前文:
《Tomcat源码:启动类Bootstrap与Catalina的加载》
《Tomcat源码:StandardServer与StandardService》
《Tomcat源码:StandardEngine、StandardHost、StandardContext、StandardWrapper》
《Tomcat源码:连接器与Executor、Connector》
《Tomcat源码:ProtocolHandler与Endpoint》
前言
前文中我们介绍到NioEndpoint的start方法启动了Acceptor与Poller这两个异步线程来处理连接请求,本文我们就来接着介绍这两个组件。
目录
一、Acceptor
在前文的Endpoint的startAcceptorThread方法中,创建了Acceptor对象,并使用异步线程调用了其run方法,下面我们就来介绍下Acceptor对象。
1、构造方法
Acceptor的构造方法传入了一个endpoint对象,看过前文的我们知道这里是一个NioEndpoint对象。
public abstract class AbstractEndpoint<S,U> {
protected void startAcceptorThread() {
acceptor = new Acceptor<>(this);
String threadName = getName() + "-Acceptor";
acceptor.setThreadName(threadName);
Thread t = new Thread(acceptor, threadName);
t.setPriority(getAcceptorThreadPriority());
t.setDaemon(getDaemon());
t.start();
}
}
public class Acceptor<U> implements Runnable {
private final AbstractEndpoint<?,U> endpoint;
public Acceptor(AbstractEndpoint<?,U> endpoint) {
this.endpoint = endpoint;
}
}2、run方法
由于run方法较长,这里只展示下核心步骤,首先是接收到请求后判断是否已达最大连接数,如果允许则分配SocketChannel,最后进行连接的配置以及处理器的分配。
@Override
public void run() {
int errorDelay = 0;
long pauseStart = 0;
try {
// Loop until we receive a shutdown command
while (!stopCalled) {
// ...
try {
//if we have reached max connections, wait
endpoint.countUpOrAwaitConnection();
U socket = null;
try {
// Accept the next incoming connection from the server
// socket
socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept();
} catch (Exception ioe) {
// We didn't get a socket
// ...
}
// Configure the socket
if (!stopCalled && !endpoint.isPaused()) {
// setSocketOptions() will hand the socket off to
// an appropriate processor if successful
if (!endpoint.setSocketOptions(socket)) {
endpoint.closeSocket(socket);
}
} else {
endpoint.destroySocket(socket);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// ...
}
}
} finally {
stopLatch.countDown();
}
state = AcceptorState.ENDED;
}countUpOrAwaitConnection
countUpOrAwaitConnection是endpoint中的方法,用于判断连接数是否已达最大,这里会获取我们在前文中介绍的endpoint时提及的connectionLimitLatch。
public abstract class AbstractEndpoint<S,U> {
private int maxConnections = 8*1024;
protected void countUpOrAwaitConnection() throws InterruptedException {
if (maxConnections==-1) {
return;
}
LimitLatch latch = connectionLimitLatch;
if (latch!=null) {
latch.countUpOrAwait();
}
}
}LimitLatch
connectionLimitLatch的实现类为LimitLatch,通过其源码可以发现其定义了三个成员变量sync、count、limit分别用来管理并发锁、记录请求数与最大连接限制。
public abstract class AbstractEndpoint<S,U> {
protected LimitLatch initializeConnectionLatch() {
if (maxConnections==-1) {
return null;
}
if (connectionLimitLatch==null) {
connectionLimitLatch = new LimitLatch(getMaxConnections());
}
return connectionLimitLatch;
}
}
public class LimitLatch {
private final Sync sync;
private final AtomicLong count;
private volatile long limit;
public LimitLatch(long limit) {
this.limit = limit;
this.count = new AtomicLong(0);
this.sync = new Sync();
}
}tryAcquireShared
回到上文中判断最大连接数的步骤latch.countUpOrAwait,我们进入到LimitLatch 中来看下。这里最终会进入tryAcquireShared方法,将count加1后判断是否已超出限制,然后再做进一步判断与处理。
public class LimitLatch {
public void countUpOrAwait() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1);
}
private class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
@Override
protected int tryAcquireShared(int ignored) {
long newCount = count.incrementAndGet();
if (!released && newCount > limit) {
// Limit exceeded
count.decrementAndGet();
return -1;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
}serverSocketAccept
这一步也是调用的endpoint中的方法,从下文的源码中可以看出这里是从endpoint执行init方法时创建的ServerSocketChannel中获取SocketChannel 连接。在nio中,可以认为一个 SocketChannel 对象代表一个服务端与客户端的连接。
public class NioEndpoint extends AbstractJsseEndpoint<NioChannel,SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected SocketChannel serverSocketAccept() throws Exception {
SocketChannel result = serverSock.accept();
// ...
