| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 25839 | Accepted: 8365 |
Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
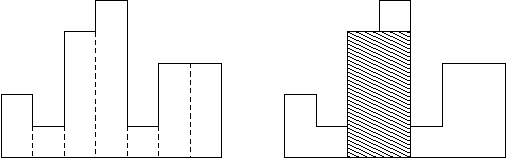
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1<=n<=100000. Then follow n integers h1,...,hn, where 0<=hi<=1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
4 1000 1000 1000 1000
0
Sample Output
8
4000分别正序,倒序单调栈求每个点的左右边界,方法不太理解,(脑子不够用吧。。。)
用一个递增单调栈,围绕的还是以每个点为基点,找他的左边界Li,右边界Ri。ans=(Ri-Li)*a[i].,找出最大的ans。
重点在于如何运用单调栈来求L[],R[]:(栈里面是编号)
当a[i]大于等于栈顶元素值时,进栈,L[i]=i,R[i]=i;
小于栈顶元素时,更新L[i],R[i]就与st[top]有关了。a[i]<a[top]说明a[i]的左边大于a[i],a[i]的左边界可以往左扩。一直扩到栈内元素值小于a[i]时不能再往左扩(假设此时扩到x)。此时a[i]的左边界更新为X的左边界。此时为a[i]更新左边界提供贡献的栈内元素的右边界就可以扩到i-1了。(方便计算,更新右边界时我设置为=i)此时a[i]=st[top]我们采取更新a[i]的左边界为a[top]的左边界。
如:
1 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
加上a[n+1]用于计算最后的右边界:
序列:1 2 1 4 5 1 3 3(-1)
编号:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
i=1:1进栈,L[1]=1,R[1]=2;(1)
i=2:2>st[top]=1。2进栈。L[2]=2,R[2]=3;(1,2)
i=3:1<st[top]=2。L[3]=2;R[3]=4;R[2]=3,2出栈。a[i]=a[1],L[3]=1,3进栈。(1,3)
i=4:进栈(1,3,4)。L[4]=4,R[4]=5.
i=5:进栈(1,3,4,5) L[5]=5,R[5]=6;
i=6:1<5 更新开始,R[5]=6,5出栈;1<a[4],R[4]=6,4出栈;1==a[3],R[3]=6;L[6]=L[1]=1。R[6]=7。(1,3,6)
i=7:进栈。L[7]=7,R[7]=8。(1,3,6,7)
i=8:进栈。L[8]=7,R[8]=9。(1,3,6,7,8)
i=9:-1<a[8],R[8]=9,8出栈;-1<a[7],R[7]=9;7出栈;-1<a[6],R[6]=9。R[3]=9.......到最后一个。
于是得到了,每个点的左右边界:
i: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
L:1 2 1 4 5 1 7 7
R:9 3 9 6 6 9 9 9
把例子画出来,辅助理解。理解每步过程才能处理细节问题,比如此题,a[i]==a[st[top]]时的情况还是要注意处理的。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=100010;
ll a[maxn];
ll st[maxn];
ll L[maxn],R[maxn];
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n)
{
ll top=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%lld",&a[i]);
a[n+1]=-1;
for(ll i=1;i<=n+1;i++)
{
L[i]=i;R[i]=i+1;
while(top>0&&a[i]<a[st[top]])
{
L[i]=L[st[top]];
R[st[top]]=i;
top--;
}
if(top&&a[st[top]]==a[i]) L[i]=L[st[top]];
st[++top]=i;
}
ll ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
ans=max(ans,(R[i]-L[i])*a[i]);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}






















 3670
3670











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








