A 288μW Programmable Deep-Learning Processor with 270KB On-Chip Weight Storage Using Non-Uniform Memory Hierarchy for Mobile Intelligence
单位:Michigan,CubeWorks(密歇根大学,CubeWorks公司)
又是一款做DNN加速的面向IOT的专用芯片,主要特点是有L1~L4四级不同速度、能耗的层次化存储。通过对全连接矩阵x向量的计算流程优化,最终可以在0.65V 3.9MHz下获得374GOPS/W的能效表现及288uW的能耗指标[1]。主要还是低功耗,288uW可以做到常开了。
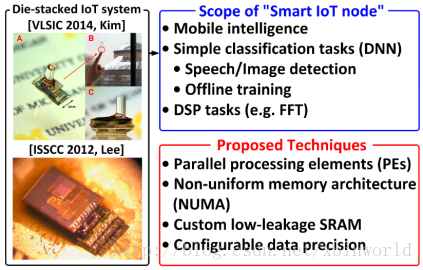
IoT DLA(Deep Learning Accelerator)的愿景和实操:IoT的结点将具有移动感知能力,同时可以运行简单的语音/图像检测和离线学习能力,可以完成部分DSP的计算工作。当前的技术采用了高并行的PE以及非标准的memory结构NUMA,定制的低漏电流SRAM,同时对数据位宽采用精度可配的管理方式。
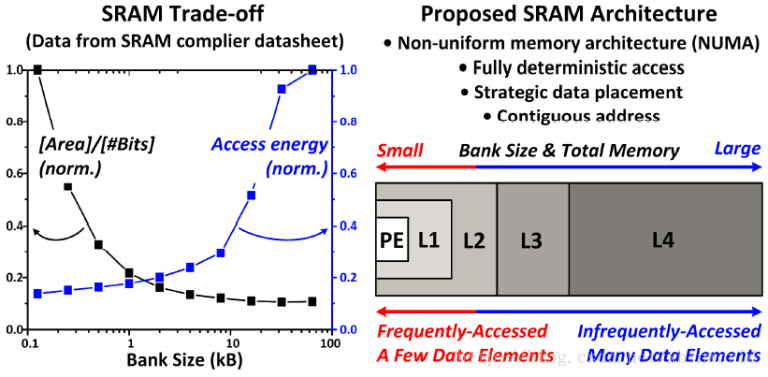
和传统的计算相比,深度学习的访存次数大大增加,计算的不确定性也十分明显,传统的层次化存储结构(寄存器-Cache-DRAM-HDD/SSD)已经难以满足需求(Cache作用不明显,访存不规则但是服从统计学分布规律)。因此,采用非一致的存储架构、提高存储的bit密度,以及使用长字节表达+可变精度的数据格式,可以有效提升深度学习的访存、能效表现。
采用的多层存储结构:采用非一致性的NUMA,建立确定性访存机制,提出数据分配机制以及数据的连续地址存放。
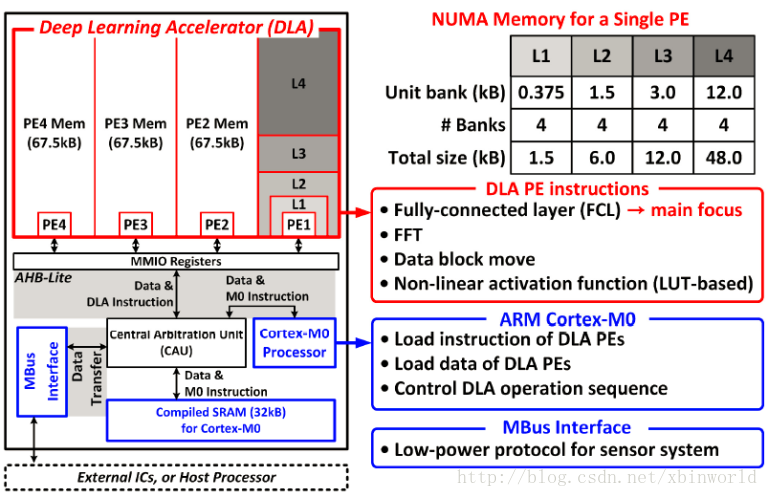
DLA的设计:每个PE均具有共计67.5kB的4层存储结构,通过AHB与主控芯片相连,通过MMIO寄存器进行数据交互。——AHB Lite和寄存器交互使得数据交换能耗低;
