1.网络模型
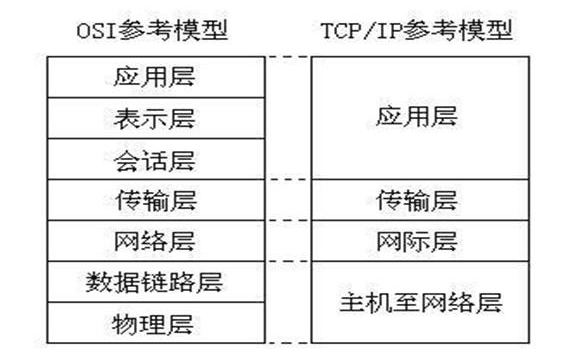
OSI参考模型:应用层,表示层,会话层,传输层,网络层,数据链路层,物理层;
TCP/IP参考模型:应用层,传输层,网际层,主机至网络层;
一般来说开发处于传输层和网际层
应用层协议有:FTP,HTTP等;
传输层协议有:UDP,TCP等;
网际层协议有:IP;
通常用户操作的是应用层,而编程人员要做的是处理传输层和网际层,各层对数据进行封装成包和解包;
2.网络通信三要素
(1).IP地址
概述:网络中的设备标识,不容易记忆,可用主机名表示,两者存在映射关系;
特别:本地回环地址:127.0.0.1;本地主机名:localhost;
Java中对IP地址的描述:java.net.InetAddress
InetAddress中的一些基本方法:
byte[] getAddress():返回此InetAddress对象的原始IP地址;
static InetAddress getByAddress(byte[] addr):在给定原始IP地址的情况下返回InetAddress对象;
static InetAddress[] getAllByName(String host):在给定主机的情况下,根据系统上配置的名称返回IP地址所组成的数组;需要遍历;
static InetAddress getByName(Sting hostName):在给定主机名的情况下确定主机的IP地址;
String getHostAddress():返回IP地址字符串;
String getHostName():返回此IP地址的主机名;
static InetAddress getLocalHost():返回本地主机;
示例:
- package com.zr.day23;
- import java.net.*;
- class InetAddressDemo
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException
- {
-
- InetAddress ia = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
-
- String ip = ia.getHostAddress();
- String host = ia.getHostName();
- System.out.println(ip+"::"+host);
-
-
- InetAddress[] ias = InetAddress.getAllByName("www.baidu.com");
- for(InetAddress i : ias)
- {
- String iip = i.getHostAddress();
- String ihost = i.getHostName();
- System.out.println(iip+":::"+ihost);
- }
-
-
- InetAddress iia = InetAddress.getByName("180.97.33.108");
- String iiip = iia.getHostAddress();
- String iiihost = iia.getHostName();
- System.out.println(iiip+"::::"+iiihost);
- }
- }
(2).端口号
概述:用于标识应用程序的逻辑地址;
特别:有效端口:0~65535;其中系统使用或保留端口是:0~1024;
在定义端口的时候要特别注意不能重用,否则会出现Address already in use 的BindException;
(3).传输协议
通信规则,传输层的通信协议有:TCP,UDP;
UDP:
1).将数据以及源和目的封装成数据报包,面向无连接;
2).每个数据包大小限制在64K范围内;
3).不可靠协议;
4),速度快;
TCP:
1).通信时要建立连接,形成数据传输的通道;
2).在连接中进行大量数据传输;
3).可靠协议,通过三次握手完成连接;
4).必须建立连接,效率稍低;
Socket:
Socket就是为网络服务提供的一种机制,通信的两端都有Socket,数据在两个Socket之间通过IO传输;
3.UDP通信
(1).UDP协议的Socket对象和数据报包对象;
DatagramSocket:
构造方法:
1).DatagramSocket():构造数据报套接字,有系统分配可以的端口;
2).DatagramSocket():构造数据报套接字,自定义绑定的端口号;
常用方法:
1).void close():关闭此数据报套接字;
2).void receive(DatagramPacket p):从此套接字接收数据报包,用数据报包对象来接收;
3).void send(DatagramPacket p):从此套接字发送指定的数据报包,数据都被封装到了数据报包对象中;
DatagramPacket:
构造方法:
1).用来接收的:DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length)
2).用来发送的:DatagramPacket(byte[] buf, int length, InetAddress address, int port)
常用方法:用来获取数据报包中的各种成分
InetAddress getAddress():此数据报将要发送或者被接受的主机地址;
byte[] getData():返回数据缓冲区;
int getLength():返回将要发送或接收的数据的长度;
int getPort():返回主机的端口号;
(2).UDP发送端
具体步骤:
1).建立UDPSocket服务;
2).提供数据,并将数据封装为数据报包对象;
3).通过Socket服务的发送功能,将数据报包发送出去;
4).关闭Socket服务;
具体代码实现:
- import java.net.*;
-
- class UDPSend
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
- {
-
- DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9999);
-
-
- byte[] buf = "this is sharon".getBytes();
- DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("10.0.0.227"),10000);
-
- ds.send(dp);
-
- ds.close();
- }
- }
(3).UDP接收端
具体步骤:
1).建立UDPSocket服务,并且监听某个端口,明确哪些数据被接受后由该应用程序处理;
2).建立一个数据报包对象,用来封装接收的数据,使用数据报包对象提供的丰富的方法来获取有用的信息;
3).通过Socket服务的接收功能,获取网络数据;
4).关闭Socket服务;
具体代码实现:
- import java.net.*;
-
- class UDPRec
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
- {
-
- DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10000);
-
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
-
- ds.receive(dp);
-
-
- String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
-
- int port = dp.getPort();
-
- String data = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
-
- System.out.println(ip+"::"+port+":"+data);
-
- ds.close();
- }
- }
(4).UDP通信示例
1).键盘录入
-
- import java.io.*;
- import java.net.*;
-
- class UDPKeySend
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
-
- BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
-
- DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
- for(String line=null; (line=br.readLine())!=null;)
- {
-
- if("over".equals(line))
- break;
-
- byte[] buf = line.getBytes();
- DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("10.0.0.227"),10001);
-
- ds.send(dp);
- }
-
- br.close();
-
- ds.close();
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
- class UDPKeyRec
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
-
- DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(10001);
-
- while(true)
- {
-
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
-
- ds.receive(dp);
-
- String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
- int port = dp.getPort();
- String data = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
- System.out.println(ip+"::"+port+":"+data);
- }
- }
- }
2).UDP聊天通信
-
-
- import java.io.*;
- import java.net.*;
-
- class Send implements Runnable
- {
-
- private DatagramSocket ds;
- Send(DatagramSocket ds)
- {
- this.ds = ds;
- }
-
- public void run()
- {
- try
- {
-
- BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
-
- String line = null;
- while((line=br.readLine())!=null)
- {
- if("over".equals(line))
- break;
-
- byte[] buf = line.getBytes();
-
- DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length,InetAddress.getByName("10.0.0.227"),10002);
- ds.send(dp);
- }
- br.close();
- ds.close();
- }
- catch (Exception e)
- {
- throw new RuntimeException("发送端创建失败");
- }
- }
- }
-
-
- class Rec implements Runnable
- {
- private DatagramSocket ds;
- Rec(DatagramSocket ds)
- {
- this.ds = ds;
- }
- public void run()
- {
- try
- {
- while(true)
- {
-
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf,buf.length);
-
- ds.receive(dp);
-
- String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
- int port = dp.getPort();
- String data = new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength());
- System.out.println(ip+"::"+port+":"+data);
- }
- }
- catch (Exception e)
- {
- throw new RuntimeException("接收端创建失败");
- }
- }
- }
-
- class UDPChatDemo
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
- {
- DatagramSocket send = new DatagramSocket();
- DatagramSocket rec = new DatagramSocket(10002);
- new Thread(new Send(send)).start();
- new Thread(new Rec(rec)).start();
- }
- }
4.TCP通信
(1).TCP协议下的Socket和ServerSocket
java.net.Socket:客户端对象;
1).构造方法:客户端对象在创建时需要指定所要连接的服务器;
无参构造:Socket():没有指定要连接的服务器;
可以使用方法:void connnet(SocketAddress endPoint):来连接指定的服务器;
有参构造:Socket(InnetAddress address, int port):在创建客户端对象时就指定要连接的服务器;
有参构造:Socket(String host, int port):
2).常用方法:
close():关闭此套接字;
void bind(SocketAddress bindpoint):绑定本地地址;
