2.1.2. DEFINE_INSN 模式的概览
[ 一个作为 RTL 表达式的 define_insn 包含了 4 或 5 个操作数:
1. 一个可选的名字。名字的出现表示,这个指令模式可以为编译器的 RTL 产生遍执行一个固定的标准任务。这个遍知道某些名字,并使用具有这些名字的模式,如果这些名字在机器描述中定义了的话。
通过在名字的位置写入一个空字符串来表示名字的缺席。匿名的指令模式不会用于产生 RTL 代码,但它们可能允许合并多个简单的 insn 。
不认识因而不用于 RTL 生成的名字是没有效用的;它们等同于匿名。
以‘ * ’字符开头的名字仅用在 RTL 转储( dump )中识别这个指令;在其他方面,它完全等同于匿名的模式。
2. RTL 模板( template )是一个由不完整的( imcomplete ) RTL 表达式构成的 vector ,它显示了指令看起来应该像什么。它是不完整的,因为它可能包含了代表指令中操作数的表达式 match_operand , match_operator ,及 match_dup 。
3. 一个条件——包含一个 C 表达式的字符串,该表达式为一个确定一个指令体是否匹配这个模式的最终测试。
4. 输出模板:一个显示如何把匹配的 insn 输出为汇编代码的字符串。在这个字符串中,‘ % ’指示了在何处替换一个操作数的值。当简单替换不够通用,由一段 C 代码来计算该输出。
5. 可选地,一个包含匹配这个模式的 insn 的属性值的 vector 。 ]
现在 define_insn 被识别出来了,而 infile 当前停留在字符串“ cmpdi_ccno_1_rex64 ”的第一个字符上。接下来, read_rtx 根据格式“ sEsTV ”处理其内容。
read_rtx (continued)
578 /* If what follows is `: mode ', read it and
579 store the mode in the rtx. */
580
581 i = read_skip_spaces (infile);
582 if (i == ':')
583 {
584 read_name (tmp_char, infile);
585 for (j = 0; j < NUM_MACHINE_MODES; j++)
586 if (! strcmp (GET_MODE_NAME (j), tmp_char))
587 break ;
588
589 if (j == MAX_MACHINE_MODE)
590 fatal_with_file_and_line (infile, "unknown mode `%s'", tmp_char);
591
592 PUT_MODE (return_rtx, (enum machine_mode) j);
593 }
594 else
595 ungetc (i, infile);
596
597 for (i = 0; i < GET_RTX_LENGTH (GET_CODE (return_rtx)); i++)
598 switch (*format_ptr++)
599 {
600 /* 0 means a field for internal use only.
601 Don't expect it to be present in the input. */
602 case '0':
603 break ;
604
605 case 'e':
606 case 'u':
607 XEXP (return_rtx, i) = read_rtx (infile);
608 break ;
609
610 case 'V':
611 /* 'V' is an optional vector: if a closeparen follows,
612 just store NULL for this element. */
613 c = read_skip_spaces (infile);
614 ungetc (c, infile);
615 if (c == ')')
616 {
617 XVEC (return_rtx, i) = 0;
618 break ;
619 }
620 /* Now process the vector. */
621
622 case 'E':
623 {
624 /* Obstack to store scratch vector in. */
625 struct obstack vector_stack;
626 int list_counter = 0;
627 rtvec return_vec = NULL_RTVEC;
628
629 c = read_skip_spaces (infile);
630 if (c != '[')
631 fatal_expected_char (infile, '[', c);
632
633 /* add expressions to a list, while keeping a count */
634 obstack_init (&vector_stack);
635 while ((c = read_skip_spaces (infile)) && c != ']')
