一、概述
Operator 的运行机制是作为自定义扩展资源注册到Controller Manager,通过List-Watch的方式监听对应资源的变化。controller-runtime 是 Kubernetes 社区提供可供快速搭建一套 实现了controller 功能的工具,对client-go进行了封装,用户无需自行实现Controller的功能了,只需关注Reconciler即可。
二、main函数入口
func main() {
// 1.构建controllerManager
mgr, err := ctrl.NewManager(ctrl.GetConfigOrDie(), ctrl.Options{
Scheme: scheme,
MetricsBindAddress: metricsAddr,
Port: 9443,
HealthProbeBindAddress: probeAddr,
LeaderElection: enableLeaderElection,
LeaderElectionID: "1de8eaa9.demo.kubebuilder.io",
})
// 2.将reconciler添加到controllerManager中
if err = (&controllers.MyNginxReconciler{
Client: mgr.GetClient(),
Scheme: mgr.GetScheme(),
}).SetupWithManager(mgr); err != nil {
setupLog.Error(err, "unable to create controller", "controller", "MyNginx")
os.Exit(1)
}
//+kubebuilder:scaffold:builder
setupLog.Info("starting manager")
// 3.启动controllerManager
if err := mgr.Start(ctrl.SetupSignalHandler()); err != nil {
setupLog.Error(err, "problem running manager")
os.Exit(1)
}
}
2.1 SetupWithManager
SetupWithManager做了三件事情:
- 构建一个controller,并加入到controllerManager中
- 为该controller设置watch对象,也就是myappv1.MyNginxUss{}
- 为该controller设置Reconciler,也就是MemcachedReconciler
// SetupWithManager sets up the controller with the Manager.
func (r *MyNginxReconciler) SetupWithManager(mgr ctrl.Manager) error {
return ctrl.NewControllerManagedBy(mgr).
//设置监听对象
For(&myappv1.MyNginxUss{}).
//创建controller
Complete(r)
}
// Complete builds the Application Controller.
func (blder *Builder) Complete(r reconcile.Reconciler) error {
_, err := blder.Build(r)
return err
}
// Build builds the Application Controller and returns the Controller it created.
func (blder *Builder) Build(r reconcile.Reconciler) (controller.Controller, error) {
if r == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("must provide a non-nil Reconciler")
}
if blder.mgr == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("must provide a non-nil Manager")
}
if blder.forInput.err != nil {
return nil, blder.forInput.err
}
// Checking the reconcile type exist or not
if blder.forInput.object == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("must provide an object for reconciliation")
}
// Set the ControllerManagedBy
//创建controller
if err := blder.doController(r); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Set the Watch
//创建watch
if err := blder.doWatch(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return blder.ctrl, nil
}
先看doController():
func (blder *Builder) doController(r reconcile.Reconciler) error {
globalOpts := blder.mgr.GetControllerOptions()
ctrlOptions := blder.ctrlOptions
if ctrlOptions.Reconciler == nil {
//设置reconciler
ctrlOptions.Reconciler = r
}
//省略代码
......
// Build the controller and return.
//创建controller
blder.ctrl, err = newController(blder.getControllerName(gvk), blder.mgr, ctrlOptions)
return err
}
//newController就是调用这个方法
// New returns a new Controller registered with the Manager. The Manager will ensure that shared Caches have
// been synced before the Controller is Started.
func New(name string, mgr manager.Manager, options Options) (Controller, error) {
//创建了controller
c, err := NewUnmanaged(name, mgr, options)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Add the controller as a Manager components
//将controller加入到Manage中
return c, mgr.Add(c)
}
func (cm *controllerManager) Add(r Runnable) error {
cm.Lock()
defer cm.Unlock()
return cm.add(r)
}
func (cm *controllerManager) add(r Runnable) error {
// Set dependencies on the object
if err := cm.SetFields(r); err != nil {
return err
}
//将controller加入到controllerManager的runnables,controller也是一种runnable
//controllerManager启动的时候会启动所有的runnable
return cm.runnables.Add(r)
}
再看doWatch():
func (blder *Builder) doWatch() error {
// Reconcile type
typeForSrc, err := blder.project(blder.forInput.object, blder.forInput.objectProjection)
if err != nil {
return err
}
//设置src是source.Kind
src := &source.Kind{Type: typeForSrc}
hdler := &handler.EnqueueRequestForObject{}
allPredicates := append(blder.globalPredicates, blder.forInput.predicates...)