InputStream getInputStream():返回此套接字的输入流;
OutputStream getOutputStream():返回此套接字的输出流;
InnetAddress getInnetAddress():返回此套接字连接的地址;
int getPort():返回套接字连接到的远程端口;
InnetAddress getLocalAddress():获取套接字绑定的本地地址;
int getLocalPort():返回套接字绑定的本地端口;
void shutdownInput():关闭此套接字的输入流;
void shutdownOutput():关闭此套接字的输出流;
java.net.ServerSocket:服务器端对象
构造方法:服务器对象在创建时要绑定指定的端口,以便处理特定端口的应用程序;
ServerSocket():空参,没有指定数字标识;
ServerSocket(int port):创建绑定特定端口的服务器套接字;
ServerSocket(int port, int backlog):绑定特定端口,同时指定可以连接到该服务器的带有指定数字标识的客户端对象的最大数目;
ServerSocket(int port ,int basklog, InnetAddress bindAdd):指定端口,设置数量,同时绑定本地地址;
常用方法:
Socket accept():侦听并接受此套接字的连接,获取客户端的套接字对象,利用该对象中的流和客户端进行通信数据传输;
void close():关闭此套接字;
InnetAddress getInnetAddress():返回此服务器套接字的本地地址;
int getLocalPort():返回此套接字在其上侦听的端口;
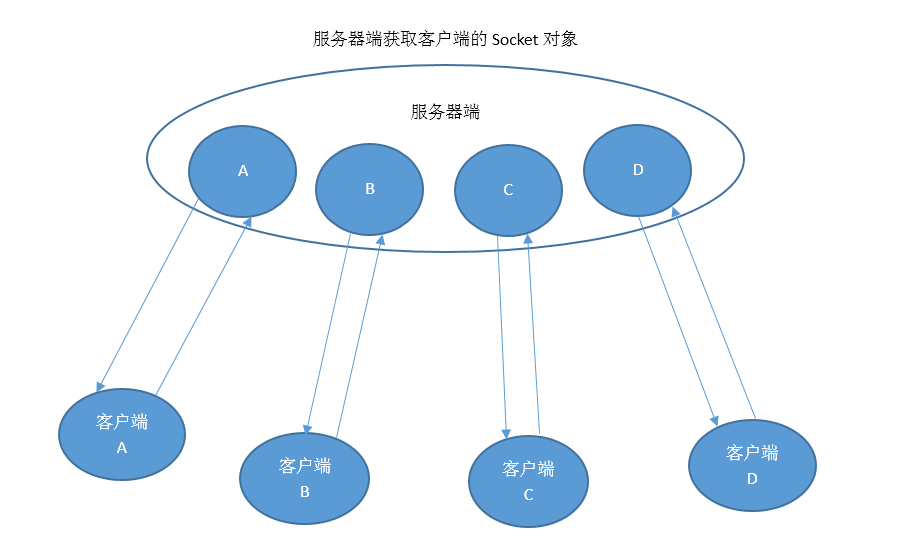
(2).客户端和服务器端的通信原理
服务器端创建对象,指定要侦听的端口;
在客户端对象创建时,需要建立服务器连接,指定要连接的服务器;
建立连接后通过Socket中的IO流进行数据的传输;
原理图:
(3).TCP简单的发送与接收示例
-
- import java.net.*;
- import java.io.*;
-
-
-
-
- class Client
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
-
-
- Socket s = new Socket("10.0.0.170",20000);
-
- OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
-
- byte[] buf = "你好,服务端".getBytes();
- out.write(buf);
-
- s.close();
- }
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- class Server
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
-
- ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(20000);
-
- Socket s = ss.accept();
-
- String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
- System.out.println(ip+" connecting ...");
-
- InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
-
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- int len = in.read(buf);
- System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
- s.close();
- }
- }
(4).TCP客户端和服务端的互访
-
- import java.net.*;
- import java.io.*;
-
- class Client1
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
-
- Socket s = new Socket("10.0.0.170",20001);
-
- OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
- out.write("尼豪,服务端!".getBytes());
-
- InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- int len = in.read(buf);
- System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
-
- s.close();
- }
- }
-
- class Server1
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
- {
-
- ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(20001);
-
- Socket s = ss.accept();
-
- String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
- System.out.println(ip+" connneted ...");
-
- InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- int len = in.read(buf);
- System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
-
- Thread.sleep(5000);
-
- OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
- out.write("hello, client, welcom".getBytes());
-
- s.close();
- }
- }
(5).文本转换服务器
(6).TCP复制文件
-
- import java.net.*;
- import java.io.*;
-
-
- class FileClient
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
-
- Socket s = new Socket("10.0.0.170",20004);
-
- BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("demo.txt"));
-
- PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
- for(String line=null; (line = br.readLine())!=null; System.out.println("正在上传..."))
