1、二叉树的前序遍历:

public class Solution {
/**
* @param root TreeNode类
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public void preorder(java.util.List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) { //遇到空节点则返回
return;
}
list.add(root.val); // 先遍历根节点
preorder(list, root.left); // 再去左子树
preorder(list, root.right); // 再去右子树
}
public int[] preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
// 添加遍历结果的数组
java.util.List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
// 递归前序遍历
preorder(list, root);
int[] arr = new int[list.size()]; //新建数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = list.get(i);
}
return arr;
}
}2、二叉树的中序遍历:

import java.util.*;
/*
* public class TreeNode {
* int val = 0;
* TreeNode left = null;
* TreeNode right = null;
* public TreeNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param root TreeNode类
* @return int整型一维数组
*/
public void inorder(java.util.List<Integer> list, TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) { //遇到空节点则返回
return;
}
inorder(list, root.left); // 再去左子树
list.add(root.val); // 先遍历根节点
inorder(list, root.right); // 再去右子树
}
public int[] inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
// 添加遍历结果的列表
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
// 递归中序遍历
inorder(list, root);
int[] arr = new int[list.size()]; //新建数组
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = list.get(i);
}
return arr;
}
}3、二叉树的后续遍历

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public void postorder(List<Integer> treelist, TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(treelist, root.left);
postorder(treelist, root.right);
treelist.add(root.val);
}
//后续遍历
public int[] postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) {
// 后续遍历,先创建一个list
List<Integer> treeList = new ArrayList();
postorder(treeList, root); // 递归遍历
int[] arr = new int[treeList.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = treeList.get(i);
}
return arr;
}
}4、反转链表:
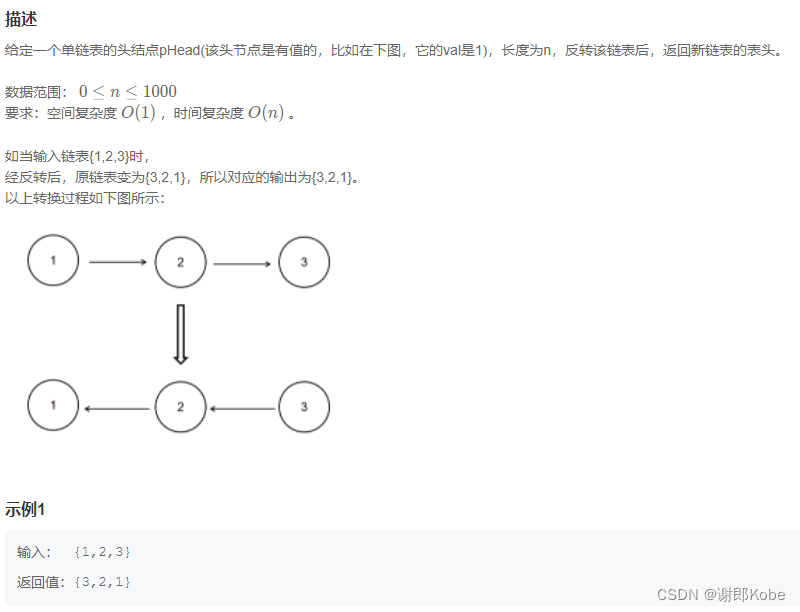
(1)简单的方法是用双链表进行求解:
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
// 双链表求解
ListNode newHead = null; // 新链表
while (head != null) {
// 先保存访问节点的下一个结点,保存起来(留着下一步访问)
ListNode temp = head.next;
// 每次访问的原链表结点都会成为新链表的头结点;其实就是把新链表挂到访问的原链表结点后面就行
head.next = newHead;
newHead = head;
// 重新赋值,继续访问
head = temp;
}
return newHead;
}
}(2)复杂点的用stack(栈)
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
//把链表节点全部摘掉放到栈中
while (head != null) {
stack.push(head);
head = head.next;
}
if (stack.isEmpty())
return null;
ListNode node = stack.pop();
ListNode dummy = node;
//栈中的结点全部出栈,然后重新连成一个新的链表
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
ListNode tempNode = stack.pop();
node.next = tempNode;
node = node.next;
}
//最后一个结点就是反转前的头结点,一定要让他的next
//等于空,否则会构成环
node.next = null;
return dummy;
}5、字符串变形

public String trans(String s, int n) {
// 字符串变形
if (s.length() == 0){
return s;
}
String a[] = s.split(" ", -1); // 这个-1很重要
System.out.println(a.length);
// 字符数组result
char[] result = new char[n];
int num = 0; //数字num=0,用来记录操作
for (int i = a.length-1; i >= 0; i--) { //逆向看
//遍历string数组的 一项字符串
for (char c:a[i].toCharArray()) {
result[num++] = Character.isUpperCase(c)? Character.toLowerCase(c):Character.toUpperCase(c);
}
if (i!=0) {
result[num++] = ' '; //添加一个空格
}
}
// System.out.println(num);
return String.valueOf(result);
}6、最长公共前缀

