1.dijkstra算法简介
即为了求最短路径问题,对于算法中基础图论这一块,总会不可避免的求两点之间的距离。最短路径问题中,两个点之间不一定只有一条路径,那么如何才能找出最短的那一条呢,不妨尝试一下dijkstra这个大神的帮助
2.话不多说,我们直接开始聊算法步骤
1.在一张图中,题目一般会告诉你很多点,以及每个点之间的距离,让你求起点比如说点D到各个点的最短距离。在这张图中,我们以D表示为起点,同时创建两个数组S和U,以数组S表示已经记录下来的各个点与起点D的最短路径,数组U表示未记录下来的各个点与起点D的最短路径的距离。
2.我们将起点D与起点D的的距离记为0(虽然看起来像废话),将每一次起点可以接触到的点的最小距离计入S中,对于不能接触到的点视为与起点的距离无穷大,每加入一个点进行一次更新。刚开始时,当只有D点即起点时,D可以接触到C和E,而其它点不能接触到,我们认为S={D(0)}(其中只有D已知,而0表示D与起点的距离)U={A(无穷大),B(无穷大),C(3),E(4),F(无穷大),G(无穷大)}。

3.当我们加入C点后,此时起点D可以通过C点接触到B点和F点,因此B和F不再是无穷大而是最短距离,这时我们更新S和U数组,即为S={D(0),C(3)},U={A(无穷大),B(13),C(3),E(4),F(9),G(无穷大)}。
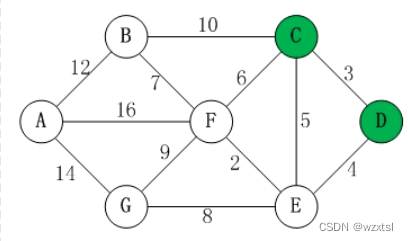