- {
- out.println(line);
- }
-
-
- s.shutdownOutput();
-
- br.close();
-
-
- InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- int len = in.read(buf);
- System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
-
- s.close();
- }
- }
-
- class FileServer
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
- {
-
- ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(20004);
-
- Socket s = ss.accept();
-
- BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
-
- PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("tcp_copy.txt"),true);
- for(String line=null; (line=in.readLine())!=null; System.out.println("继续上传..."))
- {
- pw.println(line);
- }
- pw.close();
-
- OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
- out.write("上传成功!".getBytes());
-
- s.close();
- }
- }
(7).TCP上传图片
-
- import java.io.*;
- import java.net.*;
-
- class PicClient
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
-
- Socket s = new Socket("10.0.0.170",20005);
-
- FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("demo.png");
-
- OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
- byte[] bytebuf = new byte[1024];
- for(int len=0; (len=fis.read(bytebuf))!=-1;System.out.println("正在上传..."))
- {
- out.write(bytebuf,0,len);
- }
-
- s.shutdownOutput();
- fis.close();
-
- InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- int len = in.read(buf);
- System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
-
- s.close();
- }
- }
-
- class PicServer
- {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
- {
-
- ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(20005);
-
- Socket s = ss.accept();
- String ip = s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
- System.out.println(ip+" connected....");
-
- InputStream in = s.getInputStream();
-
- FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("copy.jpg");
- byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
- for(int len=0; (len=in.read(buf))!=-1; System.out.println("继续上传。。。"))
- {
- fos.write(buf,0,len);
- }
- fos.close();
-
- OutputStream out = s.getOutputStream();
- out.write("pic上传成功!".getBytes());
-
- s.close();
- }
- }
(8).TCP并发上传
(9).TCP并发登陆
5.服务器端和客户端之间的访问形式
(1).自定义服务端,浏览器客户端
自定义服务端代码:运行服务端开启服务器;
- import java.io.*;
- import java.net.*;
-
-
- class ServerDemo
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
- {
-
- ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(20008);
-
- Socket s=ss.accept();
-
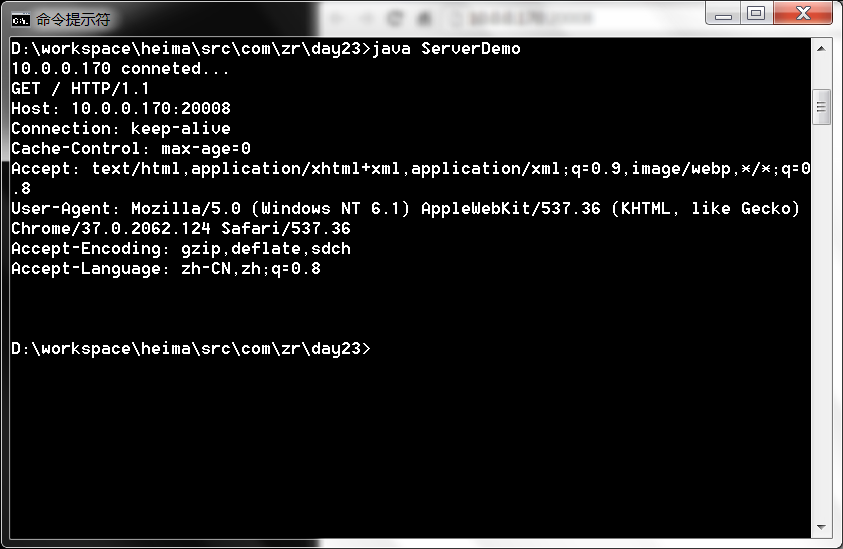
- String ip=s.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
- System.out.println(ip+" conneted...");
-
- InputStream in=s.getInputStream();
- byte[] buf=new byte[1024];
- int len=in.read(buf);
-
- System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
-
- PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(s.getOutputStream(),true);
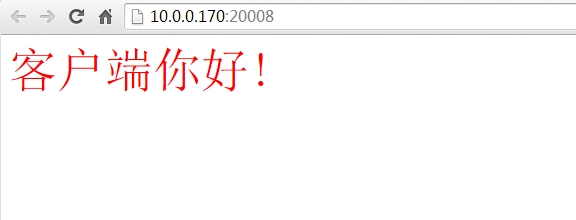
- out.println("<font color='red' size='7'>客户端你好!</font>");
-
- s.close();
