一、Caffeine介绍
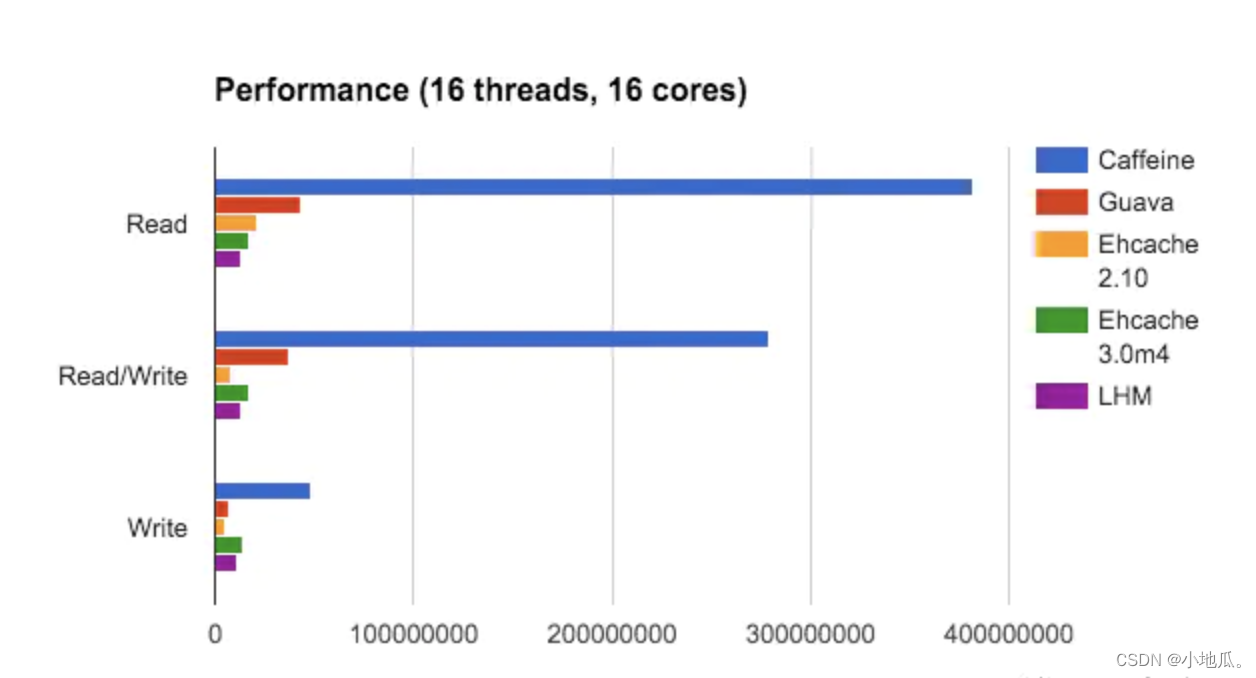
Caffeine是一个基于Java 8的高性能本地缓存框架,采用了W-TinyLFU(LUR和LFU的优点结合)算法,实现了缓存高命中率、内存低消耗。缓存性能接近理论最优,属于是Guava Cache的增强版。在并发读、并发写、并发读写三个场景下Caffeine的性能最优。
二、使用方式
1、在pom.xml 中添加 caffeine 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
</dependency>2、参数说明
| 参数 | 说明 |
| expireAfterWrite | 写缓存后n秒钟过期 |
| expireAfterAccess | 读写缓存后n秒钟过期 |
| refreshAfterWrite | 写入后多久刷新,刷新是基于访问(支持异步和同步刷新)。 只阻塞当前数据加载的线程,其他线程返回旧值,刷新完成才会返回新的取值。 |
| expireAfter | 自定义淘汰策略, Caffeine 通过时间轮算法来实现不同key 的不同过期时间 |
| maximumSize | 缓存key最大个数 |
| weakKeys | key设置为弱引用,在 GC 时可以直接淘汰 |
| weakValues | value设置为弱引用,在 GC 时可以直接淘汰 |
| softValues | value设置为软引用,在内存溢出前可以直接淘汰 |
| executor | 选择自定义线程池,默认线程池是 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() |
| maximumWeight | 设置缓存最大权重 |
| weigher | 设置具体key权重 |
| recordStats | 缓存的统计数据,比如命中率等 |
| removalListener | 缓存淘汰监听器 |
| writer | 缓存写入、更新、淘汰的监听器 |
3、创建对象
private LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
//cache最大缓存数
.maximumSize(500)
//设置写缓存后n秒钟过期
.expireAfterWrite(17, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();4、缓存类型
4.1 手动加载cache:提供搜索查找、更新和移除缓存元素。缓存数据不存在,需要手动加载。
Cache<String, List<Integer>> cache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.maximumSize(500)
.build(new CacheLoader<String, List<Integer>>() {
@Override
public List<Integer> load(String key){
return createCache(key);
}
});
private static final String KEY = "key";
private void getCache() {
//1.查询缓存,没有返回null
List<Integer> list = cache.getIfPresent(KEY);
//2.查找缓存,不存在生成缓存,生成失败返回null
list = cache.get(KEY, k -> createCache(KEY));
//3.添加或者更新一个缓存元素
cache.put(KEY, list);
//4.移除一个缓存元素
cache.invalidate(KEY);
}4.2 自动加载Loading Cache:LoadingCache比Cache多了如果缓存不存在,会通过CacheLoader.load生成对应的缓存数据到缓存中,实现自动加载。
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(500)
.build(key -> createCache(key));
private void getLoadingCache() {
//1.查找缓存,不存在生成缓存,生成失败返回null
List<Integer> list = loadingCache.get(KEY);
//2.批量查找缓存,如果缓存不存在则生成缓存
List<String> requestKeys = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, List<Integer>> map = loadingCache.getAll(requestKeys);
}4.3 手动异步加载Async Cache:AsyncCache是Cache异步形式,提供了Executor生成缓存并返回CompletableFuture的能力。默认的线程池实现是 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 。也可以使用Caffeine.executo设置自定义的线程池。