return result;
}
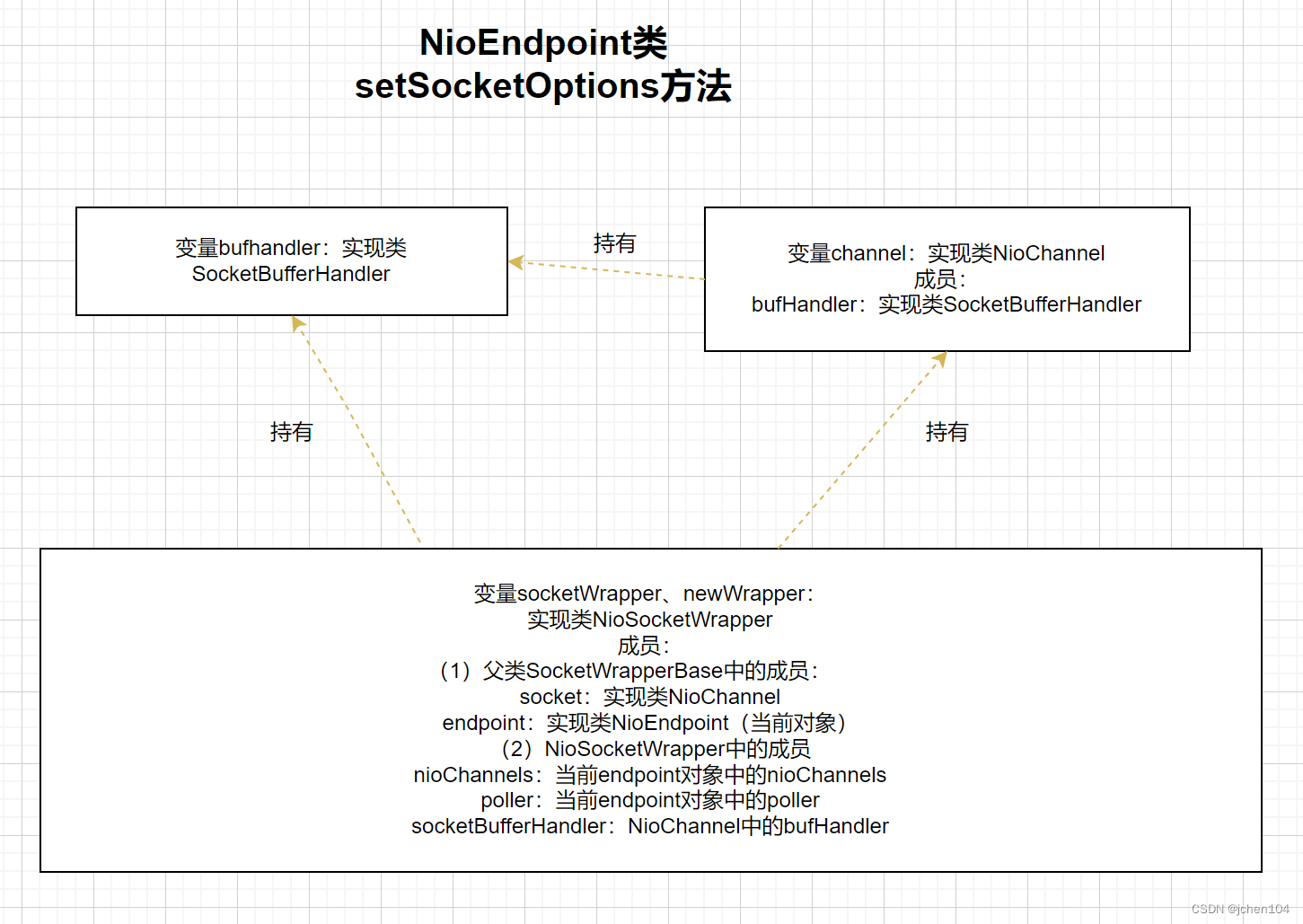
}setSocketOptions
setSocketOptions也是endpoint中的方法,这里会执行以下几步:
(1)尝试从SynchronizedStack<NioChannel> nioChannels 中获取信道
(2)如果上一步未获取到则创建SocketBufferHandler对象
(3)使用SocketBufferHandler对象创建NioChannel对象
(4)使用NioChannel与NioEndpoint对象创建NioSocketWrapper对象
(5)为NioChannel对象设置SocketChannel与NioSocketWrapper对象作为属性
(6)为NioSocketWrapper对象设置属性并注册入poller中
public class NioEndpoint extends AbstractJsseEndpoint<NioChannel,SocketChannel> {
@Override
protected boolean setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket) {
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = null;
try {
// Allocate channel and wrapper
NioChannel channel = null;
if (nioChannels != null) {
channel = nioChannels.pop();
}
if (channel == null) {
SocketBufferHandler bufhandler = new SocketBufferHandler(
socketProperties.getAppReadBufSize(),
socketProperties.getAppWriteBufSize(),
socketProperties.getDirectBuffer());
if (isSSLEnabled()) {
channel = new SecureNioChannel(bufhandler, this);
} else {
channel = new NioChannel(bufhandler);
}
}
NioSocketWrapper newWrapper = new NioSocketWrapper(channel, this);
channel.reset(socket, newWrapper);
connections.put(socket, newWrapper);
socketWrapper = newWrapper;
// Set socket properties
// Disable blocking, polling will be used
socket.configureBlocking(false);
socketProperties.setProperties(socket.socket());
socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());
socketWrapper.setWriteTimeout(getConnectionTimeout());
socketWrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(NioEndpoint.this.getMaxKeepAliveRequests());
poller.register(socketWrapper);
return true;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
try {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.socketOptionsError"), t);
} catch (Throwable tt) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(tt);
}
if (socketWrapper == null) {
destroySocket(socket);
}
}
// Tell to close the socket if needed
return false;
}
}SocketBufferHandler
SocketBufferHandler对象里包含了两个 ByteBuffer 对象,一个读一个写。
public SocketBufferHandler(int readBufferSize, int writeBufferSize,
boolean direct) {
this.direct = direct;
if (direct) {
readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(readBufferSize);
writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(writeBufferSize);
} else {
readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(readBufferSize);
writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(writeBufferSize);
}
}NioChannel
NioChannel 中将SocketBufferHandler 与SocketChannel 、NioSocketWrapper 作为成员变量,初始化时只设置了一个SocketBufferHandler,而另外两个成员会在rest时设置。
public class NioChannel implements ByteChannel, ScatteringByteChannel, GatheringByteChannel {
protected final SocketBufferHandler bufHandler;
protected SocketChannel sc = null;
protected NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = null;
public NioChannel(SocketBufferHandler bufHandler) {
this.bufHandler = bufHandler;
}
// Reset the channel
public void reset(SocketChannel channel, NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper) throws IOException {
this.sc = channel;
this.socketWrapper = socketWrapper;
bufHandler.reset();
}
}NioSocketWrapper
NioSocketWrapper是更多组件的封装,可以看到这里从NioEndpoint中获取了nioChannels 与poller,又从niochannel中获取了socketBufferHandler,而其父类中则保存了作为参数传入的SocketChannel 与当前的endpoint对象。
public static class NioSocketWrapper extends SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> {
public NioSocketWrapper(NioChannel channel, NioEndpoint endpoint) {
super(channel, endpoint);
nioChannels = endpoint.getNioChannels();
poller = endpoint.getPoller();
socketBufferHandler = channel.getBufHandler();
readLock = (readPending == null) ? new Object() : readPending;
writeLock = (writePending == null) ? new Object() : writePending;
}
}
public abstract class SocketWrapperBase<E> {
public SocketWrapperBase(E socket, AbstractEndpoint<E,?> endpoint) {
this.socket = socket;
this.endpoint = endpoint;
if (endpoint.getUseAsyncIO() || needSemaphores()) {
readPending = new Semaphore(1);
writePending = new Semaphore(1);
} else {
readPending = null;
writePending = null;
}
}
}
方法的最后将封装好的NioSocketWrapper对象注册到了poller对象中,由此将连接请求转发了过去。
大致梳理下Acceptor的作用就是使线程在一个循环里一直接受客户端连接,生成 SocketChannel 对象,并把这个 SocketChannel 对象封装成 NioChannel 和 NioSocketWrapper 对象,并注册到 Poller 对象中等待进一步处理。
二、Poller与PollerEvent
1、PollerEvent
PollerEvent是向Poller对象的事件队列插入的待处理的事件的抽象,可以被Poller缓存循环回收利用以避免GC。
可以看到构造方法内部实际是调用了rest方法将设置传入的两个参数,即我们上一节中介绍的NioSocketWrapper 与intOps(请求关注的事件类型,是连接、读还是写)。
/**
* PollerEvent, cacheable object for poller events to avoid GC
*/
public static class PollerEvent {
private NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper;
private int interestOps;
public PollerEvent(NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper, int intOps) {
reset(socketWrapper, intOps);
}
