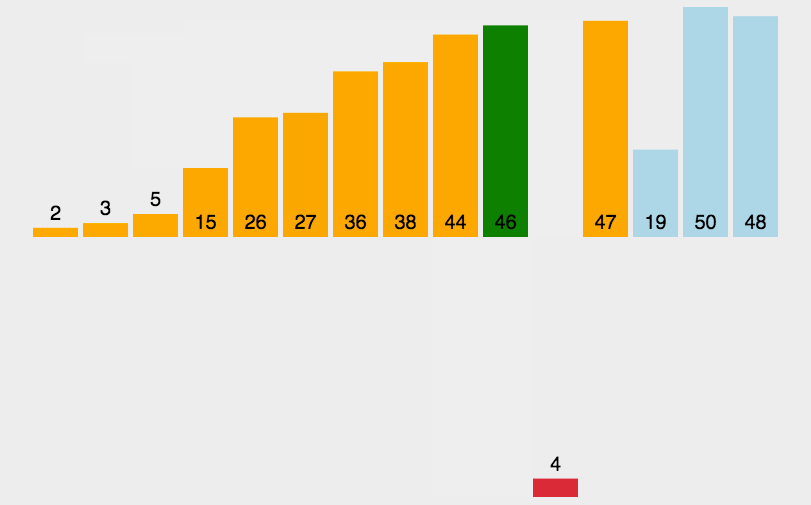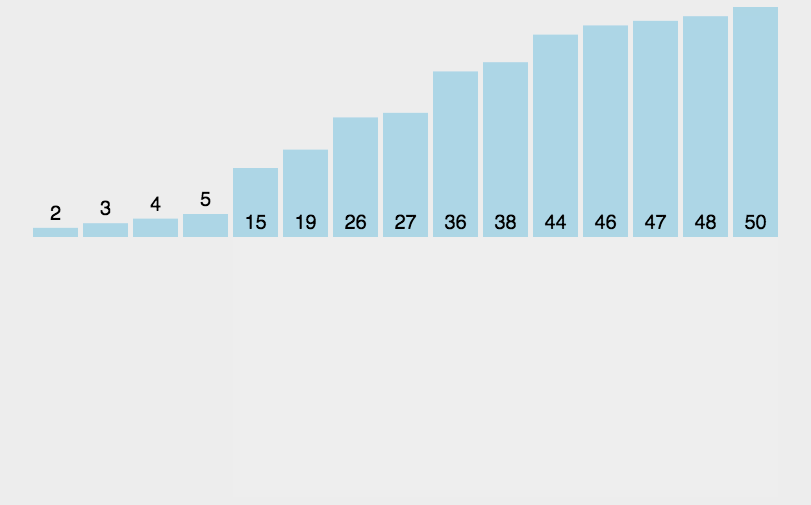
从头(第二个索引)开始每次向前比较将每次比较最小的放在相应的位置。
package day3_插入排序;
public class test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = {8,1,9,4,5,3,7,6,2};
sort(arr);
print(arr);
}
private static void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
private static void sort(int [] arr) {
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j=i;j>0;j--) {
if(arr[j]<arr[j-1]){
swap(arr,j,j-1);
}
}
}
}
//优化后
private static void sortsecond(int[] arr){
if(arr==null || arr.length<2){
return;
}
for(int end=1;end<arr.length;end++){
for(int pre=end-1;pre>=0 && arr[pre]>=arr[pre+1];pre--){//arr[pre]>=arr[pre+1]后者不能用end,因为end随内循环变化。
System.out.println();
print(arr);
swap(arr,pre,pre+1);
}
}
private static void swap(int[] arr ,int i,int j) {
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
希尔排序(改良版插入排序)
package day4_希尔排序;
public class test4_second_knuth {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr ={4,5,6,7,8,9,1,5,4,6};
sort(arr);
print(arr);
}
private static void sort(int[] arr) {
int h=1;
while(h<=arr.length/3){
h=h*3+1;
}
for (int gap=h;gap>0;gap=(gap-1)/3) {
for(int i=gap;i<arr.length;i++){//依次向后挪动。
for (int j=i;j>gap-1;j-=gap){//从当前向前左边进行比较。
if(arr[j]<arr[j-gap]){
swap(arr,j,j-gap);
}
}
}
}
}
private static void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
}
private static void swap(int[] arr ,int i,int j) {
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
归并排序(使用的是递归思想)
时间复杂度:N*logN
时间复杂度计算:
N*(1/2)x=1
解得:x=log2N(对应logN)
空间复杂度:N
package day5_归并排序;
public class test_second {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//int[] arr={1,4,7,8,3,6,9};
int[] arr={1,8,5,4,3,2,9,4};
sort(arr,0,arr.length-1);
print(arr);
}
static void print(int[] arr) {
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void sort(int[] arr,int left,int right) {
if(left==right) return;
//分成两半
int mid=left+(right-left)/2;//或者mid=(left+right)/2;
//左边排序
sort(arr,left,mid);
//右边排序
sort(arr,mid+1,right);
//对拆分后的每一部分进行归并排序
merge(arr,left,mid+1,right);
}
static void merge(int[] arr,int leftPtr,int rightPtr,int rightBound) {
int mid=rightPtr-1;
int i=leftPtr;
int j=rightPtr;
int k=0;
int[] temp=new int[rightBound-leftPtr+1];
while (i<=mid && j<=rightBound) {
temp[k++] = arr[i]<=arr[j] ? arr[i++] :arr[j++];
}
while(i<=mid) temp[k++]=arr[i++];
while(j<=rightBound) temp[k++]=arr[j++];
for (int m = 0; m < temp.length; m++) {
arr[leftPtr+m]=temp[m];
}
}
static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j){
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
快速排序(同样是递归思想)
时间复杂度:
- 最优(平均):o(N*logN)
- 最差:o(N2)根据递归计算:n+(n-1)+(n-2)+……+1
空间复杂度:o(log2N)
package day6_快速排序;
import static day1.test1.print;
public class test6_first {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={7,3,2,10,8,1,9,5,4,6};