//调用Controller的Watch()
if err := blder.ctrl.Watch(src, hdler, allPredicates...); err != nil {
return err
}
//省略代码
......
}
// Watch implements controller.Controller.
func (c *Controller) Watch(src source.Source, evthdler handler.EventHandler, prct ...predicate.Predicate) error {
c.mu.Lock()
defer c.mu.Unlock()
// Inject Cache into arguments
if err := c.SetFields(src); err != nil {
return err
}
if err := c.SetFields(evthdler); err != nil {
return err
}
for _, pr := range prct {
if err := c.SetFields(pr); err != nil {
return err
}
}
// Controller hasn't started yet, store the watches locally and return.
//
// These watches are going to be held on the controller struct until the manager or user calls Start(...).
// Controller还未启动时,将watchDescription添加到startWatches中,就返回了。
// Controller启动时会启动startWatches中的watch
// controller启动时留意startWatches
if !c.Started {
c.startWatches = append(c.startWatches, watchDescription{src: src, handler: evthdler, predicates: prct})
return nil
}
c.Log.Info("Starting EventSource", "source", src)
return src.Start(c.ctx, evthdler, c.Queue, prct...)
}
也看一下watchDescription的定义:
// watchDescription contains all the information necessary to start a watch.
type watchDescription struct {
src source.Source
handler handler.EventHandler
predicates []predicate.Predicate
}
2.2 controllerManager启动
回过头看下mgr.Start(),Manager实际就是controllerManager实例。mgr.Start()会调用所有controllerManager的runnables的Start(),所以,直接看Controller的Start():
// Start implements controller.Controller.
func (c *Controller) Start(ctx context.Context) error {
// use an IIFE to get proper lock handling
// but lock outside to get proper handling of the queue shutdown
c.mu.Lock()
if c.Started {
return errors.New("controller was started more than once. This is likely to be caused by being added to a manager multiple times")
}
c.initMetrics()
// Set the internal context.
c.ctx = ctx
// 创建工作队列
c.Queue = c.MakeQueue()
go func() {
<-ctx.Done()
c.Queue.ShutDown()
}()
wg := &sync.WaitGroup{}
err := func() error {
defer c.mu.Unlock()
// TODO(pwittrock): Reconsider HandleCrash
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
// NB(directxman12): launch the sources *before* trying to wait for the
// caches to sync so that they have a chance to register their intendeded
// caches.
// 遍历controller的startWatches,这是之前doWatch()添加进来的
for _, watch := range c.startWatches {
c.Log.Info("Starting EventSource", "source", fmt.Sprintf("%s", watch.src))
// 调用src.Start,src是source.Kind
if err := watch.src.Start(ctx, watch.handler, c.Queue, watch.predicates...); err != nil {
return err
}
}
// Start the SharedIndexInformer factories to begin populating the SharedIndexInformer caches
c.Log.Info("Starting Controller")
for _, watch := range c.startWatches {
syncingSource, ok := watch.src.(source.SyncingSource)
if !ok {
continue
}
if err := func() error {
// use a context with timeout for launching sources and syncing caches.
sourceStartCtx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, c.CacheSyncTimeout)
defer cancel()
// WaitForSync waits for a definitive timeout, and returns if there
// is an error or a timeout
if err := syncingSource.WaitForSync(sourceStartCtx); err != nil {
err := fmt.Errorf("failed to wait for %s caches to sync: %w", c.Name, err)
c.Log.Error(err, "Could not wait for Cache to sync")
return err
}
return nil
}(); err != nil {
return err
}
}
// All the watches have been started, we can reset the local slice.
