前言:
一直以来,饱受文件路径的困惑,自己翻阅印象笔记中记录的此类记录,发现很多都是杂乱,根本不能简单话的解释这个问题。本篇的目的是总结以前的笔记,加上自己测试的例子,能明白准确的记录下这个问题。内容的话仅包含常见的java程序读取文件,不包含java web和jsp的读取文件方式。
问题一:Class.getResource和ClassLoader.getResource的分析
我经常写读取property结尾的key=value的文件,以一个PropertiesUtil工具类为例,代码如下:
public class PropertiesUtil {
private static Properties scheduleProp;
private static Properties urlProp;
private static Properties daoProp;
private static Properties executorProp;
private static Properties serviceProp;
public static Properties getProSchedule() {
try {
if(scheduleProp==null) { scheduleProp = new Properties(); scheduleProp.load(PropertiesUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("scheduletask.properties"));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return scheduleProp;
}这里的ClassLoader的getResourceAsStream返回的是InputStream流,我们需要关注的是传入的String name。首先,Java中的getResourceAsStream有以下几种:
1. Class.getResourceAsStream(String path) : path 不以’/’开头时默认是从此类所在的包下取资源,以’/’开头则是从ClassPath根下获取。其只是通过path构造一个绝对路径,最终还是由ClassLoader获取资源。
2. Class.getClassLoader.getResourceAsStream(String path) :默认则是从ClassPath根下获取,path不能以’/’开头,最终是由ClassLoader获取资源。
函数的源代码
java.lang.ClassLoader.getResourceAsStream()
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
return url != null ? url.openStream() : null;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
java.lang.ClassLoader.getResource()
public URL getResource(String name) {
URL url;
if (parent != null) {
url = parent.getResource(name);
} else {
url = getBootstrapResource(name);
}
if (url == null) {
url = findResource(name);
}
return url;
}
java.lang.Class.getResourceAsStream()
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
name = resolveName(name);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(name);
}
return cl.getResourceAsStream(name);
}
java.lang.Class.getResource()
public java.net.URL getResource(String name) {
name = resolveName(name);
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(name);
}
return cl.getResource(name);
}
private String resolveName(String name)
{
if (name == null)
{
return name;
}
if (!name.startsWith("/"))
{
Class c = this;
while (c.isArray()) {
c = c.getComponentType();
}
String baseName = c.getName();
int index = baseName.lastIndexOf('.');
if (index != -1)
{
name = baseName.substring(0, index).replace('.', '/')
+"/"+name;
}
} else
{//如果是以"/"开头,则去掉
name = name.substring(1);
}
return name;
}PS: 这里强调一下,实际上的Class的函数是调用ClassLoader的方法。另外为什么class的可以(“/”),classLoader为什么不可以,resolveName这个函数里面就可以看出来了。
问题二:File和FileInputStream路径分析
以TestFile代码展示用例:
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
String path=this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource("1.txt").getPath();
String filePath=this.getClass().getResource("/1.txt").getFile();
System.out.println(path);
System.out.println(filePath);
File file=new File(path);
File file1=new File("/1.txt");
File file2=new File("1.txt");
String path1=file1.getAbsolutePath();
String path2=file2.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println(path1);
System.out.println(path2);
ioRead(file);
nioRead(file);
ioRead(path);
}
public void ioRead(File file) throws IOException{
FileInputStream in =new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
in.read(b);
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
public void nioRead(File file)throws IOException{
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel channel=in.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.read(buffer);
byte[]b=buffer.array();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
public void ioRead(String file) throws IOException{
FileInputStream in =new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
in.read(b);
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
public void nioRead(String file)throws IOException{
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel channel=in.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.read(buffer);
byte[]b=buffer.array();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}程序排版,文件排版和结果截图:
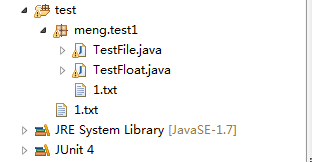
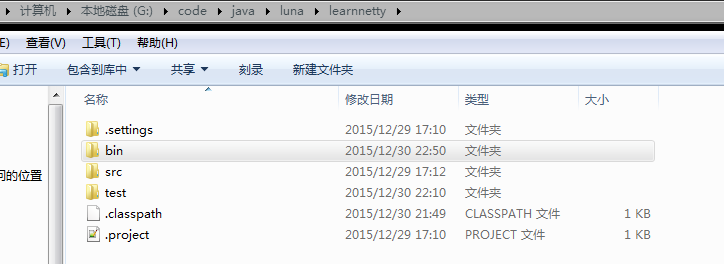
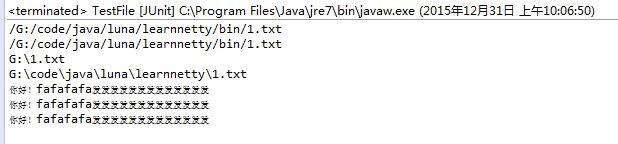
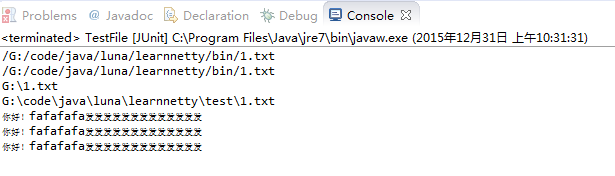
如果把 File file2=new File(“1.txt”); 改为File file2=new File(“test/1.txt”);
结果截图如下:
- 根据上面的截图,我们可以知道File和FileInputStream的相对路径是相当于工程文件learnnetty为基准,而绝对路径是以文件系统为基准的。
- 对于class和classloader得到的URL信息,是基于生成bin目录下的class。相对路径是class的当前目录,而绝对路径是以bin为根目录。
PS:这里classloader和class的getresource的函数不同可以参考第一个问题。






















 377
377

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