下面是重点:
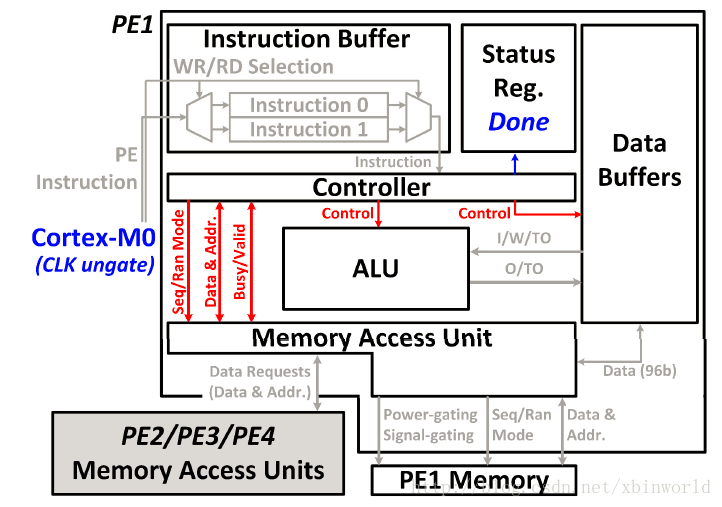
DLA的PE设计:整体工作流程:
1、instruction buffer用于接受由主控核(Cortex-M0)发出的指令,经由WR/RD进行选择,将192b的指令输出到中心controller;
2、中心controller(CTR)将状态寄存器Status Reg置位“Running”;
3、访存单元(Mem)通过中心controller和PE进行数据交互,CTR定义MemAU数据访存模式(序列Seq/随机Ran),PE通过CTR和MemAU进行访存操作;同时MemAU采用了power gating和signal gating技术;对于外存的访问请求,也通过MemAU处理,优先级为:Cortex-M0>外部PE>所在PE;
4、CTR向Data Buffer发起数据请求,完成:解压MemAU输入的96b数据,打包发出输出的96b数据,并采用临近数据存储方式进行操作;
