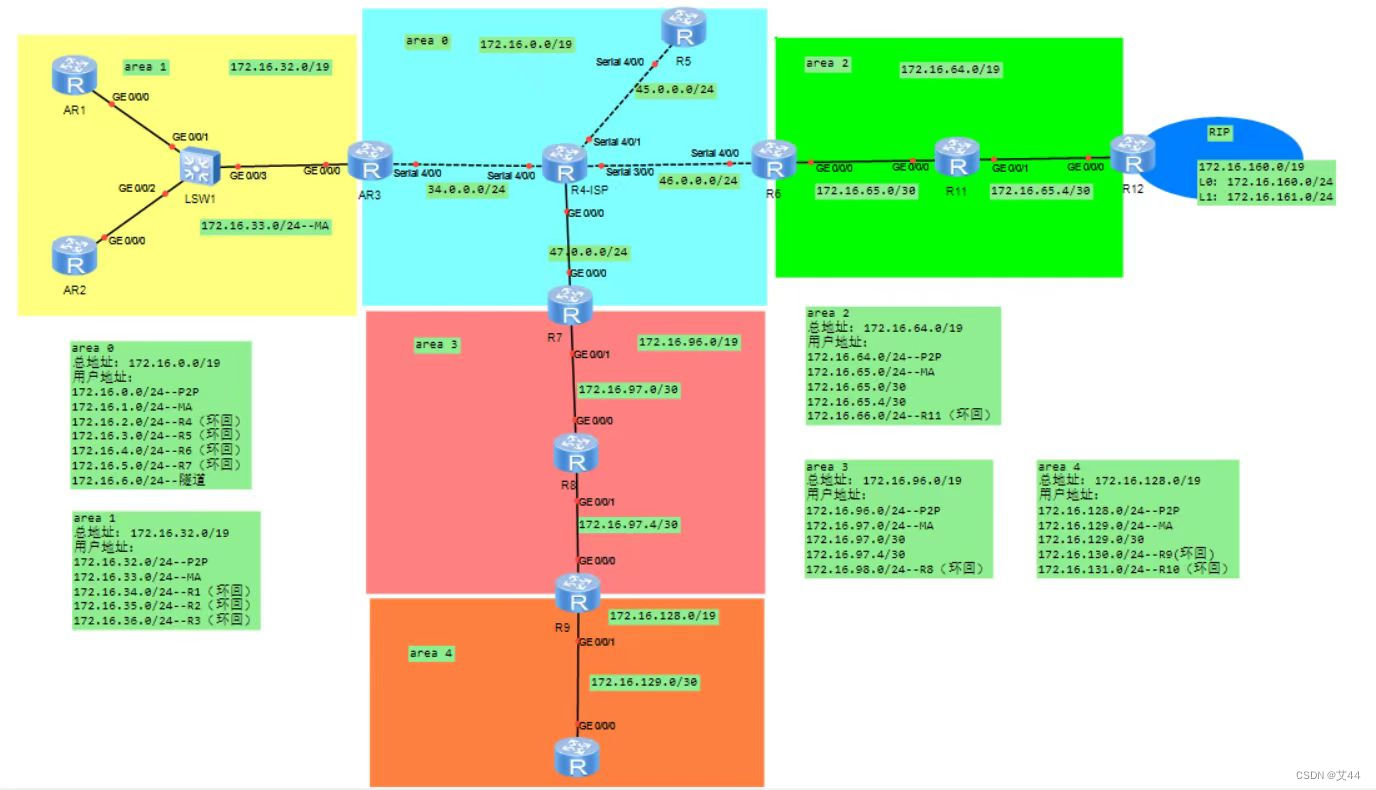
拓扑图
实验要求
1、R4为ISP,其上只配置IP地址;R4与其他所直连设备间均使用公有IP;
2、R3-R5、R6、R7为MGRE环境,R3为中心站点;
3、整个OSPF环境IP基于172.16.0.0/16划分;除了R12有两个环回,其他路由器均有一个环回IP
4、所有设备均可访问R4的环回;
5、减少LSA的更新量,加快收敛,保障更新安全;
6、全网可达;
实验思路
1.路由规划(基于172.16.0.0/16划分)并配置内外网IP地址
area 0
总地址:172.16.0.0/19
用户地址:
172.16.0.0/24--P2P
172.16.1.0/24--MA
172.16.2.0/24--R4
172.16.3.0/24--R5
172.16.4.0/24--R6(环回)
172.16.5.0/24--R7(环回)
172.16.6.0/24--隧道
area 1
总地址:172.16.32.0/19
用户地址:
172.16.32.0/24--P2P
172.16.33.0/24--MA
172.16.34.0/24--R1(环回)
172.16.35.0/24--R2(环回)
172.16.36.0/24--R3(环回)
area 2
总地址:172.16.64.0/19
用户地址:
172.16.64.0/24--P2P
172.16.65.8/24--MA
172.16.65.0/30
172.16.65.4/30
172.16.66.0/24--R11(环回)
area 3
总地址:172.16.96.0/19
用户地址:
172.16.96.0/24--P2P
172.16.97.0/24--MA
172.16.97.0/30
172.16.97.4/30
172.16.98.0/24--R8(环回)
area 4
总地址:172.16.128.8/19
用户地址:
172.16.128.0/24--P2P
172.16.129.0/24--MA
172.16.129.0/30
172.16.138.8/24--R9(环回)
172.16.131.8/24--R18(环回)
2.ip地址配置
R1
[R1]int g 0/0/0
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.33.1 24
[R1-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R1-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.34.1 24
[R1]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 3
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 3
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 2
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.33.1/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.34.1/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
R2
[R2]int g 0/0/0
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.33.2 24
[R2-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R2-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.35.2 24
[R2-LoopBack0]q
[R2]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 3
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 3
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 2
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.33.2/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.35.2/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
R3
[R3]int g 0/0/0
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.33.3 24
[R3-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R3-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.36.3 24
[R3-LoopBack0]int s 4/0/0
[R3-Serial4/0/0]ip add 34.0.0.3 24
[R3-Serial4/0/0]q
[R3]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 5
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 5
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.33.3/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.36.3/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
Serial1/0/0 unassigned down down
Serial1/0/1 unassigned down down
Serial4/0/0 34.0.0.3/24 up up
Serial4/0/1 unassigned down down
R4
[R4]int s 4/0/0
[R4-Serial4/0/0]ip add 34.0.0.4 24
[R4-Serial4/0/0]int s 4/0/1
[R4-Serial4/0/1]ip add 45.0.0.4 24
[R4-Serial4/0/1]int s 3/0/0
[R4-Serial3/0/0]ip add 46.0.0.4 24
[R4-Serial3/0/0]int g 0/0/0
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 47.0.0.4 24
[R4-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R4-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.2.4 24
[R4-LoopBack0]q
[R4]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 6
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 7
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 6
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 7
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 47.0.0.4/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.2.4/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