//int[] arr={4,5};
sort(arr,0,arr.length-1);
print(arr);
}
public static void sort(int[] arr,int leftBound,int rightBound){
if(leftBound>=rightBound) return;
int mid=partition(arr,leftBound,rightBound);
sort(arr,leftBound,mid-1);
sort(arr,mid+1,rightBound);
}
static int partition(int[] arr, int leftBound, int rightBound) {
int left=leftBound;
int right=rightBound-1;
int pivot=arr[rightBound];
while(left<right){
while(left<=right && arr[left]<=pivot) left++;//left<=right是为了防止最右边的轴比所有值都大,以避免最后一次被调换位置。
while(left<right && arr[right]>pivot) right--;//arr[right]>不等于是为了防止和轴相同的数在两边都有的情况。
if(left<right) swap(arr,left,right);
}
if(arr[left]>=pivot) swap(arr,left,rightBound);//防止未进入改循环直接执行swap
return left;
}
static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j){
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
第二个稍有不同
package day6_快速排序;
import static day1.test1.print;
public class test6_first {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={7,3,2,10,8,1,9,5,4,6};
//int[] arr={4,5};
sort(arr,0,arr.length-1);
print(arr);
}
public static void sort(int[] arr,int leftBound,int rightBound){
if(leftBound>=rightBound) return;
int mid=partition(arr,leftBound,rightBound);
sort(arr,leftBound,mid-1);
sort(arr,mid+1,rightBound);
}
static int partition(int[] arr, int leftBound, int rightBound) {
int left=leftBound;
int right=rightBound-1;
int pivot=arr[rightBound];
while(left<=right){//防止未进入改循环直接执行swap
while(left<=right && arr[left]<=pivot) left++;//left<=right是为了防止最右边的轴比所有值都大,以避免最后一次被调换位置。
while(left<=right && arr[right]>pivot) right--;//arr[right]>不等于是为了防止和轴相同的数在两边都有的情况。left<=right 与上面的稍有不同。
if(left<right) swap(arr,left,right);
}
//if(arr[left]>=pivot)
swap(arr,left,rightBound);
return left;
}
static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j){
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
}
计数排序
非比较排序
同思想的一种
适用范围:量大但是范围小
该代码相对于普通的计数排序,更加稳定,更适用于面向对象。
时间复杂度:o(n+k)-> o(n)
空间复杂度:o(n+k)->o(n)
package day7_计数排序;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class test_first {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={0,5,2,4,1,3,5,7,8,9,6,10};
int[] result=sort(arr);
System.out.println("result: "+Arrays.toString(result));
}
private static int[] sort(int[] arr) {
int[] count=new int[12];
int[] result=new int[arr.length];
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
count[arr[i]]++;
}
System.out.println("count1: "+Arrays.toString(count));
for(int i=1;i<arr.length;i++){
count[i]=count[i]+count[i-1];
}
System.out.println("count2: "+Arrays.toString(count));
for(int i=arr.length-1;i>=0;i--){
result[--count[arr[i]]]=arr[i];
}
return result;
}
}
count1: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
count2: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 12]//该数组的每个元素是每一个数的最后一个的位置+1.
