1 函数原型
puts():将str指向的内存空间中存储的字符串写入到标准输出流stdout,函数原型如下:
int puts(const char *str)
cstdio库描述如下:
1. Write string to stdout.
2. Writes the C string pointed by str to the standard output (stdout) and appends a newline character ('\n').
3. The function begins copying from the address specified (str) until it reaches the terminating null character ('\0').
4. This terminating null-character is not copied to the stream.
5. Notice that puts not only differs from fputs in that it uses stdout as destination, but it also appends a newline character at the end automatically (which fputs does not).
2 参数
puts()函数只有一个参数str:
- 参数str是一个指向char类型的指针,即str可以是一个字符指针变量名,也可以是一个字符数组名,甚至可以是一个字符串常量。
cstdio库描述如下:
1. C string to be printed.
3 返回值
puts()函数的返回值类型为int型:
- 输出成功,返回一个非负数值(vs2019中返回0);
- 输出失败,返回EOF。
cstdio库描述如下:
1. On success, a non-negative value is returned.
2. On error, the function returns EOF and sets the error indicator (ferror).
4 输出机制
puts()函数发送字符到标准输出流stdout,直至遇到空字符’\0’:
- 读取str指向的内存空间中存储的字符串;
- 发送空字符’\0’之前的所有字符,包括空格、制表符等字符;
- 将空字符’\0’替换为换行符’\n’并输出。
特别说明:puts()函数与gets()函数刚好相反,gets()函数将换行符’\n’转换为空字符’0’,而puts()函数将空字符’\0’转换为换行符’\n’。
5 示例
以字符数组和字符串常量的形式输出字符串,示例代码如下所示:
int main()
{
char str[20] = "hello world";
int ret = 0;
ret = puts(str);
printf("Return value is %d\n", ret);
ret = puts("i love you xduryan");
printf("Return value is %d\n", ret);
return 0;
}
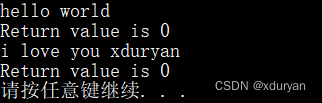
代码运行结果如下所示:






















 1042
1042











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