636 {
637 ungetc (c, infile);
638 list_counter++;
639 obstack_ptr_grow (&vector_stack, read_rtx (infile));
640 }
641 if (list_counter > 0)
642 {
643 return_vec = rtvec_alloc (list_counter);
644 memcpy (&return_vec->elem[0], obstack_finish (&vector_stack),
645 list_counter * sizeof (rtx));
646 }
647 XVEC (return_rtx, i) = return_vec;
648 obstack_free (&vector_stack, NULL);
649 /* close bracket gotten */
650 }
651 break ;
652
653 case 'S':
654 /* 'S' is an optional string: if a closeparen follows,
655 just store NULL for this element. */
656 c = read_skip_spaces (infile);
657 ungetc (c, infile);
658 if (c == ')')
659 {
660 XSTR (return_rtx, i) = 0;
661 break ;
662 }
663
664 case 'T':
665 case 's':
666 {
667 char *stringbuf;
668
669 /* The output template slot of a DEFINE_INSN,
670 DEFINE_INSN_AND_SPLIT, or DEFINE_PEEPHOLE automatically
671 gets a star inserted as its first character, if it is
672 written with a brace block instead of a string constant. */
673 int star_if_braced = (format_ptr[-1] == 'T');
674
675 stringbuf = read_string (&rtl_obstack, infile, star_if_braced);
676
677 /* For insn patterns, we want to provide a default name
678 based on the file and line, like "*foo.md:12", if the
679 given name is blank. These are only for define_insn and
680 define_insn_and_split, to aid debugging. */
681 if (*stringbuf == '/0'
682 && i == 0
683 && (GET_CODE (return_rtx) == DEFINE_INSN
684 || GET_CODE (return_rtx) == DEFINE_INSN_AND_SPLIT))
685 {
686 char line_name[20];
687 const char *fn = (read_rtx_filename ? read_rtx_filename : "rtx");
688 const char *slash;
689 for (slash = fn; *slash; slash ++)
690 if (*slash == '/' || *slash == '//' || *slash == ':')
691 fn = slash + 1;
692 obstack_1grow (&rtl_obstack, '*');
693 obstack_grow (&rtl_obstack, fn, strlen (fn));
694 sprintf (line_name, ":%d", read_rtx_lineno );
695 obstack_grow (&rtl_obstack, line_name, strlen (line_name)+1);
696 stringbuf = (char *) obstack_finish (&rtl_obstack);
697 }
698
699 if (star_if_braced)
700 XTMPL (return_rtx, i) = stringbuf;
701 else
702 XSTR (return_rtx, i) = stringbuf;
703 }
704 break ;
705
706 case 'w':
707 read_name (tmp_char, infile);
708 validate_const_int (infile, tmp_char);
709 #if HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT == HOST_BITS_PER_INT