AsyncCache<String, List<Integer>> asyncCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(500)
.buildAsync();
private void getAsyncCache() {
//1.查询缓存,没有返回null
CompletableFuture<List<Integer>> graph = asyncCache.getIfPresent(KEY);
//2.查找缓存,如果不存在,异步生成
graph = asyncCache.get(KEY, k -> createCache(KEY));
//3.添加或者更新一个缓存元素
asyncCache.put(KEY, graph);
//4.移除一个缓存元素
asyncCache.synchronous().invalidate(KEY);
}4.4 自动异步加载Async Loading Cache:AsyncLoadingCache是LoadingCache的异步形式,返回一个包含取值的CompletableFuture。
AsyncLoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> asyncLoadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(500)
.buildAsync(key->{
log.info("缓存不存在异步加载");
return createCache(key);
});
//查找不存在异步生成
CompletableFuture<Graph> graph = cache.get(key);
//批量查找不存在异步生成
CompletableFuture<Map<Key, Graph>> graphs = cache.getAll(keys);5、驱逐策略
Caffeine提供三类驱逐策略:基于大小、基于时间、基于引用。
5.1 基于大小
//1:个数(大小)
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumSize(500)
.build();
//2.基于缓存内元素权重
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.maximumWeight(200)
.weigher((String key, List<Integer> list) -> list.size())
.build();备注:maximumWeight 与 maximumSize 不可以同时使用。
5.2 基于时间
//1.设置写缓存后n秒钟过期
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterWrite(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
//2.设置读写缓存后n秒钟过期,类似于Guava Cache的expireAfterWrite
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfterAccess(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
//3.自定义策略需要自己实现Expiry接口。
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.expireAfter(new Expiry<String, String>() {
//创建多久后过期
@Override
public long expireAfterCreate(@NonNull String key, @NonNull String value, long currentTime) {
return currentTime;
}
//更新多久后过期
@Override
public long expireAfterUpdate(@NonNull String key, @NonNull String value, long currentTime, @NonNegative long currentDuration) {
return currentTime;
}
//读多久后过期
@Override
public long expireAfterRead(@NonNull String key, @NonNull String value, long currentTime, @NonNegative long currentDuration) {
return currentTime;
}
})
.build();5.3 基于引用
//1.当key和缓存都不存在其他强引用的时候
