文章目录
一、什么是多线程
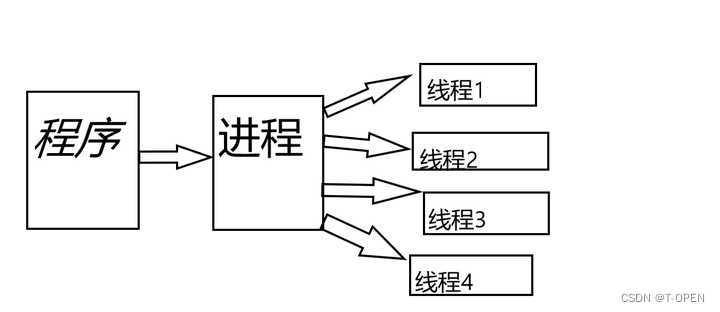
多线程是指在一个程序中同时执行多个独立的任务或操作。每个任务或操作都是由一个单独的线程来执行,而这些线程共享程序的资源和内存空间。与单线程相比,多线程可以提高程序的运行效率和响应速度,因为它可以充分利用 CPU 的多核处理能力,同时也可以避免某些操作阻塞其他操作的问题。
二、为什么要用多线程
在我们开发系统过程中,比如会遇到一个接口会需要调用很多的接口,譬如 请求我的购物车,那么就需要去调用 用户信息的rpc、商品详情的rpc、库存rpc、优惠券 等等好多个服务的接口, 最终全部获取完毕后,就汇总结果,返回给客户端。如果按顺序执行按顺序执行则会非常耗时,多线程去请求则会很快。
三、springboot中如何使用多线程
在springboot开启多线程 只需要2个注解 2部即可。
3.1 配置线程池
这里我们把@EnableAsync 放在线程池配置类上,也可以放在启动类上都可以。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class TaskPoolConfig {
@Bean("taskExecutor")
public Executor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);//核心线程数目
executor.setMaxPoolSize(20);//指定最大线程数
executor.setQueueCapacity(200);//队列中最大的数目
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);//线程空闲后的最大存活时间
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("ratel-task-");//线程名称前缀
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
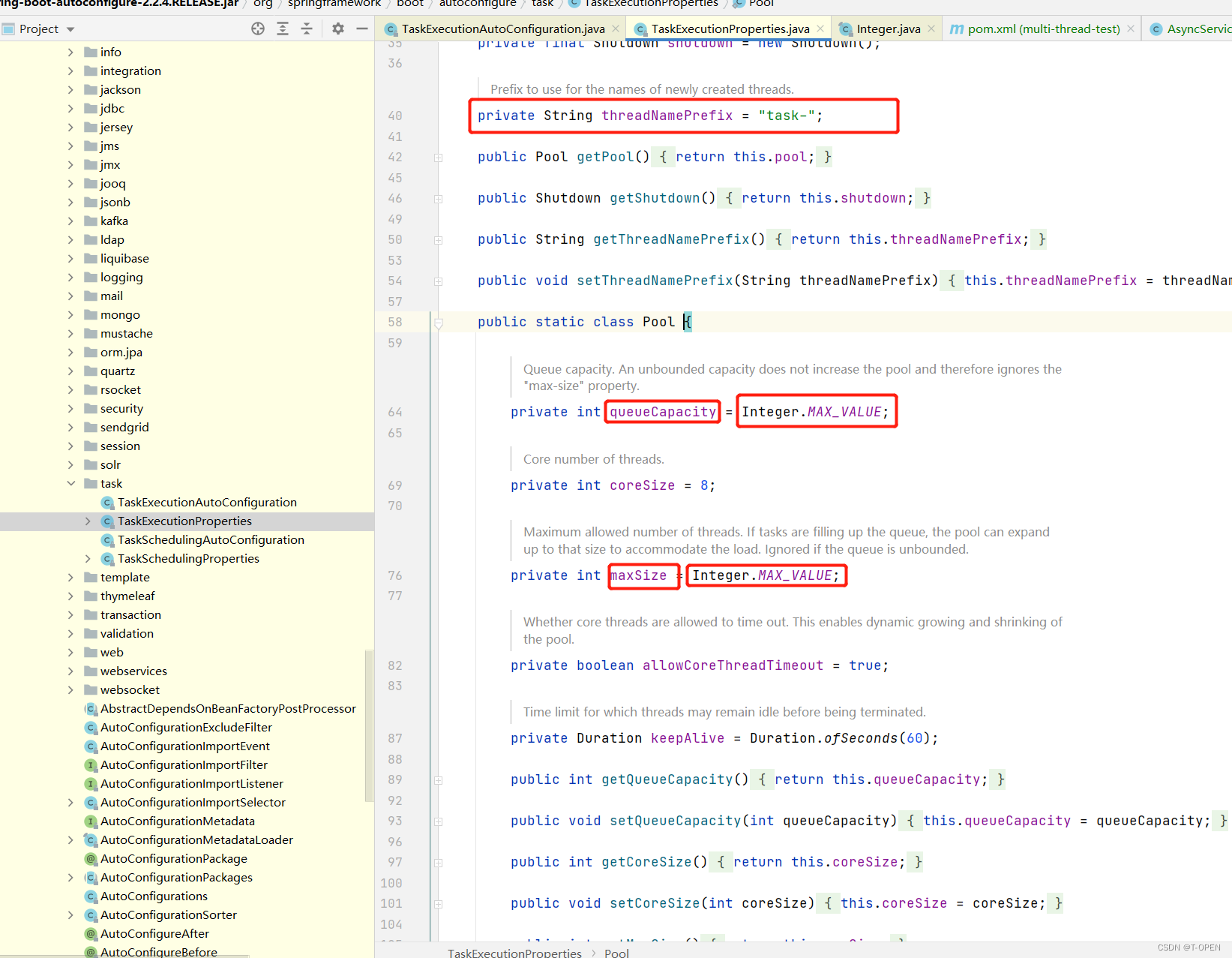