710 tmp_wide = atoi (tmp_char);
711 #else
712 #if HOST_BITS_PER_WIDE_INT == HOST_BITS_PER_LONG
713 tmp_wide = atol (tmp_char);
714 #else
715 /* Prefer atoll over atoq, since the former is in the ISO C99 standard.
716 But prefer not to use our hand-rolled function above either. */
717 #if defined (HAVE_ATOLL) || !defined (HAVE_ATOQ)
718 tmp_wide = atoll (tmp_char);
719 #else
720 tmp_wide = atoq (tmp_char);
721 #endif
722 #endif
723 #endif
724 XWINT (return_rtx, i) = tmp_wide;
725 break ;
726
727 case 'i':
728 case 'n':
729 read_name (tmp_char, infile);
730 validate_const_int (infile, tmp_char);
731 tmp_int = atoi (tmp_char);
732 XINT (return_rtx, i) = tmp_int;
733 break ;
734
735 default :
736 fprintf (stderr ,
737 "switch format wrong in rtl.read_rtx(). format was: %c./n",
738 format_ptr[-1]);
739 fprintf (stderr , "/tfile position: %ld/n", ftell (infile));
740 abort ();
741 }
742
743 c = read_skip_spaces (infile);
744 if (c != ')')
745 fatal_expected_char (infile, ')', c);
746
747 return return_rtx;
748 }
‘ S ’,‘ T ’,‘ s ’几乎都是相同的,除了‘ S ’是可选的,而‘ T ’依赖于 RTL 输入器。更具体些,如果字符串以‘ * ’或‘ @ ’开头,‘ T ’要求不同的解释方式。函数 read_string 获取这个内容。
325 static char *
326 read_string (struct obstack *ob, FILE *infile, int star_if_braced) in read-rtl.c
327 {
328 char *stringbuf;
329 int saw_paren = 0;
330 int c;
331
332 c = read_skip_spaces (infile);
333 if (c == '(')
334 {
335 saw_paren = 1;
336 c = read_skip_spaces (infile);
337 }
338
339 if (c == '"')
340 stringbuf = read_quoted_string (ob, infile);
341 else if (c == '{')
342 {
343 if (star_if_braced)
344 obstack_1grow (ob, '*');
345 stringbuf = read_braced_string (ob, infile);
346 }
347 else
348 fatal_with_file_and_line (infile, "expected `/"' or `{', found `%c'", c);
349
350 if (saw_paren)
351 {
352 c = read_skip_spaces (infile);
353 if (c != ')')
354 fatal_expected_char (infile, ')', c);
355 }
356
357 return stringbuf;
358 }
在 md 文件中,在 define_insn 模式中的输出模板可能被‘ ” ’对包括起来,它通过显示如何输出匹配 insn 的汇编代码。但是如果它以‘ * ’开头,余下的字符串就被假定为一段 C 程序。另一个例外,则是‘ @ ’,它表示一系列的模板,每个独占一行。另外如果输出模板被写作一个大括号块,它也被假定为 C 代码。不过,当构建 RTL 对象时,只有一个样式还起作用——字符串形式。上面,从 341 到 345 行,大括号块被以星号开头的字符串替代。 681 到 696 行,在模式名以‘ * ’开头的情形下,构建了内部名字。在 read_rtx 的 700 及 702 行, XTMPL 及 XSTR 都是访问 rtunion 的 rtstr 域中的字符串,不过以不同的验证条件。
然后就是对应以下部分的‘ E ’:
[(set (reg 17)