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.weakKeys()
.weakValues()
.build();
//2.进行GC的时候
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.softValues()
.build(); 6、刷新机制
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
//只阻塞当前数据加载的线程,其他线程返回旧值。刷新完毕才会返回新的取值
.refreshAfterWrite(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();说明:刷新机制依赖于读操作,比如设置1天过期,到期没有访问也不会自动刷新,get方法内 源码afterRead()方法后的refreshIfNeeded()方法根据同步或异步刷新。
7、统计功能
Caffeine.recordStats()可以打开数据收集功能。使用Cache.stats()方法将会返回一个CacheStats对象,包含一些统计指标,如:
- hitRate(): 查询缓存的命中率
- evictionCount(): 被驱逐的缓存数量
- averageLoadPenalty(): 新值被载入的平均耗时
LoadingCache<String, List<Integer>> loadingCache = Caffeine.newBuilder()
.recordStats()
.build(key -> createCache(key));三、淘汰算法
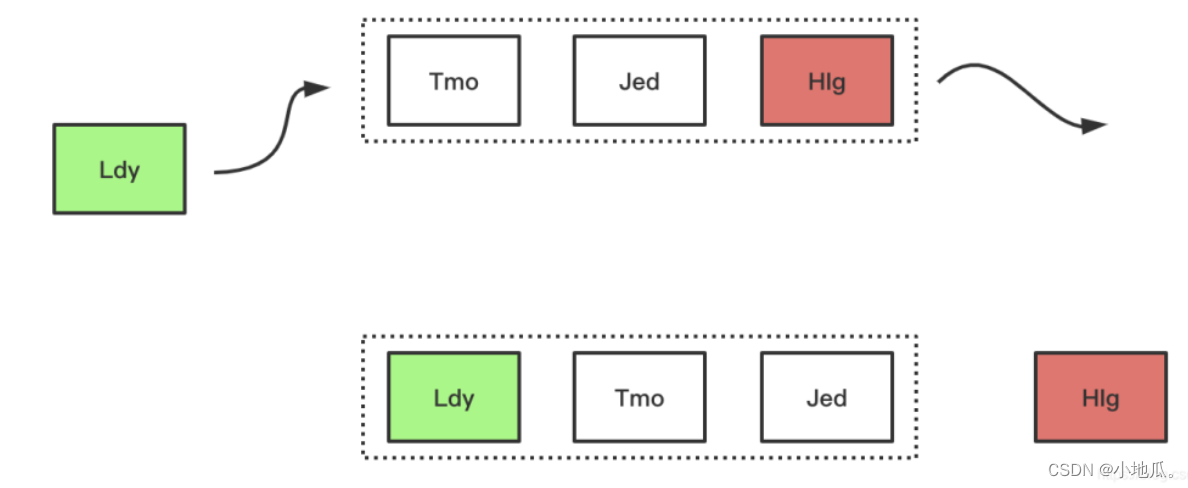
1、FIFO(先进先出)算法
FIFO是类似队列的算法,如果空间满了需要加入新数据先进入缓存的数据会被优先被淘汰。
淘汰过程:
优点:最简单,最公平的一种数据淘汰算法,逻辑简单,易于实现。
缺点:缓存命中率低。
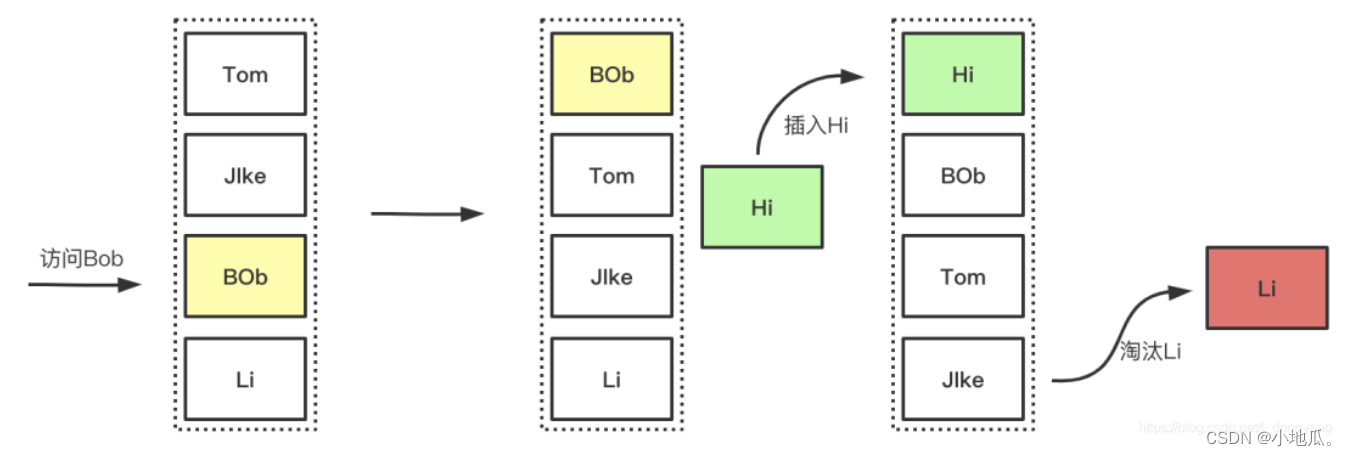
2、LRU(最近最久未使用)算法
如果空间用尽需要加入新数据会优先淘汰最久未被访问(访问少的在未来被访问的概率也是最低的)的数据。LRU是以时间先后顺序来衡量要淘汰的数据。适用于局部突发流量场景。
淘汰过程:
 优点:
优点:
- 实现简单,一般情况下会有很好的命中率,比较常用。
- 有效的对访问比较频繁的数据进行保护,提高热点数据的命中率。
- 局部突发流量场景,对突发性的稀疏流量(n个1,n个2,突然来了1个3,3就属于突然稀疏流量)表现很好。
缺点: 在存在周期性(比如12345,12345的访问)的局部热点数据场景,空间满了会导致周期性的局部热点数据被淘汰。不能很好的处理偶发性,周期性的数据,影响命中率。
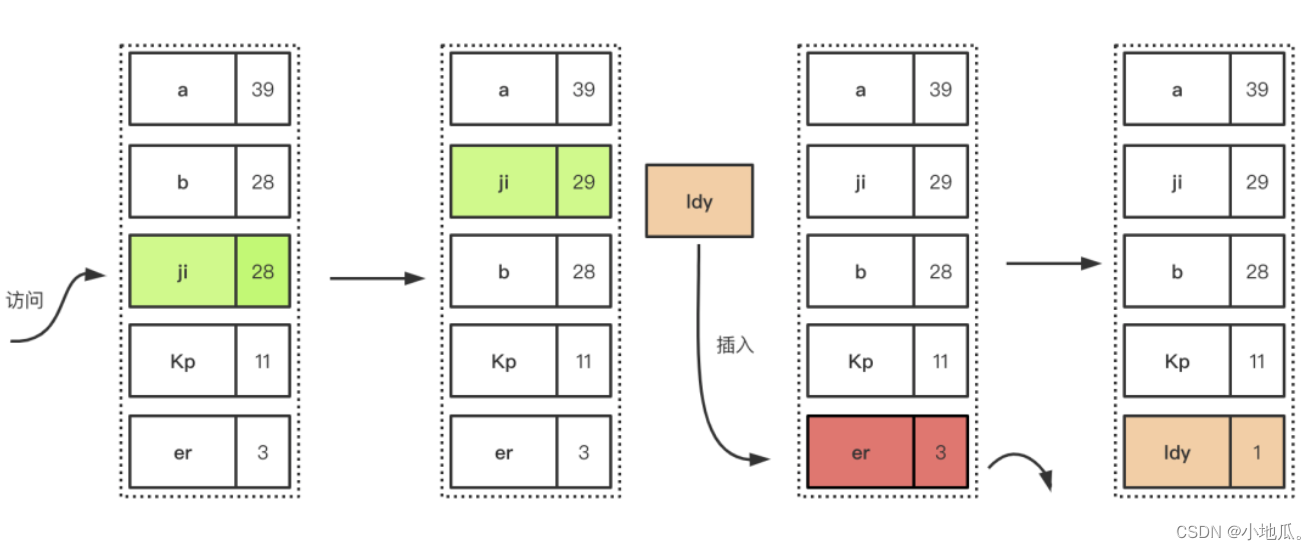
3、LFU(最近最少使用)算法
如果空间用尽需要加入新数据会优先淘汰时间段内访问次数最低(访问次数少的在未来被使用的概率也很小)的数据。LFU是以时间段内的使用次数衡量淘汰的数据。适用于局部周期性流量场景。
淘汰过程:插入数据满了,优先淘汰在一定时间间隔内的访问频率最低的元素。
 优点:
优点:
- LFU适用于局部周期性的场景,有很好的命中率。
- 在局部周期性流量场景下,LFU是以次数为基准,能准确的保证和提高命中率。
缺点:
- 需要记录数据的访问频次,需要额外的空间开销。
- 需要给每个记录项维护频率信息,每次访问都需要更新,增加时间开销。
- 对突发性的稀疏流量场景下,算法命中率会下降。原因:LFU针对访问次数的大小淘汰,前期访问的数据,累计次数很大,新来的缓存数据累加时间短。老的记录占用缓存,过去的一些大量被访问的记录,在之后不一定会继续使用,一直占用位置。突发的稀疏流量,很容易被淘汰。导致缓存命中率下降。
4、TinyLFU算法
TinyLFU是为了解决LFU上面的三个缺点而设计出来的。
(1)减少访问频率的存储的空间开销 和 访问记录更新的时间开销 采用Count–Min Sketch 算法。Count–Min Sketch算法类似布隆过滤器,基于概率统计,存储访问频率,节省空间。
工作原理:
1.某个key计算出4个hash函数,落在不同的位置,每当元素被访问时针对hash计算找到对应的位置,将进行次数加1。
2.查询某个key的频率,需要取得4个索引位置的频率信息,取4个位置中的最小值返回。
实现方案:
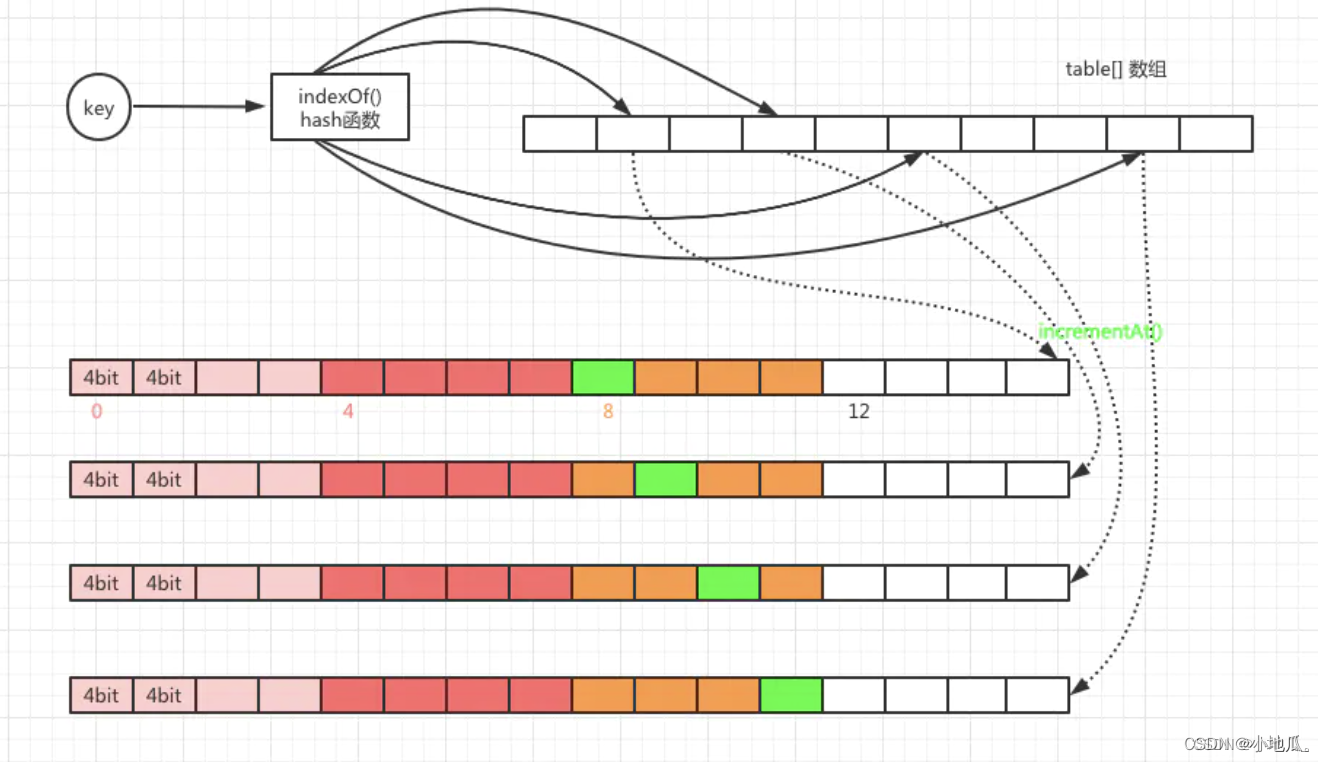
节约空间开销方式:默认访问频次最高15次(15次就算是热点数据了),用4位就可以存储15。一个long类型64位置,每个long分成16份4位。一个key对应4个hash值,一个long就可以存储4个key的访问次数。一个long类型数组大小就是容量的4倍。节约了4分之3的空间。
(2)提升对局部热点数据的算法命中率 ,使用保鲜机制,尽量让缓存保持相对"新鲜",访问越大越不新鲜,适当降低保证新鲜度。Caffeine有一个新鲜度机制,剔除掉过去频率很高,之后不经常使用的缓存。具体操作就是整体的统计计数(所有key的频率统计和的最大值)达到某一个取值时,所有记录的频率统计除以2。