//
// We should never hold watches more than necessary, each watch source can hold a backing cache,
// which won't be garbage collected if we hold a reference to it.
c.startWatches = nil
// Launch workers to process resources
c.Log.Info("Starting workers", "worker count", c.MaxConcurrentReconciles)
wg.Add(c.MaxConcurrentReconciles)
for i := 0; i < c.MaxConcurrentReconciles; i++ {
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
// Run a worker thread that just dequeues items, processes them, and marks them done.
// It enforces that the reconcileHandler is never invoked concurrently with the same object.
// 启动workers来处理资源
for c.processNextWorkItem(ctx) {
}
}()
}
c.Started = true
return nil
}()
if err != nil {
return err
}
<-ctx.Done()
c.Log.Info("Shutdown signal received, waiting for all workers to finish")
wg.Wait()
c.Log.Info("All workers finished")
return nil
}
// Start is internal and should be called only by the Controller to register an EventHandler with the Informer
// to enqueue reconcile.Requests.
func (ks *Kind) Start(ctx context.Context, handler handler.EventHandler, queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface,
prct ...predicate.Predicate) error {
// Type should have been specified by the user.
if ks.Type == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("must specify Kind.Type")
}
// cache should have been injected before Start was called
if ks.cache == nil {
return fmt.Errorf("must call CacheInto on Kind before calling Start")
}
// cache.GetInformer will block until its context is cancelled if the cache was already started and it can not
// sync that informer (most commonly due to RBAC issues).
ctx, ks.startCancel = context.WithCancel(ctx)
ks.started = make(chan error)
go func() {
var (
i cache.Informer
lastErr error
)
// Tries to get an informer until it returns true,
// an error or the specified context is cancelled or expired.
if err := wait.PollImmediateUntilWithContext(ctx, 10*time.Second, func(ctx context.Context) (bool, error) {
// Lookup the Informer from the Cache and add an EventHandler which populates the Queue
// 从Cache中获取Informer
i, lastErr = ks.cache.GetInformer(ctx, ks.Type)
if lastErr != nil {
kindMatchErr := &meta.NoKindMatchError{}
if errors.As(lastErr, &kindMatchErr) {
log.Error(lastErr, "if kind is a CRD, it should be installed before calling Start",
"kind", kindMatchErr.GroupKind)
}
return false, nil // Retry.
}
return true, nil
}); err != nil {
if lastErr != nil {
ks.started <- fmt.Errorf("failed to get informer from cache: %w", lastErr)
return
}
ks.started <- err
return
}
// 向Informer中添加EventHandler
i.AddEventHandler(internal.EventHandler{Queue: queue, EventHandler: handler, Predicates: prct})
if !ks.cache.WaitForCacheSync(ctx) {
// Would be great to return something more informative here
ks.started <- errors.New("cache did not sync")
}
close(ks.started)
}()
return nil
}
type Kind struct {
// Type is the type of object to watch. e.g. &v1.Pod{}
Type client.Object
// cache used to watch APIs
cache cache.Cache
// started may contain an error if one was encountered during startup. If its closed and does not
// contain an error, startup and syncing finished.
started chan error
startCancel func()
}
先来看下processNextWorkItem()处理资源对象:
// processNextWorkItem will read a single work item off the workqueue and
// attempt to process it, by calling the reconcileHandler.
func (c *Controller) processNextWorkItem(ctx context.Context) bool {
obj, shutdown := c.Queue.Get()
if shutdown {
// Stop working
return false
}
// We call Done here so the workqueue knows we have finished
// processing this item. We also must remember to call Forget if we
// do not want this work item being re-queued. For example, we do
// not call Forget if a transient error occurs, instead the item is
// put back on the workqueue and attempted again after a back-off
// period.