result: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
基数排序
可用于字符串排序。
该算法不稳定
时间复杂度:o(n)
空间复杂度:o(k*n)
根据每一位进行计数排序,从低位到高位排。
package day7_基数排序;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class test_second {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]=new int[]{1,3,4566,9,814,0,89,4,5,0,0,5467498};
radixSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
public static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
int max = arr[0];//假设第一个数就是最大数
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
int maxLength = (max + " ").length();//获取最大数字的位数
for (int i = 1; i <= maxLength; i++) {
int[] count = new int[arr.length];//定义一个一维数组,表示i位上小于等于下标的数有几个,
int[] bucket = new int[arr.length];//辅助数组 暂存数据
//表示i位上等于下标的数有几个
for (int index = 0; index < arr.length; index++) {
int digit = getDigit(arr[index], i);
count[digit]++;
}
//表示i位上小于等于下标的数有几个,
for(int index=1; index<arr.length; index++){
count[index] += count[index-1];
}
//从后向前遍历 经过此次排序 排第几
for(int index = arr.length-1; index>=0; index--){
int digit = getDigit(arr[index], i);
count[digit]--;
bucket[count[digit]]=arr[index];
}
//重新写回原数组
for(int index = 0; index <arr.length; index++){
arr[index] = bucket[index];
}
}
}
private static int getDigit(int x, int index){//获取第 index 位上的数
for(int i=1; i<index; i++){
x=x/10;
}
return x%10;
}
}
前缀和
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr={1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
test.RangeSum2 rs= new test.RangeSum2(arr);//创建对象
int result=rs.rangeSum(1,5);
System.out.println(result);
}
public static class RangeSum2 {//静态内部类
private int[] preSum;
public RangeSum2(int[] arr){
int N=arr.length;
preSum=new int[N];
preSum[0]=arr[0];
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
preSum[i]=preSum[i-1]+arr[i];
}
}
public int rangeSum(int L,int R){
return L==0 ? preSum[R] : preSum[R]-preSum[L-1];
}
}
}
随机数(黑盒版)
public class test_first {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int testTimes=10000000;
int count=0;
for (int i=0;i<testTimes;i++){
if(f2()==0){
count++;
}
}
System.out.println((double)count/(double)testTimes);
int[] counts=new int[8];
for(int i=0;i<testTimes;i++){
int num=f5();
counts[num]++;
}
for(int i=0;i<8;i++){
System.out.println(i+"出现了"+counts[i]+"次");
}
}
//黑盒
//只能用这个随机返回1-5的方法,去实现下面的功能。
public static int f1(){
return (int) (Math.random()*5+1);
}
//随即机制,只能用f1
//等概率返回0和1
public static int f2(){
int ans=0;
do{
ans=f1();
}while(ans==3);
return ans<3 ? 0 :1;
}
//得到000~111做到等概率
//0~7 随机数
public static int f3(){
return (f2()<<2)+(f2()<<1)+(f2()<<0);
}
//0~6 随机数
public static int f4(){
int ans=0;
do{
ans=f3();
}while(ans==7);
return ans;
}
//1~7 随机数
public static int f5(){
int ans=0;
do{
ans=f3();
}while(ans==7);
return ans+1;
}
}
对数器的运用
用来检查代码的正确性。
package day10_对数器的运用;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int maxLen=50;
int maxValue=1000;
int testTime=100000;
for(int i=0;i<testTime;i++){
int[] arr1=lenRandomValueRandom(maxLen,maxValue);
int[] arr2=copyArray(arr1);
selectSort(arr1);
insertSort(arr2);
if(!isSorted(arr1)){
System.out.println("排序错了");
}
}
System.out.println("排序正确");
}
//深克隆一个新的数组
public static int[] copyArray(int[] arr){
int[] ans=new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
ans[i]=arr[i];
}
return ans;
}
//判断排序的正误
public static boolean isSorted(int[] arr){
if(arr.length<2) return true;
int max=arr[0];
for(int i=1;i< arr.length;i++){
if(max>arr[i]) return false;
max=Math.max(max,arr[i]);//每一步更新max的值。
}
return true;
}
public static int[] lenRandomValueRandom(int maxLen,int maxValue){
int len =(int) (Math.random()*maxLen);
int[] ans=new int[len];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
ans[i]=(int)(Math.random()*maxValue);
}
return ans;
}
public static void swap(int[] arr,int i,int j){
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[j];
arr[j]=temp;
}
public static void selectSort(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
int minpos=i;
for (int j = i+1; j < arr.length; j++) {
minpos= arr[minpos]<arr[j] ? minpos : j;
}
swap(arr,minpos,i);
}
}
public static void insertSort(int[] arr){
if(arr==null || arr.length<2){
return;
}
// for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
// for(int j=i;j<arr.length;j--){
// if(arr[j]<=arr[j-1]){
// swap(arr,i,j-1);
// }
// }
// }
for(int end=1;end<arr.length;end++){
for(int pre=end-1;pre>0 && arr[pre]>=arr[pre+1];pre--){
