(1)写一个程序,打印出1到100间的整数
/****************** Exercise ******************
* Write a program that prints values from one to
* 100.
***********************************************/
public class To100{
public static void main (String [] args)
{
for(int i=0; i<=100; i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
(2) 修改练习(1),在值为47时用一个break退出程序。亦可换成return试试。
/****************** Exercise ******************
* Modify Exercise (1)so that the program exits by
* using the break keyword at value 47. Try using
* return instead.
***********************************************/
public class Break47{
public static void main (String [] args)
{
for(int i=0; i<=100; i++){
System.out.println(i);
if(i == 47){
break;
}
//if(i == 47)break;
//if(i == 47)return;
}
}
}
(3) 创建一个switch语句,为每一种case都显示一条消息。并将switch置入一个for循环里,令其尝试每
一种case。在每个case后面都放置一个break,并对其进行测试。然后,删除break,看看会有什么情况出
现。
/****************** Exercise*****************
* Create a switch statement that prints a
* message for each case, and put the switch
* inside a for loop that tries each case. Put a
* break after each case and test it, then remove
* the breaks and see what happens.
***********************************************/
public class SwitchDemo{
public static void main (String [] args)
{
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
switch(i){
case 1:System.out.println("case 1");
break;
case 2:System.out.println("case 2");
break;
case 3:System.out.println("case 3");
break;
default: System.out.println("default");
}
}
}
}
public class SwitchDemo2 {
public static void main (String [] args)
{
for (int i=0; i<5; i++){
switch (i){
case 1:System.out.println("case1");
case 2:System.out.println("case2");
case 3:System.out.println("case3");
default:
System.out.println("default");
}
}
}
}
输出结果:

===================================================================
《Using Scanner for Input from Console》
http://www.particle.kth.se/~lindsey/JavaCourse/Book/Part1/Java/Chapter09/scannerConsole.html
For example, the following code snippet shows how to read an integer from the keyboard(从键盘读取一个整数)
Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);代码例子:
int i = scanner.nextInt ()
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
/** Demonstrate the Scanner class for input of numbers.**/
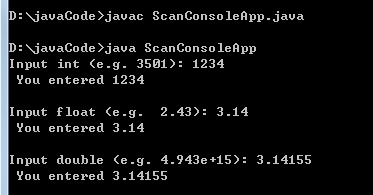
public class ScanConsoleApp
{
public static void main (String arg[]) {
// Create a scanner to read from keyboard
Scanner scanner = new Scanner (System.in);
try {
System.out.printf ("Input int (e.g. %4d): ",3501);
int int_val = scanner.nextInt ();
System.out.println (" You entered " + int_val +"\n");
System.out.printf ("Input float (e.g. %5.2f): ", 2.43);
float float_val = scanner.nextFloat ();
System.out.println (" You entered " + float_val +"\n");
System.out.printf ("Input double (e.g. %6.3e): ",4.943e15);
double double_val = scanner.nextDouble ();
System.out.println (" You entered " + double_val +"\n");
}
catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println ("Mismatch exception:" + e );
}
} // main
} // class ScanConsoleApp
=====================================================================
再来一个例子,强化一下:
//1). 导入 Scanner 类
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TestScanner{
public static void main(String [] args){
//1. 在控制台输入整数
//2). 创建 Scanner 对象
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
//3. 调用 Scanner 对象的 nextInt() 方法读入输入的整数
System.out.print("a=");
int a = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("您已经输入的整数 a: " + a);
}
}
练习题:
求1到100之间所有偶数的和。用for和while语句分别完成。
public class TestFor{
public static void main (String [] args)
{
/* for loop 1-100 even number sum */
int total = 0;
for (int i=1; i<=100; i++) {
if (i%2 == 0){
System.out.println(i);
total = total + i;
}
}
System.out.println(total);
}
}
public class TestWhile {
public static void main (String [] args)
{
/* while loop 1-100 even number sum */
int flag = 1;
int total = 0;
while (flag<=100) {
if (flag%2==0){
total = total + flag;//total+=flag;
}
flag+=flag;
}
System.out.println(total);
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
从键盘读入个数不确定的整数,并判断读入的正数和负数的个数,输入为0时结束输入。
*/
public class ScannerTest {
public static void main (String [] args)
{
int positive_nums = 0;
int negitive_nums = 0;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true){
System.out.println("please input a int number a= ");
int a = sc.nextInt();
if (a>0){
positive_nums += 1;
}
else if (a<0){
negitive_nums += 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
System.out.println("the sum of positive numbers is " + positive_nums);
System.out.println("the sum of negitive numbers is " + negitive_nums);
}
}
























 221
221

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