5、CTR对ALU发起数据,ALU通过IO口从Data Buffer中读取数据,可以进行如下计算:4个乘法计算(8bit)、4个乘法计算(16bit)、10个加法器、6个移位器;基于查找表的多项式差值计算单元,用于激活函数的计算;
6、计算任务完成后,Cortex-M0发出信号,CTR将Status Reg置位Done。
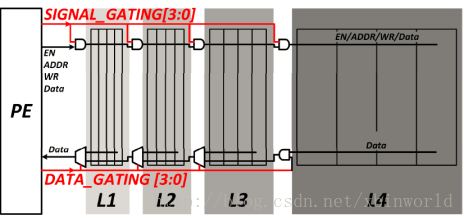
有信号开关的SRAM结构:通过SIGNAL_GATING[3:0]和DATA_DATING[3:0]进行数据的存储层级选择。
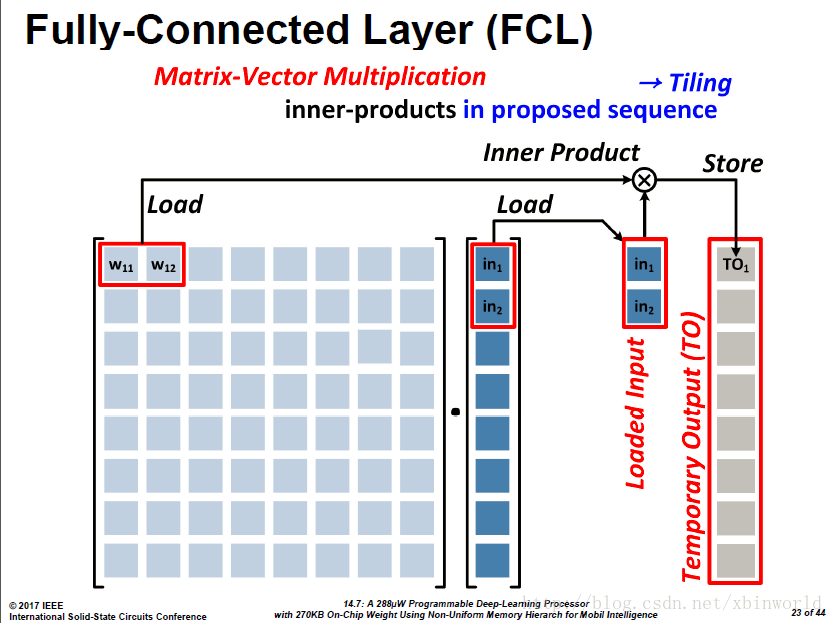
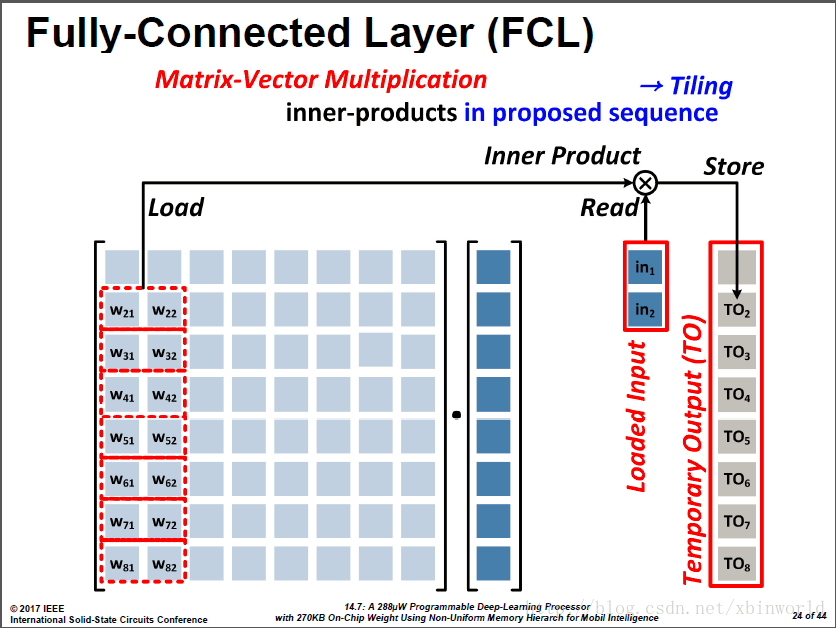
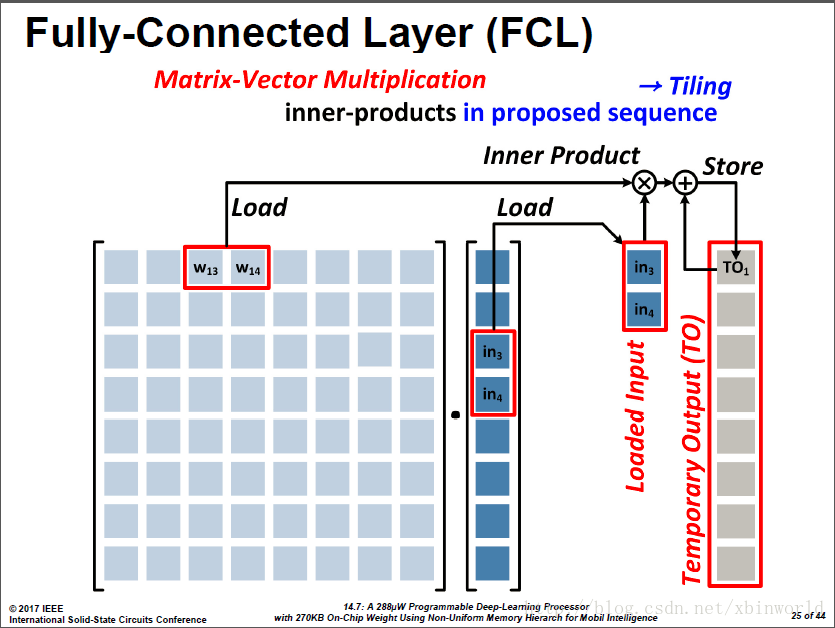