第一步是可选,但是建议还是配一下,默认的线程池可能会导致内存溢出,查看源码可知:默认情况@Async 异步任务,SpringBoot 也是会进行线程池的默认配置的,默认设置的线程数是 8 个,taskQueue 的大小是无界(queueCapacity = Integer.MAX_VALUE),线程名前缀是 : task-
3.2 在方法上使用@Async注解让方法异步去执行任务
service方法,这里模拟了一个发邮件的接口,为了模拟真实情况,这里让线程一开始就睡眠2000MS
public class AsyncService {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncService.class);
@Async("taskExecutor")
public String sendEmail(int time) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2000);
String result = String.format("----这是第 %s 次,发送email", time);
logger.info(result);
return result;
}
}
controller接口,这里我们循环调用了5次
@RequestMapping("/sendEmail")
public String sendEmail() throws InterruptedException {
List<String> resultList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
resultList.add(asyncService.sendEmail(i));
}
return "send ok";
}
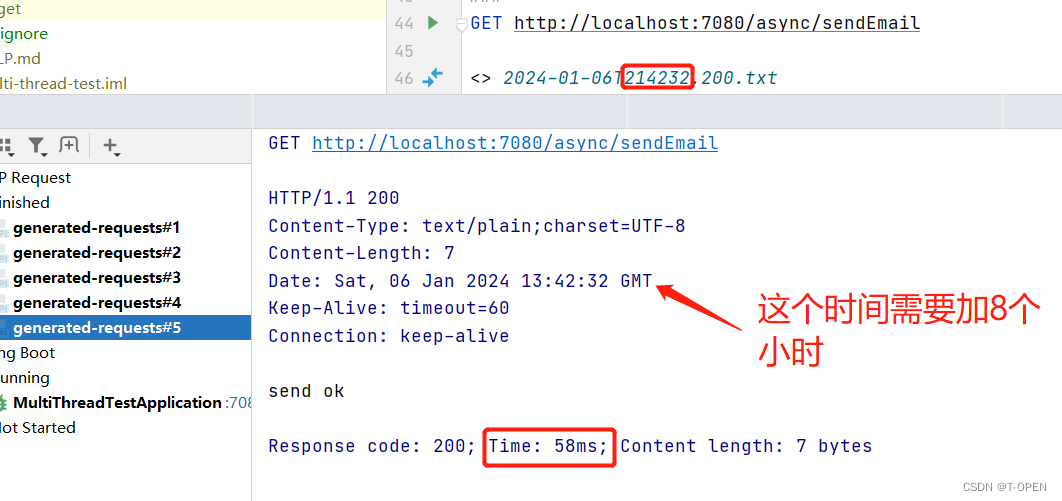
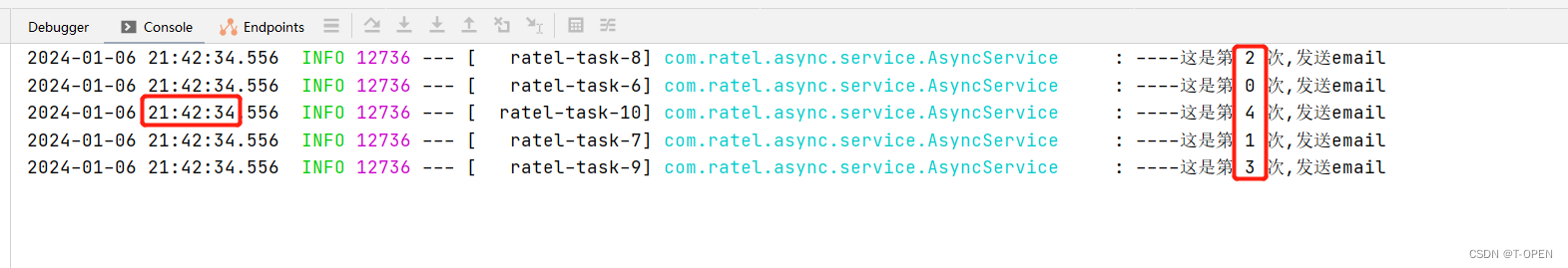
由下图可知,我在21点42分32秒,发送请求,仅仅只用了58接口就返回 send ok了,再看第二张图也是睡眠2000ms后,也就是21点42分34秒,才执行的发送邮件的任务,且 5次也是乱序执行的。这就达到了多线程发送邮件的需求了。
3.3 如何拿到异步执行的结果呢?