swap(arr,pre,pre+1);
}
}
}
}
二分查找法及其判断正误
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int maxSize = 50;
int maxValue = 1000;
int testTime = 100000;
boolean succeed=true;
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int[] arr = generateRandomArray(maxSize, maxValue);
Arrays.sort(arr);
int value = (int)((maxValue+1)*Math.random())-(int)(maxValue*Math.random());
if(text(arr,value)!=find(arr,value)){
System.out.println("出错了");
succeed=false;
break;
}
}
System.out.println(succeed ? "nice" : "fuck!");
}
public static boolean find(int[] arr,int num){
if(arr==null || arr.length==0) return false;
int L=0;
int R=arr.length-1;
while(L<=R){
int mid=(L+R)/2;
if(arr[mid]==num){
return true;
}else if(arr[mid]<num){
L=mid+1;
}else{
R=mid-1;
}
}
return false;
}
public static boolean text(int[] sortedArr,int num){
for (int cur : sortedArr) {
if(cur==num) return true;
}
return false;
}
public static int[] generateRandomArray(int maxSize, int maxValue) {
int[] arr=new int[(int)((maxSize+1)*Math.random())];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i]=(int)((maxValue+1)*Math.random())-(int)(maxValue*Math.random());
}
return arr;
}
}
二分查找符合条件并且最靠近左边的值位置
//找到最左边符合的值
public class test_nearleft {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int maxSize = 10;
int maxValue = 1000;
int testTime = 100000;
boolean succeed=true;
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int[] arr = generateRandomArray(maxSize, maxValue);
Arrays.sort(arr);
int value = (int)((maxValue+1)*Math.random())-(int)(maxValue*Math.random());//让value值有正有负
if(test(arr,value)!=moreLeftNoLessNumIndex(arr,value)){
print(arr);
System.out.println(value);
System.out.println(test(arr,value));
System.out.println(moreLeftNoLessNumIndex(arr,value));
succeed=false;
break;
}
}
System.out.println(succeed ? "nice" : "fuck!");
}
public static int moreLeftNoLessNumIndex(int[] arr,int num){
if(arr==null || arr.length==0) return -1;
int L=0;
int R=arr.length-1;
int ans=-1;
while(L<=R){
int mid=(L+R)/2;
if(arr[mid]>=num)
{
ans=mid;//返回大于num但是位置最靠近左边的数的位置索引
R=mid-1;
}else{
L=mid+1;
}
}
return ans;
}
public static int test(int[] arr,int value){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i]>=value) return i;//只要大于或等于即立刻返回该数的索引值
}
return -1;
}
public static int[] generateRandomArray(int maxSize, int maxValue) {
int[] arr=new int[(int)((maxSize+1)*Math.random())];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i]=(int)((maxValue+1)*Math.random())-(int)(maxValue*Math.random());
}
return arr;
}
public static void print(int[] arr){
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
二分查找局部最小值
public class test11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int maxLen=50;
int maxValue=100;
int testTime=1000000;
System.out.println("start");
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int[] arr=randomArray(maxLen,maxValue);
int ans = oneMinIndex(arr);
if(!check(arr,ans)){
print(arr);
System.out.println(ans);
break;
}
}
System.out.println("end");
}
public static int oneMinIndex(int[] arr){
if(arr==null || arr.length==0){
return -1;
}
int N=arr.length;
if(N==1) return 0;
if(arr[0]<arr[1]) return 0;
if(arr[N-1]<arr[N-2]) return N-1;
int L=1;
int R=N-2;
int mid=0;
while(L<R){
mid= L+(R-L)/2;
if(arr[mid]>arr[mid+1]){
L=mid+1;
}else if(arr[mid]>arr[mid-1]){
R=mid-1;
}else{
return mid;
}
}
return L;
}
public static int[] randomArray(int maxLen,int maxValue){
int len=(int)(Math.random()*maxLen);
int[] arr=new int[len];
if(len>0){
arr[0]=(int)(Math.random()*maxValue);
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
do{
arr[i]=(int)(Math.random()*maxValue);
}while(arr[i]==arr[i-1]);
}
}
return arr;
}
public static boolean check(int[] arr,int minIndex){
// if(arr.length==0) return minIndex==-1;
// int left =minIndex-1;
// int right=minIndex+1;
// boolean leftBigger=left>=0 ? arr[left] >arr[minIndex] : true;
// boolean rightBigger=right<arr.length ? arr[right] >arr[minIndex] : true;
// return leftBigger && rightBigger;
if(arr.length<= 1) return true;
if(minIndex==0) return arr[minIndex]<arr[minIndex+1];
if(minIndex==arr.length-1) return arr[minIndex]<arr[minIndex-1];
return arr[minIndex]<arr[minIndex+1] && arr[minIndex] < arr[minIndex-1];
}
public static void print (int[] arr){
for (int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
动态数组
arraylist在时间复杂度上和普通的数组一样,并且还支持扩容。
