理解buffer
三个重要属性
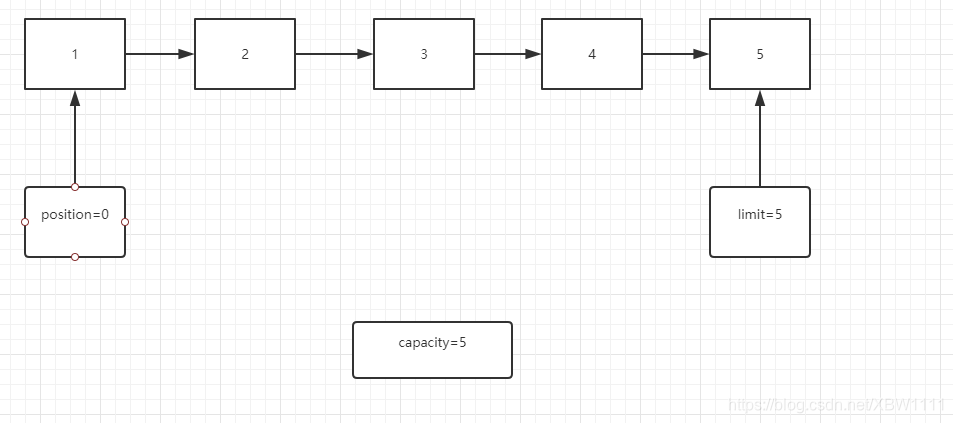
- position 可读或可写的元素的下一个元素索引
- limit 不可读写的元素的第一个元素位置 绝对不会大于capacity (初始化=capacity)
- capacity 可包含元素的总大小
用两张图简单理解一下概念
- 初始化5个元素
ByteBuffer intBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
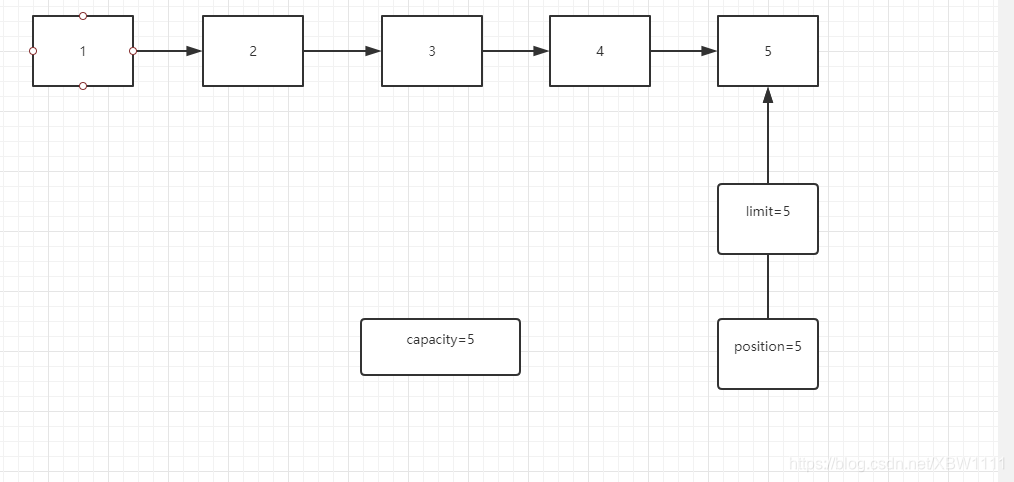
- 填满5个元素的时候
byte[] v = "ccccc".getBytes();
for (byte c : v) {
intBuffer.put(c);
}
三个重要方法
- clear
官方注释
* <li><p> {@link #clear} makes a buffer ready for a new sequence of
* channel-read or relative <i>put</i> operations: It sets the limit to the
* capacity and the position to zero. </p></li>
初始化结构数据 将position设置为0,limit设置等于capacity
- flip
官方注释
* <li><p> {@link #flip} makes a buffer ready for a new sequence of
* channel-write or relative <i>get</i> operations: It sets the limit to the
* current position and then sets the position to zero. </p></li>
翻转数据 ,将poistion 设置为0 ,limit设置为当前poition位置
- rewind
* <li><p> {@link #rewind} makes a buffer ready for re-reading the data that
* it already contains: It leaves the limit unchanged and sets the position
* to zero. </p></li>
不改变当前limit,用于重新put数据的时候,使用
- 理解demo
try {
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("b.txt");
FileChannel infileChannel = inputStream.getChannel();
FileChannel outfileChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer intBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
// intBuffer.rewind()
while (true) {
//初始化结构,便于读取后面的数据
intBuffer.clear();
int read = infileChannel.read(intBuffer);
if (-1 == read) {
break;
}
//取数据
intBuffer.flip();
outfileChannel.write(intBuffer);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
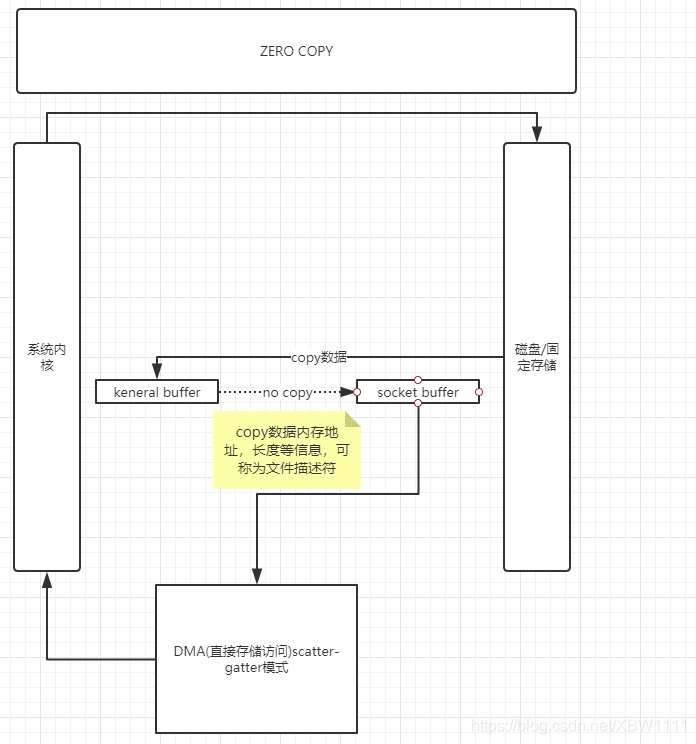
ZERO COPY
IO流
操作文件 发送命令 jvm—>内核->硬件 ,反之回馈数据 其中发生两次内存拷贝
第一次 硬件缓存拷贝到内核缓存, 第二次内核缓存拷贝到JVM缓存中,获得数据。
NIO流
得益于unix和linux系统的优化和支持,操作数据的时候可以在内核直接完成,不需要通过两次拷贝。
第一次拷贝将数据放到内核缓存中,socketbuffer 读取文件描述符信息。 DMA(直接内存存取)通过文件描述符知道数据的内存地址和文件大小信息,就实现0拷贝过程























 241
241











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








