单链表—— Singly Linked List
一、单链表的定义
单链表:线性表的链式存储,它是通过一组任意的存储单元来存储线性表中的数据元素,不需要使用地址连续的存储单元,因此它不要求在逻辑上相邻的两个元素在物理位置上也相邻。
二、单链表的特点
①不能随机访问:遍历查找访问
②存储密度不高:每个节点既要存数据元素又要存指针
③拓展容量方便:直接用建立单链表拓展
④插入、删除操作方便:知道位置直接插入和删除
三、单链表的实现方式
实现方式:不带头结点和带头结点,一般带头结点比不带头结点好
带头结点:写操作代码方便,一般用带头结点,不明确的都是带头结点的
不带头结点:写操作代码麻烦,要区分第一个数据和后续数据的处理
注:这两种方式主要是:类型描述相同,初始化和判空不同
四、单链表上的操作
单链表的类型描述
typedef struct LNode{ //定义单链表结点类型
int data; //数据域,可以是别的各种数据类型,本文统一用int类型
struct LNode *next; //指针域
}LNode, *LinkList;
初始化和判空

不带头结点的初始化和判空
//初始化
void InitList(LinkList &L){
L = NULL;
L->next = NULL;
}
//判空操作
bool Empty(LinkList L){
if(L == NULL){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
带头结点的初始化和判空
//初始化
void InitList(LinkList &L){
L = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkList));
L->next = NULL;
}
//判空操作
bool Empty(LinkList L){
if(L->next == NULL){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
建立单链表
头插法建立单链表
用于链表的逆置
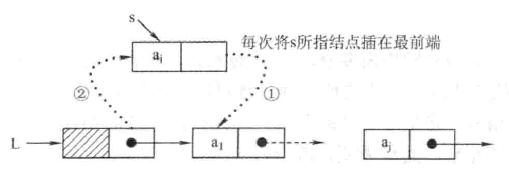
//头插法建立单链表
LinkList HeadInsert(LinkList &L){
InitList(L); //初始化
int x;
cin>>x;
while(x!=9999){ //输入9999表示结束
LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data = x;
s->next = L->next;
L->next = s;
cin>>x;
}
return L;
}
尾插法建立单链表