哈希表和有序表
哈希表不管怎么增删改查它的时间复杂度都是常数时间,但是要比查询和加减乘除要差一些。
public class test11_t {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String>map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("anana","djdjdj");
System.out.println(map.containsKey("anana"));
System.out.println(map.get("anana"));
//true
//djdjdj
}
}
有序列表,时间复杂度:o(logN),自动排序。
TreeMap<Integer,String> treeMap1=new TreeMap<>();
treeMap1.put(3,"wo3");
treeMap1.put(4,"wo3");
treeMap1.put(0,"wo3");
System.out.println(treeMap1.firstKey());
System.out.println(treeMap1.lastKey());
System.out.println(treeMap1.floorKey(2));//<=2找最近的
System.out.println(treeMap1.ceilingKey(2));//>2找最近的
/*
* 0
4
0
3
*
*
* */
Node node3=new Node(3);
Node nod4=new Node(4);
treeMap1.put(node3,"sdfasdf");//不能排序所以才不能创建。
单双链表反转
package day_12单双链表反转;
import day_11哈希表和有序表.test11_t;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import static day_12单双链表反转.test12.Node.*;
public class test12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("单链表测试:");
int len=50;
int value=100;
int testTime=10;
System.out.println("start");
for(int i=0;i<testTime;i++){
Node node1=generateRandomLinkedList(len,value);
List<Integer>list1=getLInkedListOriginOrder(node1);
node1=resverLinkedList(node1);
if(!checkLinkedListReverse(list1,node1)){
System.out.println("erro");
}
}
System.out.println("end");
System.out.println("单链表测试结束");
System.out.println("双链表测试开始:");
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
DoubleNode node2=generateRandomDoubleList(len,value);
List<Integer> list2=getDoubleListOrignOrder(node2);
node2=testReverseDoubleList(node2);
if(!checkDoubleListReverse(list2,node2)){
System.out.println("erro");
System.out.println(list2);
System.out.println(list2);
}
}
System.out.println("end");
System.out.println("双链表测试结束。");
}
public static class Node{
public int value;
public Node next;
public Node(int v){
value=v;
}
}
public static Node resverLinkedList(Node head){
Node pre=null;
Node next=null;
while(head!=null){
next=head.next;
head.next=pre;
pre=head;
head=next;
}
return pre;
}
public static Node generateRandomLinkedList(int len,int value){
int size=(int)(Math.random()+(len+1));//可让链表生成为len长度。
if(size==0) return null;
size--;
Node head=new Node(((int)(Math.random()*(value+1))));
Node pre=head;
while(size!=0){
Node cur=new Node((int)(Math.random()*(value+1)));
pre.next=cur;
pre=cur;
size--;
}
return head;
}
public static Node testReversedLinkedList(Node head){
if(head!=null) return null;
ArrayList<Node> list=new ArrayList<>();
while(head!=null){
list.add(head);
head=head.next;
}
list.get(0).next=null;
int N=list.size();
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
list.get(i).next=list.get(i-1);
}
return list.get(N-1);
}
public static List<Integer> getLInkedListOriginOrder(Node head){
List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();
while(head!=null){
ans.add(head.value);
head=head.next;
}
return ans;
}
public static boolean checkLinkedListReverse(List<Integer> origin,Node head){
for(int i=origin.size()-1;i>=0;i--){
if (!origin.get(i).equals(head.value)){
return false;
}
head=head.next;
}
return true;
}
//双链表
public static class DoubleNode{
public int value;
public DoubleNode last;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode(int v){
value=v;
}
}
//第一种反转方式。
public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head){
DoubleNode pre=null;
DoubleNode next=null;
while(head!=null){
next=head.next;
head.next=pre;
head.last=next;
pre=head;
head=next;
}
return pre;
}
//第二种反转方式,过度涉及到数据结构
public static DoubleNode testReverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head){
if(head==null){ return null;}
ArrayList<DoubleNode> list =new ArrayList<>();
while(head!=null){
list.add(head);
head=head.next;
}
list.get(0).next=null;
DoubleNode pre=list.get(0);
int N=list.size();
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
DoubleNode cur=list.get(i);
cur.last=null;
cur.next=pre;
pre.last=cur;
pre=cur;
}
return list.get(N-1);
}
public static DoubleNode generateRandomDoubleList(int len,int value){
int size=(int)(Math.random()*(len+1));//生成[0,len]长度的数。
if(size==0){
return null;
}
size--;
DoubleNode head=new DoubleNode((int)(Math.random()*(value)));
DoubleNode pre=head;
while(size!=0){
DoubleNode cur=new DoubleNode((int)(Math.random()*(value+1)));
pre.next=cur;
cur.last=pre;
pre=cur;
size--;
}
return head;
}
