Asio中的异步操作不仅包括 异步的客户端服务端的连接和异步的数据读写,还包括很多可以异步执行的操作。
Asio中有三种方式异步执行你指定的方法:post()、dispach()、wrap()。
- post()这个方法能立即返回,并且请求一个io_service实例调用制定的函数操作(function handler),之后会在某一个盗用io_service.run()的线程中执行。
- dispach()这个方法请求一个io_service实例调用函数操作,但是如果当前线程执行了io_service.run(),它就会直接调用handler。
- wrap()这个方法包装一个方法,当它被调用时它会调用io_service.dispach().
post()例子:
#include <boost/thread.hpp>
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace boost::asio;
io_service service;
void func(int i) {
std::cout << "func called, i= " << i << std::endl;
}
void worker_thread() {
service.run();
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
service.post(boost::bind(func, i));
boost::thread_group threads;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
threads.create_thread(worker_thread);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::millisec(500));
threads.join_all();
getchar();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
运行结果:

上面的程序中有三个线程启动了io_server.run(),循环请求执行func(int i )方法,io_service会选择一个线程去执行func方法。所以无法确定顺序。
dispach()例子:
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <iostream>
using namespace boost::asio;
io_service service;
void func(int i) {
std::cout << "func called, i= " << i << std::endl;
}
void run_dispatch_and_post() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i += 2) {
service.dispatch(std::bind(func, i));
service.post(std::bind(func, i + 1));
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
service.post(run_dispatch_and_post);
service.run();
getchar();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
运行结果:

程序先输出偶数后输出奇数,因为偶数使用dispatch()执行,又因为主线程调用了service.run(),所以直接调用,而post执行偶数时,是直接返回的,而后在调用。
wrap()例子
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <boost/thread.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
using namespace boost::asio;
io_service service;
void dispatched_func_1() {
std::cout << "dispatched 1" << std::endl;
}
void dispatched_func_2() {
std::cout << "dispatched 2" << std::endl;
}
void test(std::function<void()> func) {
std::cout << "test" << std::endl;
service.dispatch(dispatched_func_1);
func();
}
void service_run() {
service.run();
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
test(service.wrap(dispatched_func_2));
boost::thread th(service_run);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::millisec(500));
th.join();
getchar();
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
运行结果:
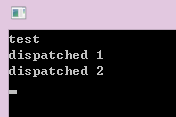
service.warp()把dispatched_func_2包装成一个函数,传给test(),当test函数去执行func()时,跟service.dispatch(dispatched_func_1);是等价的。
《Boost.Asio C++ Network Programming》

























 197
197

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