TinyLFU 的算法流程:缓存空间不够时,TinyLFU找到要淘汰的元素(频率最小的元素),新元素放入缓存,替代要淘汰的元素。
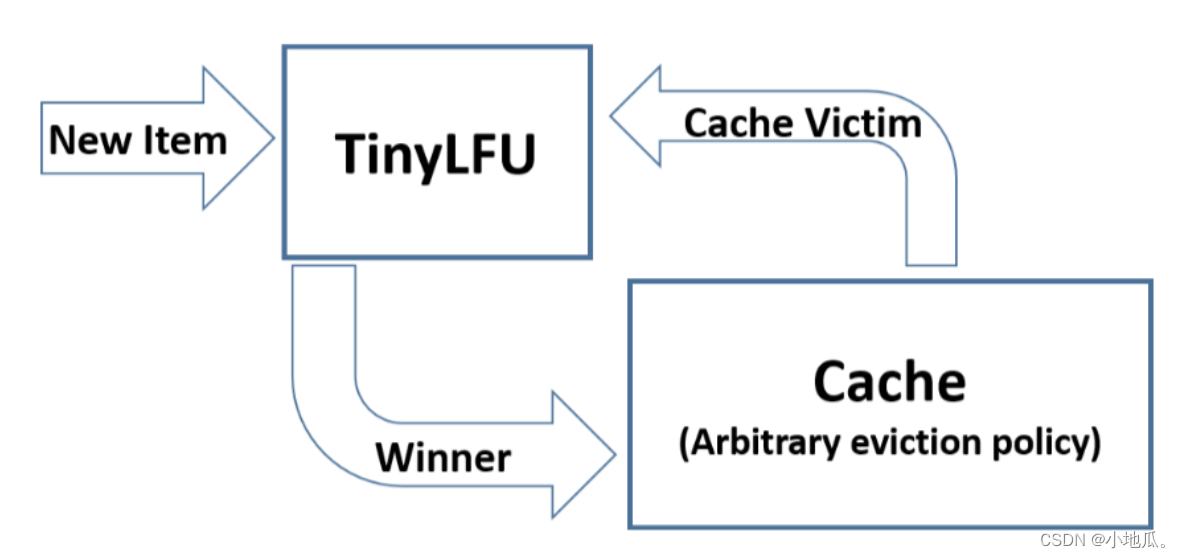
5、W-TinyLFU算法
TinyLFU在面对突发性的稀疏流量变现比较差,因为新的记录还没有建立足够多的频率就被淘汰了,导致命中率下降。W-TinyLFU是对TinyLFU的一个优化,加入了LRU应对局部突发流量,实现缓存命中率最优。W-TinyLFU= LRU(适合局部突发流量)+LFU(适合局部周期流量)。
设计图:
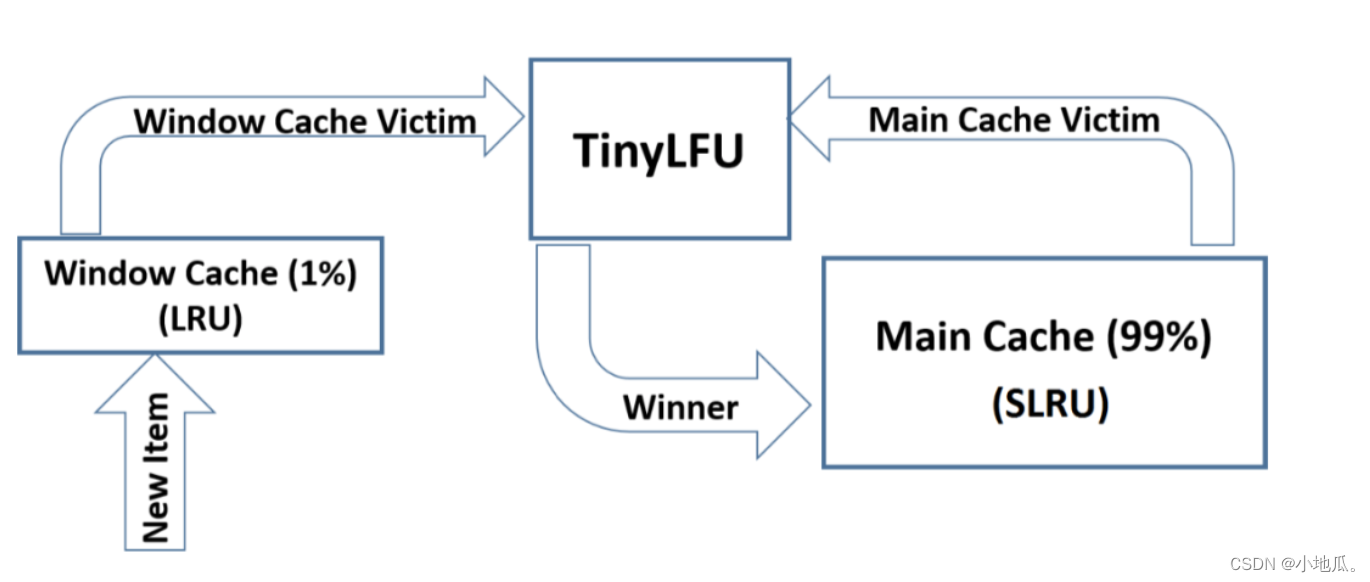
W-TinyLFU将缓存分为2大区域:window cache(应对局部突发流量) 和 main cache(应对局部周期流量)。main cache又拆分成Protected Cache(保护区)和Probation Cache(考察区)两个区域,这两个区域都是基于LRU的Cache。Caffeine的默认比例:LRU(1%),剩下99%中protected(80%),probation(20%)。这时整体性能和命中率表现得最好(已经过实验验证)。 在运行时可以根据统计数据(statistics)去动态调整。
W-TinyLFU算法写入流程:新的缓存项写入缓存,先写入window cache区,如果window cache区满了,根据LRU把淘汰出来的数据放到Probation(考察)区域。如果Probation区满了,与probation中通过lru淘汰的数据进行使用TinyLFU pk。胜者留在Probation区域,输者被淘汰。Probation中的数据被访问了,则移动到Protected。如果Protected满了,protected根据LRU淘汰到probation。
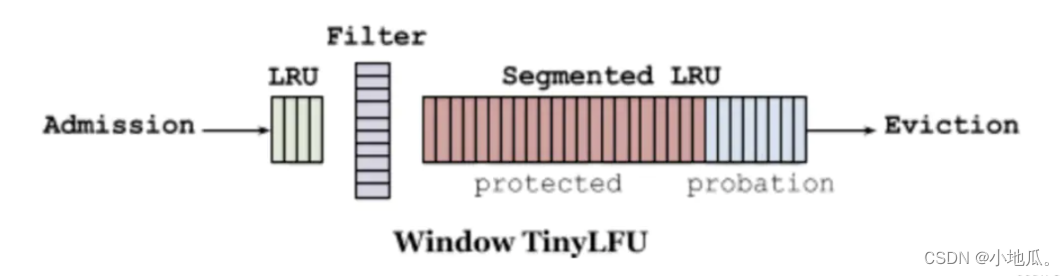 优点:
优点:
- 使用Count-Min Sketch算法存储访问频率,极大的节省空间。
- TinyLFU会 定期进行新鲜度提升、 访问次数的衰减操作,应对访问模式变化。
- 使用W-LRU机制能够提高缓存命中率。
四、Caffeine代码实现
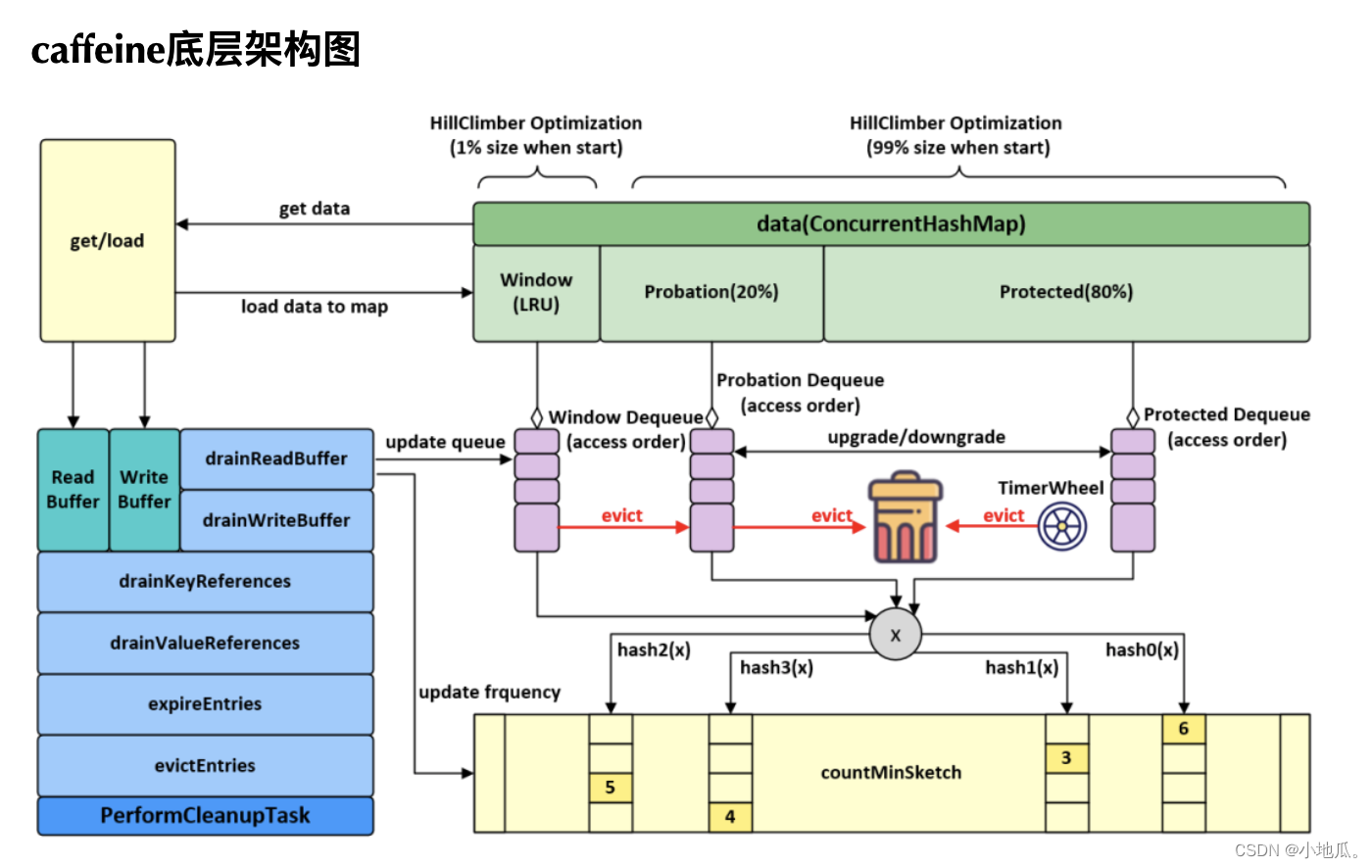
缓存操作执行流程:
- 通过put操作将数据放入data属性中(ConcurrentHashMap)。
- 创建AddTask任务,放入(offer)写缓存:writeBuffer。
- 从writeBuffer中获取任务并执行其run方法,追加记录频率:代码实现在frequencySketch().increment(key)。
- 往window区写入数据。
- 如果数据超过window区大小,将数据移到probation区。
- 比较从window区晋升的数据和probation区的老数据的频率,输者被淘汰,从data中删除。
相关代码:
1.Count–Min Sketch算法写入频率 和 查询频率 和 保新机制 代码实现:
//1.Count–Min Sketch 算法 写入频率 使用FrequencySketch.increment(key)方法实现:
public void increment(@NonNull E e) {
if (!this.isNotInitialized()) {
//根据key的hashCode通过一个哈希函数得到一个hash值
int hash = this.spread(e.hashCode());
//Caffeine把64long分成16份,4bit一份,start是定位到具体的份的位置。
//用hash值低两位作为随机数,左移2位,得到小于16的值
//start 值:0、4、8、12
int start = (hash & 3) << 2;
//indexOf根据hash取获得四个元素在table数组下标的index,
int index0 = this.indexOf(hash, 0);
int index1 = this.indexOf(hash, 1);
int index2 = this.indexOf(hash, 2);
int index3 = this.indexOf(hash, 3);
//根据index和start(+1, +2, +3)的值,把table[index]对应的等分追加1
boolean added = this.incrementAt(index0, start);
added |= this.incrementAt(index1, start + 1);
added |= this.incrementAt(index2, start + 2);
added |= this.incrementAt(index3, start + 3);
//key的访问次数是否达到有个最大值
//size为key的访问次数之合。sampleSize为最大值。size每统计一次+1