public static List<Integer> getDoubleListOrignOrder(DoubleNode head){
List<Integer> ans=new ArrayList<>();
while(head!=null){
ans.add(head.value);
head=head.next;
}
return ans;
}
public static boolean checkDoubleListReverse(List<Integer> origin, DoubleNode head) {
DoubleNode end = null;
for (int i = origin.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (!origin.get(i).equals(head.value)) {
return false;
}
end = head;
head = head.next;
}
for (int i = 0; i < origin.size(); i++) {
if (!origin.get(i).equals(end.value)) {
return false;
}
end = end.last;
}
return true;
}
}
单双链表实现队列和栈
package day_13单链表实现队列;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Stack;
public class test13 {
public static class Node<V> {
public V value;
public Node<V> next;
public Node(V v) {
value = v;
next = null;
}
}
public static class MyQueue<V> {
private Node<V> head;
private Node<V> tail;
private int size;
public MyQueue() {
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public void offer(V value) {
Node<V> cur = new Node<>(value);
if (tail == null) {
head = cur;
tail = cur;
} else {
tail.next = cur;
tail = cur;
}
size++;
}
public V poll() {//该段的代码的逻辑实现判断链表不为空后再进行出队列的操作,如果反过来则是head指null时就判断已经空了,然而并未,所以会出现ans为null。
V ans = null;
if (head != null) {
ans = head.value;
head = head.next;
size--;
}
if (head == null) {
tail = null;
}
return ans;
}
public V peek() {
V ans = null;
if (head != null) {
ans = head.value;
}
return ans;
}
}
//栈
public static class MyStack<V> {
private Node<V> head;
private int size;
public MyStack() {
head = null;
size = 0;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public void push(V value) {
Node<V> cur = new Node<>(value);
if (head == null) {
head = cur;
} else {
cur.next = head;
head = cur;
}
size++;
}
public V pop() {
V ans = null;
if (head != null) {
ans = head.value;
head = head.next;
size--;
}
return ans;
}
public V peek() {
return head != null ? head.value : null;
}
}
public static void testQueue() {
MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyQueue<>();
Queue<Integer> test = new LinkedList<>();
int testTime = 5000000;
int maxValue = 200000000;
System.out.println("测试开始!");
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
if (myQueue.isEmpty() != test.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
if (myQueue.size() != test.size()) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
double decide = Math.random();
if (decide < 0.33) {
int num = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue);
myQueue.offer(num);
test.offer(num);
} else if (decide < 0.66) {
if (!myQueue.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = myQueue.poll();
int num2 = test.poll();
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
}
} else {
if (!myQueue.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = myQueue.peek();
int num2 = test.peek();
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
}
}
}
if (myQueue.size() != test.size()) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
while (!myQueue.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = myQueue.poll();
int num2 = test.poll();
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
}
System.out.println("测试结束!");
}
public static void testStack() {
MyStack<Integer> myStack = new MyStack<>();
Stack<Integer> test = new Stack<>();
int testTime = 5000000;
int maxValue = 200000000;
System.out.println("测试开始!");
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
if (myStack.isEmpty() != test.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
if (myStack.size() != test.size()) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
double decide = Math.random();
if (decide < 0.33) {
int num = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue);
myStack.push(num);
test.push(num);
} else if (decide < 0.66) {
if (!myStack.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = myStack.pop();
int num2 = test.pop();
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
}
} else {
if (!myStack.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = myStack.peek();
int num2 = test.peek();
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
}
}
}
if (myStack.size() != test.size()) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
while (!myStack.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = myStack.pop();
int num2 = test.pop();
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
