map与multimap为关联容器,结构如下
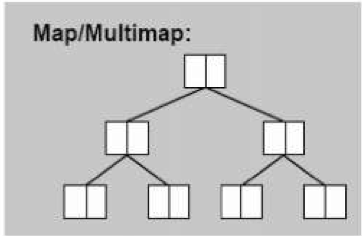
map底层实现依然是rb_tree 他的data可以改,但是key不能改,因此map仍然具有自动排序的功能
我们无法使用迭代器改变元素的key(const key),但是可以改变元素的data.
map的key必须独一无二,multimap的key可以重复
map的定义函数
template <typename _Key, typename _Tp, typename _Compare = std::less<_Key>, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> > > class map { public: typedef _Key key_type; typedef _Tp mapped_type; typedef std::pair<const _Key, _Tp> value_type; typedef _Compare key_compare; typedef _Alloc allocator_type; ... }
参数1 class key 键值key
参数2 class T data
参数3 class compare 排序key的函数 默认为less() 升序
参数4 alloc 分配器
map的基本使用
一 定义
//构造函数 map<int, int> c; c[1] = 10; c[2] = 20; c[3] = 30; c[4] = 40; c[5] = 50; for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //operator = map<int, int> c1; c1 = c; for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl;
二 迭代器操作 map的迭代器就是红黑树的迭代器
//迭代器操作 /* map<int, int> c; c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)}); */ //begin() map<int, int>::iterator iter; iter = c.begin(); cout<< "begin(): "<<"["<< iter->first <<"] = " << iter->second <<endl; //end() iter = c.end(); iter--; cout<<"end(): " <<"["<< iter->first <<"] = " << iter->second <<endl; //rbegin()反向头迭代器 map<int, int>::reverse_iterator riter; riter = c.rbegin(); cout << "rbegin(): "<<"["<< riter->first <<"] = " << riter->second <<endl; //rend()反向头迭代器 riter = c.rend(); riter--; cout << "rend(): "<<"["<< riter->first <<"] = " << riter->second <<endl; //cbegin() const 迭代器 正向 头迭代器 map<int, int>::const_iterator citer; citer = c.cbegin(); cout << "cbegin(): "<<"["<< citer->first <<"] = " << citer->second <<endl; //cend() const 迭代器 反向 尾迭代器 citer = c.cend(); citer--; cout<< "cend(): "<<"["<< citer->first <<"] = " << citer->second <<endl;
三 容量
//容量 /* map<int, int> c; c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)}); */ //是否为kong cout << "empty: " << c.empty() <<endl; //元素个数 cout << "size: " << c.size() <<endl; //最大容量 cout << "max_size: " << c.max_size() <<endl;
四 基本操作
//基本操作 /* map<int, int> c; c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)}); */ //operator[] 这个和其他容器的operator有些不同,如果[index] 的index(key) 在map中存在则直接返回该key对应的data ,如果不存在则想该位置插入默认值 cout << "operator[]: " << c[1] << endl; cout << "operator[]: " << c[10] << endl; //这时你会发现 map自动插入一个c[10] for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //at() 取data cout<< "at(): " << c.at(3) << endl; //插入insert() map 不允许key重复 插入重复key 不会报错但插入不成功 c.insert(pair<int, int>(6, 15)); cout <<"insetr(): "; for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; map<int, int> c_insert; map<int, int>::iterator insert_iter = c_insert.begin(); c_insert.insert(insert_iter,pair<int, int>(100, 10000)); cout <<"insetr(): "; for(auto i : c_insert) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //删除 map<int,int>::iterator erase_iter = c.begin(); c.erase(erase_iter); cout <<"erase(): "; for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //指定下表删除 c.erase(10); cout <<"erase(): "; for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //指定元素删除 erase_iter = c.find(6); if(erase_iter != c.end()) { cout<<"found index: "<< erase_iter->first <<endl; c.erase(erase_iter); } else{ cout<< "Not found" <<endl; } for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //交换swap map<int, int> c_swap1; c_swap1.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)}); map<int, int> c_swap2; cout<<"swap() before: "<<endl; cout<<"c_swap1: "; for(auto i : c_swap1) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; cout<<"c_swap2: "; for(auto i : c_swap2) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; cout<<"swap() after: "; c_swap2.swap(c_swap1); cout<<"c_swap1: "; for(auto i : c_swap1) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; cout<<"c_swap2: "; for(auto i : c_swap2) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //清除clear c_insert.clear(); cout <<"clear(): "; for(auto i : c_insert) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //elements() 插入 如果存在什么也不做 如果不存在插入 map<int, int>::iterator element_iter = c_swap2.begin(); auto xxx = c_swap2.emplace(pair<int, int>(7,60)); if(xxx.second) { cout << "不存在" <<endl; } else { cout<< "存在" <<endl; } cout <<"elements(): "; for(auto i : c_swap2) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //emplace_hint() 插入 element_iter = c.emplace_hint(element_iter, pair<int, int>(7,60)); cout <<"emplace_hint(): "; if(element_iter != c_swap2.end()) { cout<< "存在" <<endl; } else{ cout << "不存在" <<endl; }
五 操作函数
//函数 /* map<int, int> c; c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)}); */ //key_comp 返回key排序的函数 返回仿函数 cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(1,2) <<endl; //会返回1 因为1<2 cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(2,1) <<endl; //会返回0 因为2>1 cout<<"key_comp(): " << c.key_comp()(1,1) <<endl; //会返回0 因为1=1 //value_comp 返回取value和key数据包中的 取key函数 返回仿函数 pair<int,int> value_comp_pair = *c.begin(); iter = c.begin(); cout << c.value_comp()(*iter++,value_comp_pair) << endl;
六 算法
//算法 /* map<int, int> c; c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)}); */ //find() 指定key 返回对应pair cout <<"find(1): " << c.find(1)->second << endl;; //count() key出现的次数 cout <<"count(1): " << c.count(1)<< endl;; c.erase(4); //lower_bound 返回键值>=给定元素的第一个位置 auto lower_boundObj = c.lower_bound(8); if(lower_boundObj->first) cout<<lower_boundObj->first<<endl; else cout<< "Not found lower_boundObj" << endl; for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //upper_bound 返回键值>给定元素的第一个位置 auto upper_boundObj = c.upper_bound(4); if(upper_boundObj->first) cout<<upper_boundObj->first<<endl; else cout<< "Not found upper_bound" << endl; for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; //equal_range()返回该元素所在区间(闭区间),返回值是一个pair<iterator, iterator>类型,first代表所在区间的起点迭代器,second表示所在区间的终点迭代器 auto equal_rangeObj = c.equal_range(3); if(equal_rangeObj.first->first) { cout<<equal_rangeObj.first->first<<endl; } else cout<< "NOT equal_rangeObj.first" << endl; if(equal_rangeObj.second->second) { cout<<equal_rangeObj.second->first<<endl; } else cout<< "NOT second" << endl;
七 自定义比较函数 map 默认为升序 改为降序
class my_compare_ { public: bool operator()(int a, int b) { return a > b; } }; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { map<int, int, my_compare_> c; c.insert({pair<int, int>(1,10),pair<int, int>(2,20),pair<int, int>(3,30),pair<int, int>(4,40),pair<int, int>(5,50),pair<int, int>(6,60)}); for(auto i : c) { cout<<"["<< i.first <<"] = " << i.second <<" "; } cout << endl; return 0; }





















 3174
3174











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








