list_head结构体
2.1、简介
原型:此结构体所构成的链表如上面的双向循环链表图示
此结构体在linux内核中被大量的引用,几乎所有内核当中需要构成链表结构的地方都用到了这个结构体。例如内核的总线设备就用到了这个结构体
2.2、此结构体的作用
例如现在有任意给定的一个结构体需要组成一个双向链表,则可以在此结构体当中加入list_head结构体用来进行链表的构建,例如结构体原型如下下面是根据此结构体以及list_head文件中的函数编写的测试文件,使用GCC4.8.1进行编译
上述代码经过编译之后运行的结果如下
4 (null)
3 test
2 (null)
1 (null)
0 hehe
后经修改
为
运行结果如下
0 hehe
1 (null)
2 (null)
3 test
4 (null)
由此可以得知此链表的结构为一个双向链表。
2.3、实现方法
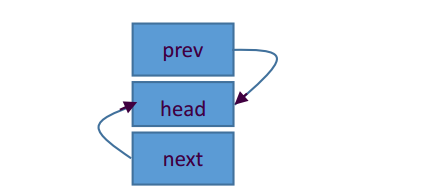
首先是头结点的创建以及初始化此时head的结构体成员均指向自己,形如
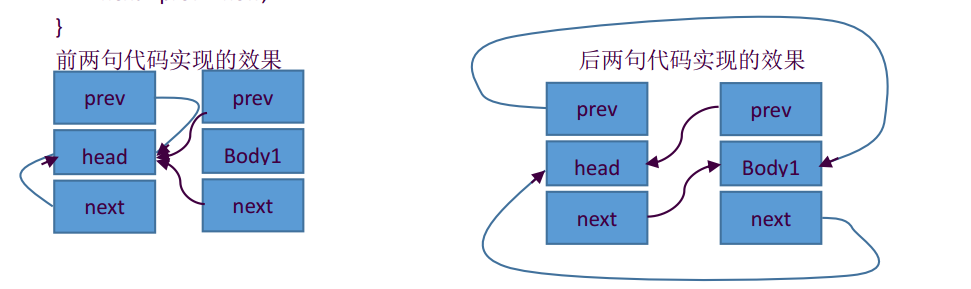
链表的添加过程
由结构体内部的list_head结构体得到结构体所在的位置
反映到代码 mlist_entry(mod, struct test_list, test) 得到
(struct test_list *)((unsigned int)mod - (unsigned int)(&((( struct test_list *)(0))-> test)))
分层次解析
((( struct test_list *)(0))-> test) 定义一个test_list结构体变量0,使其指向其中的test成员。
(&((( struct test_list *)(0))-> test))) 取此成员所在的地址,由于起始为0地址,所以现在获得的地址就是test_list结构体开始到其test成员的偏移值,将其强制转换为unsigned int型变量
((unsigned int)mod - (unsigned int)(&((( struct test_list *)(0))-> test))) 拿取得的list_head结构体mod的位置减去偏移值得到当前mod所在的test_list结构体的起始位置,最后将这个值强制转换为test_list结构体指针,之后就得到一个test_list的地址,也就是当前list_head结构体所在的那个test_list。
其余诸如链表的删除等等操作相对容易理解,不再赘述






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