4.到最后,我们记为S={D(0),C(3),E(4),F(6),G(12),B(13),A(22)},这时候我们如果想知道起点D到所有点的最短路径,直接从S中寻找即可。
3.经典入坑例题(板子)
题目描述
在每年的校赛里,所有进入决赛的同学都会获得一件很漂亮的t-shirt。但是每当我们的工作人员把上百件的衣服从商店运回到赛场的时候,却是非常累的!所以现在他们想要寻找最短的从商店到赛场的路线,你可以帮助他们吗?
输入描述
输入包括多组数据。每组数据第一行是两个整数N、M(N<=100,M<=10000),N表示成都的大街上有几个路口,标号为1的路口是商店所在地,标号为N的路口是赛场所在地,M则表示在成都有几条路。N=M=0表示输入结束。接下来M行,每行包括3个整数A,B,C(1<=A,B<=N,1<=C<=1000),表示在路口A与路口B之间有一条路,我们的工作人员需要C分钟的时间走过这条路。
输入保证至少存在1条商店到赛场的路线。
输出描述
对于每组输入,输出一行,表示工作人员从商店走到赛场的最短时间
样例输入 1
2 1 1 2 3 3 3 1 2 5 2 3 5 3 1 2 0 0
样例输出 1
3 2
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct edge
{
int pos;//点
int w;//距离
} edge;
typedef struct node
{
int pos;//点
int dis;//距离
//一般来说比较函数写在结构体内会比写在外部快
bool operator<(const node &x) const
{
return x.dis < dis;
//x相当于当前正在比较的值,这个函数就是x从小到大排。
//存储用优先队列时会相反,同是上面这个函数会按r从大到小排。
}
} node;
vector<edge> connects[100001];//创建一个容器,vector中标示了u与v之间的距离w
void add_edge(int u, int v, int w)
{
connects[v].push_back({u, w});//表示v与u之间距离为w
connects[u].push_back({v, w});//表示u与v之间距离为w
return;
}
int n, m;
bool vis[100001];//记录是否访问了这个点
int dist[100001];//记录起点到点n的距离
const int INF = 998244353;
void init(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
vis[i] = 0;//初始化全部点开始时都没有访问过
connects[i].clear();//将上一次的数据清空
dist[i] = INF;//将起点还接触不到的点与起点的距离设置为无穷大
}
return;
}
//这里使用了队列对dijkstra算法进行了优化
void Dijkstra_queue(int start)
{
dist[start] = 0;//起点与起点的距离设置为0
priority_queue<node> q;//创建一个优先队列
q.push((node){start, 0});//放入队列当中
while (!q.empty())//对队列进行操作,当队列为空后停止
{
int pos = q.top().pos;
int dis = q.top().dis;
q.pop();
if (vis[pos])//访问过直接跳过
continue;
vis[pos] = 1;//标记为访问过
for (int i = 0; i < connects[pos].size(); i++)
{
int v = connects[pos][i].pos;
int w = connects[pos][i].w;
if (dist[v] > dist[pos] + w)//如果1到点v的距离大于1到点pos加上pos到点v的距离,距离进项更新
{
dist[v] = dist[pos] + w;//1到点v的最短距离就等于1到点pos加上pos到点v的距离
q.push((node){v, dist[v]});//计入到队列当中
}
}
}
return;
}
void solve()
{
init(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int u,v,w;//w表示输入的u与v之间的距离
cin>>u>>v>>w;
add_edge(u,v,w);//将距离edge加入connect中记录下来
}
Dijkstra_queue(1);//表示从起点1到其他点的最短路径
cout<<dist[n]<<endl;//得出起点1到点n的最短路径
}
int main()
{
while (~scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) && !(n == 0 && m == 0))//常规操作
{
solve();
}
system("pause");
}例题二(我愿称之为升级版本)
Frogger
题目描述
Freddy Frog is sitting on a stone in the middle of a lake. Suddenly he notices Fiona Frog who is sitting on another stone. He plans to visit her, but since the water is dirty and full of tourists’ sunscreen, he wants to avoid swimming and instead reach her by jumping.
Unfortunately Fiona’s stone is out of his jump range. Therefore Freddy considers to use other stones as intermediate stops and reach her by a sequence of several small jumps.
To execute a given sequence of jumps, a frog’s jump range obviously must be at least as long as the longest jump occuring in the sequence.
The frog distance (humans also call it minimax distance) between two stones therefore is defined as the minimum necessary jump range over all possible paths between the two stones.
You are given the coordinates of Freddy’s stone, Fiona’s stone and all other stones in the lake. Your job is to compute the frog distance between Freddy’s and Fiona’s stone.
输入描述
The input will contain one or more test cases. The first line of each test case will contain the number of stones n (2<=n<=200). The next n lines each contain two integers xi,yi (0 <= xi,yi <= 1000) representing the coordinates of stone #i. Stone #1 is Freddy’s stone, stone #2 is Fiona’s stone, the other n-2 stones are unoccupied. There’s a blank line following each test case. Input is terminated by a value of zero (0) for n.
输出描述
For each test case, print a line saying “Scenario #x” and a line saying “Frog Distance = y” where x is replaced by the test case number (they are numbered from 1) and y is replaced by the appropriate real number, printed to three decimals. Put a blank line after each test case, even after the last one.
样例输入 1
2 0 0 3 4 3 17 4 19 4 18 5 0
样例输出 1
Scenario #1 Frog Distance = 5.000 Scenario #2 Frog Distance = 1.414
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define INF 998244353
#define maxn 205
double mp[maxn][maxn],path[maxn];//mp为两点之间的距离,path为起点到i点的最大值
bool vis[maxn];//标记是否被访问
int n;
int cnt=1;
map <int,pair<int,int> > m;//用来储存x和y坐标 注意不能是<int,pair<int,int>> > >要用空格分开
struct node{
int num;//num存储石头编号
double dis;//表示从起点到num石头的最小距离
node(int a,double b){//将函数初始化
num=a;
dis=b;
}
bool friend operator <(node a,node b){//只有<重载操作符函数时,如果将<改为>为什么不行,出现error C2784的错误
//<为从大到小排列,>为从小到大排列
return a.dis>b.dis;
}
};
double dis(int a,int b){
return sqrt(pow((double)(m[a].first-m[b].first),2)+pow((double)(m[a].second-m[b].second),2));
}
void dijkstra(){
priority_queue<node>q;
node start(0,0);
path[0]=0;
q.push(start);
while(!q.empty()){
node p=q.top();
q.pop();
if(vis[p.num]==true){
continue;
}
vis[p.num]=true;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(path[i]>max(mp[i][p.num],path[p.num])&&vis[i]==false){
path[i]=max(mp[i][p.num],path[p.num]);//更新path数组
node temp(i,path[i]);
q.push(temp);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
while(cin>>n&&n!=0){
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++){
fill(mp[i],mp[i]+maxn,INF);//初始化
mp[i][i]=0;
}
fill(path,path+maxn,INF);//memset(path,INF,sizeof path);
fill(vis,vis+maxn,false);//memset(vis,false,sizeof vis);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>m[i].first>>m[i].second;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
mp[i][j]=mp[j][i]=dis(i,j);
}
}
dijkstra();
cout<<"Scenario #"<<cnt<<endl;
cout<<"Frog Distance ="<<fixed << setprecision(3)<<path[1]<<endl;
cout<<endl;
cnt++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}入坑不易,多看几次(n次)





















 241
241











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