public void reset(NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper, int intOps) {
this.socketWrapper = socketWrapper;
interestOps = intOps;
}
public NioSocketWrapper getSocketWrapper() {
return socketWrapper;
}
public int getInterestOps() {
return interestOps;
}
public void reset() {
reset(null, 0);
}
}2、poller
Poller类在构造方法中会获取一个选择器,这是NIO中的关键组件,用于获取就绪事件。
public class Poller implements Runnable {
private Selector selector;
public Poller() throws IOException {
this.selector = Selector.open();
}
register
先来看下上文中涉及的register方法,这个方法是将新连接的套接字创建为PollerEvent对象并缓存起来。这里的第一步是向NioSocketWrapper 中注册关注事件,这里默认是读事件,然后调用createPollerEvent方法创建PollerEvent对象最后调用addEvent对象进行缓存。
/**
* Registers a newly created socket with the poller.
*
* @param socketWrapper The socket wrapper
*/
public void register(final NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper) {
socketWrapper.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);//this is what OP_REGISTER turns into.
PollerEvent pollerEvent = createPollerEvent(socketWrapper, OP_REGISTER);
addEvent(pollerEvent);
}createPollerEvent、addEvent
createPollerEvent方法尝试从缓存中获取现有的PollerEvent,如果没有则新建一个,有的话则调用rest方法重置其套接字等设置。
addEvent则是将上一步获取到的PollerEvent加入到events事件缓存中,等待分配线程处理。
public class Poller implements Runnable {
private final SynchronizedQueue<PollerEvent> events =
new SynchronizedQueue<>();
private PollerEvent createPollerEvent(NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper, int interestOps) {
PollerEvent r = null;
if (eventCache != null) {
r = eventCache.pop();
}
if (r == null) {
r = new PollerEvent(socketWrapper, interestOps);
} else {
r.reset(socketWrapper, interestOps);
}
return r;
}
private void addEvent(PollerEvent event) {
events.offer(event);
if (wakeupCounter.incrementAndGet() == 0) {
selector.wakeup();
}
}
}run
然后来看poller的run方法,首先调用了events()方法,获取就绪事件数量keyCount ,遍历这些就绪事件并调用processKey方法处理,传入的参数为连接的SelectionKey与NioSocketWrapper。
PS:selectionKey表示channel在Selector中注册的标识,每个Channel向Selector注册时,都将会创建一个selectionKey
public class Poller implements Runnable {
public void run() {
// Loop until destroy() is called
while (true) {
boolean hasEvents = false;
try {
if (!close) {
hasEvents = events();
if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) {
// If we are here, means we have other stuff to do
// Do a non blocking select
keyCount = selector.selectNow();
} else {
keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);
}
wakeupCounter.set(0);
}
if (close) {
// ...