if (added && ++this.size == this.sampleSize) {
this.reset();
}
}
}
int indexOf(int item, int i) {
long hash = ((long)item + SEED[i]) * SEED[i];
hash += hash >>> 32;
return (int)hash & this.tableMask;
}
//j表示16等分的下标,index对应等分的位置
boolean incrementAt(int i, int j) {
//offset当于在64位中的下标 16 * 4
int offset = j << 2;
//统计数最大为15
long mask = 15L << offset;
//如果结果不等于15 就追加1,等于15就不追加。
if ((this.table[i] & mask) != mask) {
long[] var10000 = this.table;
var10000[i] += 1L << offset;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
//2.查询某个key的访问次数
@NonNegative
public int frequency(@NonNull E e) {
if (this.isNotInitialized()) {
return 0;
} else {
int hash = this.spread(e.hashCode());
//得到下标
int start = (hash & 3) << 2;
int frequency = 2147483647;
//循环四次,分别获取在table数组中不同的下标位置
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int index = this.indexOf(hash, i);
//定位到table[index] + 等分的位置,再根据mask取出计数值
int count = (int)(this.table[index] >>> (start + i << 2) & 15L);
//取四个中的较小值
frequency = Math.min(frequency, count);
}
return frequency;
}
}
//3.保新机制代码实现
void reset() {
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < this.table.length; ++i) {
count += Long.bitCount(this.table[i] & 1229782938247303441L);
this.table[i] = this.table[i] >>> 1 & 8608480567731124087L;
}
this.size = (this.size >>> 1) - (count >>> 2);
}2.evictEntries()淘汰方法入口:
//最大的个数限制
long maximum;
//当前的个数
long weightedSize;
//window区的最大限制
long windowMaximum;
//window区当前的个数
long windowWeightedSize;
//protected区的最大限制
long mainProtectedMaximum;
//protected区当前的个数
long mainProtectedWeightedSize;
//1.window区的LRU queue 缓存1%的数据
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
protected AccessOrderDeque<Node<K, V>> accessOrderWindowDeque() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//probation区的LRU queue 缓存main内数据的20%
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
protected AccessOrderDeque<Node<K, V>> accessOrderProbationDeque() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//protected区的LRU queue 缓存main内数据的80%
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
protected AccessOrderDeque<Node<K, V>> accessOrderProtectedDeque() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//淘汰方法入口
