不重复元素集合Set接口定义如下
public interface Set<E> {
void add(E e);
boolean contains(E e);
void remove(E e);
int getSize();
boolean isEmpty();
}
复杂度分析:
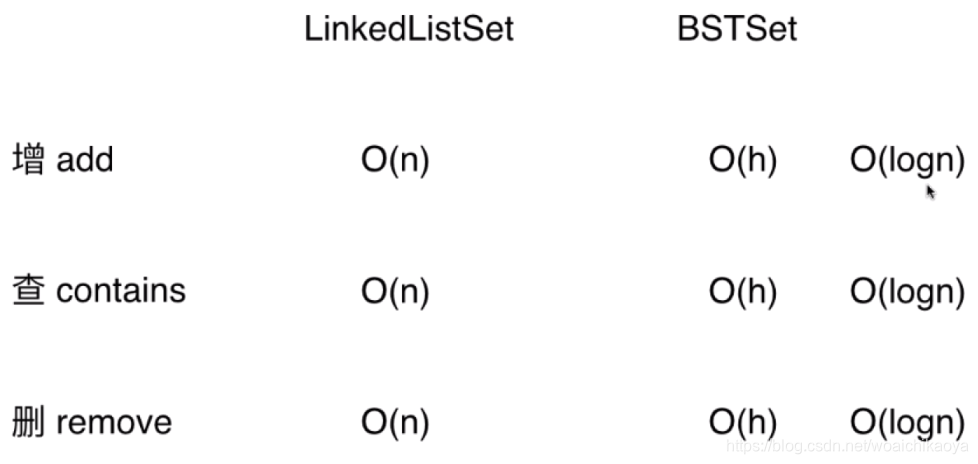
LinkedListSet
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class LinkedListSet <E> implements Set<E>{
private LinkedList<E> linkedList;
public LinkedListSet() {
linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
}
@Override
public void add(E e) {
if (!linkedList.contains(e)) {
linkedList.addFirst(e);
}
}
@Override
public boolean contains(E e) {
return linkedList.contains(e);
}
@Override
public void remove(E e) {
linkedList.removeElement(e);
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return linkedList.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return linkedList.isEmpty();
}
}
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node {
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node (E e, Node next) {
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node (E e) {
this(e, null);
}
public Node () {
this(null, null);
}
}
private Node dummyHead;
private int size;
public LinkedList() {
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public void add(E e, int index) {
if (index < 0 && index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("failed");
Node preNode = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
preNode = preNode.next;
}
preNode.next = new Node(e, preNode.next);
size++;
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
add(e, 0);
}
public void addLast(E e) {
add(e, size);
}
public boolean contains(E e) {
Node curNode = dummyHead.next;
while (curNode != null) {
if (curNode.e.equals(e))
return true;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return false;
}
public E remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 && index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("failed");
Node preNode = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
preNode = preNode.next;
}
Node tempNode = preNode.next;
preNode.next = tempNode.next;
tempNode.next = null;
size--;
return tempNode.e;
}
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(0);
}
public E removeLast() {
return remove(size-1);
}
public void removeElement(E e) {
Node preNode = dummyHead;
while (preNode != null) {
if (preNode.next.e.equals(e))
break;
preNode = preNode.next;
}
if (preNode.next != null) {
Node tempNode = preNode.next;
preNode.next = tempNode.next;
tempNode.next = null;
size--;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
Node curNode = dummyHead.next;
while (curNode != null) {
res.append(curNode.e + "->");
curNode = curNode.next;
}
res.append("Null");
return res.toString();
}
}
BSTSet
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class BSTSet <E extends Comparable<E>> implements Set<E> {
private MyBST<E> myBST;
public BSTSet() {
myBST = new MyBST<>();
}
@Override
public void add(E e) {
myBST.add(e);
}
@Override
public boolean contains(E e) {
return myBST.contains(e);
}
@Override
public void remove(E e) {
myBST.remove(e);
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return myBST.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return myBST.isEmpty();
}
}
import javax.swing.plaf.InsetsUIResource;
public class MyBST <E extends Comparable<E>> {
private class Node {
public E e;
public Node left, right;
public Node(E e) {
this.e = e;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
private Node root;
private int size;
public MyBST() {
this.root = null;
this.size = 0;
}
public void add(E e) {
root = add(root, e);
}
private Node add(Node node, E e) {
if (node == null) {
size++;
return new Node(e);
}
if (e.compareTo(node.e) < 0) {
node.left = add(node.left, e);
} else if (e.compareTo(node.e) > 0) {
node.right = add(node.right, e);
}
return node;
}
public void preOrder() {
preOrder(root);
System.out.println("Null");
}
private void preOrder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
System.out.print(node.e + "->");
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
public void inOrder() {
inOrder(root);
System.out.println("Null");
}
private void inOrder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
inOrder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.e + "->");
inOrder(node.right);
}
public void postOrder() {
postOrder(root);
System.out.println("Null");
}
private void postOrder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
System.out.print(node.e + "->");
}
public E minimum() {
if (size == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("BST is empty");
return minimum(root).e;
}
private Node minimum(Node node) {
if (node.left == null) {
return node;
}
return minimum(node.left);
}
public void removeMin() {
removeMin(root);
}
private Node removeMin(Node node) {
if (node.left == null) {
size--;
Node rightNode = node.right;
node.right = null;
return rightNode;
}
node.left = removeMin(node.left);
return node;
}
public E maximum() {
if (size == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("BST is empty");
return maximum(root).e;
}
private Node maximum(Node node) {
if (node.right == null)
return node;
return maximum(node.right);
}
public E removeMax() {
E e = maximum();
root = removeMax(root);
return e;
}
private Node removeMax(Node node) {
if (node.right == null) {
size--;
Node leftNode = node.left;
node.left = null;
return leftNode;
}
node.right = removeMax(node.right);
return node;
}
public void remove(E e) {
root = remove(root, e);
}
private Node remove(Node node, E e) {
if (node == null)
return null;
if (e.compareTo(node.e) == 0) {
if (node.left == null) {
size--;
Node rightNode = node.right;
node.right = null;
return rightNode;
} else if (node.right == null) {
size--;
Node leftNode = node.left;
node.left = null;
return leftNode;
} else {
Node precursor = maximum(node.left);
precursor.left = removeMax(node.left);
precursor.right = node.right;
node.left = node.left = null;
return precursor;
}
} else if (e.compareTo(node.e) < 0) {
node.left = remove(node.left, e);
} else {
node.right = remove(node.right, e);
}
return node;
}
public boolean contains(E e) {
return contains(root, e);
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
private boolean contains(Node node, E e) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (e.compareTo(node.e) == 0) {
return true;
}
if (e.compareTo(node.e) < 0) {
return contains(node.left, e);
} else {
return contains(node.right, e);
}
}
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
}























 2183
2183

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