}
// Either we timed out or we woke up, process events first
if (keyCount == 0) {
hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());
}
} catch (Throwable x) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorLoopError"), x);
continue;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator =
keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
// Walk through the collection of ready keys and dispatch
// any active event.
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) sk.attachment();
// Attachment may be null if another thread has called
// cancelledKey()
if (socketWrapper != null) {
processKey(sk, socketWrapper);
}
}
// Process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
}
getStopLatch().countDown();
}
}events
来看events方法,内部会遍历PollerEvent 缓存集合events,获取其中的NioSocketWrapper 、SocketChannel 以及关注的事件interestOps 。如果是注册事件则将当前通道的OP_READ事件注册到selector上,同时添加附件NioSocketWrapper 对象,如果是别的事件则将其附加到 SocketChannel 关联的 SelectionKey 。
public boolean events() {
boolean result = false;
PollerEvent pe = null;
for (int i = 0, size = events.size(); i < size && (pe = events.poll()) != null; i++ ) {
result = true;
NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = pe.getSocketWrapper();
SocketChannel sc = socketWrapper.getSocket().getIOChannel();
int interestOps = pe.getInterestOps();
if (sc == null) {
log.warn(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.nullSocketChannel"));
socketWrapper.close();
} else if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) {
try {
sc.register(getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper);
} catch (Exception x) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x);
}
} else {
final SelectionKey key = sc.keyFor(getSelector());
if (key == null) {
socketWrapper.close();
} else {
final NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper) key.attachment();
if (attachment != null) {
try {
int ops = key.interestOps() | interestOps;
attachment.interestOps(ops);
key.interestOps(ops);
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper);
}
} else {
cancelledKey(key, socketWrapper);
}
}
}
if (running && eventCache != null) {
pe.reset();
eventCache.push(pe);
}
}
return result;
}processKey
run方法中调用processKey方法来处理请求,首先是判断socketWrapper.getSendfileData() 不为 null 的话就调用 processSendfile 方法处理。
然后判断是读还是写事件,NioSocketWrapper 是在上文中的setSocketOptions方法创建的,这里的readOperation、writeOperation 为空,readBlocking、writeBlocking为false,因此最终实际上会调用processSocket方法,该方法由AbstractEndpoint类实现,我们会在以后介绍。
protected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper) {
try {
if (close) {
cancelledKey(sk, socketWrapper);
} else if (sk.isValid()) {
if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable()) {
if (socketWrapper.getSendfileData() != null) {
processSendfile(sk, socketWrapper, false);
} else {
unreg(sk, socketWrapper, sk.readyOps());
boolean closeSocket = false;
// Read goes before write
if (sk.isReadable()) {
if (socketWrapper.readOperation != null) {
if (!socketWrapper.readOperation.process()) {
closeSocket = true;
}
} else if (socketWrapper.readBlocking) {
synchronized (socketWrapper.readLock
) {
socketWrapper.readBlocking = false;
socketWrapper.readLock.notify();
}
} else if (!processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) {
closeSocket = true;
}
}
if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) {
if (socketWrapper.writeOperation != null) {
if (!socketWrapper.writeOperation.process()) {
closeSocket = true;
}
} else if (socketWrapper.writeBlocking) {
synchronized (socketWrapper.writeLock) {
socketWrapper.writeBlocking = false;
socketWrapper.writeLock.notify();
}
} else if (!processSocket(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) {
closeSocket = true;
}
}
if (closeSocket) {
cancelledKey(sk, socketWrapper);
}
}
}
} else {
// Invalid key
cancelledKey(sk, socketWrapper);
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
cancelledKey(sk, socketWrapper);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.keyProcessingError"), t);
}
}
到这里我们基本介绍完了请求是如何从Acceptor流转到Poller中的,异步线程Acceptor在接收到请求后会创建了SocketChannel 对象,接着先封装为NioSocketWrapper,再封装为PollerEvent,然后转交给Poller线程处理。Poller线程在拿到PollerEvent后会取出其中的SocketChannel对象并注册相关事件,最后调用processKey来进行下一步处理。
参考资料:
























 562
562











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