}
System.out.println("测试结束!");
}
public static void main(String[] args){
testQueue();
testStack();
}
}
双链表实现双端队列
package day_14双链表实现双端队列;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class test14 {
public static class Node<V>{
public V value;
public Node<V> next;
public Node<V> last;
public Node(V v){
value=v;
next=null;
last=null;
}
public static class MyDeque<V>{
private Node<V> head;
private Node<V> tail;
private int size;
public MyDeque(){
head=null;
tail=null;
size=0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
public void pushHead(V value){
Node<V> cur=new Node<>(value);
if(head==null){
head=cur;
tail=cur;
}else{
cur.next=head;
head.last=cur;
head=cur;
}
size++;
}
public void pushTail(V value){
Node<V> cur=new Node<>(value);
if(head==null){
head=cur;
tail=cur;
}else{
tail.next=cur;
cur.last=tail;
tail=cur;
}
size++;
}
public V pollHead(){
V ans=null;
if(head==null){
return ans;
}
size--;
ans=head.value;
if(head==tail){
head=null;
tail=null;
}else{
head=head.next;
head.last=null;
}
return ans;
}
public V pollTail(){
V ans=null;
if(head==null){
return ans;
}
size--;
ans=tail.value;
if(head==tail){
head=null;
tail=null;
}else{
tail=tail.last;
tail.next=null;
}
return ans;
}
public V peekHead(){
V ans=null;
if(head==null){
return ans;
}
return head.value;
}
public V peekTail(){
V ans=null;
if(tail==null){
return ans;
}
return tail.value;
}
}
}
public static void testDeque() {
Node.MyDeque<Integer> myDeque = new Node.MyDeque<>();
Deque<Integer> test = new LinkedList<>();
int testTime = 5000000;
int maxValue = 200000000;
System.out.println("测试开始!");
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
if (myDeque.isEmpty() != test.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Oops!_empty");
}
if (myDeque.size() != test.size()) {
System.out.println("Oops!_size");
}
double decide = Math.random();
if (decide < 0.33) {
int num = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue);
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
myDeque.pushHead(num);
test.addFirst(num);
} else {
myDeque.pushTail(num);
test.addLast(num);
}
} else if (decide < 0.66) {
if (!myDeque.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
num1 = myDeque.pollHead();
num2 = test.pollFirst();
} else {
num1 = myDeque.pollTail();
num2 = test.pollLast();
}
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!_poll!=D");
}
}
} else {
if (!myDeque.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
if (Math.random() < 0.5) {
num1 = myDeque.peekHead();
num2 = test.peekFirst();
} else {
num1 = myDeque.peekTail();
num2 = test.peekLast();
}
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!_peek!=");
}
}
}
}
if (myDeque.size() != test.size()) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
while (!myDeque.isEmpty()) {
int num1 = myDeque.pollHead();
int num2 = test.pollFirst();
if (num1 != num2) {
System.out.println("Oops!_poll!=");
}
}
System.out.println("测试结束!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testDeque();
}
}
K个节点的组内逆序调整
package day_14k个节点的组内逆序调整;
public class test14_k {
public static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value){
val=value;
}
public ListNode(int value,ListNode n){
val=value;
next=n;
}
}
public static void reverse(ListNode start,ListNode end){
end=end.next;
ListNode pre=null;
ListNode cur=start;
ListNode next=null;
while(cur!=end){
next=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=next;
}
start.next=end;
}
public static ListNode getGroupEnd(ListNode start,int k){
while(--k!=0 && start!=null){
start=start.next;
}
return start;
}
public static ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head,int k){
ListNode start=head;
ListNode end=getGroupEnd(start,k);
if(end==null) return head;
//先定第一组
head=end;
reverse(start,end);
//第一组结束,下面是剩下组的排序。
ListNode lastEnd=start;
while(lastEnd.next!=null){
start=lastEnd.next;
end=getGroupEnd(start,k);
if(end==null) return head;
reverse(start,end);
lastEnd.next=end;//将每一组的下一个当作尾巴
lastEnd=start;//将每一组结尾节点当作时开始节点
}
return head;
}
}
两个链表相加
package day_15两个链表的相加;
import java.util.List;
public class test15_f {
public static class ListNode{
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val=val;
}
public ListNode(int val,ListNode next){
this.val=val;
this.next=next;
}
}
public static ListNode addTwoNumber(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){