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param strs string字符串一维数组
* @return string字符串
*/
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
//边界条件判断
if (strs == null || strs.length == 0)
return "";
//默认第一个字符串是他们的公共前缀
String pre = strs[0];
int i = 1;
while (i < strs.length) {
//不断的截取
while (strs[i].indexOf(pre) !=
0) // indexOfindexOf用于返回[目标字符串]在[源字符串]中的位置,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1
pre = pre.substring(0, pre.length() -
1); //如果不是共同前缀的话,那么说明pre太长,从右向左减一位
i++;
}
return pre;
}
}7、用两个栈来实现队列

import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
// 用两个栈实现队列
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>(); //定义stack
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node); // 将值插入进第一个栈中
}
public int pop() {
if (stack2.size() <= 0) {
while (stack1.size() != 0) {
stack2.push(
stack1.pop()); // 置换一下;队列是先进先出,而栈则是先进后出
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}8、包含min函数的栈

import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer>stack1 = new
Stack<Integer>(); //新建一个栈对象:用来存正常的数值
Stack<Integer>stack2 = new
Stack<Integer>(); //新建一个栈对象:用来栈顶存放最小值(排序好的)
// 包含min函数的栈:Min表示获取此时栈中最小元素
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node); //将value压入栈stack1中
if (stack2.size() == 0 ||
stack2.peek() > node) { //比栈顶元素大的,我们就不压入
stack2.push(node);
} else {
stack2.push(stack2.peek()); //重复加入min值,因为统一pop
}
}
public void pop() {
stack1.pop(); //弹出栈顶元素
stack2.pop();
}
public int top() {
return stack1.peek(); //查看栈顶元素
}
public int min() {
return stack2.peek(); //查看栈顶元素
}
}
9、有效括号序列

import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
/**
*
* @param s string字符串
* @return bool布尔型
*/
public boolean isValid (String s) {
// 判断字符串是否合法?
char[] s_char = s.toCharArray();
Stack<Character>stack1 = new Stack<Character>(); //新建一个栈
for (int i = 0; i < s_char.length; i++) {
if (s_char[i] == '[') {
stack1.push(']'); //如果是左括号的话,那么栈压入右括号
} else if (s_char[i] == '(') {
stack1.push(')');
} else if (s_char[i] == '{') {
stack1.push('}');
} else if (stack1.isEmpty() ||
s_char[i] != stack1.pop()) { //1、栈为空,说明第一个字符错了; 2、如果右括号,则比较栈顶
return false;
}
}
return stack1.isEmpty(); //如果是空的话,则说明没问题
}
}10、滑动窗口的最大值
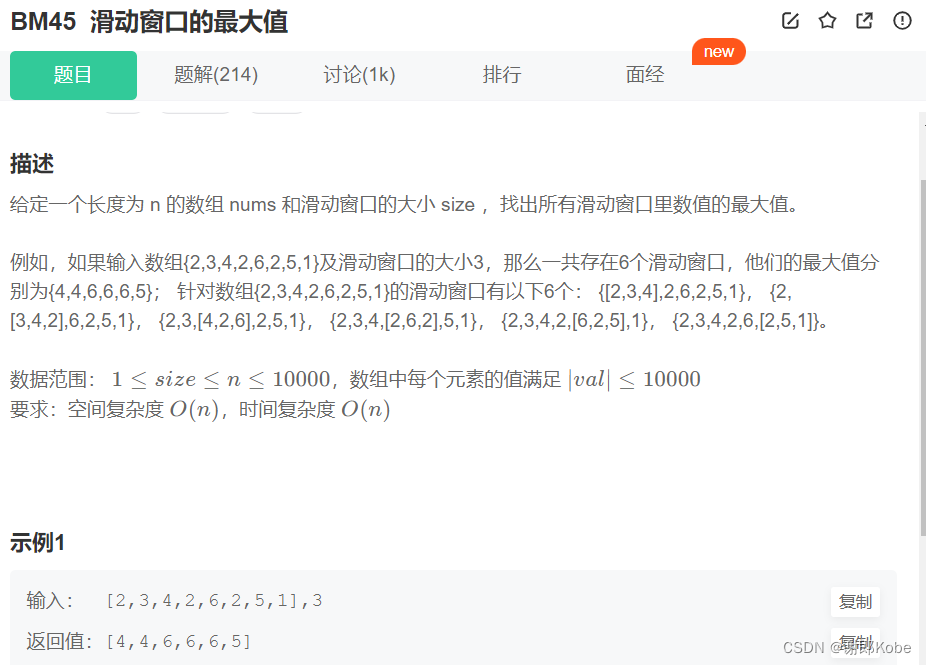
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int [] num, int size) {
if (size == 0) {//避免size为0时候报错
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); //新建一个
return list1;
}
// 给定一个长度为n的数组,滑动窗口的大小size,找出所有滑动窗口里数值的最大值
int n_hua = num.length - size + 1; //滑动窗口数量
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new
ArrayList<Integer>(); //新建一个Integer数组
int max_window = 0; //统计每轮滑动窗口最大值
for (int i = 0; i < n_hua; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < i + size; j++) {
if (j == i) {
max_window = num[j];
} else {
if (num[j] > max_window) { //当出现小于最大值的时候
max_window = num[j];
}
}
}
list1.add(max_window);
}
return list1;
}
}
11、最小的k个数