(compare (match_operand:DI 0 "nonimmediate_operand" "r,?mr")
(match_operand:DI 1 "const0_operand" "n,n")))]
这部分必须被封装在“ [] ”中。上面在 read_rtx 的 630 行执行这个测试,并且因为内容本身是一个表达式,因此 read_rtx 在 639 行递归来进一步处理这个表达式。在这里是 set 表达式,并且在 rtl.def 中,我们可以找到以下定义。
746 DEF_RTL_EXPR(SET, "set", "ee", 'x')
这个 1 有两个孩子。因此在 605 行, read_rtx 再一次递归,一次是为 reg 表达式,另一处是 compare 表达式。毫无疑问,在 rtl.def 里, compare 表达式同样有两个表达式形式(‘ e ’)的孩子,它们都是 match_operand 表达式。
129 DEF_RTL_EXPR(MATCH_OPERAND, "match_operand", "iss", 'm')
130 DEF_RTL_EXPR(REG, "reg", "i00", 'o')
由格式串指引, read_rtx 很容易地周游各处,最后我们可以得到如下的,对应上面模式的一个 rtx 对象。
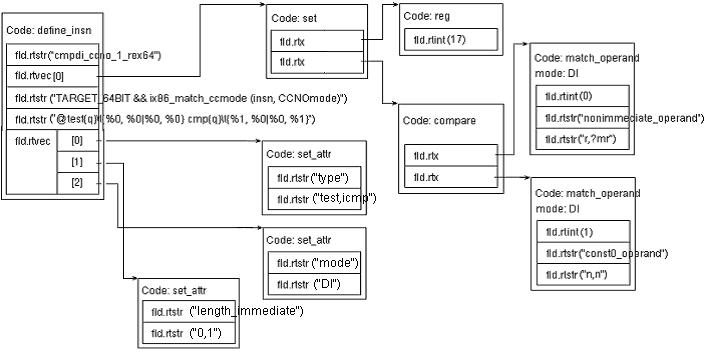
图 1 : genconditions - define_insn 模式的例子
同样的,在机器描述文件中,所有的模式,除了 define_constants ,都得到处理,并分配如上的一个 rtx 对象。接着这个 rtx 对象需要以某种方式被记录起来。
264 static void
265 process_rtx (rtx desc, int lineno) in gensupport.c
266 {
267 switch (GET_CODE (desc))
268 {
269 case DEFINE_INSN:
270 queue_pattern (desc, &define_insn_tail , read_rtx_filename , lineno);
271 break ;
272
273 case DEFINE_COND_EXEC:
274 queue_pattern (desc, &define_cond_exec_tail , read_rtx_filename , lineno);
275 break ;
276
277 case DEFINE_ATTR:
278 queue_pattern (desc, &define_attr_tail , read_rtx_filename , lineno);
279 break ;
280
281 case INCLUDE:
282 process_include (desc, lineno);
283 break ;
284
285 case DEFINE_INSN_AND_SPLIT:
286 {
287 const char *split_cond;
288 rtx split;
289 rtvec attr;
290 int i;
291
292 /* Create a split with values from the insn_and_split. */
293 split = rtx_alloc (DEFINE_SPLIT);
294
295 i = XVECLEN (desc, 1);
296 XVEC (split, 0) = rtvec_alloc (i);
297 while (--i >= 0)
298 {
299 XVECEXP (split, 0, i) = copy_rtx (XVECEXP (desc, 1, i));
300 remove_constraints (XVECEXP (split, 0, i));
301 }
302
303 /* If the split condition starts with "&&", append it to the
304 insn condition to create the new split condition. */
305 split_cond = XSTR (desc, 4);
306 if (split_cond[0] == '&' && split_cond[1] == '&')
307 split_cond = concat (XSTR (desc, 2), split_cond, NULL);
308 XSTR (split, 1) = split_cond;
309 XVEC (split, 2) = XVEC (desc, 5);
310 XSTR (split, 3) = XSTR (desc, 6);
311
312 /* Fix up the DEFINE_INSN. */
313 attr = XVEC (desc, 7);
314 PUT_CODE (desc, DEFINE_INSN);
315 XVEC (desc, 4) = attr;
316
317 /* Queue them. */
318 queue_pattern (desc, &define_insn_tail , read_rtx_filename , lineno);