defer c.Queue.Done(obj)
ctrlmetrics.ActiveWorkers.WithLabelValues(c.Name).Add(1)
defer ctrlmetrics.ActiveWorkers.WithLabelValues(c.Name).Add(-1)
c.reconcileHandler(ctx, obj)
return true
}
func (c *Controller) reconcileHandler(ctx context.Context, obj interface{}) {
// Update metrics after processing each item
reconcileStartTS := time.Now()
defer func() {
c.updateMetrics(time.Since(reconcileStartTS))
}()
// Make sure that the the object is a valid request.
req, ok := obj.(reconcile.Request)
if !ok {
// As the item in the workqueue is actually invalid, we call
// Forget here else we'd go into a loop of attempting to
// process a work item that is invalid.
c.Queue.Forget(obj)
c.Log.Error(nil, "Queue item was not a Request", "type", fmt.Sprintf("%T", obj), "value", obj)
// Return true, don't take a break
return
}
log := c.Log.WithValues("name", req.Name, "namespace", req.Namespace)
ctx = logf.IntoContext(ctx, log)
// RunInformersAndControllers the syncHandler, passing it the Namespace/Name string of the
// resource to be synced.
// 调用Reconciler函数来处理,这是用户真正去编写业务逻辑的地方
result, err := c.Reconcile(ctx, req)
switch {
case err != nil:
// 如果业务逻辑处理出错,重新添加到限速队列中去
c.Queue.AddRateLimited(req)
ctrlmetrics.ReconcileErrors.WithLabelValues(c.Name).Inc()
ctrlmetrics.ReconcileTotal.WithLabelValues(c.Name, labelError).Inc()
log.Error(err, "Reconciler error")
case result.RequeueAfter > 0:
// The result.RequeueAfter request will be lost, if it is returned
// along with a non-nil error. But this is intended as
// We need to drive to stable reconcile loops before queuing due
// to result.RequestAfter
c.Queue.Forget(obj)
c.Queue.AddAfter(req, result.RequeueAfter)
ctrlmetrics.ReconcileTotal.WithLabelValues(c.Name, labelRequeueAfter).Inc()
case result.Requeue:
// 重新加入队列
c.Queue.AddRateLimited(req)
ctrlmetrics.ReconcileTotal.WithLabelValues(c.Name, labelRequeue).Inc()
default:
// Finally, if no error occurs we Forget this item so it does not
// get queued again until another change happens.
// 正常处理了资源
c.Queue.Forget(obj)
ctrlmetrics.ReconcileTotal.WithLabelValues(c.Name, labelSuccess).Inc()
}
}
2.3 cache
我们已经知道了从工作队列拿出资源,并交由用户Reconcile函数处理,但是还不知道资源是什么时候放入工作队列的。cache是对informer的封装。
// Cache knows how to load Kubernetes objects, fetch informers to request
// to receive events for Kubernetes objects (at a low-level),
// and add indices to fields on the objects stored in the cache.
type Cache interface {
// Cache acts as a client to objects stored in the cache.
client.Reader
// Cache loads informers and adds field indices.
Informers
}
Cache的初始化流程中,Cache主要创建了InformersMap,Scheme中的每个GVK都会创建对应的Informers;每个Informer都会通过List-Watch函数对相应的GVK进行List和Watch操作。这里直接来看下cache的启动流程,回过头看controllerManager启动mgr.Start()
func (cm *controllerManager) Start(ctx context.Context) (err error) {
//省略代码
//......
// Start and wait for caches.
if err := cm.runnables.Caches.Start(cm.internalCtx); err != nil {
if err != wait.ErrWaitTimeout {
return err
}
}
//省略代码
//......
