在处理大量并发任务的时候,如果按照传统的方式,一个请求一个线程来处理请求任务,大量的线程创建和销毁将消耗过多的系统资源,还增加了线程上下文切换的开销,而通过线程池技术就可以很好的解决这些问题,线程池技术通过在系统中预先创建一定数量的线程,当任务请求到来时从线程池中分配一个预先创建的线程去处理任务,线程在完成任务之后还可以重用,不会销毁,而是等待下次任务的到来.
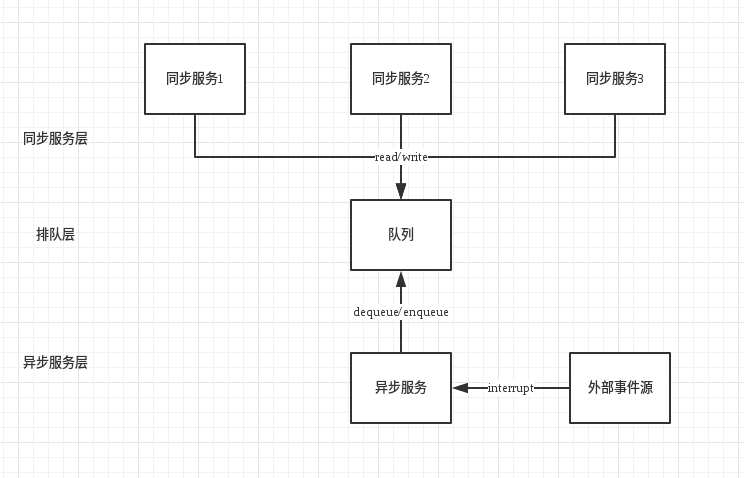
分层
半同步半异步线程池分为三层:
同步服务层: 它处理来自上层的任务请求,上层的请求可能是并发的,这些请求不是马上就会被处理的,而是将这些任务放到一个同步排队层中,等待处理.
同步排队层: 来自上层的任务请求都会加到排队层中等待处理.
异步服务层: 这一层中会有多个线程同时处理排队层中的任务,异步服务层从同步排队层中取出任务并行的处理.
线程池实现
#include <list>
#include <mutex>
#include <thread>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <atomic>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
/********************************同步队列******************************/
template <typename T>
class SyncQueue
{
public:
SyncQueue(int maxSize): m_maxSize(maxSize), m_needStop(false) { }
//添加事件
void Put(const T& x)
{
Add(x);
}
//添加事件
void Put(T && x)
{
//调用内部接口,进行完美转发
Add(std::forward<T>(x));
}
//从队列中取事件,取所有事件
void Take(std::list<T> &list)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
//当不满足任何一个则等待,但是若m_needStop为true是因为任务要终止了所以不阻塞
m_notEmpty.wait(locker, [this]{return (m_needStop || NotEmpty()); });
if (m_needStop)
{
return;
}
list = std::move(m_queue);
m_notFull.notify_one();
}
//取一个事件
void Take(T &t)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
m_notEmpty.wait(locker, [this]{return m_needStop || NotEmpty(); });
if (m_needStop)
{
return;
}
t = m_queue.front();
m_queue.pop_front();
m_notFull.notify_one();
}
//终止同步队列
void Stop()
{
{
//锁作用域就在这对大括号内
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
//将终止标志设为true
m_needStop = true;
}
//唤醒所有进程一一终止
m_notFull.notify_all();
m_notEmpty.notify_all();
}
//队列为空
bool Empty()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
return m_queue.empty();
}
//队列为满
bool Full()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
return m_queue.size() == m_maxSize;
}
//队列大小
size_t Size()
{
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
return m_queue.size();
}
//队列大小
int Count()
{
return m_queue.size();
}
private:
//队列不为满
bool NotFull() const
{
bool full = (m_queue.size() >= m_maxSize);
if (full)
{
cout << "the queue is full, need wait..." << endl;
}
return !full;
}
//队列不为空
bool NotEmpty() const
{
bool empty = m_queue.empty();
if (empty)
{
cout << "the queue is empty, need wait..., 异步层的线程ID: " << this_thread::get_id() << endl;
}
return !empty;
}
//向队列中添加事件,若不为满且终止标志为false则添加事件
template <typename F>
void Add(F && x)
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> locker(m_mutex);
//当不满足任何一个则等待,但是若m_needStop为true是因为任务要终止了所以不阻塞
m_notFull.wait(locker, [this]{return m_needStop || NotFull(); });
if (m_needStop)
{
return;
}
m_queue.push_back(std::forward<F>(x));
m_notEmpty.notify_one();
}
private:
//缓冲区
std::list<T> m_queue;
//互斥量
std::mutex m_mutex;
//队列不为空的条件变量
std::condition_variable m_notEmpty;
//队列不为满的条件变量
std::condition_variable m_notFull;
//任务队列最大长度
int m_maxSize;
//终止的标识,当为true时代表同步队列要终止
bool m_needStop;
};
/**************************线程池********************************/
//传递给同步队列的最大个数
const int MaxTaskCount = 100;
class ThreadPool
{
public:
using Task = std::function<void()>;
//构造函数,默认参数hardware_concurrency()获取CPU核心数量
ThreadPool(int numThreads = std::thread::hardware_concurrency()):m_queue(MaxTaskCount)
{
cout << "numThreads: " << numThreads << endl;
Start(numThreads);
}
~ThreadPool()
{
Stop();
}
//保证多线程环境下只调用一次StopThreadGroup函数
void Stop()
{
std::call_once(m_flag, [this]{ StopThreadGroup(); });
}
//添加任务,右值完美转发
void AddTask(Task && task)
{