319 queue_pattern (split, &other_tail , read_rtx_filename , lineno);
320 break ;
321 }
322
323 default :
324 queue_pattern (desc, &other_tail , read_rtx_filename , lineno);
325 break ;
326 }
327 }
指令与属性是紧密相关的,但到目前为止,我们仍然需要把它们分别保存,函数 queue_pattern 仅是把指定的 rtx 对象放入对应的列表。
139 static void
140 queue_pattern (rtx pattern, struct queue_elem ***list_tail, in gensupport.c
141 const char *filename, int lineno)
142 {
143 struct queue_elem *e = xmalloc (sizeof (*e));
144 e->data = pattern;
145 e->filename = filename;
146 e->lineno = lineno;
147 e->next = NULL;
148 **list_tail = e;
149 *list_tail = &e->next;
150 }
上面,在 process_rtx 的 281 行,在机器描述文件中,我们可以通过使用 include 语句包含另外的机器描述文件。这里在 process_include 中,这些被包含的机器描述文件将被读入,并以相同的方式处理。另一个特殊的模式是 define_insn_and_split 。它是组合模式,在这里它被分解成 define_insn 及 define_split 。通过下面的例子,我们可以看到其处理:
4225 (define_insn_and_split "*fix_truncsi_1" in i386.md
4226 [(set (match_operand:SI 0 "nonimmediate_operand" "=m,?r")
4227 (fix:SI (match_operand 1 "register_operand" "f,f")))]
4228 "TARGET_80387 && FLOAT_MODE_P (GET_MODE (operands[1]))
4229 && !reload_completed && !reload_in_progress
4230 && !SSE_FLOAT_MODE_P (GET_MODE (operands[1]))"
4231 "#"
4232 "&& 1"
4233 [(const_int 0)]
4234 {
4235 ix86_optimize_mode_switching = 1;
4236 operands[2] = assign_386_stack_local (HImode, 1);
4237 operands[3] = assign_386_stack_local (HImode, 2);
4238 if (memory_operand (operands[0], VOIDmode))
4239 emit_insn (gen_fix_truncsi_memory (operands[0], operands[1],
4240 operands[2], operands[3]));
4241 else
4242 {
4243 operands[4] = assign_386_stack_local (SImode, 0);
4244 emit_insn (gen_fix_truncsi_nomemory (operands[0], operands[1],
4245 operands[2], operands[3],
4246 operands[4]));
4247 }
4248 DONE;
4249 }
4250 [(set_attr "type" "fistp")
4251 (set_attr "mode" "SI")])
这个模式通过 read_rtx 的处理后,我们可以得到如下 rtx 对象。
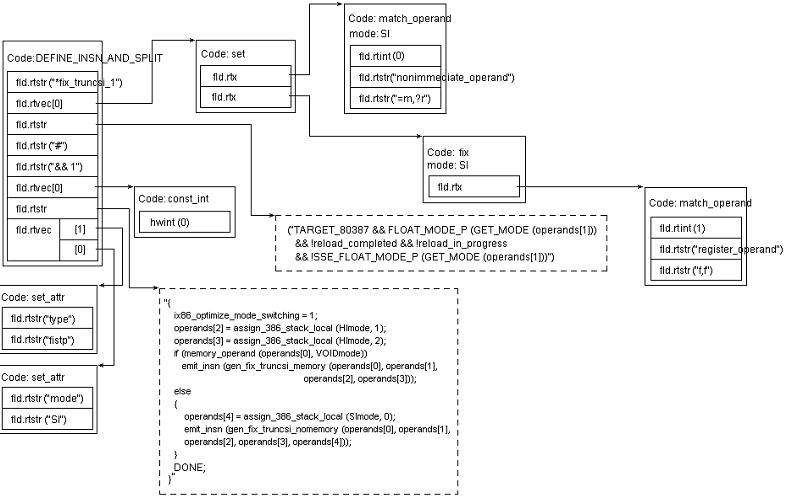
图 2 : genconditions - define_insn_and_split 模式的例子,图 1
在被 285 行的 case 块处理后,我们可以得到如下的两个 rtx 对象:
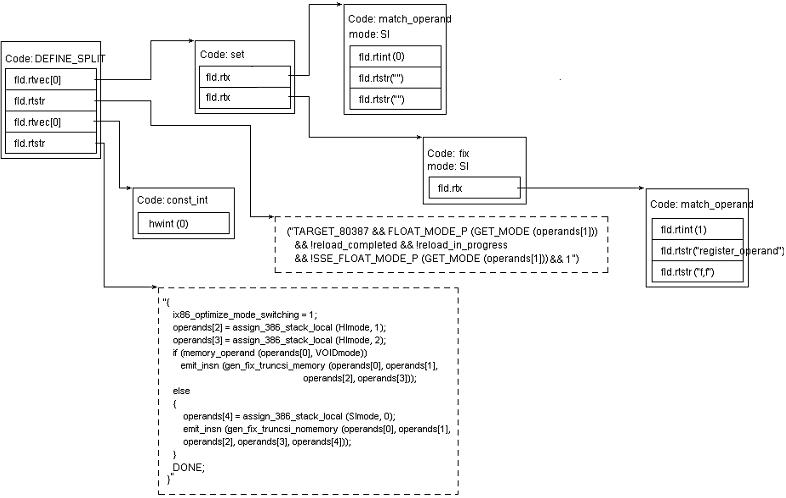
图 3 : genconditons - define_insn_and_split 模式的例子,图 2
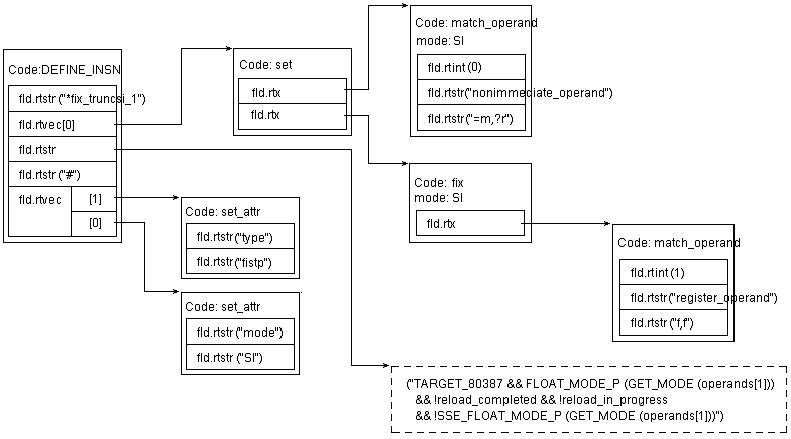
图 4 : gencodntion - define_insn_and_split 模式的例子,图 3






















 2058
2058

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