int len1=ListLength(head1);
int len2=ListLength(head2);
ListNode l=len1>len2?head1:head2;
ListNode s=l==head1?head2:head1;
ListNode curL=l;
ListNode curS=s;
ListNode last=curL;
int curNum=0;
int carry=0;
while(curS!=null){
curNum=curL.val+curS.val+carry;
curL.val=(curNum%10);
carry=curNum/10;
last=curL;
curL=curL.next;
curS=curS.next;
}
while(curL!=null){
curNum=curL.val+carry;
curL.val=(curNum%10);
carry=curNum/10;
last=curL;
curL=curL.next;
}
if(carry!=0){
last.next=new ListNode(1);
}
return l;
}
public static int ListLength(ListNode head){
int len=0;
while(head!=null){
len++;
head=head.next;
}
return len;
}
}
位图
功能:用一个变量将多个数存储在里面
实现:
public class test16_f {
public static class BitMap{
private long[] bits;
public BitMap(int max){
bits=new long[(max+64)>>6];
}
public void add(int num){
bits[(num>>6)] |=(1L<<(num&63));
}
public void delete(int num){
bits[(num)>>6] &= ~(1L<<(num&63));
}
public boolean contains(int num){
return (bits[(num>>6)] & (1L<<(num & 63)))!=0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("测试开始!");
int max = 10000;
BitMap bitMap = new BitMap(max);
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
int testTime = 10000000;
for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {
int num = (int) (Math.random() * (max + 1));
double decide = Math.random();
if (decide < 0.333) {
bitMap.add(num);
set.add(num);
} else if (decide < 0.666) {
bitMap.delete(num);
set.remove(num);
} else {
if (bitMap.contains(num) != set.contains(num)) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
break;
}
}
}
for (int num = 0; num <= max; num++) {
if (bitMap.contains(num) != set.contains(num)) {
System.out.println("Oops!");
}
}
System.out.println("测试结束!");
}
}
位运算实现加减乘除运算
加减乘除
public class test_s {
public static int add(int a,int b){
int sum=a;
while(b!=0){
sum=a^b;
b=(a&b)<<1;
a=sum;
}
return sum;
}
public static int minus(int a,int b){//减法
return add(a,negNum(b));
}
public static int negNum(int b) {//相反数
return add(~b,1);
}
public static int multi(int a,int b){//乘法
int res=0;
while(b!=0){
if((b&1)!=0){
res=add(res,a);
}
a<<=1;
b>>>=1;//无符号右移
}
return res;
}
public static int div(int a,int b){
int x= isNeg(a) ? negNum(a) : a ;
int y =isNeg(b) ? negNum(b) : b ;
int res = 0;
for (int i=30;i>=0;i=minus(i,1)) {
if ((x >> i) >= y) {
res |= (1 << i);
x=minus(x,y<<i);
}
}
return isNeg(a) ^ isNeg(b) ? negNum(res) : res;
}
public static int divide(int a,int b){//避免最小值的问题
if(a== Integer.MIN_VALUE && b==Integer.MIN_VALUE){
return 1;
}else if(b==Integer.MIN_VALUE){
return 0;
}else if(a==Integer.MIN_VALUE){
if(b==negNum(1)){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}else{
int c = div(add(a,1),b);
return add(c,div(minus(a,multi(c,b)),b));
}
}else{
return div(a,b);
}
}
public static boolean isNeg(int n) {
return n < 0 ;
}
}
对数器的排序
public static class Student{
public String name;
public int id;
public int age;
public Student(String name,int id,int age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.id=id;
}
}
//谁id小谁在前面
public static class IdComparator implements Comparator<Student>{
// 如果返回负数,认为第一个参数应该排在前面
// 如果返回正数,认为第二个参数应该排在前面
// 如果返回0,认为谁放前面无所谓
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.id-o2.id;
}
}
public static class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Student>{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.age-o2.age;
}
}
public static void printStudents(Student[] students){
for (Student student : students) {
System.out.println(student.id+" "+student.age+" "+student.name);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("张三", 5, 27);
Student s2 = new Student("李四", 1, 17);
Student s3 = new Student("王五", 4, 29);
Student s4 = new Student("赵六", 3, 9);
Student s5 = new Student("左七", 2, 34);
Student[] students = { s1, s2, s3, s4, s5 };
printStudents(students);
System.out.println("=======");
Arrays.sort(students, new IdComparator());//规定排序规则
printStudents(students);
System.out.println("=======");
ArrayList<Student> arrList = new ArrayList<>();
arrList.add(s1);
arrList.add(s2);
arrList.add(s3);
arrList.add(s4);
arrList.add(s5);
for (Student s : arrList) {
System.out.println(s.name + ", " + s.id + ", " + s.age);
}
System.out.println("=======");
arrList.sort(new AgeComparator());/规定排序规则
for (Student s : arrList) {
System.out.println(s.name + ", " + s.id + ", " + s.age);
}
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