Serial1/0/0 unassigned down down
Serial1/0/1 unassigned down down
Serial2/0/0 unassigned down down
Serial2/0/1 unassigned down down
Serial3/0/0 46.0.0.4/24 up up
Serial3/0/1 unassigned down down
Serial4/0/0 34.0.0.4/24 up up
Serial4/0/1 45.0.0.4/24 up up
R5
[R5]int s 4/0/0
[R5-Serial4/0/0]ip add 45.0.0.5 24
[R5-Serial4/0/0]int l0
[R5-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.3.5 24
[R5-LoopBack0]q
[R5]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 3
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 3
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 4
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.3.5/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
Serial4/0/0 45.0.0.5/24 up up
Serial4/0/1 unassigned down down
R6
[R6]int s 4/0/0
[R6-Serial4/0/0]ip add 46.0.0.6 24
[R6-Serial4/0/0]int g 0/0/0
[R6-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.65.1 30
[R6-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R6-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.4.6 24
[R6-LoopBack0]q
[R6]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 3
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 3
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.65.1/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.4.6/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
Serial4/0/0 46.0.0.6/24 up up
Serial4/0/1 unassigned down down
R7
[R7]int g 0/0/0
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 47.0.0.7 24
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g 0/0/1
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.97.1 30
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[R7-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.5.7 24
[R7-LoopBack0]q
[R7]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 1
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 1
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 47.0.0.7/24 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.97.1/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.5.7/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
R8
[R8]int g 0/0/0
[R8-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.97.2 30
[R8-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g 0/0/1
[R8-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.97.5 30
[R8-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[R8-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.98.8 24
[R8-LoopBack0]q
[R8]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 1
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 1
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.97.2/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.97.5/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.98.8/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
R9
[R9]int g 0/0/0
[R9-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.97.6 30
[R9-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g 0/0/1
[R9-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.128.1 30
[R9-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[R9-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.130.9 24
[R9-LoopBack0]q
[R9]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 1
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 1
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.97.6/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.128.1/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.130.9/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
R10
[R10]int g 0/0/0