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
void evictEntries() {
if (!evicts()) {
return;
}
// 淘汰window区的记录
//candidate 第一个 准备从Window区晋升的元素
int candidates = evictFromWindow();
//淘汰Main区的记录
evictFromMain(candidates);
}
//新数据直接到窗口缓存区,超过Window区大小,需要进入到probation区
//使用LRU淘汰
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
int evictFromWindow() {
int candidates = 0;
Node next;
//判断头节点,是否超过区域最大限制,超过限制需要和probation区要淘汰的数据进行pk
for(Node node = (Node)this.accessOrderWindowDeque().peek(); this.windowWeightedSize() > this.windowMaximum() && node != null; node = next) {
next = node.getNextInAccessOrder();
if (node.getPolicyWeight() != 0) {
node.makeMainProbation();
//window区删除node
this.accessOrderWindowDeque().remove(node);
//node移动到probation区
this.accessOrderProbationDeque().add(node);
++candidates;
this.setWindowWeightedSize(this.windowWeightedSize() - (long)node.getPolicyWeight());
}
}
return candidates;
}
//主缓存取 数据进入probation队列后,如果超过最大容量,需要淘汰数据
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
void evictFromMain(int candidates) {
int victimQueue = 1;
//victim是probation queue的头部
Node<K, V> victim = (Node)this.accessOrderProbationDeque().peekFirst();
//candidate是probation queue的尾部(刚晋升过来的数据)
Node candidate = (Node)this.accessOrderProbationDeque().peekLast();
//当缓存容量不够时需要处理
while(this.weightedSize() > this.maximum()) {
if (candidates == 0) {
candidate = null;
}
if (candidate == null && victim == null) {
if (victimQueue == 1) {
victim = (Node)this.accessOrderProtectedDeque().peekFirst();
victimQueue = 2;
} else {
if (victimQueue != 2) {
break;
}
victim = (Node)this.accessOrderWindowDeque().peekFirst();
victimQueue = 0;
}
} else if (victim != null && victim.getPolicyWeight() == 0) {
victim = victim.getNextInAccessOrder();
} else if (candidate != null && candidate.getPolicyWeight() == 0) {
candidate = candidate.getPreviousInAccessOrder();
--candidates;
} else {
Node evict;
if (victim == null) {
evict = candidate.getPreviousInAccessOrder();
Node<K, V> evict = candidate;
candidate = evict;
--candidates;
this.evictEntry(evict, RemovalCause.SIZE, 0L);
} else if (candidate == null) {
evict = victim;
victim = victim.getNextInAccessOrder();
this.evictEntry(evict, RemovalCause.SIZE, 0L);