m_queue.Put(std::forward<Task> (task));
}
//添加任务
void AddTask(const Task && task)
{
m_queue.Put(task);
}
private:
//建立numThreads个数的线程组
void Start(int numThreads)
{
m_running = true;
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; i++)
{
//多个线程依次的处理
m_threadgroup.push_back(std::make_shared<std::thread>(&ThreadPool::RunInThread, this));
}
}
//取出任务队列中的全部,依次执行
void RunInThread()
{
while (m_running)
{
std::list<Task> list;
m_queue.Take(list);
for (auto & task : list)
{
if (!m_running)
{
return ;
}
//执行任务
task();
}
}
}
//终止所有任务的执行
void StopThreadGroup()
{
//终止同步队列
m_queue.Stop();
m_running = false;
for (auto thread : m_threadgroup)
{
if (thread)
{
thread->join();
}
}
m_threadgroup.clear();
}
private:
//处理任务的线程组
std::list<std::shared_ptr<std::thread>> m_threadgroup;
//同步队列
SyncQueue<Task> m_queue;
//运行的标志,flase代表终止
atomic_bool m_running;
//保证在函数在多线程环境中只被调用一次
std::once_flag m_flag;
};
int main()
{
ThreadPool pool;
//pool.Start(2);
std::thread thd1([&pool]
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
auto thdId = this_thread::get_id();
pool.AddTask([thdId]
{
cout << "1.thread id: " << thdId << endl;
});
}
});
std::thread thd2([&pool]
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
auto thdId = this_thread::get_id();
pool.AddTask([thdId]
{
cout << "2.thread id: " << thdId << endl;
});
}
});
this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(2));
getchar();
pool.Stop();
thd1.join();
thd2.join();
}对象池
对象池对于创建开销较大的对象来说很有意义,为了避免重复创建开销较大的对象,可以通过对象池来优化.
对象池的思路比较简单,实现创建好一批对象,放到一个集合中,每当程序需要新的对象时,就从对象池中获取,程序用完该对象后都会把该对象归还给对象池.这样会避免重复创建对象,提高程序性能.
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
//要成为不可复制的类,典型的方法是将类的复制构造函数和赋值运算符设置为private或protected
//为了使ObjectPool为不可复制的类,我们定义了类NonCopyable,只需继承起则可为不可复制的类
class NonCopyable
{
protected:
NonCopyable() = default;
~NonCopyable() = default;
NonCopyable(const NonCopyable&) = delete;
NonCopyable& operator =(const NonCopyable &) = delete;
};
//对象最大个数
const int MaxObjectNum = 10;
template <typename T>
class ObjectPool : NonCopyable
{
template <typename... Args>
using Constructor = function<shared_ptr<T> (Args...)>;
private:
//定义multimap类型的私有成员通过Constructor<Args...>类型获得字符串,则通过字符串类型一对多的对应特定的对象.
multimap<string, shared_ptr<T>> m_object_map;
public:
//初始化创建对象
template <typename... Args>
void Init(size_t num, Args ...args)
{
if (num <= 0 || num > MaxObjectNum)
{
throw std::logic_error("Object num out of range");
}
//Init时的模板类型不同所得到的constructName字符串不同
//所以相同的初始化类型对应m_object_map中的first相同,不同类型的则不同
auto constructName = typeid(Constructor<Args...>).name();
//cout << "Init: " << constructName << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
//删除器中不直接删除对象,而是回收到对象池中,以供下次使用
m_object_map.emplace(constructName,
shared_ptr<T>(new T(std::forward<Args>(args)...), [this, constructName](T *p)
{
cout << "dis: " << constructName << endl;
m_object_map.emplace(std::move(constructName),shared_ptr<T>(p));
}));
}
}
//从对象池获取一个对象
template <typename... Args>
std::shared_ptr<T> Get()
{
string constructName = typeid(Constructor<Args...>).name();
cout << constructName << endl;
//通过Get的模板类型得到对应的字符串,通过该字符串找到所有该字符串的对应
auto range = m_object_map.equal_range(constructName);
//从该类型对应的对象中获取其中一个
for (auto it = range.first; it != range.second; it++)
{
auto ptr = it -> second;
m_object_map.erase(it);
return ptr;
}
return nullptr;
}
};





















 5576
5576











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