//尾插法建立单链表
LinkList TailInsert(LinkList &L){
InitList(L);
LNode *s,*r=L;
int x;
cin>>x;
while(x!=9999){
s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data = x;
r->next = s;
r = s;
cin>>x;
}
r->next = NULL;
return L;
}
插入
时间复杂度=O(1)
带头结点的插入
//将x插入到单链表L的第i个位置上
bool Insert(LinkList &L, int i, int e){
if(i<1) return false;
LNode *p = GetElem(L,i-1); //查找第i个位置
return InsertNextNode(p, e); //用后插操作,插在p后面
}
不带头结点的插入
//将x插入到单链表L的第i个位置上
bool Insert(LinkList &L, int i, int e){
if(i<1) return false;
if(i==1){
LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data = e;
s->next = L;
L = s;
return true;
}
LNode *p = GetElem(L,i-1); //查找第i个位置
return InsertNextNode(p, e); //用后插操作,插在p后面
}
指定结点的后插操作
//后插操作:在p结点之后插入元素e
bool InsertNextNode(LNode *p, int e){
if(p==NULL) return false;
LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(s==NULL) return false;
s->data = e;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
return true;
}
指定结点的前插操作
还是插在p后面,只不过让p和插入结点的值交换
//前插操作:在p结点之前插入元素e
bool InsertPriorNode(LNode *p, int e){
if(p==NULL) return false;
LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(s==NULL) return false;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
s->data = p->data;
p->data = e;
return true;
}
删除
按位序删除
//删除操作:将单链表中的第i个结点删除
bool Delete(LinkList &L, int i int &e){
if(i<1 || i>Length(L))
return false;
LNode *p = GetElem(L,i-1); //查找第i个位置
LNode *q = p->next;
e = q->data;
p->next = q->next;
free(q);
return true;
}
按位序删除的时间复杂度:
最好情况:删除第一个,不需查找位置,循环0次,最好时间复杂度=O(1)
最坏情况:删除最后一个,需查找第n位,循环n次,最坏时间复杂度=O(n)
平均情况:删除任意一个,平均时间复杂度=O(n)
指定结点的删除
时间复杂度=O(n)
方法:p的后一个为q,p指向q的下一个,把q的值给p,最后释放q
//删除指定结点p
bool Delete(LNode *p){
if(p==NULL) return false;
LNode *q = p->next;
p->data = q->data
p->next = q->next;
free(q);
return true;
}
查找
按位查找
平均时间复杂度=O(n)
//按位查找:查找在单链表L中第i个位置的结点
LNode *GetElem(LinkList L, int i){
int j=0;
LNode *p = L;
if(i<0) return NULL;
while(p && j<i){
p = p->next;
j++;
}
return p; //如果i大于表长,p=NULL,直接返回p即可
}
按值查找
平均时间复杂度=O(n)
//按值查找:查找e在L中的位置
LNode *LocateElem(LinkList L, int e){
LNode *p = L->next;
while(p && p->data != e){
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
求表长
平均时间复杂度=O(n)
//求表的长度
int Length(LinkList L){
int len = 0;
LNode *p = L;
while(P->next){
p = p->next;
len++;
}
return len;
}
遍历
//遍历操作
void PrintList(LinkList L){
LNode *p = L->next;
while(p){
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p = p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
五、完整代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode, *LinkList;
//初始化
void InitList(LinkList &L){
L = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkList));
L->next = NULL;
}
//遍历操作
void PrintList(LinkList L){
LNode *p = L->next;
while(p){
cout<<p->data<<" ";
p = p->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
//求单链表的长度
int Length(LinkList L){
LNode *p = L->next;
int len = 0;
while(p){
len++;
p = p->next;
}
return len;
}
//头插法建立单链表
LinkList HeadInsert(LinkList &L){
InitList(L); //初始化
int x;
cin>>x;
while(x!=9999){
LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data = x;
s->next = L->next;
L->next = s;
cin>>x;
}
return L;
}
//尾插法建立单链表
LinkList TailInsert(LinkList &L){
InitList(L);
LNode *s,*r=L;
int x;
cin>>x;
while(x!=9999){
s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data = x;
r->next = s;
r = s;
cin>>x;
}
r->next = NULL;
return L;
}
//按值查找:查找x在L中的位置
LNode *LocateElem(LinkList L, int x){
LNode *p = L->next;
while(p && p->data != x){
p = p->next;
}
return p;
}
//按位查找:查找在单链表L中第i个位置的结点
LNode *GetElem(LinkList L, int i){
int j=1;
LNode *p = L->next;
if(i==0)return L;
if(i<1)return NULL;
while(p && j<i){
p = p->next;
j++;
}
return p; //如果i大于表长,p=NULL,直接返回p即可
}
//将x插入到单链表L的第i个位置上
void Insert(LinkList &L, int i, int x){
LNode *p = GetElem(L,i-1);
LNode *s = (LNode *)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data = x;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
}
//删除操作:将单链表中的第i个结点删除
void Delete(LinkList &L, int i){
if(i<1 || i>Length(L)){
cout<<"delete failed: index is wrong."<<endl;
return;
}
LNode *p = GetElem(L,i-1);
LNode *q = p->next;
p->next = q->next;
free(q);
}
int main(){
//初始化,尾插法建立单链表
LinkList L = TailInsert(L);
//插入:在第二个位置插入结点,数据域为888,并遍历单链表
Insert(L,2,888);
cout<<"在第二个位置插入888: ";
PrintList(L);
//删除:删除第四个结点
Delete(L,4);
cout<<"删除第四个结点后:";
PrintList(L);
//按位查找:查找第三个结点,并输出其数据域的值
LNode *p = GetElem(L,3);
cout<<"第三个结点的值为:"<<p->data<<endl;
//按值查找:查找数据域为2的结点的指针
LNode *q = LocateElem(L,2);
cout<<"数据为2的结点的下一个结点的值为:"<<q->next->data<<endl;
//输出单链表的长度
cout<<"单链表的长度:"<<Length(L)<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
























 3256
3256











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