} else {
K victimKey = victim.getKey();
K candidateKey = candidate.getKey();
Node evict;
if (victimKey == null) {
evict = victim;
victim = victim.getNextInAccessOrder();
this.evictEntry(evict, RemovalCause.COLLECTED, 0L);
} else if (candidateKey == null) {
--candidates;
evict = candidate;
candidate = candidate.getPreviousInAccessOrder();
this.evictEntry(evict, RemovalCause.COLLECTED, 0L);
} else if ((long)candidate.getPolicyWeight() > this.maximum()) {
//节点超过最大个数限制直接淘汰
--candidates;
evict = candidate;
candidate = candidate.getPreviousInAccessOrder();
this.evictEntry(evict, RemovalCause.SIZE, 0L);
} else {
--candidates;
//根据数据victimKey和candidateKey访问频率比较,失败的淘汰
if (this.admit(candidateKey, victimKey)) {
//candidateKey胜出,淘汰victimKey
evict = victim;
victim = victim.getNextInAccessOrder();
this.evictEntry(evict, RemovalCause.SIZE, 0L);
candidate = candidate.getPreviousInAccessOrder();
} else {
//victimKey胜出,淘汰candidateKey
evict = candidate;
candidate = candidate.getPreviousInAccessOrder();
this.evictEntry(evict, RemovalCause.SIZE, 0L);
}
}
}
}
}
}
//在window队列通过lru淘汰出来的"候选者candidate"与
//probation队列通过lru淘汰出来的"被驱逐者victim"进行频率比较,失败者将被从cache中真正移除。
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
boolean admit(K candidateKey, K victimKey) {
int victimFreq = this.frequencySketch().frequency(victimKey);
int candidateFreq = this.frequencySketch().frequency(candidateKey);
//频率高获胜
if (candidateFreq > victimFreq) {
return true;
} else if (candidateFreq <= 5) {
return false;
} else {
//随机淘汰 (为了防止hash冲突攻击)
int random = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt();
return (random & 127) == 0;
}
}
//probation区域的数据移动到protected区域过程
//当数据被访问时并且该数据在probation中,这个数据就会移动到protected中去,
//同时通过lru从protected中淘汰一个数据进入到probation中
/** Promote the node from probation to protected on an access. */
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
void reorderProbation(Node<K, V> node) {
if (!accessOrderProbationDeque().contains(node)) {
// Ignore stale accesses for an entry that is no longer present
return;
} else if (node.getPolicyWeight() > mainProtectedMaximum()) {
return;
}
// If the protected space exceeds its maximum, the LRU items are demoted to the probation space.