用Python的话,很简单(不得不说,处理数组还是Python比较流氓):
# @param input int整型一维数组
# @param k int整型
# @return int整型一维数组
#
class Solution:
def GetLeastNumbers_Solution(self, input: List[int], k: int) -> List[int]:
if k==0 or len(input)==0:
list1 = [] # 返回空数组
return list1
else:
input.sort() # 数组排序
return input[:k] # 输出前k位
用Java:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
ArrayList <Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); //新建ArrayList
if(k==0||input.length==0){
return list1; //返回空值
}
Arrays.sort(input); // 对数组input进行排序(且记是Arrays)
for (int i=0; i<k;i++){
list1.add(input[i]); // 塞到新建的Arraylist中
}
return list1;
}
}12、寻找第k大的数

Python依然简单粗暴:
# @param a int整型一维数组
# @param n int整型
# @param K int整型
# @return int整型
#
class Solution:
def findKth(self, a: List[int], n: int, K: int) -> int:
# 找出数组中第 k 大的数
if K == 0 or n == 0:
list1 = [] # 返回空数组
return list1
else:
a.sort() # 数组排序
a.reverse() # 数组反转
return a[K-1] # 输出前k位Java的话:
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int findKth(int[] a, int n, int K) {
// write code here
if(n==0){
return 0;
}
Arrays.sort(a); //对数组a进行排序
return a[n-K];
}
}13、数据流中的中位数

Java的写法:
import java.util.*; //需要单独写一个包
public class Solution {
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // 新建一个列表
public void Insert(Integer num) {
if (list1.isEmpty()) {
list1.add(num); // 如果列表没数据,则进行插入
} else {
int i = 0; //这里就是把i单拉出来的目的是 方便插入操作
for (; i < list1.size(); i++) { //列表求长度是size()
if (num < list1.get(i)) {
break;
}
}
list1.add(i, num); // 插入相应位置
}
}
public Double GetMedian() {
// 该方法:获取当前读取数据的中位数
if (list1.size() % 2 == 0) { //偶数的话
int n = list1.size() / 2;
double a = list1.get(n); //获取中间靠右的值
double b = list1.get(n - 1); //获取中间靠左的值
return (a + b) / 2;
} else {
int n = list1.size() / 2;
double a = list1.get(n); //获取中间的值
return a;
}
}
}
14、两个整型数组求交集
import java.util.*; //其中Arrays、HashSet以及set都在util里边
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>(); // 用到了哈希表(去重问题)
for (int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++){
set1.add(nums1[i]);
}
Set<Integer> resSet = new HashSet<>(); //收集一致的数字
for (int j=0;j<nums2.length;j++){
if (set1.contains(nums2[j])){
resSet.add(nums2[j]); //把b中数字,a中存在的放到哈希表中
}
}
int[] res = new int[resSet.size()];
int k = 0;
for (Integer v : resSet){ // 把哈希表中内容,赋值给int[]
res[k] = v;
k++;
}
return res;
}
15、两个整型数组求并集
import java.util.*; //其中Arrays、HashSet以及set都在util里边
//Integer的默认值是null, int是0.因此用Integer还是比较合适的
public Integer[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>(); // 用到了哈希表(去重问题)
for (int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++) {
set1.add(nums1[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++) {
set1.add(nums2[i]);
}
//将set转换成int
Integer[] unionArray = {};
unionArray = set1.toArray(unionArray);
// printing the union of two arrays.
System.out.println( "Union of two arrays: " + Arrays.toString(unionArray));
return unionArray;
}





















 870
870











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