[R10-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.129.2 30
[R10-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R10-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.131.10 24
[R10-LoopBack0]q
[R10]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 3
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 3
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 2
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.129.2/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.131.10/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
R11
[AR11-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.65.2 30.
[AR11-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int g 0/0/1
[AR11-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]ip add 172.16.65.5 30
[AR11-GigabitEthernet0/0/1]int l0
[AR11-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.66.11 24
[AR11-LoopBack0]q
[AR11]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 1
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 1
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.65.2/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 172.16.65.5/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.66.11/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
R12
[R12]int g 0/0/0
[R12-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ip add 172.16.65.6 30
[R12-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]int l0
[R12-LoopBack0]ip add 172.16.160.12 24
[R12-LoopBack0]int l1
[R12-LoopBack1]ip add 172.16.161.12 24
[R12-LoopBack1]q
[R12]dis ip int b
*down: administratively down
^down: standby
(l): loopback
(s): spoofing
The number of interface that is UP in Physical is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Physical is 2
The number of interface that is UP in Protocol is 4
The number of interface that is DOWN in Protocol is 2
Interface IP Address/Mask Physical Protocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0 172.16.65.6/30 up up
GigabitEthernet0/0/1 unassigned down down
GigabitEthernet0/0/2 unassigned down down
LoopBack0 172.16.160.12/24 up up(s)
LoopBack1 172.16.161.12/24 up up(s)
NULL0 unassigned up up(s)
3.在R3-R5-R6-R7上配置缺省指向公网R4
[R3]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 34.0.0.4
[R5]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 45.0.0.4
[R6]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 46.0.0.4
[R7]ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0 47.0.0.4
4.配置MGRE R3作为中心站点 R5-R6-R7作为分支站点
R3
[R3]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 172.16.6.3 24
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]source s4/0/0
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 100
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry multicast dynamicR5
[R5]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R5-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 172.16.6.5 24
[R5-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[R5-Tunnel0/0/0]source s 4/0/0
[R5-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 100
[R5-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 172.16.6.3 34.0.0.3 register
R6
[R6]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R6-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 172.16.6.6 24
[R6-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[R6-Tunnel0/0/0]source s4/0/0
[R6-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 100
[R6-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 172.16.6.3 34.0.0.3 registerR7
[R7]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R7-Tunnel0/0/0]ip add 172.16.6.7 24