// This is deferred to the adaption phase at the end of the maintenance cycle.
setMainProtectedWeightedSize(mainProtectedWeightedSize() + node.getPolicyWeight());
accessOrderProbationDeque().remove(node);
accessOrderProtectedDeque().add(node);
node.makeMainProtected();
}3.动态调整window区和protected区的大小 climb()方法:
//与上次命中率之差的阈值
static final double HILL_CLIMBER_RESTART_THRESHOLD = 0.05d;
//步长(调整)的大小(跟最大值maximum的比例)
static final double HILL_CLIMBER_STEP_PERCENT = 0.0625d;
//步长的衰减比例
static final double HILL_CLIMBER_STEP_DECAY_RATE = 0.98d;
/** Adapts the eviction policy to towards the optimal recency / frequency configuration. */
//climb方法的主要作用就是动态调整window区的大小(相应的,main区的大小也会发生变化,两个之和为100%)。
//因为区域的大小发生了变化,那么区域内的数据也可能需要发生相应的移动。
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
void climb() {
if (!evicts()) {
return;
}
//确定window需要调整的大小
determineAdjustment();
//如果protected区有溢出,把溢出部分移动到probation区。因为下面的操作有可能需要调整到protected区。
demoteFromMainProtected();
long amount = adjustment();
if (amount == 0) {
return;
} else if (amount > 0) {
//增加window的大小
increaseWindow();
} else {
//减少window的大小
decreaseWindow();
}
}
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
void determineAdjustment() {
//如果frequencySketch还没初始化,则返回
if (frequencySketch().isNotInitialized()) {
setPreviousSampleHitRate(0.0);
setMissesInSample(0);
setHitsInSample(0);
return;
}
//总请求量 = 命中 + miss
int requestCount = hitsInSample() + missesInSample();
//默认下sampleSize = 10 * maximum。没达到最大值返回。
if (requestCount < frequencySketch().sampleSize) {
return;
}
//命中率的公式 = 命中 / 总请求
double hitRate = (double) hitsInSample() / requestCount;
//命中率的差值
double hitRateChange = hitRate - previousSampleHitRate();
//本次调整的大小,是由命中率的差值和上次的stepSize决定的
double amount = (hitRateChange >= 0) ? stepSize() : -stepSize();
//下次的调整大小:如果命中率的之差大于0.05,则重置为0.065 * maximum,否则按照0.98来进行衰减
double nextStepSize = (Math.abs(hitRateChange) >= HILL_CLIMBER_RESTART_THRESHOLD)
? HILL_CLIMBER_STEP_PERCENT * maximum() * (amount >= 0 ? 1 : -1)
: HILL_CLIMBER_STEP_DECAY_RATE * amount;
setPreviousSampleHitRate(hitRate);
setAdjustment((long) amount);
setStepSize(nextStepSize);
setMissesInSample(0);
setHitsInSample(0);
}
//减少protected区溢出的部分
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
void demoteFromMainProtected() {
long mainProtectedMaximum = mainProtectedMaximum();
long mainProtectedWeightedSize = mainProtectedWeightedSize();
if (mainProtectedWeightedSize <= mainProtectedMaximum) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < QUEUE_TRANSFER_THRESHOLD; i++) {
if (mainProtectedWeightedSize <= mainProtectedMaximum) {
break;
}
Node<K, V> demoted = accessOrderProtectedDeque().poll();
if (demoted == null) {
break;
}
demoted.makeMainProbation();
accessOrderProbationDeque().add(demoted);
mainProtectedWeightedSize -= demoted.getPolicyWeight();
}
setMainProtectedWeightedSize(mainProtectedWeightedSize);
}
//增加window区的大小
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
void increaseWindow() {
if (mainProtectedMaximum() == 0) {
return;
}
long quota = Math.min(adjustment(), mainProtectedMaximum());
setMainProtectedMaximum(mainProtectedMaximum() - quota);
setWindowMaximum(windowMaximum() + quota);
demoteFromMainProtected();
for (int i = 0; i < QUEUE_TRANSFER_THRESHOLD; i++) {
Node<K, V> candidate = accessOrderProbationDeque().peek();
boolean probation = true;
if ((candidate == null) || (quota < candidate.getPolicyWeight())) {
candidate = accessOrderProtectedDeque().peek();
probation = false;
}
if (candidate == null) {
break;
}
int weight = candidate.getPolicyWeight();
if (quota < weight) {
break;
}
quota -= weight;
if (probation) {
accessOrderProbationDeque().remove(candidate);
} else {
setMainProtectedWeightedSize(mainProtectedWeightedSize() - weight);
accessOrderProtectedDeque().remove(candidate);
}
setWindowWeightedSize(windowWeightedSize() + weight);
accessOrderWindowDeque().add(candidate);
candidate.makeWindow();
}
setMainProtectedMaximum(mainProtectedMaximum() + quota);
setWindowMaximum(windowMaximum() - quota);
setAdjustment(quota);
}
//和increaseWindow方法差不多
@GuardedBy("evictionLock")
void decreaseWindow() {
if (windowMaximum() <= 1) {
return;
}
long quota = Math.min(-adjustment(), Math.max(0, windowMaximum() - 1));
setMainProtectedMaximum(mainProtectedMaximum() + quota);
setWindowMaximum(windowMaximum() - quota);
for (int i = 0; i < QUEUE_TRANSFER_THRESHOLD; i++) {
Node<K, V> candidate = accessOrderWindowDeque().peek();
if (candidate == null) {
break;
}
int weight = candidate.getPolicyWeight();
if (quota < weight) {
break;
}
quota -= weight;
setMainProtectedWeightedSize(mainProtectedWeightedSize() + weight);
setWindowWeightedSize(windowWeightedSize() - weight);
accessOrderWindowDeque().remove(candidate);
accessOrderProbationDeque().add(candidate);
candidate.makeMainProbation();
}
setMainProtectedMaximum(mainProtectedMaximum() - quota);
setWindowMaximum(windowMaximum() + quota);
setAdjustment(-quota);
}参考资料:




















 2537
2537











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