本芯片主要能做FC的计算,全连接层的运算(Fully-Connected Layer, FCL):分解为矩阵x向量+激活函数。核心是Matrix-Vector Multiplication(MVM)。
为了降低中间结果数量以及写出带宽,采用的折叠式的求和:两两加和的结果是一个临时结果,换下一个两列的时候,把前面的临时结果读出来,加完之后再写回去。
因此,基于这样的计算模式,论文采用:
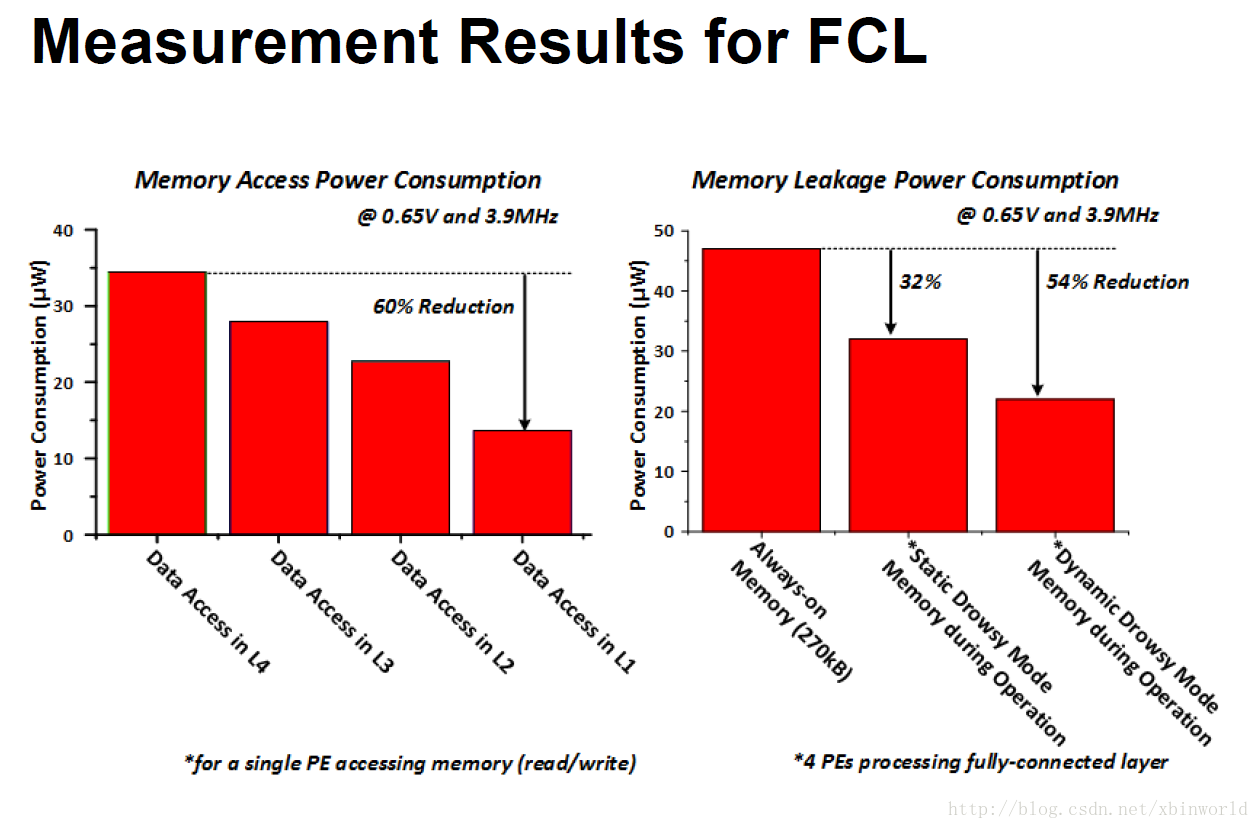
基于以上的MVM计算方式,TO是访问频率最高的数据->存在L1 Mem;权重w重用度低->存在L4 Mem
重用度低就是指不会重复读,只会按顺序读,因此放在较大较远的L4中;而临时结果需要反复读写,量也不大,所以放在较小较近的L1中。
对于不同层Memory的访存功耗对比:
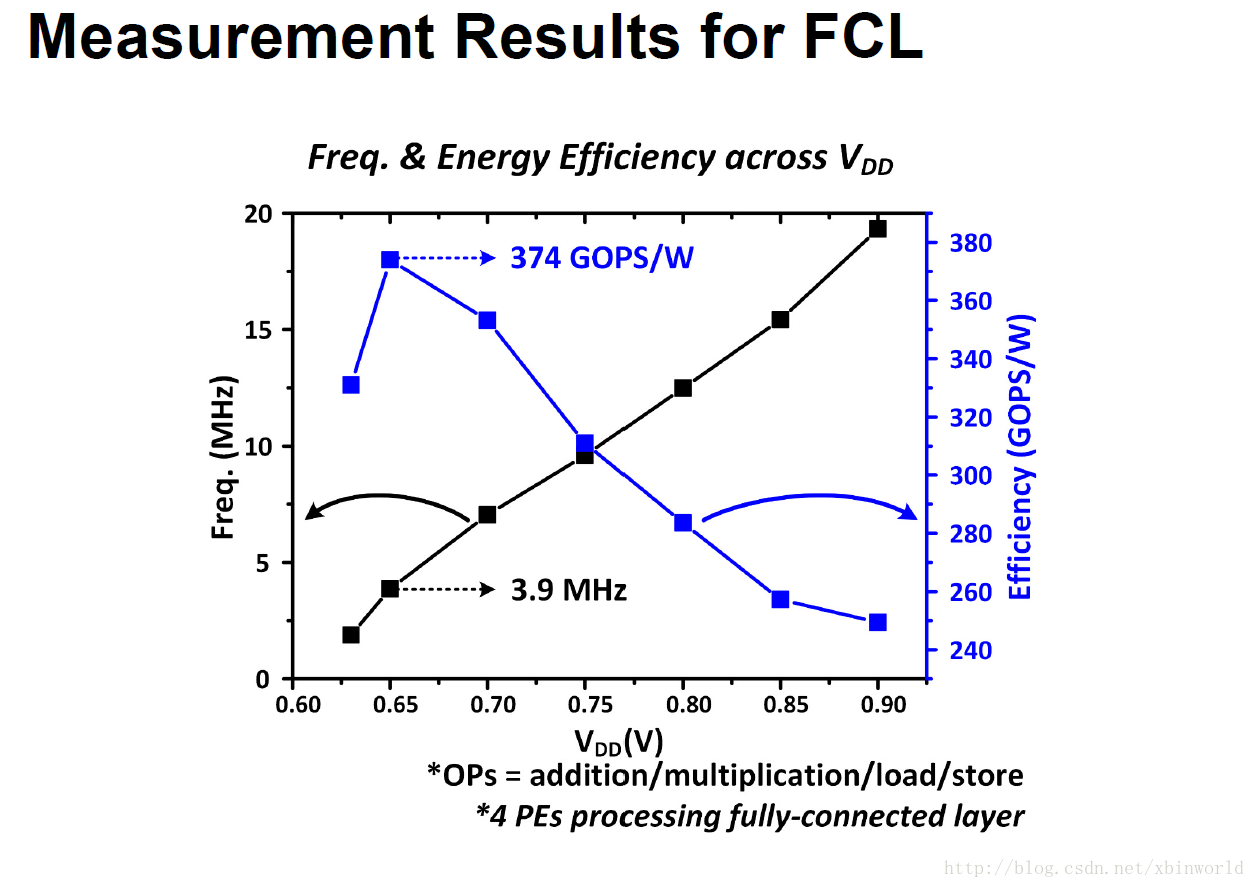
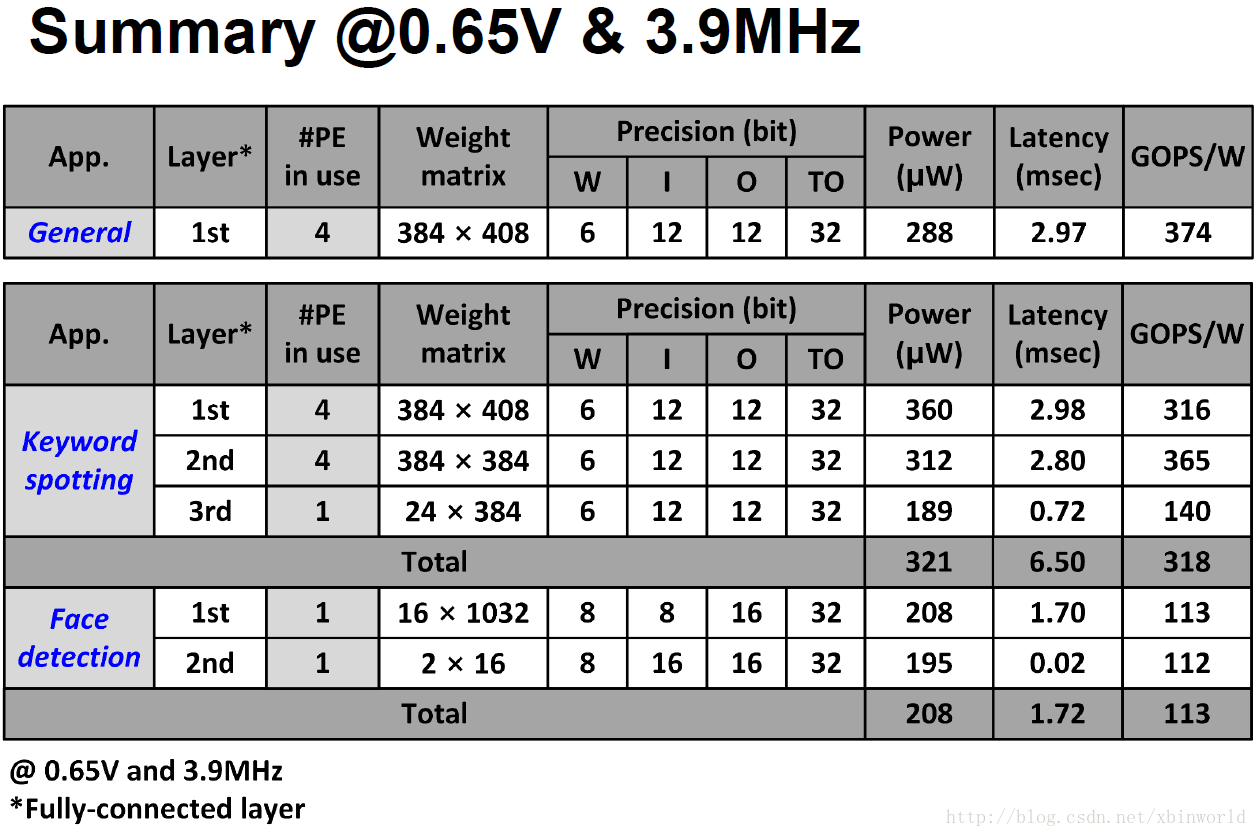
芯片性能表现及对比:在0.65V 3.9MHz下,运行FCL平均能耗为288uW,能效为374GOPS/W,同时支持6~31bit不同位宽的计算。
总结:一款面向IoT的低功耗深度学习加速器
1、在低功耗、高效率下实现DNN
2、延迟在几个ms的级别,可以应对IoT的实时性要求
vvvvvvvv# 参考资料
[1] https://reconfigdeeplearning.com/2017/02/09/isscc-2017-session-14-slides14-7
[2] A 288μW Programmable Deep-Learning Processor with 270KB On-Chip Weight Storage Using Non-Uniform Memory Hierarchy for Mobile Intelligence























 398
398











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