- ss.close();
- }
- }
在客户端通过浏览器访问,在地址栏中输入:主机ip地址和端口号;
运行结果:
(2).Tomcat服务端,浏览器客户端
可以再本地开启Tomcat服务器,然后通过浏览器访问tomcat服务器;
Tomcat服务器的默认端口是8080;
(3).Tomcat服务端,自定义浏览器客户端
自定义浏览器需要向服务器发送的消息头如下:
自定义的浏览器只要想服务器发送如上的消息头,以及指定正确地端口就可以访问tomcat服务器;
(4).Tomcat服务端,自定义图形化界面浏览器客户端
自定义的浏览器:
- package com.zr.day23;
- import java.net.*;
- import java.awt.*;
- import java.awt.event.*;
- import java.io.*;
- class FrameDemo
- {
- private Frame f;
- private TextField tf;
- private Button b;
- private TextArea ta;
- FrameDemo()
- {
- init();
- }
- public void init()
- {
- f = new Frame("我的浏览器窗口");
- f.setBounds(300,200,500,500);
- f.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
- b = new Button("转到");
- tf = new TextField(50);
- ta = new TextArea(25,60);
- f.add(tf);
- f.add(b);
- f.add(ta);
- myEvent();
- f.setVisible(true);
- }
- public void show()
- {
- ta.setText("");
- String urltext = tf.getText();
- try
- {
-
- URL url =new URL(urltext);
-
- URLConnection conn = url.openConnection();
-
- InputStream in = conn.getInputStream();
-
- byte[] buf=new byte[1024*1024];
-
- int len=in.read(buf);
-
- ta.append(new String(buf,0,len));
- }
- catch(Exception e)
- {
- throw new RuntimeException("浏览器访问失败");
- }
- }
- public void myEvent()
- {
- f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter(){
- @Override
- public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
- {
- System.exit(0);
- }
- });
- tf.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter(){
- @Override
- public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e)
- {
- if(e.getKeyCode()==KeyEvent.VK_ENTER)
- {
- show();
- }
- }
- });
- b.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
-
- @Override
- public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
- {
- show();
- }
- });
- }
- }
- class MyIE
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- new FrameDemo();
- }
- }
6.其他对象
(1).java.net.URL
URL:统一资源定位符;
构造方法:
URL(String spec):以字符串形式创建URL对象
URL(String protocol, String host, int port, String file):以详细的形式创建URL对象
常用方法:
String getFile():文件名
String getHost():主机名
String getPath():路径
int getPort():端口,一般的输入的网址中没有端口号,此时获取的端口是-1,在这里可以进行判断处理,为端口设置一个有效的默认值;
String getProtocol():协议
String getQuery():查询部分
URLConnetion openConnetion():
InputStream openStrean():打开到此URL的连接,返回一个用于从该连接读入的输入流;
(2).java.net,URLConnection:直接子类:HttpURLConnection
表示到URL所引用的远程对象的连接;
构造方法:
URLConnection(URL url):构造一个到指定URL的URL连接;
常用方法:
URL getURL():获取URL对象;
InputStream getInputStream()
OutputStream getOutputStream()
(3).java.net.SocketAddress:直接子类:InnetSocketAddress
抽象的SocketAddress,和InnetAddress的区别
SocketAddress:封装的是套接字地址,包括IP地址和端口号,也可以是主机名和端口号;
InnetAddress:封装的是IP地址;
(4).域名解析
在进行网络访问时,我们通常输入的是比较容易记忆的域名而不是IP地址,这时提交访问请求,系统会先在本地(c:\windows\system32\drivers\ext\host)查找域名和地址的映射关系;
在本地如果有要访问的域名的映射,直接获取IP地址访问;
在本地没有映射时,会访问公网的DNS服务器,服务器查询映射,向主机返回IP地址,然后通过IP地址访问指定的服务器






















 6294
6294

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