[R7-Tunnel0/0/0]tunnel-protocol gre p2mp
[R7-Tunnel0/0/0]source g 0/0/0
[R7-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp network-id 100
[R7-Tunnel0/0/0]nhrp entry 172.16.6.3 34.0.0.3 register5.启用ospf协议并优化路由(减少路由条目)
R1
[R1]ospf 1 router-id 1.1.1.1
[R1-ospf-1]a 1
[R1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]network 172.16.33.0 0.0.0.255
[R1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]network 172.16.34.0 0.0.0.255
[R1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]stub no-summary
R2
[R2]ospf 1 router-id 2.2.2.2
[R2-ospf-1]a 1
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]net 172.16.33.0 0.0.0.255
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]net 172.16.35.0 0.0.0.255
[R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]stub no-summaryR3
[R3]ospf 1 router-id 3.3.3.3
[R3-ospf-1]a 1
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]net 172.16.33.3 0.0.0.0
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]net 172.16.36.0 0.0.0.255
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]stub no-summary R5
[R5]ospf 1 router-id 5.5.5.5
[R5-ospf-1]a 0
[R5-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.3.0 0.0.0.255R6
[R6]ospf 1 router-id 6.6.6.6
[R6-ospf-1]a 2
[R6-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]net 172.16.65.1 0.0.0.0
[R6-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]nssa no-summary
[R6-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]q
[R6-ospf-1]a 0
[R6-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.4.0 0.0.0.255
R7
[R7]ospf 1 router-id 7.7.7.7
[R7-ospf-1]a 3
[R7-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]net 172.16.97.1 0.0.0.0
[R7-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]nssa no-summary
[R7-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]q
[R7-ospf-1]a 0
[AR7-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]net 172.16.5.0 0.0.0.255R8
[R8]ospf 1 router-id 8.8.8.8
[R8-ospf-1]a 3
[R8-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]net 172.16.97.2 0.0.0.0
[R8-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]net 172.16.97.5 0.0.0.0
[R8-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]net 172.16.98.0 0.0.0.255
[R8-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]nssa no-summaryR9
[R9]ospf 1 router-id 9.9.9.9
[R9-ospf-1]asbr-summary 172.16.128.0 255.255.224.0
[R9-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]nssa no-summary
[R9-ospf-1]a 3
[R9-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]net 172.16.97.6 0.0.0.0
[R9]ospf 2 router-id 9.9.9.9
[R9-ospf-2]a 4
[R9-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.4]net 172.16.129.1 0.0.0.0
[R9-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.4]net 172.16.130.0 0.0.0.255
R9(将进程1和进程2互相发布到对方的OSPF进程中)
[R9]ospf 1
[R9-ospf-1]import-route ospf 2
[R9-ospf-1]q
[R9]ospf 2
[R9-ospf-2]import-route ospf 1
R9(发缺省:area 4 进入R9进程2 删掉进程1 发一条缺省给R10)
[R9-ospf-2]default-route-advertise注:解决路由表中缺少area 4的问题
R10
[R10]ospf 2 r
[R10]ospf 2 router-id 10.10.10.10
[R10-ospf-2]a 4
[R10-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.4]net 172.16.129.2 0.0.0.0
[R10-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.4]net 172.16.131.0 0.0.0.255R11
[R11]ospf 1 router-id 11.11.11.11
[R11-ospf-1]a 2
[R11-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]net 172.16.65.2 0.0.0.0
[R11-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]net 172.16.65.5 0.0.0.0
[R11-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]nssa no-summary
R12
[R12]ospf 1 router-id 12.12.12.12