}
实际会调用InformersMap的Start()方法,这里的核心逻辑就是启动所有的Informer
// pkg/cache/internal/deleg_map.go
func (m *InformersMap) Start(ctx context.Context) error {
go m.structured.Start(ctx)
go m.unstructured.Start(ctx)
go m.metadata.Start(ctx)
<-ctx.Done()
return nil
}
// pkg/cache/internal/informers_map.go
func (ip *specificInformersMap) Start(ctx context.Context) {
func() {
ip.mu.Lock()
defer ip.mu.Unlock()
ip.stop = ctx.Done()
// 启动Informer
for _, informer := range ip.informersByGVK {
go informer.Informer.Run(ctx.Done())
}
ip.started = true
close(ip.startWait)
}()
<-ctx.Done()
}
资源什么时候放入工作队列?
informer的工作原理参考informer机制源码分析,这里只需要注意informer监听到资源变更后会触发在informer注册的EventHandler,前面doWatch()方法中,向informer注册了&handler.EnqueueRequestForObject{},资源在这里加入到工作队列。
type EnqueueRequestForObject struct{}
// Create implements EventHandler.
func (e *EnqueueRequestForObject) Create(evt event.CreateEvent, q workqueue.RateLimitingInterface) {
if evt.Object == nil {
enqueueLog.Error(nil, "CreateEvent received with no metadata", "event", evt)
return
}
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
Name: evt.Object.GetName(),
Namespace: evt.Object.GetNamespace(),
}})
}
// Update implements EventHandler.
func (e *EnqueueRequestForObject) Update(evt event.UpdateEvent, q workqueue.RateLimitingInterface) {
switch {
case evt.ObjectNew != nil:
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
Name: evt.ObjectNew.GetName(),
Namespace: evt.ObjectNew.GetNamespace(),
}})
case evt.ObjectOld != nil:
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
Name: evt.ObjectOld.GetName(),
Namespace: evt.ObjectOld.GetNamespace(),
}})
default:
enqueueLog.Error(nil, "UpdateEvent received with no metadata", "event", evt)
}
}
// Delete implements EventHandler.
func (e *EnqueueRequestForObject) Delete(evt event.DeleteEvent, q workqueue.RateLimitingInterface) {
if evt.Object == nil {
enqueueLog.Error(nil, "DeleteEvent received with no metadata", "event", evt)
return
}
q.Add(reconcile.Request{NamespacedName: types.NamespacedName{
Name: evt.Object.GetName(),
Namespace: evt.Object.GetNamespace(),
}})
}
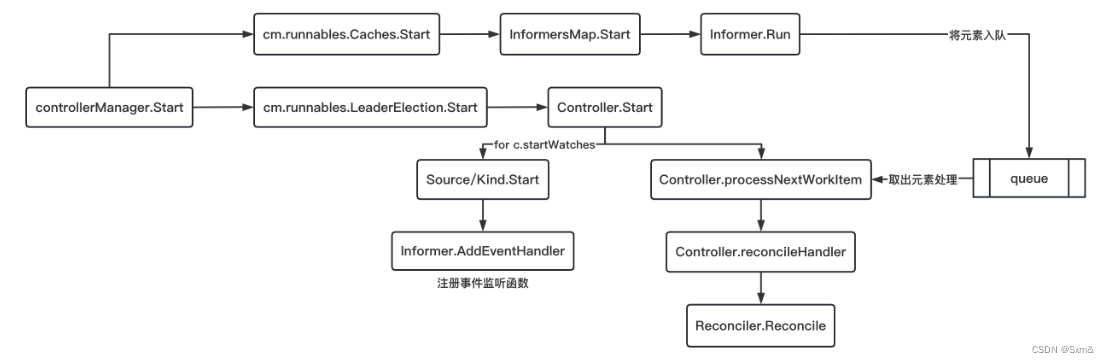
Manager启动整体流程如下:
三、总结
Controller会先向Informer注册资源的eventHandler;然后Cache会启动Informer,Informer向APIServer发出请求,建立连接;当Informer检测到有资源变动后,使用Controller注册进来的eventHandler判断是否推入工作队列中;当工作队列中有元素被推入时,Controller会将元素取出,并执行用户侧的Reconciler。























 1076
1076











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