这里可能会有人问了,如果我想要每次请求的返回结果咋弄呢?有时候我们不止希望异步执行任务,还希望任务执行完成后会有一个返回值,在java中提供了Future泛型接口,用来接收任务执行结果,springboot也提供了此类支持,使用实现了ListenableFuture接口的类如AsyncResult来作为返回值的载体。比如上例中,我们希望返回一个类型为String类型的值,可以将返回值改造为:
service方法
@Async("taskExecutor")
public Future<String> test1(int time) throws InterruptedException {
int i = RandomUtil.randomInt(0, 1000);
String result = String.format("1111111111这是第 %s 次,睡眠 %s ms", time, i);
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(i);
logger.info(result);
return AsyncResult.forValue(result);
}
controller 方法
@RequestMapping("/test3")
public List<String> test3() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
List<String> resultList = new LinkedList<>();
Future<String> stringFuture0 = asyncService.test1(0);
Future<String> stringFuture1 = asyncService.test1(1);
Future<String> stringFuture2 = asyncService.test1(2);
Future<String> stringFuture3 = asyncService.test1(3);
Future<String> stringFuture4 = asyncService.test1(4);
resultList.add(stringFuture0.get());
resultList.add(stringFuture1.get());
resultList.add(stringFuture2.get());
resultList.add(stringFuture3.get());
resultList.add(stringFuture4.get());
return resultList;
}
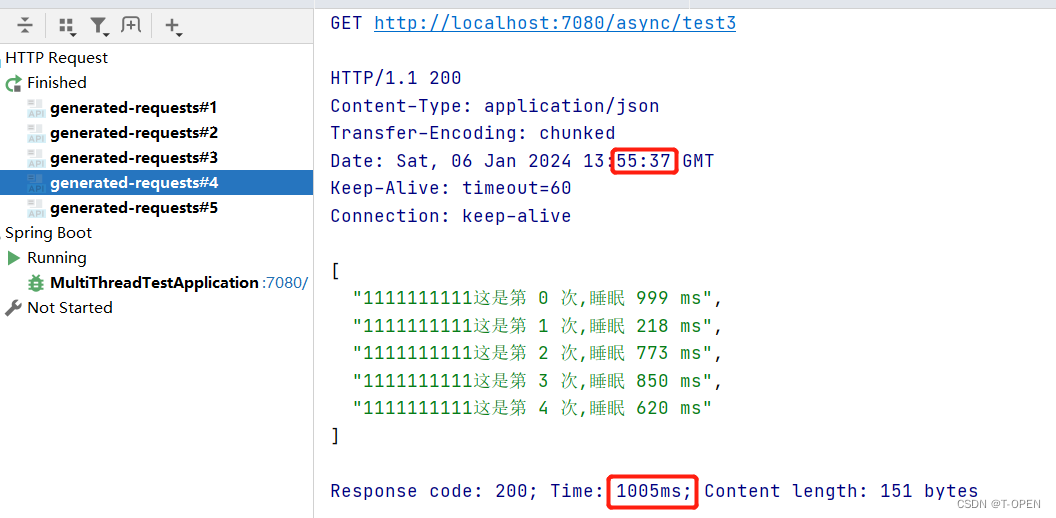
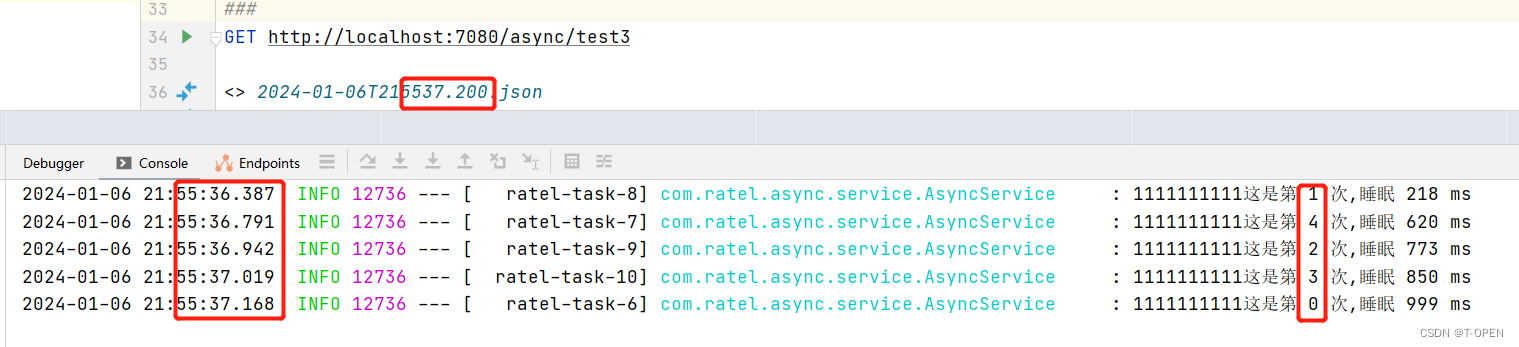
通过下图可以看到 我们已经能异步拿回结果了,且结果也是在最慢的一次任务执行完毕以后,返回的。
四、@Async 不生效的原因
4.1 忘记写再启动类或者配置类上增加 @EnableAsync 开启异步功能
4.2 异步方法所在的类没有被spring管理
异步方法所在类必须用@Controller/@RestController/@Service/@Componet等注解,加入到Ioc里才行。
4.3 异步方法和调用方法在同一个类中
当异步方法和调用方法在同一个类中时,是没办法通过Ioc里的bean来执行异步方法的,从而变成同步方法。比如下面的写法
@Service
public class Test{
public void test() {
a();
}
@Async
public void a() {
}
}
一个老外写的文章说明了@Async有两个限制: https://www.baeldung.com/spring-async

翻译一下就是:
1.它只能应用于公共方法
2.从同一个类中调用异步方法将不起作用
原因很简单方法需要是公共以便可以代理。“自我调用不起作用”,因为它绕过了代理,直接调用底层方法。
4.4 调用的方法是异步,但是取结果的姿势不对
直接在调用处 调用 asyncService.test1(i).get(),等待拿出异步结果,这样只能是串行执行了。看下面的结果图一目了然。
@RequestMapping("/test1")
public List<String> test1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
List<String> resultList = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