[R12-ospf-1]a 2
[R12-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]net 172.16.65.6 0.0.0.0
R12配置rip
[R12]rip 1
[R12-rip-1]v 2
[R12-rip-1]undo summary
[R12-rip-1]net 172.16.0.0重发rip到ospf上,优化R12的ospf配置
[R12]ospf 1
[R12-ospf-1]asbr-summary 172.16.160.0 255.255.224.0
[R12-ospf-1]import-route rip 1
[R12-ospf-1]a 2
[R12-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]nssa no-summary6.在MGRE和内网启用OSPF协议进行宣告
R3
[R3]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast
R5
[R5]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R5-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast
[R5-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf dr-priority 0R6
[R6]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R6-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast
[R6-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf dr-priority 0R7
[R7]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R7-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf network-type broadcast
[R7-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf dr-priority 07、配置NULL 0接口防环
R3
[R3]ip route-static 172.16.32.0 19 NULL 0R6
[R6]ip route-static 172.16.64.0 19 NULL 0R7
[R7]ip route-static 172.16.96.0 19 NULL 0R9
[R9]ip route-static 172.16.128.0 19 NULL 0R12
[R12]ip route-static 172.16.160.0 19 NULL 08、配置NAT
R3
[R3]acl 2000
[R3-acl-basic-2000]rule permit source 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255
[R3-acl-basic-2000]q
[R3]int Serial 4/0/0
[R3-Serial4/0/0]nat outbound 2000R6
[R6]acl 2000
[R6-acl-basic-2000]rule permit source 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255
[R6-acl-basic-2000]q
[R6]int Serial 4/0/0
[R6-Serial4/0/0]nat outbound 2000R7
[R7]acl 2000
[R7-acl-basic-2000]rule permit source 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255
[R7-acl-basic-2000]q
[R7]int GigabitEthernet 0/0/0
[R7-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]nat outbound 20009、OSPF认证
[R1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456 [R2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.1]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456
[R3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456[R5-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456[R6-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456
[R6-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456[R7-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456
[R7-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456[R9-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.3]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456
[R9-ospf-2-area-0.0.0.4]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456[R10-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.4]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456[R11-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.2]authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 123456[R12-GigabitEthernet0/0/0]ospf authentication-mode md5 1 cipher 12345610.加快收敛
1.减少计时时间
[R3]int Tunnel 0/0/0
[R3-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf timer hello 10[R5]int t 0/0/0
[R5-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf timer hello 10[R6]int t 0/0/0
[R6-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf timer hello 10[R7]int t 0/0/0
[R7-Tunnel0/0/0]ospf timer hello 1011.实验测试
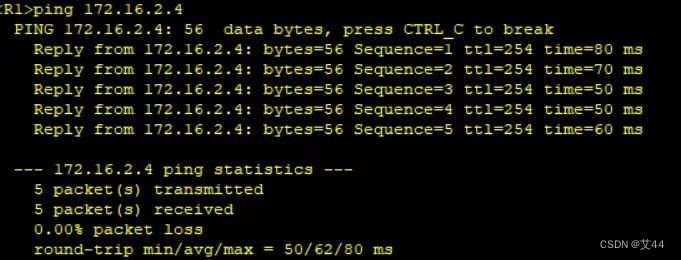



查看路由表
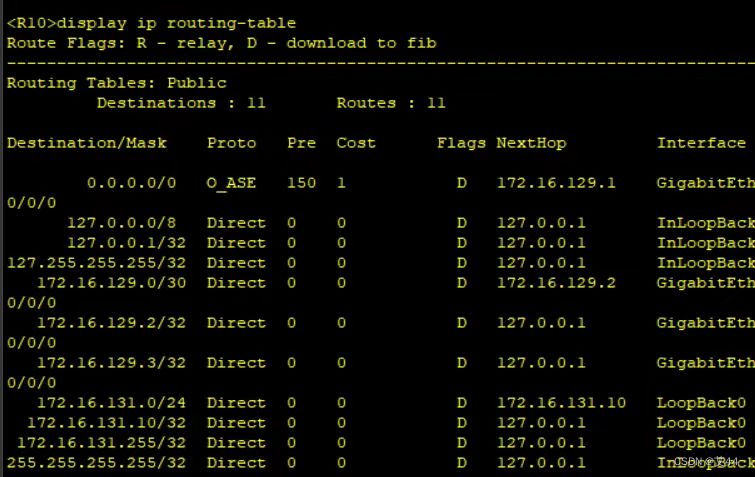

至此实验结束






















 97
97











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