resultList.add(asyncService.test1(i).get());
}
return resultList;
}

改成下面这中就能正常返回并行执行,并拿回所有的结果了。
@RequestMapping("/test4")
public List<String> test4() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
List<String> resultList = new LinkedList<>();
List<Future<String>> futureList= new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Future<String> stringFuture = asyncService.test1(i);
futureList.add(stringFuture);
}
for (Future<String> future : futureList) {
resultList.add(future.get());
}
return resultList;
}

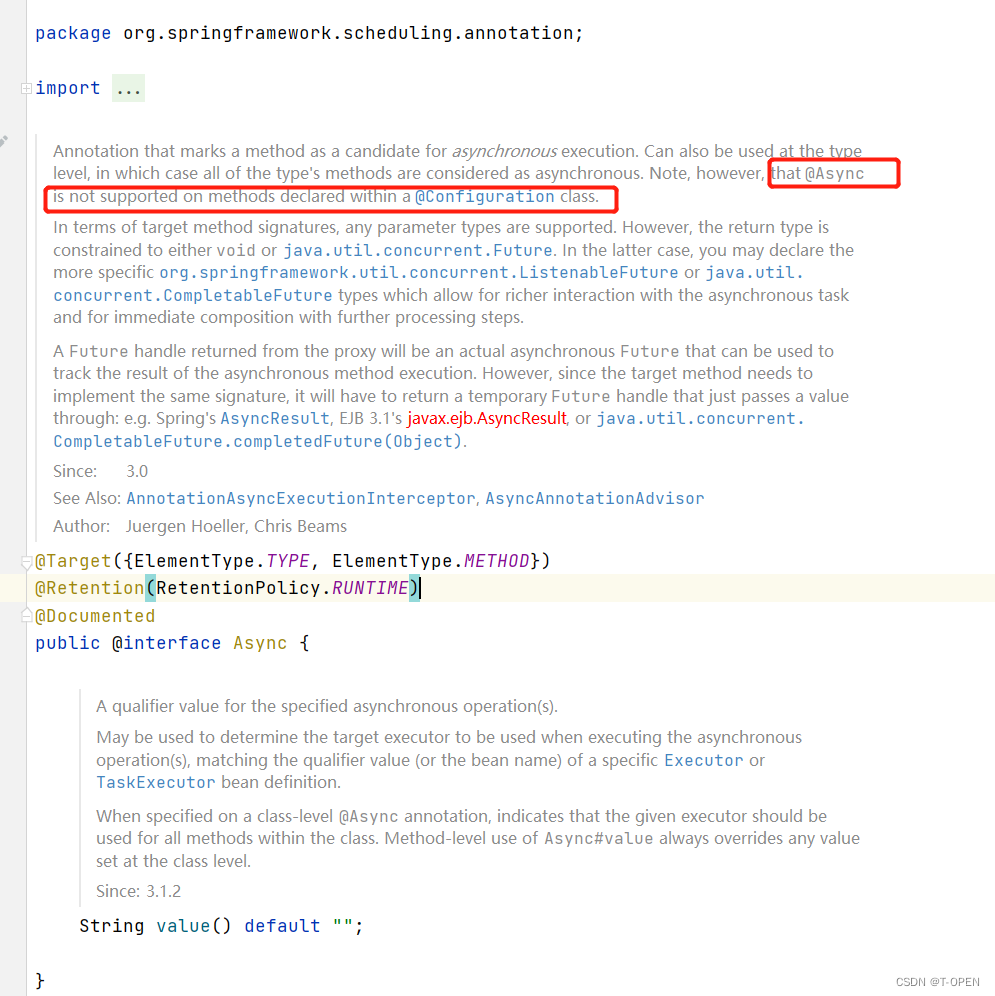
4.5 不支持在配置类上使用
查看springboot源码:就得知不能再配置类上使用。
Note, however, that @Async is not supported on methods declared within a @Configuration class.
参考的文档:
- spring官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/4.2.9.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/#scheduling-annotation-support-async
- baeldung文档:https://www.baeldung.com/spring-async


























 1347
1347











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










